Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2
, S., Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831, Oct 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) in mitigating complications and deaths from SARS-CoV-2. Author reports that over 300 clinical studies have shown that proper doses of vitamin D effectively prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2, reducing complications, hospitalizations, and deaths by approximately 50%.
1.
Jaurrieta-Largo et al., A Machine Learning Approach to Understanding the Genetic Role in COVID-19 Prognosis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms Related to Inflammation, Vitamin D, and ACE2, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26167975.
2.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
3.
Kow et al., Vitamin D and COVID‐19: How much more evidence do we need?, Nutrition in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1002/ncp.11349.
4.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
5.
Hewison, M., COVID-19 and our understanding of vitamin D and immune function, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106710.
6.
Wimalawansa, S., Vitamin D Deficiency Meets Hill’s Criteria for Causation in SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility, Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17030599.
7.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
8.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
9.
Wojciulik et al., The impact of genetic polymorphism on course and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, Przeglad Epidemiologiczny, doi:10.32394/pe/194862.
10.
Wimalawansa (B), S., Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2, Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831.
11.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
12.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
13.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
14.
Wimalawansa (C), S., Unlocking Insights: Navigating COVID-19 Challenges and Emulating Future Pandemic Resilience Strategies with Strengthening Natural Immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691.
15.
Imran et al., Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 Patients, Clinical Nutrition Open Science, doi:10.1016/j.nutos.2024.07.004.
16.
Grant, W., Vitamin D and viral infections: Infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.007.
17.
Polonowita et al., Molecular Quantum and Logic Process of Consciousness—Vitamin D Big-Data in COVID-19—A Case for Incorporating Machine Learning In Medicine, European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical sciences, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649.
18.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
19.
Gotelli et al., Understanding the immune-endocrine effects of vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a role in protecting against neurodamage?, Neuroimmunomodulation, doi:10.1159/000533286.
20.
Cutolo et al., Involvement of the secosteroid vitamin D in autoimmune rheumatic diseases and COVID-19, Nature Reviews Rheumatology, doi:10.1038/s41584-023-00944-2.
21.
Schloss et al., Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3.
22.
Arora et al., Global Dietary and Herbal Supplement Use during COVID-19—A Scoping Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030771.
23.
Nicoll et al., COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11226818.
24.
Foshati et al., Antioxidants and clinical outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of observational and interventional studies, Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3034.
25.
Quesada-Gomez et al., Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716.
26.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
27.
Grant (B) et al., A Narrative Review of the Evidence for Variations in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Thresholds for Optimal Health, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030639.
28.
Shah Alam et al., The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686.
29.
Griffin et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: implications for COVID-19, Clinical Medicine, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035.
30.
Kohlmeier et al., When Mendelian randomisation fails, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000265.
31.
Brenner, H., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 Infections and Deaths—Accumulating Evidence from Epidemiological and Intervention Studies Calls for Immediate Action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411.
32.
Mercola et al., Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients 2020, 12:11, 3361, doi:10.3390/nu12113361.
33.
Basha et al., Is the shielding effect of cholecalciferol in SARS CoV-2 infection dependable? An evidence based unraveling, Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2020.10.005.
34.
Xu et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5.
35.
Alexander et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358.
36.
Andrade et al., Vitamin A and D deficiencies in the prognosis of respiratory tract infections: A systematic review with perspectives for COVID-19 and a critical analysis on supplementation, SciELO preprints, doi:10.1590/SciELOPreprints.839.
37.
Grant (C) et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, 12:4, 988, doi:10.3390/nu12040988.
38.
McCullough et al., Daily oral dosing of vitamin D3 using 5000 TO 50,000 international units a day in long-term hospitalized patients: Insights from a seven year experience, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.010.
39.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (E, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1468.
40.
EFSA (B), Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4096.
Wimalawansa et al., 16 Oct 2024, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 1 author, study period May 2020 - June 2024.
Contact: suniljw@hotmail.com.
Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2
Biology, doi:10.3390/biology13100831
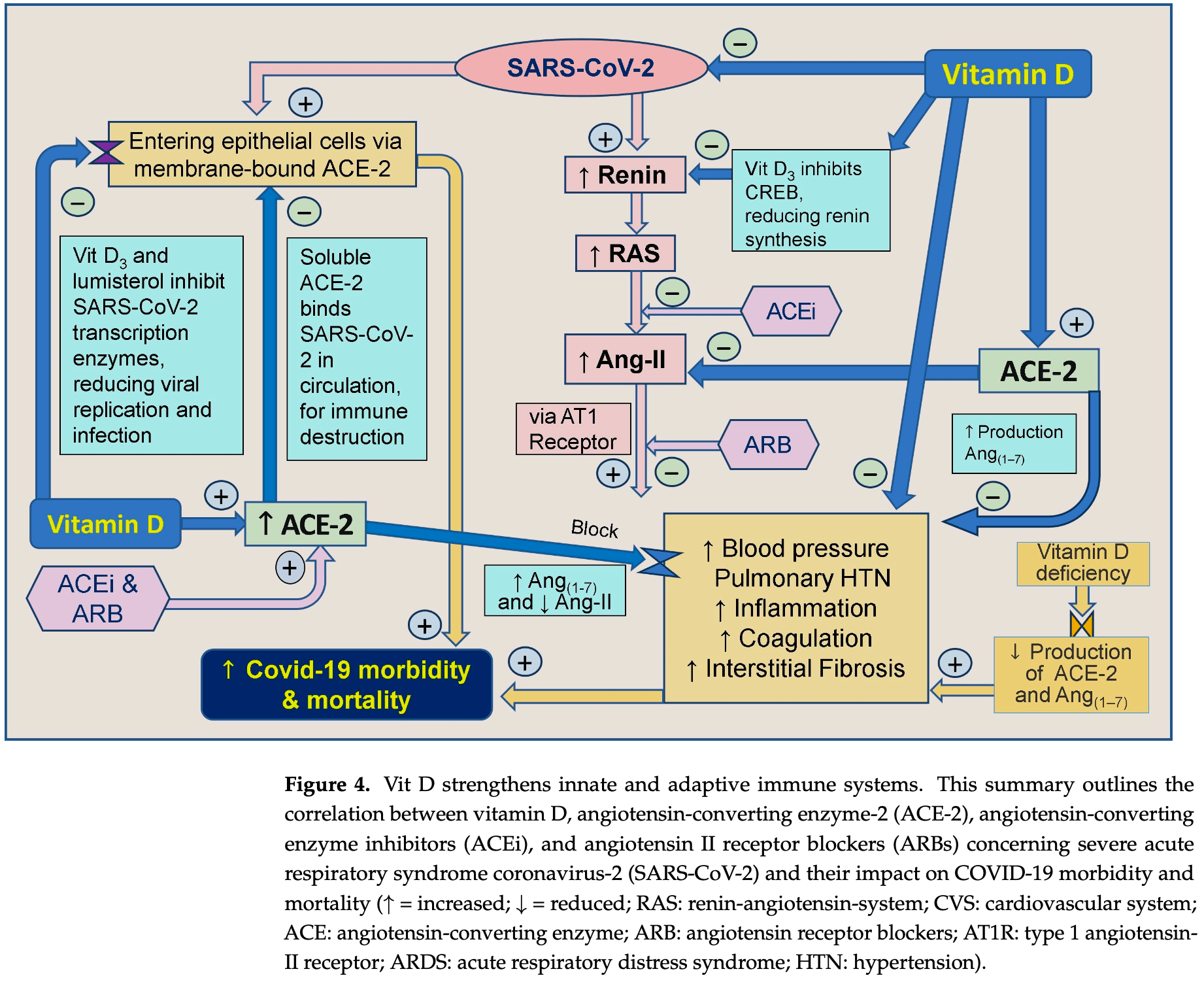
Simple Summary: The SARS-CoV-2 virus that caused COVID-19 devastated families, social structures, and economies worldwide. This pandemic has overwhelmed healthcare systems, increased deaths and disabilities, and triggered a global socio-economic crisis. Although the COVID-19 vaccines were developed rapidly, their effectiveness significantly decreased by the end of 2021 due to mutated viruses evading the immune system. As a result, despite high vaccination rates in industrialized countries, significant outbreaks occurred due to immune evasion associated with viral mutations. Over 300 clinical studies have shown that vitamin D (and ivermectin) are widely available and economical agents that promote immune system function. Proper doses of vitamin D effectively prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2, reducing complications, hospitalizations, and deaths by approximately 50%. Those with vitamin D deficiency fare the worse. SARS-CoV-2 activates the renin-angiotensin system by increasing renin expression, leading to elevated levels of the inflammatogenic and vasoconstrictor peptide angiotensin-II. SARS-CoV-2 viruses cause widespread inflammation, blood clots, and lung damage through multiple mechanisms, leading to impaired tissue oxygenation and death. In addition to enhancing the immune system, vitamin D increases ACE-2 enzyme levels, which breaks down angiotensin-II and reduces SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammation. It also lowers blood pressure and mitigates abnormal clotting. While the virus enters human cells through ACE-2 receptors, excess ACE-2 spills into the bloodstream and neutralizes viruses. This manuscript discusses how vitamin D mitigates the harmful effects of COVID-19.
References
Abeywardhana, Premathilaka, Bandaranayake, Perera, Peiris, In silico study of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD and human ACE-2 affinity dynamics across variants and Omicron subvariants, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28406
Adamczak, The role of Toll-Like receptors and vitamin D in cardiovascular diseases-A review, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18112252
Adams, Sharma, Gacad, Singer, Metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 by cultured pulmonary alveolar macrophages in sarcoidosis, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI111147
Ahmadi, Mirzaei, Hossein-Nezhad, Shariati, Vitamin D receptor FokI genotype may modify the susceptibility to schizophrenia and bipolar mood disorder by regulation of dopamine D1 receptor gene expression, Minerva Med
Akhtar, Benter, Danjuma, Doi, Hasan et al., Pharmacotherapy in COVID-19 patients: A review of ACE2-raising drugs and their clinical safety, J. Drug Target, doi:10.1080/1061186X.2020.1797754
Al-Musharaf, Fouda, Turkestani, Al-Ajlan, Sabico et al., Vitamin D deficiency prevalence and predictors in early pregnancy among Arab women, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10040489
Alberca, Alberca, Role of vitamin D deficiency and comorbidities in COVID-19, World J. Virol, doi:10.5501/wjv.v11.i1.85
Aleksova, Ferro, Gagno, Cappelletto, Santon et al., COVID-19 and renin-angiotensin system inhibition: Role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)-Is there any scientific evidence for controversy?, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13101
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358
Alghatrif, Tanaka, Moore, Bandinelli, Lakatta et al., Age-associated difference in circulating ACE2, the gateway for SARS-COV-2, in humans: Results from the InCHIANTI study, Geroscience, doi:10.1007/s11357-020-00314-w
Alguwaihes, Sabico, Hasanato, Al-Sofiani, Megdad et al., Severe vitamin D deficiency is not related to SARS-CoV-2 infection but may increase mortality risk in hospitalized adults: A retrospective case-control study in an Arab Gulf country, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-021-01831-0
Alipoor, Mirsaeidi, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor, Mol. Biol. Rep, doi:10.1007/s11033-022-07700-x
Alloubani, Akhu-Zaheya, Samara, Abdulhafiz, Saleh et al., Relationship between vitamin D deficiency, diabetes, and obesity, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2019.02.021
Almuqbil, Almadani, Albraiki, Alamri, Alshehri et al., Impact of vitamin D deficiency on mental health in university students: A cross-sectionalstudy, Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare11142097
Alsafar, Grant, Hijazi, Uddin, Alkaabi et al., COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin D status among SARS-CoV-2-positive UAE residents, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051714
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubee, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Annweiler, Hanotte, Grandin De L'eprevier, Sabatier, Lafaie et al., Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771
Aranow, Vitamin D and the immune system, J. Investig. Med, doi:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755
Argano, Mallaci Bocchio, Natoli, Scibetta, Lo Monaco et al., Protective effect of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19-related intensive care hospitalization and mortality: Sefinitive evidence from meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16010130
Ashique, Gupta, Gupta, Mishra, Singh et al., Vitamin D-A prominent immunomodulator to prevent COVID-19 infection, Int. J. Rheum. Dis, doi:10.1111/1756-185X.14477
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712
Bayrak, Ozturk, Bolat, Unay, Association between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 infection in children: A case-control study, Turk. Arch. Pediatr, doi:10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2023.22217
Behl, Kaur, Aleya, Sehgal, Singh et al., CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target, Sci. Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072
Bekele, Gebreselassie, Ashenafi, Kassa, Aseffa et al., Daily adjunctive therapy with vitamin D(3) and phenylbutyrate supports clinical recovery from pulmonary tuberculosis: A randomized controlled trial in Ethiopia, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.12767
Beltran-Garcia, Osca-Verdegal, Pallardo, Ferreres, Rodriguez et al., Oxidative stress and Inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: The potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9100936
Ben-Eltriki, Hopefl, Wright, Deb, Association between vitamin D status and risk of developing severe COVID-19 infection: A meta-analysis of observational studies, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2021.1951891
Bener, Ehlayel, Tulic, Hamid, Vitamin D deficiency as a strong predictor of asthma in children, Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol, doi:10.1159/000323941
Benigni, Cassis, Remuzzi, Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging, EMBO Mol. Med, doi:10.1002/emmm.201000080
Bermejo-Jambrina, Eder, Kaptein, Van Hamme, Helgers et al., Infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 depend on heparan sulfate proteoglycans, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/embj.2020106765
Bessa, Jesus, Nunes, Pontes, Lacerda et al., Stimulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis in hypertensive pregnant rats attenuates cardiovascular dysfunction in adult male offspring, Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens, doi:10.1038/s41440-019-0321-8
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6
Bianconi, Mannarino, Figorilli, Cosentini, Batori et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its prognostic impact on patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111408
Bikle, Vitamin D and the immune system: Role in protection against bacterial infection, Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens, doi:10.1097/MNH.0b013e3282ff64a3
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Lazaretti-Castro, Formenti et al., Mechanisums in Endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-20-0665
Borges, Martini, Rogero, Current perspectives on vitamin D, immune system, and chronic diseases, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2010.07.022
Borsche, Glauner, Von Mendel, COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103596
Bosso, Thanaraj, Abu-Farha, Alanbaei, Abubaker et al., The two faces of ACE2: The role of ACE2 receptor and Its polymorphisms in hypertension and COVID-19, Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev, doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.017
Boucher, Vitamin D deficiency in British South Asians, a persistent but avoidable problem associated with many health risks (including rickets, T2DM, CVD, COVID-19 and pregnancy complications): The case for correcting this deficiency, Endocr. Connect, doi:10.1530/EC-22-0234
Bracken, Lim, Solomon, Rettko, Nguyen et al., Bi-paratopic and multivalent VH domains block ACE2 binding and neutralize SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Chem. Biol, doi:10.1038/s41589-020-00679-1
Brown, Preventing a COVID-19 pandemic-COVID-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m810
Bruhns, Sulaiman, Gaub, Bae, Davidson Knapp et al., Angiotensin-(1-7) improves cognitive function and reduces inflammation in mice following mild traumatic brain injury, Front. Behav. Neurosci, doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2022.903980
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am. J. Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402
Buitrago, Pardo, De Boland, Boland, Activation of RAF-1 through Ras and protein kinase Calpha mediates 1alpha,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in muscle cells, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M205732200
Bunyavanich, Do, Vicencio, Nasal gene expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in children and adults, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8707
Bychinin, Klypa, Mandel, Andreichenko, Baklaushev et al., Low Circulating Vitamin D in Intensive Care Unit-Admitted COVID-19 Patients as a Predictor of Negative Outcomes, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxab107
Caccamo, Ricca, Curro, Ientile, Health risks of hypovitaminosis D: A review of new molecular insights, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19030892
Cariolou, Cupp, Evangelou, Tzoulaki, Berlanga-Taylor, Importance of vitamin D in acute and critically ill children with subgroup analyses of sepsis and respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027666
Castagnoli, Votto, Licari, Brambilla, Bruno et al., Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in children and adolescents: A systematic review, JAMA Pediatr, doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcala Diaz, Lopez Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Cervero, Lopez-Wolf, Casado, Novella-Mena, Ryan-Murua et al., Beneficial effect of short-term supplementation of high dose of vitamin D(3) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, single-blinded, prospective randomized pilot clinical trial, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.863587
Chambers, Basigin binds Spike S on SARS-CoV2, Sci. Res, doi:10.4236/oalib.1108064
Chandra, Rahman, Yadav, Maurya, Kumar Shukla, Effect of adjunct Vitamin D treatment in vitamin D deficient pulmonary tuberculosis patients: A randomized, double blind, active controlled clinical trial, Indian J. Tuberc, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2023.04.026
Charoenngam, Shirvani, Reddy, Vodopivec, Apovian et al., Association of vitamin D status with hospital morbidity and mortality in adult hospitalized patients wth COVID-19, Endocr. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.02.013
Chauss, Freiwald, Mcgregor, Yan, Wang et al., Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of TH1 cells, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3
Chen, Zhao, Chen, Wang, Xiao et al., Neuronal over-expression of ACE2 protects brain from ischemia-induced damage, Neuropharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.004
Chen, Zhou, Yan, Chen, Wang et al., Association of serum total 25-hydroxy-vitamin D concentration and risk of all-cause, cardiovascular and malignancies-specific mortality in patients with hyperlipidemia in the United States, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.971720
Cheng, Wang, Wang, Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25785
Chowdhury, Sajid, Jahan, Adelusi, Maitra et al., A secondary approach with conventional medicines and supplements to recuperate current COVID-19 status, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111956
Chuang, Barajas, Qin, Nagy, Inactivation of the host lipin gene accelerates RNA virus replication through viral exploitation of the expanded endoplasmic reticulum membrane, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003944
Chung, Karnik, Saef, Bergmann, Barnard et al., SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2: The biology and clinical data settling the ARB and ACEI controversy, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102907
Cicero, Fogacci, Borghi, Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 outcomes: Mounting evidence and fewer doubts, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14173584
Ciocarlie, Motofelea, Motofelea, Dutu, Craciun et al., Exploring the role of vitamin D, vitamin D-dependent proteins, and vitamin D receptor gene variation in lung cancer risk, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms25126664
Cui, Liu, Jiang, Ding, Poon et al., Single-cell RNA expression profiling of SARS-CoV-2-related ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophectoderm and placenta, Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1002/uog.22186
D'amelio, Quacquarelli, Hypovitaminosis D and aging: Is there a role in muscle and brain health?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12030628
Da Silveira, Coelho, Vieira, Sachs, Barroso et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of the activation of the angiotensin-(1-7) receptor, MAS, in experimental models of arthritis, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000314
Dal Canto, Beulens, Elders, Rutters, Stehouwer et al., The association of vitamin D and vitamin K status with subclinical measures of cardiovascular health and all-cause mortality in older adults: The hoorn study, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxaa293
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y
Danser, Epstein, Batlle, Renin-angiotensin system blockers and the COVID-19 pandemic: At present there is no evidence to abandon renin-angiotensin system blockers, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15082
Davidson, Wysocki, Batlle, Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronavirus with ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme)-2 as their main receptor: Therapeutic implications, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15256
Davies, Mazess, Benskin, Letter to the editor in response to the article: "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.016
De Koning, Van Schoor, Penninx, Elders, Heijboer et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent depression and poor physical function in older adults: Study protocol of the D-Vitaal study, a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, BMC Geriatr, doi:10.1186/s12877-015-0148-3
De Queiroz, Lakkappa, Lazartigues, ADAM17-mMediated shedding of inflammatory cytokines in hypertension, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01154
Dejnirattisai, Zhou, Ginn, Duyvesteyn, Supasa et al., The antigenic anatomy of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.032
Del Pinto, Pietropaoli, Chandar, Ferri, Cominelli, Association between inflammatory bowel disease and Vitamin D deficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Inflamm. Bowel Dis, doi:10.1097/MIB.0000000000000546
Dellipizzi, Hilchey, Bell-Quilley, Natriuretic action of angiotensin(1-7), Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14014.x
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015
Diaz, Hypothesis: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers may increase the risk of severe COVID-19, J. Travel. Med, doi:10.1093/jtm/taaa041
Dong, Bai, Lin, Gao, Yu, Detection of the mRNA expression of human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a SARS coronavirus functional receptor in human femoral head, Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao
Dror, Morozov, Daoud, Namir, Yakir et al., Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263069
Dudenkov, Yawn, Oberhelman, Fischer, Singh et al., Changing incidence of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D values above 50 ng/mL: A 10-year population-based study, Mayo Clin. Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.02.012
Durazo-Arvizu, Dawson-Hughes, Kramer, Cao, Merkel et al., The reverse J-shaped association between serum Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and all-cause mortality: The impact of assay standardization, Am. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kww244
Durup, Jorgensen, Christensen, Schwarz, Heegaard et al., A reverse J-shaped association of all-cause mortality with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in general practice: The CopD study, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2012-1176
Dzik, Kaczor, Mechanisms of vitamin D on skeletal muscle function: Oxidative stress, energy metabolism and anabolic state, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1007/s00421-019-04104-x
Ebrahimzadeh, Mohseni, Narimani, Ebrahimzadeh, Kazemi et al., Association between vitamin D status and risk of covid-19 in-hospital mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2021.2012419
Faul, Kerley, Love, O'neill, Cody et al., Vitamin D deficiency and ARDS after SARS-CoV-2 infection, Ir. Med. J
Fedson, Treating the host response to emerging virus diseases: Lessons learned from sepsis, pneumonia, influenza and Ebola, Ann. Transl. Med, doi:10.21037/atm.2016.11.03
Fenizia, Galbiati, Vanetti, Vago, Clerici et al., SARS-CoV-2 entry: At the crossroads of CD147 and ACE2, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10061434
Fernandez, Ramirez-Mejia, Castillo, Urcuqui-Inchima, Vitamin D modulates expression of antimicrobial peptides and proinflammatory cytokines to restrict Zika virus infection in macrophages, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110232
Fletcher, Calcium plus vitamin D did not prevent hip fracture or colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women, ACP J. Club, doi:10.7326/ACPJC-2006-145-1-004
Forman, Williams, Fisher, Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D and regulation of the renin-angiotensin system in humans, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.148619
Fraga-Silva, Pinheiro, Goncalves, Alenina, Bader et al., The antithrombotic effect of angiotensin-(1-7) involves mas-mediated NO release from platelets, Mol. Med, doi:10.2119/2007-00073.Fraga-Silva
Fu, Wu, Zhang, Chen, Li et al., Preoperative vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased one-year mortality in Chinese geriatric hip fracture patients-A propensity score matching study, Clin. Interv. Aging, doi:10.2147/CIA.S395228
Gaddam, Chambers, Bhatia, ACE and ACE2 in inflammation: A tale of two enzymes, Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871528113666140713164506
Gan, You, Ying, Mu, The association between serum vitamin D levels and urinary tract infection risk in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15122690
Garg, Al-Ani, Mitchell, Hendy, Christensen, Editorial: Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North-supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity. Authors' reply, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15796
Garland, Garland, Gorham, Lipkin, Newmark et al., The role of vitamin D in cancer prevention, Am. J. Public Health, doi:10.2105/AJPH.2004.045260
Garland, Gorham, Mohr, Garland, Vitamin D for cancer prevention: Global perspective, Ann. Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2009.03.021
Gavioli, Miyashita, Hassaneen, Siau, An evaluation of serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in patients with COVID-19 in New York City, J. Am. Nutr. Assoc, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1869626
Getachew, Tizabi, Vitamin D and COVID-19: Role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27075
Ghosh, Krishnananda, Mohit Changani, Patel, Shenoy Belle, Vitamin D as a biomarker in predicting sepsis outcome at a tertiary care hospital, Asian J. Med. Sci, doi:10.3126/ajms.v14i11.57095
Giannini, Giusti, Minisola, Napoli, Passeri et al., The immunologic profile of vitamin D and its role in different immune-mediated diseases: An expert opinion, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030473
Gibson, Qin, Puah, COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): Clinical features and differences from typical pre-COVID-19 ARDS, Med. J. Aust, doi:10.5694/mja2.50674
Giordano, De Masi, Argenio, Facchiano, Structural dissection of viral Spike-protein binding of SARS CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as cellular receptor, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9081038
Giustina, Bouillon, Dawson-Hughes, Ebeling, Lazaretti-Castro et al., Vitamin D in the older population: A consensus statement, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-022-03208-3
Glasgow, Glasgow, Limonta, Solomon, Lui et al., Engineered ACE2 receptor traps potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2016093117
Gogulothu, Nagar, Gopalakrishnan, Garlapati, Kallamadi et al., Disrupted expression of genes essential for skeletal muscle fibre integrity and energy metabolism in vitamin D deficient rats, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105525
Gonen, Alaylioglu, Durcan, Ozdemir, Sahin et al., Rapid and effective vitamin D supplementation may present better clinical outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) patients by altering serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13114047
Gotelli, Soldano, Hysa, Paolino, Campitiello et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19: Narrative review after 3 years of pandemic, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14224907
Goulter, Goddard, Allen, Clark, ACE2 gene expression is up-regulated in the human failing heart, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/1741-7015-2-19
Grant, Boucher, Bhattoa, Lahore, Why vitamin D clinical trials should be based on 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.08.009
Grant, Boucher, Randomized controlled trials of vitamin D and cancer incidence: A modeling study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0176448
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7064240
Griffin, Hewison, Hopkin, Kenny, Quinton et al., Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: Implications for COVID-19, Clin. Med, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035
Grobe, Mecca, Lingis, Shenoy, Bolton et al., Prevention of angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling by angiotensin-(1-7), Am. J. Physiology. Heart Circ. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00937.2006
Gupta, Sharma, Gupta, Kalaivani, Singh et al., Effect of cholecalciferol and calcium supplementation on muscle strength and energy metabolism in vitamin D-deficient Asian Indians: A randomized, controlled trial, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2010.03816.x
Haga, Yamamoto, Nakai-Murakami, Osawa, Tokunaga et al., Modulation of TNF-alpha-converting enzyme by the spike protein of SARS-CoV and ACE2 induces TNF-alpha production and facilitates viral entry, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.0711241105
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Hastie, Pell, Sattar, Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4
Hedges, Snyder, Robison, Grifka-Walk, Blackwell et al., An ADAM17-neutralizing antibody reduces inflammation and mortality while increasing viral burden in a COVID-19 mouse model, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.918881
Hewison, Vitamin D and immune function: Autocrine, paracrine or endocrine?, Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl, doi:10.3109/00365513.2012.682862
Hewison, Vitamin D and innate and adaptive immunity, Vitam. Horm, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00002-2
Hewison, Vitamin D and the immune system: New perspectives on an old theme, Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am, doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2010.02.010
Heyden, Wimalawansa, Vitamin, Effects on human reproduction, pregnancy, and fetal well-being, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.12.011
Himani, Haq, Wimalawansa, Sharma, Putative roles of vitamin D in modulating immune response and immunopathology associated with COVID-19, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198235
Hintzpeter, Mensink, Thierfelder, Muller, Scheidt-Nave, Vitamin D status and health correlates among German adults, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602825
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hollis, Marshall, Savage, Garrett-Mayer, Kindy et al., Vitamin D3 supplementation, low-risk prostate cancer, and health disparities, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.012
Hollis, Wagner, Drezner, Binkley, Bertsch et al., Circulating vitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D in humans: An important tool to define adequate nutritional vitamin D status, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152286
Hollis, Wagner, Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy: Improvements in birth outcomes and complications through direct genomic alteration, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.mce.2017.01.039
Hong, Xiong, Huang, Wu, Lin et al., Association of vitamin D supplementation with respiratory tract infection in infants, Matern. Child. Nutr, doi:10.1111/mcn.12987
Hosseini, Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, Aghamollaei, Fasihi Ramandi, Alishiri et al., Evaluation of Th1 and Th2 mediated cellular and humoral immunity in patients with COVID-19 following the use of melatonin as an adjunctive treatment, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174193
Hou, Zhao, Martin, Kallianpur, Chung et al., New insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: An ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01673-z
Hu, Wang, Jiang, Li, Guo et al., Low vitamin D levels are associated with high viral loads in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review and meta-analysis, BMC Gastroenterol, doi:10.1186/s12876-019-1004-2
Hypponen, Laara, Reunanen, Jarvelin, Virtanen, Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: A birth-cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06580-1
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Ismailova, White, Vitamin, infections and immunity, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09679-5
Israel, Cicurel, Feldhamer, Stern, Dror et al., Vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher risks for SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity: A retrospective case-control study, Intern. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-021-02902-w
Jahan-Mihan, Stevens, Medero-Alfonso, Brace, Overby et al., The role of water-soluble citamins and vitamin D in prevention and treatment of depression and seasonal affective disorder in adults, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16121902
Jamilian, Amirani, Milajerdi, Kolahdooz, Mirzaei et al., The effects of vitamin D supplementation on mental health, and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with psychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109651
Jaun, Boesing, Luthi-Corridori, Abig, Makhdoomi et al., High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2
Jeffery, Burke, Mura, Zheng, Qureshi et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803217
Jolliffe, Camargo, Jr, Sluyter, Aglipay et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Jolliffe, Griffiths, Martineau, Vitamin D in the prevention of acute respiratory infection: Systematic review of clinical studies, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.017
Jude, Tentolouris, Rastogi, Yap, Pedrosa et al., Vitamin D prescribing practices among clinical practitioners during the COVID-19 pandemic, Health Sci. Rep, doi:10.1002/hsr2.691
Kalantari, Sepidarkish, Ghaffari, Rostami-Mansoor, Does vitamin D reduce the mortality rate of Plasmodium infection?: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Malar. J, doi:10.1186/s12936-023-04612-4
Karonova, Andreeva, Golovatuk, Bykova, Simanenkova et al., Low 25(OH)D level is associated with severe course and poor prognosis in COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13093021
Karonova, Chernikova, Golovatyuk, Bykova, Grant et al., Vitamin D intake may reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection morbidity in health care workers, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030505
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Kawahara, Suzuki, Mizuno, Tominaga, Toda et al., Active vitamin D treatment in the prevention of sarcopenia in adults with prediabetes (DPVD ancillary study): A randomised controlled trial, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(24)00009-6
Kazemi, Mohammadi, Aghababaee, Golzarand, Clark et al., Association of vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmab012
Kim, Kim, Cho, Kim, Lee et al., A critical role of toll-like receptor 2 in nerve injury-induced spinal cord glial cell activation and pain hypersensitivity, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M607277200
Koivisto, Hanel, Carlberg, Key vitamin D target genes with functions in the immune system, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12041140
Kong, Zhu, Shi, Liu, Chen et al., VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Endocrinol, doi:10.1210/me.2013-1146
Konishi, Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 are on the increase against the acquired immunity, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0271305
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm1267
Kumar, Pavan, Murti, Kumar, Dhingra et al., Rays of immunity: Role of sunshine vitamin in management of COVID-19 infection and associated comorbidities, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.09.727
Kurdi, Booz, New take on the role of angiotensin II in cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.172700
Laird, Rhodes, Kenny, Vitamin D and inflammation: Potential implications for severity of Covid-19, Ir. Med. J
Lei, Qian, Li, Zhang, Fu et al., Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus by recombinant ACE2-Ig, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16048-4
Lei, Zhang, Schiavon, He, Chen et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein impairs endothelial function via downregulation of ACE 2, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902
Li, Kong, Wei, Chen, Liu et al., 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) is a negative endocrine regulator of the renin-angiotensin system, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI0215219
Li, Liu, Tang, Ouyang, Li et al., Vitamin D inhibits palmitate-induced macrophage pro-inflammatory cytokine production by targeting the MAPK pathway, Immunol. Lett, doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2018.07.009
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature02145
Li, Wang, Mu, Zhang, The pathogenesis of thyroid autoimmune diseases: New T lymphocytes-Cytokines circuits beyond the Th1-Th2 paradigm, J. Cell. Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.27180
Li, Zhou, Vitamin D deficiency, obesity and diabetes, Cell. Mol. Biol
Lin, Keller, Weaver, Zisman, Interaction of ACE2 and integrin beta1 in failing human heart, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.05.005
Lin, Pan, Wu, Ren, Lu, Role of the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis in blood pressure regulation and its potential as an antihypertensive in functional foods, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7168
Ling, Broad, Murphy, Pappachan, Pardesi-Newton et al., High-dose cholecalciferol booster therapy is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: A cross-sectional multi-centre observational study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123799
Littorin, Blom, Scholin, Arnqvist, Blohme et al., Lower levels of plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D among young adults at diagnosis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes compared with control subjects: Results from the nationwide Diabetes Incidence Study in Sweden (DISS), Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-006-0426-x
Liu, Shi, Sumners, Direct anti-inflammatory effects of angiotensin-(1-7) on microglia, J. Neurochem, doi:10.1111/jnc.13386
Liu, Stenger, Li, Wenzel, Tan et al., Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1123933
Lordan, Notable developments for vitamin D Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, but caution warranted overall: A narrative review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030740
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi, Zarei et al., Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial, Endocr. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016
Mahoney, Damalanka, Tartell, Chung, Lourenco et al., A novel class of TMPRSS2 inhibitors potently block SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV viral entry and protect human epithelial lung cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2108728118
Malek Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2119
Maleki, Nematbakhsh, Renal blood flow response to angiotensin 1-7 versus hypertonic sodium chloride 7.5% administration after acute hemorrhagic shock in rats, Int. J. Vasc. Med, doi:10.1155/2016/6562017
Mancini, Macis, Mosetti, Luchetti, Minicozzi et al., Infrared Spectroscopy of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Protein: From Receptor Binding Domain to Spike Protein, Adv. Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202400823
Marik, Kory, Varon, Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041
Marino, Misra, Extra-Skeletal Effects of Vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11071460
Martin Gimenez, Inserra, Ferder, Garcia, Manucha, Vitamin D deficiency in African Americans is associated with a high risk of severe disease and mortality by SARS-CoV-2, J. Hum. Hypertens, doi:10.1038/s41371-020-00398-z
Martin, Das, Mansel, Jiang, Enhanced tight junction function in human breast cancer cells by antioxidant, selenium and polyunsaturated lipid, J. Cell. Biochem, doi:10.1002/jcb.21162
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Martinez-Moreno, Herencia, Montes De Oca, Munoz-Castaneda, Rodriguez-Ortiz et al., Vitamin D modulates tissue factor and protease-activated receptor 2 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.15-272872
Matsuyama, Kawase, Nao, Shirato, Ujike et al., The inhaled steroid ciclesonide blocks SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication by targeting the viral replication-transcription complex in cultured cells, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01648-20
Mclachlan, The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 are distinctly different paradigms, Clin. Hypertens, doi:10.1186/s40885-020-00147-x
Mehrabadi, Hemmati, Tashakor, Homaei, Yousefzadeh et al., Induced dysregulation of ACE2 by SARS-CoV-2 plays a key role in COVID-19 severity, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111363
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D deficiency and treatment with COVID-19 incidence, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.08.20095893
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 Test resultt, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Menshawey, Menshawey, Nabeh, Shedding light on vitamin D: The shared mechanistic and pathophysiological role between hypovitaminosis D and COVID-19 risk factors and complications, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00835-6
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Golan Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Michigami, Rickets/osteomalacia. consensus on vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in children, Clin. Calcium
Mishra, Parveen, Bajpai, Agarwal, Vitamin D deficiency and comorbidities as risk factors of COVID-19 Infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Prev. Med. Public Health, doi:10.3961/jpmph.21.640
Mitri, Muraru, Pittas, Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/ejcn.2011.118
Molloy, Murphy, Vitamin, Covid-19 and Children, Ir. Med. J
Monteil, Kwon, Prado, Hagelkruys, Wimmer et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.004
Mori, Patel, Ramprasath, Alrob, Desaulniers et al., Angiotensin 1-7 mediates renoprotection against diabetic nephropathy by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipotoxicity, Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00655.2013
Nafilyan, Bermingham, Ward, Morgan, Zaccardi et al., Risk of death following COVID-19 vaccination or positive SARS-CoV-2 test in young people in England, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36494-0
Neerukonda, Vassell, Herrup, Liu, Wang et al., Establishment of a well-characterized SARS-CoV-2 lentiviral pseudovirus neutralization assay using 293T cells with stable expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0248348
Nguyen, Raju, Da Graca, Wang, Mohamed et al., 25-hydroxyvitamin D is a predictor of COVID-19 severity of hospitalized patients, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268038
Nishikawa, Kanno, Zhou, Xiao, Suzuki et al., Massive image-based single-cell profiling reveals high levels of circulating platelet aggregates in patients with COVID-19, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-27378-2
Notz, Herrmann, Schlesinger, Kranke, Sitter et al., Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 ARDS patients, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2021.03.001
Ogata, Iwasaki, Ide, Takizawa, Tanaka et al., Role of vitamin D in energy and bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 6-month follow-up evaluation, J. Diabetes Investig, doi:10.1111/jdi.12666
Okazaki, Ikeda, Honda, Tsuno, Inoue et al., The impact of vitamin D on the onset and progress of Kawasaki disease, Pediatr. Int, doi:10.1111/ped.15191
Olliver, Spelmink, Hiew, Meyer-Hoffert, Henriques-Normark et al., Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on innate and adaptive immune responses to Streptococcus pneumoniae, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jit355
Padhi, Suvankar, Panda, Pati, Panda, Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality in the Indian population: An observational study, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14276
Patel, Zhong, Grant, Oudit, Role of the ACE2/angiotensin 1-7 axis of the renin-angiotensin system in heart failure, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307708
Pender, CD8+ T-cell deficiency, Epstein-Barr virus infection, vitamin D deficiency, and steps to autoimmunity: A unifying hypothesis, Autoimmune Dis, doi:10.1155/2012/189096
Pereira, Dantas Damascena, Galvao Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota Santana, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Pereira, Hirata, Fimia, Do Carmo, Bincoletto et al., Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) regulates autophagy in cultured astrocytes, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.C110.216580
Pilz, Tomaschitz, Marz, Drechsler, Ritz et al., Vitamin D, cardiovascular disease and mortality, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04147.x
Polonowita, Wimalawansa, Molecular quantum and logic process of consciousness-Vitamin D big-data in COVID-19-A case for incorporating machine learning in medicine, Euro. J. Biomed. Pharma. Sci, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10435649
Polonowita, Wimalawansa, The impact of withholding cost-effective early treatments, such as vitamin D, on COVID-19: An analysis using an innovative logical paradigm, World J. Adv. Pharm. Life Sci, doi:10.53346/wjapls.2023.5.2.0080
Qayyum, Mohammad, Slominski, Hassan, Tuckey et al., Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00174.2021
Quesada-Gomez, Lopez-Miranda, Entrenas-Castillo, Casado-Diaz, Nogues et al., Vitamin D endocrine system and COVID-19: Treatment with calcifediol, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14132716
Quraishi, Bittner, Blum, Hutter, Camargo et al., Association between preoperative 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and hospital-acquired infections following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, JAMA Surg, doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2013.3176
Quraishi, Bittner, Blum, Mccarthy, Bhan et al., Prospective study of vitamin D status at initiation of care in critically ill surgical patients and risk of 90-day mortality, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000000210
Quraishi, De Pascale, Needleman, Nakazawa, Kaneki et al., Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on vitamin D status and cathelicidin levels in sepsis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001148
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Raisi-Estabragh, Mccracken, Bethell, Cooper, Cooper et al., Greater risk of severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic populations is not explained by cardiometabolic, socioeconomic or behavioural factors, or by 25(OH)-vitamin D status: Study of 1326 cases from the UK Biobank, J. Public Health, doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdaa095
Raju, Luthra, Shahbaz, Almatooq, Foucambert et al., Role of vitamin D deficiency in increased susceptibility to respiratory infections among children: A systematic review, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.29205
Regenhardt, Mecca, Desland, Ritucci-Chinni, Ludin et al., Centrally administered angiotensin-(1-7) increases the survival of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats, Exp. Physiol, doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2013.075242
Riddell, Calcium plus vitamin D did not prevent fractures or colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women, Evid. Based Nurs, doi:10.1136/ebn.9.4.114
Rouzine, Rozhnova, Evolutionary implications of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination for the future design of vaccination strategies, Commun. Med, doi:10.1038/s43856-023-00320-x
Rustecka, Maret, Drab, Leszczynska, Tomaszewska et al., The Impact of COVID-19 pandemic during 2020-2021 on the vitamin D serum levels in the paediatric population in Warsaw, Poland, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061990
Sahu, Patil, Kumar, Apparsundaram, Goyal, Role of ACE2-Ang (1-7)-Mas axis in post-COVID-19 complications and its dietary modulation, Mol. Cell. Biochem, doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04275-2
Salahuddin, Ali, Hasan, Rao, Aqeel et al., Vitamin D accelerates clinical recovery from tuberculosis: Results of the SUCCINCT Study [Supplementary Cholecalciferol in recovery from tuberculosis]. A randomized, placebocontrolled, clinical trial of vitamin D supplementation in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-22
Samavati, Uhal, ACE2, much more than just a receptor for SARS-COV-2, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317
Santaolalla, Beckmann, Kibaru, Josephs, Van Hemelrijck et al., Association between vitamin D and novel SARS-CoV-2 respiratory dysfunction-A scoping review of current evidence and Its implication for COVID-19 pandemic, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.564387
Santos, Giani, Burghi, Miquet, Qadri et al., Oral administration of angiotensin-(1-7) ameliorates type 2 diabetes in rats, J. Mol. Med, doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1087-0
Santos, Sampaio, Alzamora, Motta-Santos, Alenina et al., The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS axis of the renin-angiotensin system: Focus on angiotensin-(1-7), Physiol. Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.00023.2016
Santos, Simoes E Silva, Maric, Silva, Machado et al., Angiotensin-(1-7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1432869100
Sanyal, How SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) spreads within infected hosts-What we know so far, Emerg. Top. Life Sci, doi:10.1042/ETLS20200165
Sarau, Rachabattuni, Gadde, Daruvuri, Marusca et al., Exploring the preventive potential of vitamin D against respiratory infections in preschool-age children: A cross-sectional study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16111595
Sarzani, Giulietti, Di Pentima, Giordano, Spannella, Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00189.2020
Satou, Penrose, Navar, Inflammation as a regulator of the renin-angiotensin system and blood pressure, Curr. Hypertens. Rep, doi:10.1007/s11906-018-0900-0
Sawalha, Zhao, Coit, Lu, Epigenetic dysregulation of ACE2 and interferon-regulated genes might suggest increased COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in lupus patients, medRxiv, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108410
Schauber, Dorschner, Yamasaki, Brouha, Gallo, Control of the innate epithelial antimicrobial response is cell-type specific and dependent on relevant microenvironmental stimuli, Immunology, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02399.x
Schlumpf, Reichrath, Lehmann, Sigmundsdottir, Feldmeyer et al., Fundamental questions to sun protection: A continuous education symposium on vitamin D, immune system and sun protection at the University of Zurich, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.2.1.12016
Scialo, Daniele, Amato, Pastore, Matera et al., ACE2: The major cell entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2, Lung, doi:10.1007/s00408-020-00408-4
Scragg, Sowers, Bell, Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, ethnicity, and blood pressure in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Am. J. Hypertens, doi:10.1016/j.amjhyper.2007.01.017
Seal, Bertenthal, Carey, Grunfeld, Bikle et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and COVID-19-Related Hospitalization and Mortality, J. Gen. Intern. Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-021-07170-0
Shiravi, Saadatkish, Abdollahi, Miar, Khanahmad et al., Vitamin D can be effective on the prevention of COVID-19 complications: A narrative review on molecular aspects, Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res, doi:10.1024/0300-9831/a000676
Shoemaker, Huynh, Smith, Mustad, Duarte et al., Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D and prevention of respiratory tract infections and COVID-19, Top. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1097/TIN.0000000000000284
Shu, Zhang, Dong, Long, Li et al., Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and hepatocellular carcinoma survival, J. Natl. Cancer Inst, doi:10.1093/jnci/djae116
Skultetyova, Filipova, Riecansky, Skultety, The role of angiotensin type 1 receptor in inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, Recent. Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov, doi:10.2174/157489007779606130
Smaha, Jackuliak, Kuzma, Max, Binkley et al., Vitamin D deficiency prevalence in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 significantly fecreased during the pandemic in Slovakia from 2020 to 2022 Which Was associated with decreasing mortality, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15051132
Smaha, Kuzma, Brazdilova, Nachtmann, Jankovsky et al., Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia with 25(OH)D levels lower than 12 ng/ml are at increased risk of death, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.01.044
Song, Hu, Yu, Zhao, Zhao et al., Little to no expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 on most human peripheral blood immune cells but highly expressed on tissue macrophages, Cytom. A, doi:10.1002/cyto.a.24285
Souza, Costa-Neto, Angiotensin-(1-7) decreases LPS-induced inflammatory response in macrophages, J. Cell. Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.22940
Souza, Sobrinho, Almeida, Alves, Macedo et al., Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade restores angiotensin-(1-7)-induced coronary vasodilation in hypertrophic rat hearts, Clin. Sci, doi:10.1042/CS20120519
Sposito, Pennington, David, Duggan, Northey et al., Age-differential CD13 and interferon expression in airway epithelia affect SARS-CoV-2 infection-Effects of vitamin D, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.08.002
Stagi, Rigante, Lepri, Matucci Cerinic, Falcini, Severe vitamin D deficiency in patients with Kawasaki disease: A potential role in the risk to develop heart vascular abnormalities?, Clin. Rheumatol, doi:10.1007/s10067-015-2970-6
Stoffels, Overbergh, Giulietti, Verlinden, Bouillon et al., Immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in human monocytes, J. Bone Miner. Res, doi:10.1359/JBMR.050908
Stohs, Aruoma, Vitamin D and Wellbeing beyond Infections: COVID-19 and Future Pandemics, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1786302
Sun, Zhang, Vitamin D receptor influences Intestinal barriers in health and disease, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11071129
Takase, Tsugawa, Sugiyama, Ikesue, Eto et al., Association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.04.003
Tenaillon, Matic, The impact of neutral mutations on genome evolvability, Curr. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2020.03.056
Tenali, Babu, A systematic literature review and future perspectives for handling big data analytics in COVID-19 diagnosis, New Gener. Comput, doi:10.1007/s00354-023-00211-8
Tikellis, Thomas, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) Is a key modulator of the renin angiotensin system in health and disease, Int. J. Pept, doi:10.1155/2012/256294
Tiwari, Singh, Tiwari, Chaturvedi, Gupta et al., ACE2/ANG-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis activation prevents inflammation and improves cognitive functions in streptozotocin induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease-like phenotypes, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175623
Trochoutsou, Kloukina, Samitas, Xanthou, Vitamin-D in the immune system: Genomic and non-genomic actions, Mini Rev. Med. Chem, doi:10.2174/1389557515666150519110830
Tuekprakhon, Nutalai, Dijokaite-Guraliuc, Zhou, Ginn et al., Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.005
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6
Van Ballegooijen, Beulens, Kieneker, De Borst, Gansevoort et al., Combined low vitamin D and K status amplifies mortality risk: A prospective study, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02352-8
Vargas, Vargas, Varela Millan, Fajardo Bonilla, Renin-angiotensin system: Basic and clinical aspects-A general perspective, Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.endien.2022.01.005
Veldman, Cantorna, Deluca, Expression of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) receptor in the immune system, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1006/abbi.1999.1605
Viana, Nunes, Reis, ACE2 imbalance as a key player for the poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients with age-related comorbidities-Role of gut microbiota dysbiosis, Ageing Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101123
Vieth, How to optimize vitamin D supplementation to prevent cancer, based on cellular adaptation and hydroxylase enzymology, Anticancer. Res
Vieth, Why "Vitamin D" is not a hormone, and not a synonym for 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D, its analogs or deltanoids, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.037
Voltan, Cannito, Ferrarese, Ceccato, Camozzi et al., An overview of gene regulation, ranging from metabolism to genomic effects, Genes, doi:10.3390/genes14091691
Walsh, Mccartney, Laird, Mccarroll, Byrne et al., Understanding a low vitamin D state in the context of COVID-19, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.835480
Wang, Chen, Zhang, Deng, Lian et al., CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x
Wang, Shi, Reiss, Allen, Maschietto et al., Insights into binding of single-stranded viral RNA template to the replication-transcription complex of SARS-CoV-2 for the priming reaction from molecular dynamics simulations, Biochemistry, doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00755
Wee, Azemi, Mokhtar, Yahaya, Yaacob et al., Vitamin D deficiency enhances vascular oxidative stress, inflammation, and angiotensin II levels in the microcirculation of diabetic patients, Microvasc. Res, doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2023.104574
Wei, Liu, Lu, Luo, An et al., Lethal infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice caused by SARS-CoV-2-related Pangolin coronavirus GX_P2V. BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.01.03.574008
Werneke, Gaughran, Taylor, Vitamin D in the time of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic-A clinical review from a public health and public mental health perspective, Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol, doi:10.1177/20451253211027699
Wimalawansa, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers reduce the complications associated with COVID-19 infection, World J. Pharma Res, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/2ME36
Wimalawansa, Commonsense approaches to minimizing risks from COVID-19, Open J. Pulmonol. Respir. Med, doi:10.36811/ojprm.2020.110010
Wimalawansa, Controlling chronic diseases and acute infections with vitamin D sufficiency, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15163623
Wimalawansa, Decoding the paradox: Understanding elevated hospitalization and reduced mortality in SARS-CoV-2 variants, Int. J. Front. in Sci. Technol. Res, doi:10.53294/ijfstr.2024.6.2.0031
Wimalawansa, Extra-skeletal and endocrine functions and toxicity of vitamin D, J. Endocrinol. Diabetes, doi:10.15226/2374-6890/3/3/00152
Wimalawansa, Fighting against COVID-19: Boosting the immunity with micronutrients, stress reduction, physical activity, and vitamin D, Nutr. Food Sci. J. (Sci Lit
Wimalawansa, Global epidemic of coronavirus-COVID-19: What can we do to minimize risks?, Eur. J. Biomed. Pharma Sci
Wimalawansa, Infections and autoimmunity-The immune system and vitamin D: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15173842
Wimalawansa, Overcoming infections including COVID-19, by maintaining circulating 25(OH)D concentrations above 50 ng/mL, Pathol. Lab. Med. Int, doi:10.2147/PLMI.S373617
Wimalawansa, Physiological basis for using vitamin D to improve health, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11061542
Wimalawansa, Polonowita, Boosting immunity with vitamin D for preventing complications and deaths from COVID-19
Wimalawansa, Prophylactic use of vitamin D to maintain a robust immune system against infections like SARS-CoV-2, Glob. J. Endocrinol. Metab. GJEM, doi:10.31031/GJEM.2023.03.000571
Wimalawansa, Rapidly increasing serum 25(OH)D boosts the immune system, against infections-sepsis and COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14142997
Wimalawansa, Unlocking insights: Navigating COVID-19 challenges and emulating future pandemic resilience strategies with strengthening natural immunity, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691
Wimalawansa, Vitamin D and cardiovascular diseases: Causality, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.12.016
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7546
Yalcin, Sukumaran, Al-Ruweidi, Shurbaji, Do changes in ACE-2 expression affect SARS-CoV-2 virulence and related complications: A closer Look into nembrane-bound and soluble forms, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22136703
Yang, Xie, Wu, Jiang, Zhao et al., The clinical characteristics and influencing factors of patients with severe COVID-19, Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, doi:10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2021.04.044
Ye, Tang, Liao, Shaw, Deng et al., Does serum vitamin D level affect COVID-19 infection and Its severity?-A case-control study, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1826005
Yeung, Teng, Jia, Zhang, Huang et al., T. ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2), COVID-19, and ACE inhibitor and Ang II (angiotensin II) receptor blocker use during the pandemic: The pediatric perspective, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15291
Yuan, Pan, Kong, Zheng, Szeto et al., 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M705495200
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1909
Zeng, Evans, King, Zheng, Oltz et al., SARS-CoV-2 spreads through cell-to-cell transmission, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2111400119
Zhang, Leung, Richers, Liu, Remigio et al., Vitamin D inhibits monocyte/macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production by targeting MAPK phosphatase-1, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102412
Zhang, Wu, Sun, Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and tissue barriers, Tissue Barriers, doi:10.4161/tisb.23118
Zheng, Yang, Hu, Li, Wang et al., Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-beta induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition, Biochem. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113955
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
Zisman, ACE and ACE2: A tale of two enzymes, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi043
Zold, Szodoray, Gaal, Kappelmayer, Csathy et al., Vitamin D deficiency in undifferentiated connective tissue disease, Arthritis Res. Ther, doi:10.1186/ar2533
Zuo, Miller Juve, Transitioning to a new era: Future directions for staff development during COVID-19, Med. Educ, doi:10.1111/medu.14387
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biology13100831",
"ISSN": [
"2079-7737"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/biology13100831",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The interaction of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with membrane-bound angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptors in epithelial cells facilitates viral entry into human cells. Despite this, ACE-2 exerts significant protective effects against coronaviruses by neutralizing viruses in circulation and mitigating inflammation. While SARS-CoV-2 reduces ACE-2 expression, vitamin D increases it, counteracting the virus’s harmful effects. Vitamin D’s beneficial actions are mediated through complex molecular mechanisms involving innate and adaptive immune systems. Meanwhile, vitamin D status [25(OH)D concentration] is inversely correlated with severity, complications, and mortality rates from COVID-19. This study explores mechanisms through which vitamin D inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication, including the suppression of transcription enzymes, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, and increased expression of neutralizing antibodies and antimicrobial peptides. Both hypovitaminosis D and SARS-CoV-2 elevate renin levels, the rate-limiting step in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS); it increases ACE-1 but reduces ACE-2 expression. This imbalance leads to elevated levels of the pro-inflammatory, pro-coagulatory, and vasoconstricting peptide angiotensin-II (Ang-II), leading to widespread inflammation. It also causes increased membrane permeability, allowing fluid and viruses to infiltrate soft tissues, lungs, and the vascular system. In contrast, sufficient vitamin D levels suppress renin expression, reducing RAS activity, lowering ACE-1, and increasing ACE-2 levels. ACE-2 cleaves Ang-II to generate Ang(1–7), a vasodilatory, anti-inflammatory, and anti-thrombotic peptide that mitigates oxidative stress and counteracts the harmful effects of SARS-CoV-2. Excess ACE-2 molecules spill into the bloodstream as soluble receptors, neutralizing and facilitating the destruction of the virus. These combined mechanisms reduce viral replication, load, and spread. Hence, vitamin D facilitates rapid recovery and minimizes transmission to others. Overall, vitamin D enhances the immune response and counteracts the pathological effects of SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, data suggests that widely used anti-hypertensive agents—angiotensin receptor blockers and ACE inhibitors—may lessen the adverse impacts of SARS-CoV-2, although they are less potent than vitamin D.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"biology13100831"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1096-8595",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CardioMetabolic and Endocrine Institute, North Brunswick, NJ 08902, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wimalawansa",
"given": "Sunil J.",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Biology",
"container-title-short": "Biology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-16T14:11:04Z",
"timestamp": 1729087864000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-18T12:39:41Z",
"timestamp": 1729255181000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-19T04:10:53Z",
"timestamp": 1729311053865,
"version": "3.27.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1729036800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/13/10/831/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "831",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2020.564387",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Santaolalla, A., Beckmann, K., Kibaru, J., Josephs, D., Van Hemelrijck, M., and Irshad, S. (2020). Association between vitamin D and novel SARS-CoV-2 respiratory dysfunction—A scoping review of current evidence and Its implication for COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Physiol., 11."
},
{
"article-title": "Global epidemic of coronavirus—COVID-19: What can we do to minimize risks?",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"first-page": "432",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Biomed. Pharma Sci.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.037",
"article-title": "Why “Vitamin D” is not a hormone, and not a synonym for 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D, its analogs or deltanoids",
"author": "Vieth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "571",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "89–90",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15173842",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Wimalawansa, S.J. (2023). Infections and autoimmunity-The immune system and vitamin D: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11061542",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Wimalawansa, S.J. (2023). Physiological basis for using vitamin D to improve health. Biomedicines, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jnci/djae116",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "Shu, J., Zhang, M., Dong, X., Long, J., Li, Y., Tan, P., He, T., Giovannucci, E.L., Zhang, X., and Zhou, Z. (2024). Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and hepatocellular carcinoma survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., Online ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25126664",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Ciocarlie, T., Motofelea, A.C., Motofelea, N., Dutu, A.G., Craciun, A., Costachescu, D., Roi, C.I., Silaghi, C.N., and Crintea, A. (2024). Exploring the role of vitamin D, vitamin D-dependent proteins, and vitamin D receptor gene variation in lung cancer risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes14091691",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "Voltan, G., Cannito, M., Ferrarese, M., Ceccato, F., and Camozzi, V. (2023). Vitamin D: An overview of gene regulation, ranging from metabolism to genomic effects. Genes, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18112252",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "Adamczak, D.M. (2017). The role of Toll-Like receptors and vitamin D in cardiovascular diseases-A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M607277200",
"article-title": "A critical role of toll-like receptor 2 in nerve injury-induced spinal cord glial cell activation and pain hypersensitivity",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14975",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "282",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"article-title": "Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1770",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "311",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041140",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Koivisto, O., Hanel, A., and Carlberg, C. (2020). Key vitamin D target genes with functions in the immune system. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/PLMI.S373617",
"article-title": "Overcoming infections including COVID-19, by maintaining circulating 25(OH)D concentrations above 50 ng/mL",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Pathol. Lab. Med. Int.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/abbi.1999.1605",
"article-title": "Expression of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) receptor in the immune system",
"author": "Veldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "334",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI111147",
"article-title": "Metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 by cultured pulmonary alveolar macrophages in sarcoidosis",
"author": "Adams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1856",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "72",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1359/JBMR.050908",
"article-title": "Immune regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in human monocytes",
"author": "Stoffels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "J. Bone Miner. Res.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389557515666150519110830",
"article-title": "Vitamin-D in the immune system: Genomic and non-genomic actions",
"author": "Trochoutsou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "953",
"journal-title": "Mini Rev. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"article-title": "Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Daneshkhah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2141",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers reduce the complications associated with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"first-page": "2579",
"journal-title": "World J. Pharma Res.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Rickets/osteomalacia. consensus on vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in children",
"author": "Michigami",
"first-page": "1307",
"journal-title": "Clin. Calcium",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105525",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Gogulothu, R., Nagar, D., Gopalakrishnan, S., Garlapati, V.R., Kallamadi, P.R., and Ismail, A. (2020). Disrupted expression of genes essential for skeletal muscle fibre integrity and energy metabolism in vitamin D deficient rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 197."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2021-0035",
"article-title": "Perspective: Vitamin D supplementation prevents rickets and acute respiratory infections when given as daily maintenance but not as intermittent bolus: Implications for COVID-19",
"author": "Griffin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e144",
"journal-title": "Clin. Med.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.2.1.12016",
"article-title": "Fundamental questions to sun protection: A continuous education symposium on vitamin D, immune system and sun protection at the University of Zurich",
"author": "Schlumpf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Dermatoendocrinol",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2010.07.022",
"article-title": "Current perspectives on vitamin D, immune system, and chronic diseases",
"author": "Borges",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Putative roles of vitamin D in modulating immune response and immunopathology associated with COVID-19",
"author": "Himani",
"first-page": "198235",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "292",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00421-019-04104-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of vitamin D on skeletal muscle function: Oxidative stress, energy metabolism and anabolic state",
"author": "Dzik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "825",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdi.12666",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in energy and bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 6-month follow-up evaluation",
"author": "Ogata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Investig.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2265.2010.03816.x",
"article-title": "Effect of cholecalciferol and calcium supplementation on muscle strength and energy metabolism in vitamin D-deficient Asian Indians: A randomized, controlled trial",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15163623",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Wimalawansa, S.J. (2023). Controlling chronic diseases and acute infections with vitamin D sufficiency. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04147.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, cardiovascular disease and mortality",
"author": "Pilz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "575",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.12.016",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and cardiovascular diseases: Causality",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "How to optimize vitamin D supplementation to prevent cancer, based on cellular adaptation and hydroxylase enzymology",
"author": "Vieth",
"first-page": "3675",
"journal-title": "Anticancer. Res.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.971720",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Chen, X., Zhou, M., Yan, H., Chen, J., Wang, Y., and Mo, X. (2022). Association of serum total 25-hydroxy-vitamin D concentration and risk of all-cause, cardiovascular and malignancies-specific mortality in patients with hyperlipidemia in the United States. Front. Nutr., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/ACPJC-2006-145-1-004",
"article-title": "Calcium plus vitamin D did not prevent hip fracture or colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women",
"author": "Fletcher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "ACP J. Club",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ebn.9.4.114",
"article-title": "Calcium plus vitamin D did not prevent fractures or colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women",
"author": "Riddell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Evid. Based Nurs.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EC-22-0234",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in British South Asians, a persistent but avoidable problem associated with many health risks (including rickets, T2DM, CVD, COVID-19 and pregnancy complications): The case for correcting this deficiency",
"author": "Boucher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e220234",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Connect.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2017.01.039",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy: Improvements in birth outcomes and complications through direct genomic alteration",
"author": "Hollis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "453",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10040489",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_38",
"unstructured": "Al-Musharaf, S., Fouda, M.A., Turkestani, I.Z., Al-Ajlan, A., Sabico, S., Alnaami, A.M., Wani, K., Hussain, S.D., Alraqebah, B., and Al-Serehi, A. (2018). Vitamin D deficiency prevalence and predictors in early pregnancy among Arab women. Nutrients, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.12.011",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: Effects on human reproduction, pregnancy, and fetal well-being",
"author": "Heyden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/healthcare11142097",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Almuqbil, M., Almadani, M.E., Albraiki, S.A., Alamri, A.M., Alshehri, A., Alghamdi, A., Alshehri, S., and Asdaq, S.M.B. (2023). Impact of vitamin D deficiency on mental health in university students: A cross-sectionalstudy. Healthcare, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109651",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "Jamilian, H., Amirani, E., Milajerdi, A., Kolahdooz, F., Mirzaei, H., Zaroudi, M., Ghaderi, A., and Asemi, Z. (2019). The effects of vitamin D supplementation on mental health, and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with psychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 94."
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor FokI genotype may modify the susceptibility to schizophrenia and bipolar mood disorder by regulation of dopamine D1 receptor gene expression",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Minerva Med.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16121902",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "Jahan-Mihan, A., Stevens, P., Medero-Alfonso, S., Brace, G., Overby, L.K., Berg, K., and Labyak, C. (2024). The role of water-soluble citamins and vitamin D in prevention and treatment of depression and seasonal affective disorder in adults. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12877-015-0148-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "de Koning, E.J., van Schoor, N.M., Penninx, B.W., Elders, P.J., Heijboer, A.C., Smit, J.H., Bet, P.M., van Tulder, M.W., den Heijer, M., and van Marwijk, H.W. (2015). Vitamin D supplementation to prevent depression and poor physical function in older adults: Study protocol of the D-Vitaal study, a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. BMC Geriatr., 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.017",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in the prevention of acute respiratory infection: Systematic review of clinical studies",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamasurg.2013.3176",
"article-title": "Association between preoperative 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and hospital-acquired infections following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery",
"author": "Quraishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "JAMA Surg.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "ref_48",
"unstructured": "(2024, March 25). Group-C19.com. Vitamin D for COVID-19: Real-Time Analysis of all 300 Studies. Available online: https://c19vitamind.com/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(24)00009-6",
"article-title": "Active vitamin D treatment in the prevention of sarcopenia in adults with prediabetes (DPVD ancillary study): A randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Kawahara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e255",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longev.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijtb.2023.04.026",
"article-title": "Effect of adjunct Vitamin D treatment in vitamin D deficient pulmonary tuberculosis patients: A randomized, double blind, active controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Chandra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "170",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Tuberc.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14142997",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_51",
"unstructured": "Wimalawansa, S.J. (2022). Rapidly increasing serum 25(OH)D boosts the immune system, against infections-sepsis and COVID-19. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030505",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Karonova, T.L., Chernikova, A.T., Golovatyuk, K.A., Bykova, E.S., Grant, W.B., Kalinina, O.V., Grineva, E.N., and Shlyakhto, E.V. (2022). Vitamin D intake may reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection morbidity in health care workers. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15226/2374-6890/3/3/00152",
"article-title": "Extra-skeletal and endocrine functions and toxicity of vitamin D",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/endoabs.90.P633",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Smaha, J., Jackuliak, P., Kuzma, M., Max, F., Binkley, N., and Payer, J. (2023). Vitamin D deficiency prevalence in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 significantly fecreased during the pandemic in Slovakia from 2020 to 2022 Which Was associated with decreasing mortality. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.36811/ojprm.2020.110010",
"article-title": "Commonsense approaches to minimizing risks from COVID-19",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Open J. Pulmonol. Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Fighting against COVID-19: Boosting the immunity with micronutrients, stress reduction, physical activity, and vitamin D",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Food Sci. J. (Sci Lit.)",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9081038",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Giordano, D., De Masi, L., Argenio, M.A., and Facchiano, A. (2021). Structural dissection of viral Spike-protein binding of SARS CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as cellular receptor. Biomedicines, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202400823",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Mancini, T., Macis, S., Mosetti, R., Luchetti, N., Minicozzi, V., Notargiacomo, A., Pea, M., Marcelli, A., Ventura, G.D., and Lupi, S. (2024). Infrared Spectroscopy of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Protein: From Receptor Binding Domain to Spike Protein. Adv. Sci., e2400823."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-16048-4",
"article-title": "Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus by recombinant ACE2-Ig",
"author": "Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2070",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/uog.22186",
"article-title": "Single-cell RNA expression profiling of SARS-CoV-2-related ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophectoderm and placenta",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01648-20",
"article-title": "The inhaled steroid ciclesonide blocks SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication by targeting the viral replication-transcription complex in cultured cells",
"author": "Matsuyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10-1128",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00755",
"article-title": "Insights into binding of single-stranded viral RNA template to the replication-transcription complex of SARS-CoV-2 for the priming reaction from molecular dynamics simulations",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "424",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1003944",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_63",
"unstructured": "Chuang, C., Barajas, D., Qin, J., and Nagy, P.D. (2014). Inactivation of the host lipin gene accelerates RNA virus replication through viral exploitation of the expanded endoplasmic reticulum membrane. PLoS Pathog., 10."
},
{
"article-title": "How SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) spreads within infected hosts—What we know so far",
"author": "Sanyal",
"first-page": "371",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Top. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2119",
"article-title": "A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2119",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Renin-angiotensin system: Basic and clinical aspects-A general perspective",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. (Engl. Ed.)",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871528113666140713164506",
"article-title": "ACE and ACE2 in inflammation: A tale of two enzymes",
"author": "Gaddam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "224",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1432869100",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-(1–7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8258",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/atm.2016.11.03",
"article-title": "Treating the host response to emerging virus diseases: Lessons learned from sepsis, pneumonia, influenza and Ebola",
"author": "Fedson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "421",
"journal-title": "Ann. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mvr.2023.104574",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency enhances vascular oxidative stress, inflammation, and angiotensin II levels in the microcirculation of diabetic patients",
"author": "Wee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104574",
"journal-title": "Microvasc. Res.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1146",
"article-title": "VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Kong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2116",
"journal-title": "Mol. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9100936",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_72",
"unstructured": "Beltran-Garcia, J., Osca-Verdegal, R., Pallardo, F.V., Ferreres, J., Rodriguez, M., Mulet, S., Sanchis-Gomar, F., Carbonell, N., and Garcia-Gimenez, J.L. (2020). Oxidative stress and Inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: The potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression. Antioxidants, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3126/ajms.v14i11.57095",
"article-title": "Vitamin D as a biomarker in predicting sepsis outcome at a tertiary care hospital",
"author": "Ghosh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "Asian J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M705495200",
"article-title": "1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29821",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "282",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/mja2.50674",
"article-title": "COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): Clinical features and differences from typical pre-COVID-19 ARDS",
"author": "Gibson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "Med. J. Aust.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "213",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40885-020-00147-x",
"article-title": "The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 are distinctly different paradigms",
"author": "McLachlan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Clin. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25785",
"article-title": "Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "726",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_77",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome",
"author": "Devaux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "425",
"journal-title": "J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.017",
"article-title": "The two faces of ACE2: The role of ACE2 receptor and Its polymorphisms in hypertension and COVID-19",
"author": "Bosso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20120519",
"article-title": "Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade restores angiotensin-(1–7)-induced coronary vasodilation in hypertrophic rat hearts",
"author": "Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Clin. Sci.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.22940",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-(1–7) decreases LPS-induced inflammatory response in macrophages",
"author": "Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2117",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "227",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Detection of the mRNA expression of human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a SARS coronavirus functional receptor in human femoral head",
"author": "Dong",
"first-page": "441",
"journal-title": "Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "426",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehi043",
"article-title": "ACE and ACE2: A tale of two enzymes",
"author": "Zisman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1741-7015-2-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_85",
"unstructured": "Goulter, A.B., Goddard, M.J., Allen, J.C., and Clark, K.L. (2004). ACE2 gene expression is up-regulated in the human failing heart. BMC Med., 2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.05.005",
"article-title": "Interaction of ACE2 and integrin beta1 in failing human heart",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "ref_86",
"volume": "1689",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jnc.13386",
"article-title": "Direct anti-inflammatory effects of angiotensin-(1–7) on microglia",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "163",
"journal-title": "J. Neurochem.",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajprenal.00655.2013",
"article-title": "Angiotensin 1–7 mediates renoprotection against diabetic nephropathy by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipotoxicity",
"author": "Mori",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "F812",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "306",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1000314",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of the activation of the angiotensin-(1–7) receptor, MAS, in experimental models of arthritis",
"author": "Coelho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5569",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2119/2007-00073.Fraga-Silva",
"article-title": "The antithrombotic effect of angiotensin-(1–7) involves mas-mediated NO release from platelets",
"author": "Pinheiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_90",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307708",
"article-title": "Role of the ACE2/angiotensin 1–7 axis of the renin-angiotensin system in heart failure",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1313",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00937.2006",
"article-title": "Prevention of angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling by angiotensin-(1–7)",
"author": "Grobe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H736",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiology. Heart Circ. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "292",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.172700",
"article-title": "New take on the role of angiotensin II in cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis",
"author": "Kurdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1034",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00109-013-1087-0",
"article-title": "Oral administration of angiotensin-(1–7) ameliorates type 2 diabetes in rats",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Renal blood flow response to angiotensin 1–7 versus hypertonic sodium chloride 7.5% administration after acute hemorrhagic shock in rats",
"author": "Maleki",
"first-page": "6562017",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Vasc. Med.",
"key": "ref_95",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14014.x",
"article-title": "Natriuretic action of angiotensin(1–7)",
"author": "DelliPizzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "111",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnbeh.2022.903980",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_97",
"unstructured": "Bruhns, R.P., Sulaiman, M.I., Gaub, M., Bae, E.H., Davidson Knapp, R.B., Larson, A.R., Smith, A., Coleman, D.L., Staatz, W.D., and Sandweiss, A.J. (2022). Angiotensin-(1–7) improves cognitive function and reduces inflammation in mice following mild traumatic brain injury. Front. Behav. Neurosci., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.004",
"article-title": "Neuronal over-expression of ACE2 protects brain from ischemia-induced damage",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "550",
"journal-title": "Neuropharmacology",
"key": "ref_98",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1113/expphysiol.2013.075242",
"article-title": "Centrally administered angiotensin-(1–7) increases the survival of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats",
"author": "Regenhardt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "Exp. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00023.2016",
"article-title": "The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1–7)/MAS axis of the renin-angiotensin system: Focus on angiotensin-(1–7)",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_100",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11906-018-0900-0",
"article-title": "Inflammation as a regulator of the renin-angiotensin system and blood pressure",
"author": "Satou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "Curr. Hypertens. Rep.",
"key": "ref_101",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/emmm.201000080",
"article-title": "Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging",
"author": "Benigni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_102",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_103",
"unstructured": "Samavati, L., and Uhal, B.D. (2020). ACE2, much more than just a receptor for SARS-COV-2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2",
"author": "Monteil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_104",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.066",
"article-title": "Circulating vitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D in humans: An important tool to define adequate nutritional vitamin D status",
"author": "Hollis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_105",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152286",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_106",
"unstructured": "Bold, A., Gross, H., Holzmann, E., Smetak, M., Birkmann, J., Bertsch, T., Triebel, J., Sauer, K., Wilhelm, M., and Hoeres, T. (2022). Immune activating and inhibiting effects of calcitriol on gammadelta T cells and NK cells. Immunobiology, 227."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Zdrenghea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1909",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_107",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14224907",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_108",
"unstructured": "Gotelli, E., Soldano, S., Hysa, E., Paolino, S., Campitiello, R., Pizzorni, C., Sulli, A., Smith, V., and Cutolo, M. (2022). Vitamin D and COVID-19: Narrative review after 3 years of pandemic. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"article-title": "Prophylactic use of vitamin D to maintain a robust immune system against infections like SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"first-page": "000571",
"journal-title": "Glob. J. Endocrinol. Metab. GJEM",
"key": "ref_109",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "CD8+ T-cell deficiency, Epstein-Barr virus infection, vitamin D deficiency, and steps to autoimmunity: A unifying hypothesis",
"author": "Pender",
"first-page": "189096",
"journal-title": "Autoimmune Dis.",
"key": "ref_110",
"volume": "2012",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000000210",
"article-title": "Prospective study of vitamin D status at initiation of care in critically ill surgical patients and risk of 90-day mortality",
"author": "Quraishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1365",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_111",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110232",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulates expression of antimicrobial peptides and proinflammatory cytokines to restrict Zika virus infection in macrophages",
"author": "Fernandez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110232",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_112",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12936-023-04612-4",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D reduce the mortality rate of Plasmodium infection?: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Kalantari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Malar. J.",
"key": "ref_113",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TIN.0000000000000284",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D and prevention of respiratory tract infections and COVID-19",
"author": "Shoemaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Top. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_114",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3693",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "ref_115",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.08.002",
"article-title": "Age-differential CD13 and interferon expression in airway epithelia affect SARS-CoV-2 infection—Effects of vitamin D",
"author": "Sposito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "776",
"journal-title": "Mucosal Immunol.",
"key": "ref_116",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0263069",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_117",
"unstructured": "Dror, A.A., Morozov, N., Daoud, A., Namir, Y., Yakir, O., Shachar, Y., Lifshitz, M., Segal, E., Fisher, L., and Mizrachi, M. (2022). Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15122690",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_118",
"unstructured": "Gan, Y., You, S., Ying, J., and Mu, D. (2023). The association between serum vitamin D levels and urinary tract infection risk in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 infection in children: A case-control study",
"author": "Bayrak",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "Turk. Arch. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_119",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D deficiency in increased susceptibility to respiratory infections among children: A systematic review",
"author": "Raju",
"first-page": "e29205",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "ref_120",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.12767",
"article-title": "Daily adjunctive therapy with vitamin D(3) and phenylbutyrate supports clinical recovery from pulmonary tuberculosis: A randomized controlled trial in Ethiopia",
"author": "Bekele",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "292",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_121",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2334-13-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_122",
"unstructured": "Salahuddin, N., Ali, F., Hasan, Z., Rao, N., Aqeel, M., and Mahmood, F. (2013). Vitamin D accelerates clinical recovery from tuberculosis: Results of the SUCCINCT Study [Supplementary Cholecalciferol in recovery from tuberculosis]. A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of vitamin D supplementation in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis’. BMC Infect. Dis., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000001148",
"article-title": "Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on vitamin D status and cathelicidin levels in sepsis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Quraishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1928",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_123",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CIA.S395228",
"article-title": "Preoperative vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased one-year mortality in Chinese geriatric hip fracture patients—A propensity score matching study",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Clin. Interv. Aging",
"key": "ref_124",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.02.013",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with hospital morbidity and mortality in adult hospitalized patients wth COVID-19",
"author": "Charoenngam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Pract.",
"key": "ref_125",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061990",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_126",
"unstructured": "Rustecka, A., Maret, J., Drab, A., Leszczynska, M., Tomaszewska, A., Lipinska-Opalka, A., Bedzichowska, A., Kalicki, B., and Kubiak, J.Z. (2021). The Impact of COVID-19 pandemic during 2020-2021 on the vitamin D serum levels in the paediatric population in Warsaw, Poland. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.09.22.21263977",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_127",
"unstructured": "Borsche, L., Glauner, B., and von Mendel, J. (2021). COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.02.012",
"article-title": "Changing incidence of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D values above 50 ng/mL: A 10-year population-based study",
"author": "Dudenkov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin. Proc.",
"key": "ref_128",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_129",
"unstructured": "Radujkovic, A., Hippchen, T., Tiwari-Heckler, S., Dreher, S., Boxberger, M., and Merle, U. (2020). Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"key": "ref_130",
"unstructured": "Wimalawansa, S.J., and Polonowita, A. (, January January). Boosting immunity with vitamin D for preventing complications and deaths from COVID-19. Proceedings of the COVID 19: Impact, Mitigation, Opportunities and Building Resilience “From Adversity to Serendipity,” Perspectives of Global Relevance Based on Research, Experience and Successes in Combating COVID-19 in Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Baktash",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_131",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph16010130",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_132",
"unstructured": "Argano, C., Mallaci Bocchio, R., Natoli, G., Scibetta, S., Lo Monaco, M., and Corrao, S. (2023). Protective effect of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19-related intensive care hospitalization and mortality: Sefinitive evidence from meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"article-title": "Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4240",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref_133",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14173584",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_134",
"unstructured": "Cicero, A.F.G., Fogacci, F., and Borghi, C. (2022). Vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 outcomes: Mounting evidence and fewer doubts. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114047",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_135",
"unstructured": "Gonen, M.S., Alaylioglu, M., Durcan, E., Ozdemir, Y., Sahin, S., Konukoglu, D., Nohut, O.K., Urkmez, S., Kucukece, B., and Balkan, İ.İ. (2021). Rapid and effective vitamin D supplementation may present better clinical outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) patients by altering serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_136",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/mcn.12987",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D supplementation with respiratory tract infection in infants",
"author": "Hong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e12987",
"journal-title": "Matern. Child. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_137",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0300-9831/a000676",
"article-title": "Vitamin D can be effective on the prevention of COVID-19 complications: A narrative review on molecular aspects",
"author": "Shiravi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res.",
"key": "ref_138",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D, Covid-19 and Children",
"author": "Molloy",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_139",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2020.1786302",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Wellbeing beyond Infections: COVID-19 and Future Pandemics",
"author": "Stohs",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_140",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15796",
"article-title": "Editorial: Low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North-supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity. Authors’ reply",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1438",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_141",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial",
"author": "Jaun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "ref_142",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14132716",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_143",
"unstructured": "Quesada-Gomez, J.M., Lopez-Miranda, J., Entrenas-Castillo, M., Casado-Diaz, A., Nogues, Y.S.X., Mansur, J.L., and Bouillon, R. (2022). Vitamin D endocrine system and COVID-19: Treatment with calcifediol. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"article-title": "Treatment With 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Calcifediol) Is Associated With a Reduction in the Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Marker of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: A Pilot Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1242",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Pract.",
"key": "ref_144",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3690902",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_145",
"unstructured": "Ling, S.F., Broad, E., Murphy, R., Pappachan, J.M., Pardesi-Newton, S., Kong, M.F., and Jude, E.B. (2020). High-dose cholecalciferol booster therapy is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: A cross-sectional multi-centre observational study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_146",
"unstructured": "Entrenas Castillo, M., Entrenas Costa, L.M., Vaquero Barrios, J.M., Alcala Diaz, J.F., Lopez Miranda, J., Bouillon, R., and Quesada Gomez, J.M. (2020). Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 203."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2021.2012419",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D status and risk of covid-19 in-hospital mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Ebrahimzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5033",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_147",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13051714",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_148",
"unstructured": "AlSafar, H., Grant, W.B., Hijazi, R., Uddin, M., Alkaabi, N., Tay, G., Mahboub, B., and Al Anouti, F. (2021). COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin D status among SARS-CoV-2-positive UAE residents. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111408",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its prognostic impact on patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Bianconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111408",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_149",
"volume": "91–92",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.016",
"article-title": "Letter to the editor in response to the article: “Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK biobank” (Hastie et al.)",
"author": "Davies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "643",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_150",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_151",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pubmed/fdaa095",
"article-title": "Greater risk of severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic populations is not explained by cardiometabolic, socioeconomic or behavioural factors, or by 25(OH)-vitamin D status: Study of 1326 cases from the UK Biobank",
"author": "McCracken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "J. Public Health",
"key": "ref_152",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmab012",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Kazemi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1636",
"journal-title": "Adv. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_153",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_154",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_155",
"unstructured": "Kaufman, H.W., Niles, J.K., Kroll, M.H., Bi, C., and Holick, M.F. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"article-title": "Preventing a COVID-19 pandemic-COVID-19",
"author": "Brown",
"first-page": "m810",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_156",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and inflammation: Potential implications for severity of Covid-19",
"author": "Laird",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_157",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_158",
"unstructured": "Annweiler, C., Hanotte, B., Grandin de l’Eprevier, C., Sabatier, J.M., Lafaie, L., and Celarier, T. (2020). Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 204."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_159",
"unstructured": "Annweiler, G., Corvaisier, M., Gautier, J., Dubee, V., Legrand, E., Sacco, G., and Annweiler, C. (2020). Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID Quasi-Experimental Study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.08.20095893",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_160",
"unstructured": "Meltzer, D.O., Best, T.J., Zhang, H., Vokes, T., Arora, V., and Solway, J. (2020). Association of vitamin D deficiency and treatment with COVID-19 incidence. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 Test resultt",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2019722",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_161",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.01.044",
"article-title": "Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia with 25(OH)D levels lower than 12 ng/ml are at increased risk of death",
"author": "Smaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "313",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_162",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kww244",
"article-title": "The reverse J-shaped association between serum Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and all-cause mortality: The impact of assay standardization",
"author": "Kramer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "720",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref_163",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2012-1176",
"article-title": "A reverse J-shaped association of all-cause mortality with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in general practice: The CopD study",
"author": "Durup",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2644",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_164",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-021-07170-0",
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D Status and COVID-19-Related Hospitalization and Mortality",
"author": "Seal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "853",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_165",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxab107",
"article-title": "Low Circulating Vitamin D in Intensive Care Unit-Admitted COVID-19 Patients as a Predictor of Negative Outcomes",
"author": "Bychinin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2199",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_166",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.863587",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_167",
"unstructured": "Cervero, M., Lopez-Wolf, D., Casado, G., Novella-Mena, M., Ryan-Murua, P., Taboada-Martinez, M.L., Rodriguez-Mora, S., Vigon, L., Coiras, M., and Torres, M. (2022). Beneficial effect of short-term supplementation of high dose of vitamin D(3) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, single-blinded, prospective randomized pilot clinical trial. Front. Pharmacol., 13."
},
{
"article-title": "An evaluation of serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in patients with COVID-19 in New York City",
"author": "Gavioli",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Nutr. Assoc.",
"key": "ref_168",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D status and risk of developing severe COVID-19 infection: A meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Hopefl",
"first-page": "679",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_169",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0268038",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_170",
"unstructured": "Nguyen, N.N., Raju, M.N.P., da Graca, B., Wang, D., Mohamed, N.A., Mutnal, M.B., Rao, A., Bennett, M., Gokingco, M., and Pham, H. (2022). 25-hydroxyvitamin D is a predictor of COVID-19 severity of hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.04.003",
"article-title": "Association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity",
"author": "Takase",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "256",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr. ESPEN",
"key": "ref_171",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3",
"article-title": "Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of TH1 cells",
"author": "Chauss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_172",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"article-title": "Mechanisums in Endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19",
"author": "Bilezikian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R133",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_173",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-386960-9.00002-2",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and innate and adaptive immunity",
"author": "Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Vitam. Horm.",
"key": "ref_174",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.835480",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_175",
"unstructured": "Walsh, J.B., McCartney, D.M., Laird, E., McCarroll, K., Byrne, D.G., Healy, M., O’Shea, P.M., Kenny, R.A., and Faul, J.L. (2022). Understanding a low vitamin D state in the context of COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20451253211027699",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in the time of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic—A clinical review from a public health and public mental health perspective",
"author": "Werneke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20451253211027699",
"journal-title": "Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_176",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune function: Autocrine, paracrine or endocrine?",
"author": "Hewison",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl.",
"key": "ref_177",
"volume": "243",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system",
"author": "Aranow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "881",
"journal-title": "J. Investig. Med.",
"key": "ref_178",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MNH.0b013e3282ff64a3",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system: Role in protection against bacterial infection",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "348",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_179",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.11.012",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 supplementation, low-risk prostate cancer, and health disparities",
"author": "Hollis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_180",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2010.02.010",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system: New perspectives on an old theme",
"author": "Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am.",
"key": "ref_181",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030473",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_182",
"unstructured": "Giannini, S., Giusti, A., Minisola, S., Napoli, N., Passeri, G., Rossini, M., and Sinigaglia, L. (2022). The immunologic profile of vitamin D and its role in different immune-mediated diseases: An expert opinion. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jit355",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on innate and adaptive immune responses to Streptococcus pneumoniae",
"author": "Olliver",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1474",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_183",
"volume": "208",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02399.x",
"article-title": "Control of the innate epithelial antimicrobial response is cell-type specific and dependent on relevant microenvironmental stimuli",
"author": "Schauber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "ref_184",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174193",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Th1 and Th2 mediated cellular and humoral immunity in patients with COVID-19 following the use of melatonin as an adjunctive treatment",
"author": "Hosseini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "174193",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_185",
"volume": "904",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.27180",
"article-title": "The pathogenesis of thyroid autoimmune diseases: New T lymphocytes—Cytokines circuits beyond the Th1-Th2 paradigm",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2204",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_186",
"volume": "234",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1102412",
"article-title": "Vitamin D inhibits monocyte/macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production by targeting MAPK phosphatase-1",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2127",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_187",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14276",
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity",
"author": "Panagiotou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "508",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_188",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1308",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_189",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113955",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_190",
"unstructured": "Zheng, S., Yang, J., Hu, X., Li, M., Wang, Q., Dancer, R.C.A., Parekh, D., Gao-Smith, F., Thickett, D.R., and Jin, S. (2020). Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-beta induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Pharmacol., 177."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.15-272872",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulates tissue factor and protease-activated receptor 2 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells",
"author": "Herencia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1367",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_191",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_192",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691",
"article-title": "Unlocking insights: Navigating COVID-19 challenges and emulating future pandemic resilience strategies with strengthening natural immunity",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e34691",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_193",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0803217",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3",
"author": "Jeffery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5458",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_194",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2020.1826005",
"article-title": "Does serum vitamin D level affect COVID-19 infection and Its severity?-A case-control study",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "724",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_195",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/tisb.23118",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_196",
"unstructured": "Zhang, Y.G., Wu, S., and Sun, J. (2013). Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and tissue barriers. Tissue Barriers, 1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27075",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19: Role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity",
"author": "Getachew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5285",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_197",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.21162",
"article-title": "Enhanced tight junction function in human breast cancer cells by antioxidant, selenium and polyunsaturated lipid",
"author": "Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_198",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082358",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_199",
"unstructured": "Alexander, J., Tinkov, A., Strand, T.A., Alehagen, U., Skalny, A., and Aaseth, J. (2020). Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1756-185X.14477",
"article-title": "Vitamin D-A prominent immunomodulator to prevent COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Ashique",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "ref_200",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43856-023-00320-x",
"article-title": "Evolutionary implications of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination for the future design of vaccination strategies",
"author": "Rouzine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "86",
"journal-title": "Commun. Med.",
"key": "ref_201",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cub.2020.03.056",
"article-title": "The impact of neutral mutations on genome evolvability",
"author": "Tenaillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R527",
"journal-title": "Curr. Biol.",
"key": "ref_202",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.01.30.22270133",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_203",
"unstructured": "Konishi, T. (2022). Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 are on the increase against the acquired immunity. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28406",
"article-title": "In silico study of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD and human ACE-2 affinity dynamics across variants and Omicron subvariants",
"author": "Abeywardhana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28406",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_204",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.005",
"article-title": "Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum",
"author": "Tuekprakhon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2422",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_205",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.032",
"article-title": "The antigenic anatomy of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain",
"author": "Dejnirattisai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2183",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_206",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06580-1",
"article-title": "Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes: A birth-cohort study",
"author": "Hypponen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_207",
"volume": "358",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-006-0426-x",
"article-title": "Lower levels of plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D among young adults at diagnosis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes compared with control subjects: Results from the nationwide Diabetes Incidence Study in Sweden (DISS)",
"author": "Littorin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2847",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "ref_208",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2011.118",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review",
"author": "Mitri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1005",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_209",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar2533",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in undifferentiated connective tissue disease",
"author": "Zold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R123",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res. Ther.",
"key": "ref_210",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MIB.0000000000000546",
"article-title": "Association between inflammatory bowel disease and Vitamin D deficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pietropaoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2708",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Bowel Dis.",
"key": "ref_211",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12876-019-1004-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_212",
"unstructured": "Hu, Y.C., Wang, W.W., Jiang, W.Y., Li, C.Q., Guo, J.C., and Xun, Y.H. (2019). Low vitamin D levels are associated with high viral loads in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000323941",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a strong predictor of asthma in children",
"author": "Bener",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol.",
"key": "ref_213",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2105/AJPH.2004.045260",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in cancer prevention",
"author": "Garland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Public Health",
"key": "ref_214",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annepidem.2009.03.021",
"article-title": "Vitamin D for cancer prevention: Global perspective",
"author": "Garland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "468",
"journal-title": "Ann. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref_215",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0176448",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_216",
"unstructured": "Grant, W.B., and Boucher, B.J. (2017). Randomized controlled trials of vitamin D and cancer incidence: A modeling study. PLoS ONE, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.08.009",
"article-title": "Why vitamin D clinical trials should be based on 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_217",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11071460",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_218",
"unstructured": "Marino, R., and Misra, M. (2019). Extra-Skeletal Effects of Vitamin D. Nutrients, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12030628",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_219",
"unstructured": "D’Amelio, P., and Quacquarelli, L. (2020). Hypovitaminosis D and aging: Is there a role in muscle and brain health?. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-022-03208-3",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in the older population: A consensus statement",
"author": "Giustina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "ref_220",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19030892",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_221",
"unstructured": "Caccamo, D., Ricca, S., Curro, M., and Ientile, R. (2018). Health risks of hypovitaminosis D: A review of new molecular insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2012/256294",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) Is a key modulator of the renin angiotensin system in health and disease",
"author": "Tikellis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "256294",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Pept.",
"key": "ref_222",
"volume": "2012",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_223",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2019.02.021",
"article-title": "Relationship between vitamin D deficiency, diabetes, and obesity",
"author": "Alloubani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1457",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_224",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency, obesity and diabetes",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_225",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-021-09679-5",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, infections and immunity",
"author": "Ismailova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "ref_226",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16111595",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_227",
"unstructured": "Sarau, O.S., Rachabattuni, H.C., Gadde, S.T., Daruvuri, S.P., Marusca, L.M., Horhat, F.G., Fildan, A.P., Tanase, E., Prodan-Barbulescu, C., and Horhat, D.I. (2024). Exploring the preventive potential of vitamin D against respiratory infections in preschool-age children: A cross-sectional study. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-015-2970-6",
"article-title": "Severe vitamin D deficiency in patients with Kawasaki disease: A potential role in the risk to develop heart vascular abnormalities?",
"author": "Stagi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1865",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_228",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ped.15191",
"article-title": "The impact of vitamin D on the onset and progress of Kawasaki disease",
"author": "Okazaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e15191",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Int.",
"key": "ref_229",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13093021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_230",
"unstructured": "Karonova, T.L., Andreeva, A.T., Golovatuk, K.A., Bykova, E.S., Simanenkova, A.V., Vashukova, M.A., Grant, W.B., and Shlyakhto, E.V. (2021). Low 25(OH)D level is associated with severe course and poor prognosis in COVID-19. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11357-020-00314-w",
"article-title": "Age-associated difference in circulating ACE2, the gateway for SARS-COV-2, in humans: Results from the InCHIANTI study",
"author": "AlGhatrif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "Geroscience",
"key": "ref_231",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?",
"author": "Marik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100041",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_232",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/medu.14387",
"article-title": "Transitioning to a new era: Future directions for staff development during COVID-19",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104",
"journal-title": "Med. Educ.",
"key": "ref_233",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107001",
"article-title": "Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality in the Indian population: An observational study",
"author": "Padhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107001",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_234",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41371-020-00398-z",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in African Americans is associated with a high risk of severe disease and mortality by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Inserra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "378",
"journal-title": "J. Hum. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_235",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.09.727",
"article-title": "Rays of immunity: Role of sunshine vitamin in management of COVID-19 infection and associated comorbidities",
"author": "Pavan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr. ESPEN",
"key": "ref_236",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-021-01831-0",
"article-title": "Severe vitamin D deficiency is not related to SARS-CoV-2 infection but may increase mortality risk in hospitalized adults: A retrospective case-control study in an Arab Gulf country",
"author": "Alguwaihes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1415",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_237",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3961/jpmph.21.640",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and comorbidities as risk factors of COVID-19 Infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Mishra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "J. Prev. Med. Public Health",
"key": "ref_238",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5501/wjv.v11.i1.85",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D deficiency and comorbidities in COVID-19",
"author": "Alberca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "World J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_239",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.53346/wjapls.2023.5.2.0080",
"article-title": "The impact of withholding cost-effective early treatments, such as vitamin D, on COVID-19: An analysis using an innovative logical paradigm",
"author": "Polonowita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "World J. Adv. Pharm. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_240",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00354-023-00211-8",
"article-title": "A systematic literature review and future perspectives for handling big data analytics in COVID-19 diagnosis",
"author": "Tenali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "New Gener. Comput.",
"key": "ref_241",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.53294/ijfstr.2024.6.2.0031",
"article-title": "Decoding the paradox: Understanding elevated hospitalization and reduced mortality in SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Wimalawansa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Front. in Sci. Technol. Res.",
"key": "ref_242",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-36494-0",
"article-title": "Risk of death following COVID-19 vaccination or positive SARS-CoV-2 test in young people in England",
"author": "Nafilyan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1541",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_243",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-021-02902-w",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher risks for SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity: A retrospective case-control study",
"author": "Israel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"journal-title": "Intern. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "ref_244",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Shedding light on vitamin D: The shared mechanistic and pathophysiological role between hypovitaminosis D and COVID-19 risk factors and complications",
"author": "Menshawey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref_245",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_246",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_247",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00408-020-00408-4",
"article-title": "ACE2: The major cell entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Scialo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "Lung",
"key": "ref_248",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_249",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2111400119",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spreads through cell-to-cell transmission",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2111400119",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_250",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.C110.216580",
"article-title": "Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) regulates autophagy in cultured astrocytes",
"author": "Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27875",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_251",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00189.2020",
"article-title": "Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury",
"author": "Sarzani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L325",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_252",
"volume": "319",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"article-title": "Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7432",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "ref_253",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2021.03.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 ARDS patients",
"author": "Notz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3089",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_254",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and ARDS after SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Faul",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_255",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)",
"author": "Dancer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "ref_256",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157489007779606130",
"article-title": "The role of angiotensin type 1 receptor in inflammation and endothelial dysfunction",
"author": "Skultetyova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Recent. Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_257",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11071129",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_258",
"unstructured": "Sun, J., and Zhang, Y.G. (2022). Vitamin D receptor influences Intestinal barriers in health and disease. Cells, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15082",
"article-title": "Renin-angiotensin system blockers and the COVID-19 pandemic: At present there is no evidence to abandon renin-angiotensin system blockers",
"author": "Danser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_259",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The clinical characteristics and influencing factors of patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "1295",
"journal-title": "Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "ref_260",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI0215219",
"article-title": "1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) is a negative endocrine regulator of the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_261",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.148619",
"article-title": "Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D and regulation of the renin-angiotensin system in humans",
"author": "Forman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1283",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_262",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjhyper.2007.01.017",
"article-title": "Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, ethnicity, and blood pressure in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey",
"author": "Scragg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "713",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_263",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602825",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and health correlates among German adults",
"author": "Hintzpeter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1079",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_264",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41440-019-0321-8",
"article-title": "Stimulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1–7)/Mas axis in hypertensive pregnant rats attenuates cardiovascular dysfunction in adult male offspring",
"author": "Bessa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1883",
"journal-title": "Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_265",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175623",
"article-title": "ACE2/ANG-(1–7)/Mas receptor axis activation prevents inflammation and improves cognitive functions in streptozotocin induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotypes",
"author": "Tiwari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175623",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_266",
"volume": "946",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7168",
"article-title": "Role of the ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas axis in blood pressure regulation and its potential as an antihypertensive in functional foods",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4403",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "ref_267",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-021-04275-2",
"article-title": "Role of ACE2-Ang (1–7)-Mas axis in post-COVID-19 complications and its dietary modulation",
"author": "Sahu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "225",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_268",
"volume": "477",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x",
"article-title": "CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_269",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Basigin binds Spike S on SARS-CoV2",
"author": "Chambers",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Res.",
"key": "ref_270",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10061434",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_271",
"unstructured": "Fenizia, C., Galbiati, S., Vanetti, C., Vago, R., Clerici, M., Tacchetti, C., and Daniele, T. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 entry: At the crossroads of CD147 and ACE2. Cells, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cyto.a.24285",
"article-title": "Little to no expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 on most human peripheral blood immune cells but highly expressed on tissue macrophages",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "136",
"journal-title": "Cytom. A",
"key": "ref_272",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"article-title": "Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Kratzel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_273",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11033-022-07700-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Alipoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10715",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_274",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.12.26.424442",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_275",
"unstructured": "Neerukonda, S.N., Vassell, R., Herrup, R., Liu, S., Wang, T., Takeda, K., Yang, Y., Lin, T.L., Wang, W., and Weiss, C.D. (2021). Establishment of a well-characterized SARS-CoV-2 lentiviral pseudovirus neutralization assay using 293T cells with stable expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2. PLoS ONE, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2108728118",
"article-title": "A novel class of TMPRSS2 inhibitors potently block SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV viral entry and protect human epithelial lung cells",
"author": "Mahoney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2108728118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_276",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15256",
"article-title": "Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronavirus with ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme)-2 as their main receptor: Therapeutic implications",
"author": "Davidson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1339",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_277",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22136703",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_278",
"unstructured": "Yalcin, H.C., Sukumaran, V., Al-Ruweidi, M., and Shurbaji, S. (2021). Do changes in ACE-2 expression affect SARS-CoV-2 virulence and related complications: A closer Look into nembrane-bound and soluble forms. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.01.03.574008",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_279",
"unstructured": "Wei, L., Liu, S., Lu, S., Luo, S., An, X., Fan, H., Chen, W., Li, E., Tong, Y., and Song, L. (2024). Lethal infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice caused by SARS-CoV-2-related Pangolin coronavirus GX_P2V. BioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053",
"article-title": "Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Yeung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2212",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_280",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15291",
"article-title": "ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2), COVID-19, and ACE inhibitor and Ang II (angiotensin II) receptor blocker use during the pandemic: The pediatric perspective",
"author": "South",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_281",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01673-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_282",
"unstructured": "Hou, Y., Zhao, J., Martin, W., Kallianpur, A., Chung, M.K., Jehi, L., Sharifi, N., Erzurum, S., Eng, C., and Cheng, F. (2020). New insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: An ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis. BMC Med., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M205732200",
"article-title": "Activation of RAF-1 through Ras and protein kinase Calpha mediates 1alpha,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in muscle cells",
"author": "Buitrago",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2199",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_283",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in children and adolescents: A systematic review",
"author": "Castagnoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "882",
"journal-title": "JAMA Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_284",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106765",
"article-title": "Infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 depend on heparan sulfate proteoglycans",
"author": "Eder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e106765",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_285",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111363",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_286",
"unstructured": "Mehrabadi, M.E., Hemmati, R., Tashakor, A., Homaei, A., Yousefzadeh, M., Hemati, K., and Hosseinkhani, S. (2021). Induced dysregulation of ACE2 by SARS-CoV-2 plays a key role in COVID-19 severity. Biomed. Pharmacother., 137."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01154",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_287",
"unstructured": "de Queiroz, T.M., Lakkappa, N., and Lazartigues, E. (2020). ADAM17-mMediated shedding of inflammatory cytokines in hypertension. Front. Pharmacol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein impairs endothelial function via downregulation of ACE 2",
"author": "Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1323",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "ref_288",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.918881",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_289",
"unstructured": "Hedges, J.F., Snyder, D.T., Robison, A., Grifka-Walk, H.M., Blackwell, K., Shepardson, K., Kominsky, D., Rynda-Apple, A., Walcheck, B., and Jutila, M.A. (2022). An ADAM17-neutralizing antibody reduces inflammation and mortality while increasing viral burden in a COVID-19 mouse model. Front. Immunol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0711241105",
"article-title": "Modulation of TNF-alpha-converting enzyme by the spike protein of SARS-CoV and ACE2 induces TNF-alpha production and facilitates viral entry",
"author": "Haga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7809",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_290",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152072",
"article-title": "CD147-spike protein interaction in COVID-19: Get the ball rolling with a novel receptor and therapeutic target",
"author": "Behl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152072",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "ref_291",
"volume": "808",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-27378-2",
"article-title": "Massive image-based single-cell profiling reveals high levels of circulating platelet aggregates in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Nishikawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7135",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_292",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8707",
"article-title": "Nasal gene expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in children and adults",
"author": "Bunyavanich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2427",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_293",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030740",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_294",
"unstructured": "Lordan, R. (2021). Notable developments for vitamin D Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, but caution warranted overall: A narrative review. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.691",
"article-title": "Vitamin D prescribing practices among clinical practitioners during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Jude",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e691",
"journal-title": "Health Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_295",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines",
"author": "Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e434",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Ther.",
"key": "ref_296",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111956",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_297",
"unstructured": "Chowdhury, A., Sajid, M., Jahan, N., Adelusi, T.I., Maitra, P., Yin, G., Wu, X., Gao, Y., and Wang, S. (2021). A secondary approach with conventional medicines and supplements to recuperate current COVID-19 status. Biomed. Pharmacother., 142."
},
{
"key": "ref_298",
"unstructured": "FDA (2023, May 22). Emergency Use Authorization for Vaccines Explained, Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines/emergency-use-authorization-vaccines-explained."
},
{
"article-title": "Molecular quantum and logic process of consciousness—Vitamin D big-data in COVID-19—A case for incorporating machine learning in medicine",
"author": "Polonowita",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Euro. J. Biomed. Pharma. Sci.",
"key": "ref_299",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2020.101123",
"article-title": "ACE2 imbalance as a key player for the poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients with age-related comorbidities—Role of gut microbiota dysbiosis",
"author": "Viana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101123",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_300",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.30.20047852",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_301",
"unstructured": "Sawalha, A.H., Zhao, M., Coit, P., and Lu, Q. (2020). Epigenetic dysregulation of ACE2 and interferon-regulated genes might suggest increased COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in lupus patients. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Beyerstedt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_302",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxaa293",
"article-title": "The association of vitamin D and vitamin K status with subclinical measures of cardiovascular health and all-cause mortality in older adults: The hoorn study",
"author": "Beulens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3171",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_303",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-020-02352-8",
"article-title": "Combined low vitamin D and K status amplifies mortality risk: A prospective study",
"author": "Beulens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1645",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_304",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027666",
"article-title": "Importance of vitamin D in acute and critically ill children with subgroup analyses of sepsis and respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cariolou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e027666",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "ref_305",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2018.07.009",
"article-title": "Vitamin D inhibits palmitate-induced macrophage pro-inflammatory cytokine production by targeting the MAPK pathway",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Immunol. Lett.",
"key": "ref_306",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00174.2021",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes",
"author": "Qayyum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E246",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_307",
"volume": "321",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taaa041",
"article-title": "Hypothesis: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers may increase the risk of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Diaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "taaa041",
"journal-title": "J. Travel. Med.",
"key": "ref_308",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1061186X.2020.1797754",
"article-title": "Pharmacotherapy in COVID-19 patients: A review of ACE2-raising drugs and their clinical safety",
"author": "Akhtar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "683",
"journal-title": "J. Drug Target.",
"key": "ref_309",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102907",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_310",
"unstructured": "Chung, M.K., Karnik, S., Saef, J., Bergmann, C., Barnard, J., Lederman, M.M., Tilton, J., Cheng, F., Harding, C.V., and Young, J.B. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2: The biology and clinical data settling the ARB and ACEI controversy. EBioMedicine, 58."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2016093117",
"article-title": "Engineered ACE2 receptor traps potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Glasgow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28046",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_311",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-020-00679-1",
"article-title": "Bi-paratopic and multivalent VH domains block ACE2 binding and neutralize SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Bracken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "ref_312",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13101",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and renin-angiotensin system inhibition: Role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)—Is there any scientific evidence for controversy?",
"author": "Aleksova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "410",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_313",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"article-title": "A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury",
"author": "Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_314",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
}
],
"reference-count": 314,
"references-count": 314,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/13/10/831"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Unveiling the Interplay—Vitamin D and ACE-2 Molecular Interactions in Mitigating Complications and Deaths from SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}
