Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2, BA.4, BA.51, XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.12. mAb use may create new variants that spread globally3-5, and may be associated with increased risk of autoimmune disease6, prolonged viral loads, clinical deterioration, and immune escape4,7-11 .
Regdanvimab was adopted
in 27 countries.
Feb 23 |
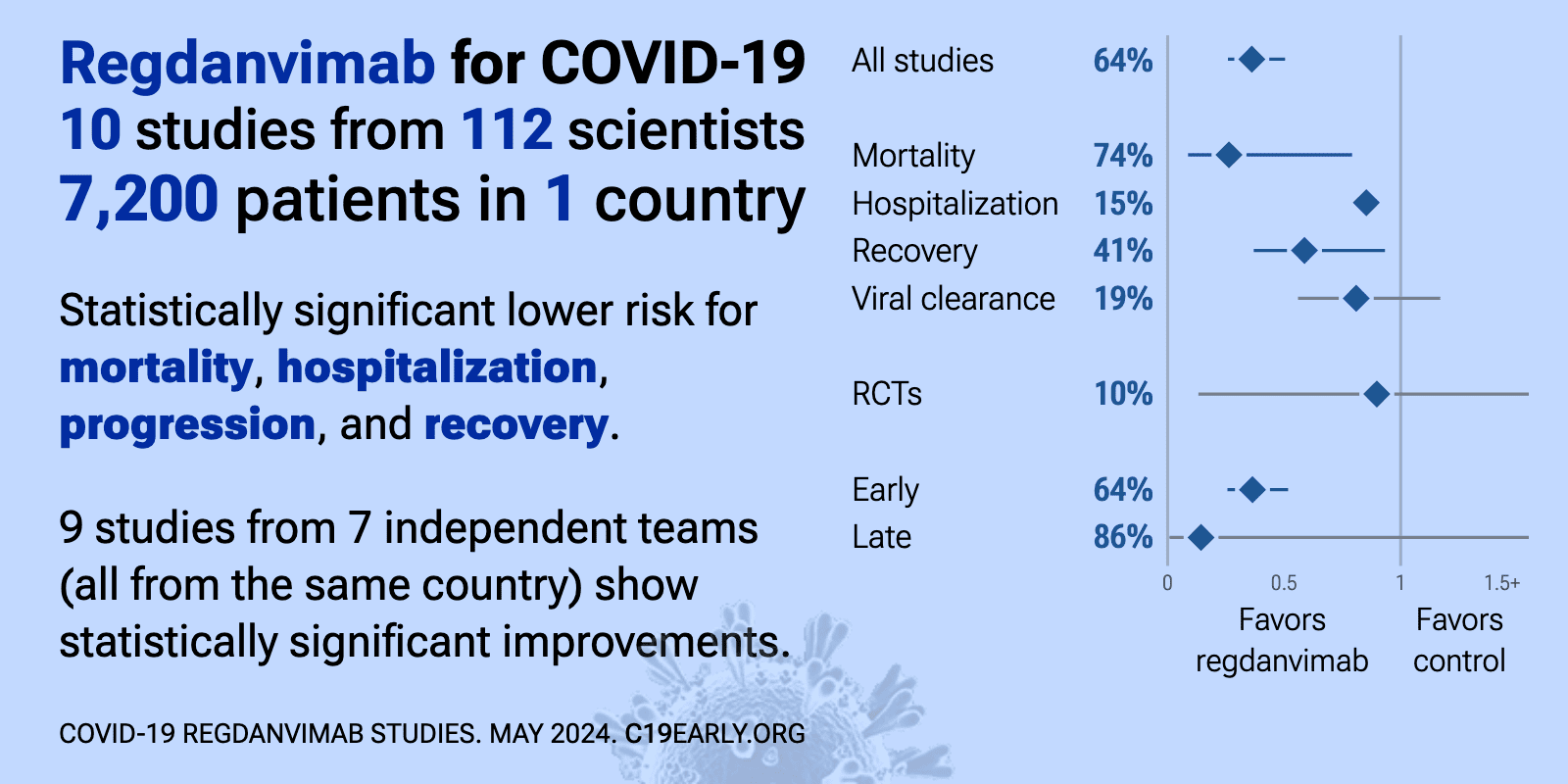
Regdanvimab reduced COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 12 studies (Version 11) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, hospitalization, progression, and recovery. 10 studies from 7 independent teams (all from the same country) show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported sh.. | ||
Mar 13 2025 |
et al., Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252 | Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024 |
| Review of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations and their impact on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antivirals. Mutations in the ORF1ab region led to decreased susceptibility to paxlovid, while nsp12 mutations reduced efficacy for remd.. | ||
Aug 11 2024 |
, D., Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1007/82_2024_268 | Monoclonal Antibody Therapies Against SARS-CoV-2: Promises and Realities |
| Review of monoclonal antibodies for SARS-CoV-2. Author notes that the omicron variant has reset achievements to date. | ||
Aug 8 2024 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciae408 | Single monoclonal antibodies should not be used for COVID-19 therapy: a call for antiviral stewardship |
| Review arguing against use of single monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 treatment, particularly in immunosuppressed patients, due to the risk of rapidly selecting for resistant viral variants. Authors suggest that while monoclonal antibod.. | ||
May 23 2024 |
et al., Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfae069.1573 | Effectiveness of regdanvimab on clinical outcomes in COVID-19 infected patients on hemodialysis |
| 59% lower mortality (p=0.002). Retrospective 230 hemodialysis patients with COVID-19, showing lower mortality with regdanvimab. Details of the adjusted results are not provided. | ||
Apr 12 2024 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-024-00971-w | Effect of Regdanvimab on Mortality in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variants: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study |
| 83% lower mortality (p=0.12), 33% lower ICU admission (p=0.49), and 55% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.01). PSM retrospective 378 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Korea showing lower progression with regdanvimab treatment. | ||
Jan 23 2024 |
et al., Kidney Research and Clinical Practice, doi:10.23876/j.krcp.23.137 | Effectiveness of regdanvimab on mortality in COVID-19 infected patients on hemodialysis |
| Retrospective 230 hospitalized COVID-19 patients on hemodialysis, reporting lower mortality with regdanvimab treatment. The results are conflicting, with for example the text reporting HR 0.28 for regdanvimab in multivariable analysis, ho.. | ||
Nov 10 2023 |
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000035987 | Clinical outcomes of mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 patients treated with Regdanvimab in delta-variant outbreak: Retrospective cohort study |
| Retrospective 101 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in South Korea examining outcomes with the monoclonal antibody treatment regdanvimab, comparing 31 patients during the delta variant outbreak period to 49 patients with pre-delta variants. .. | ||
Oct 20 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1259725 | Real-world clinical effectiveness of Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab and Regdanvimab monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 treatment in Omicron variant-dominant period |
| 415% worse viral clearance (p=0.008). Prospective study of 77 COVID-19 outpatients showing improved efficacy with tixagevimab/cilgavimab compared to regdanvimab during Omicron variant dominance. | ||
Sep 28 2023 |
et al., Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533 | In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1 |
| In vitro study showing sharply reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1 with monoclonal antibodies cilgavimab, tixagevimab, imdevimab, etsevimab, casirivim.. | ||
Sep 27 2023 |
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417 | Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023 |
| Analysis of 7,950 SARS-CoV-2 samples from central Sweden collected between March 2022 and May 2023 tracking the prevalence of omicron sublineages and mutations in the spike protein conferring resistance to monoclonal antibodies over time... | ||
May 15 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512 | Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment for SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, which exhibited decreased in vitro activity: a nationwide real-world multicenter cohort study |
| 51% lower progression (p=0.0002) and 32% lower need for oxygen therapy (p<0.0001). Retrospective 2,214 mild/moderate COVID-19 patients in South Korea, 1,095 treated with regdanivimab, showing lower oxygen requirements and lower progression to severe disease with treatment in the overall cohort, but not within the delta .. | ||
Jan 6 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035 | Regdanvimab for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the Delta variant |
| 12% shorter hospitalization (p<0.0001), 49% lower need for oxygen therapy (p<0.0001), and 68% higher hospital discharge (p<0.0001). Retrospective 722 hospitalized mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients in Korea showing lower risk of disease progression with regdanvimab treatment. | ||
Aug 21 2022 |
et al., eBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105582 (date from preprint) | A randomized, double-blind, Phase 1, single- and multiple-dose placebo-controlled study of the safety and pharmacokinetics of IN-006, an inhaled antibody treatment for COVID-19 in healthy volunteers |
| Phase 1 RCT of 23 healthy adults, showing nebulized IN-006, a reformulation of regdanvimab, was well-tolerated, with transient mild adverse events, and achieved high nasal fluid concentrations that were orders of magnitude above typical a.. | ||
Aug 8 2022 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac406 | A Randomized Clinical Trial of Regdanvimab in High-Risk Patients With Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| 86% lower ventilation (p=0.25), 91% lower ICU admission (p=0.06), 69% lower need for oxygen therapy (p<0.0001), and 69% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001). RCT 1,315 outpatients in South Korea, showing lower progression and improved recovery with regdanvimab. | ||
May 16 2022 |
et al., Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2022.100675 | Clinical Effectiveness of Regdanvimab Treatment for Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 60% lower need for oxygen therapy (p<0.0001), 44% higher hospital discharge (p=0.03), and 13% shorter hospitalization (p=0.003). Retrospective 317 hospitalized mild-moderate COVID-19 patients in South Korea showing significantly lower rates of oxygen desaturation (SpO2 <94%) at 28 days (primary outcome) with regdanvimab monoclonal antibody treatment (13%) compared .. | ||
Mar 29 2022 |
et al., Journal of Korean Medical Science, doi:10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e102 | Effectiveness and Safety of Regdanvimab in Patients With Mild-To-Moderate COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 79% lower progression (p<0.0001) and 13% shorter hospitalization (p<0.0001). Retrospective propensity score matched analysis of 970 high-risk mild-moderate COVID-19 patients in South Korea, showing regdanvimab significantly reduced risk of disease progression or death by 77% compared to standard care alone. No dea.. | ||
Mar 18 2022 |
et al., Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed7030051 | The Effectiveness of the Use of Regdanvimab (CT-P59) in Addition to Remdesivir in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Single Center Retrospective Study |
| 71% lower mortality (p=1), 64% lower ventilation (p=0.46), and 9% shorter hospitalization (p=0.56). Retrospective 124 hospitalized severe COVID-19 patients receiving oxygen and remdesivir treatment in South Korea. A subgroup of 25 patients also received the monoclonal antibody regdanvimab prior to remdesivir. The regdanvimab subgroup ha.. | ||
Mar 8 2022 |
et al., Infection & Chemotherapy, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0140 | Effectiveness of Regdanvimab at Preventing the Need for Oxygen Therapy in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 76% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.004). Retrospective 398 hospitalized mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients in South Korea eligible for regdanvimab treatment. 65 patients received regdanvimab, with significantly lower supplemental oxygen requirements (6.2% vs 20.1% in controls). .. | ||
Feb 2 2022 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac053 | Efficacy and Safety of Regdanvimab (CT-P59): A Phase 2/3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Outpatients with Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| 54% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.11), 49% lower hospitalization (p=0.2), 49% lower progression (p=0.2), and 35% faster recovery (p=0.003). Phase 2 RCT with 307 outpatients with mild-moderate COVID-19, showing regdanvimab (monoclonal antibody) resulted in a minor decrease in time to negative PCR test (primary endpoint) compared to placebo, which was not statistically signific.. | ||
Nov 23 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.772320 | Effectiveness of Regdanvimab Treatment in High-Risk COVID-19 Patients to Prevent Progression to Severe Disease |
| 82% lower severe cases (p=0.002), 45% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.05), and 8% higher hospital discharge (p=0.001). Retrospective 778 mild COVID-19 patients showing significantly lower progression to severe disease with regdanvimab treatment. | ||
References
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Focosi et al., Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 mutations associated with resistance to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies that emerge after treatment, Drug Resistance Updates, doi:10.1016/j.drup.2023.100991.
Leducq et al., Spike protein genetic evolution in patients at high-risk of severe COVID-19 treated by monoclonal antibodies, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad523.
Bruhn et al., Somatic hypermutation shapes the viral escape profile of SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibodies, eBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105770.
Ngiam et al., Early administration of neutralising monoclonal antibodies and post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2026.108435.
Choudhary et al., Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Resistance with Monoclonal Antibody Therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.09.03.21263105.
Günther et al., Variant-specific humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 escape mutants arising in clinically severe, prolonged infection, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.01.06.24300890.
Casadevall et al., Single monoclonal antibodies should not be used for COVID-19 therapy: a call for antiviral stewardship, Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciae408.