Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment for SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, which exhibited decreased in vitro activity: a nationwide real-world multicenter cohort study
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512, May 2023
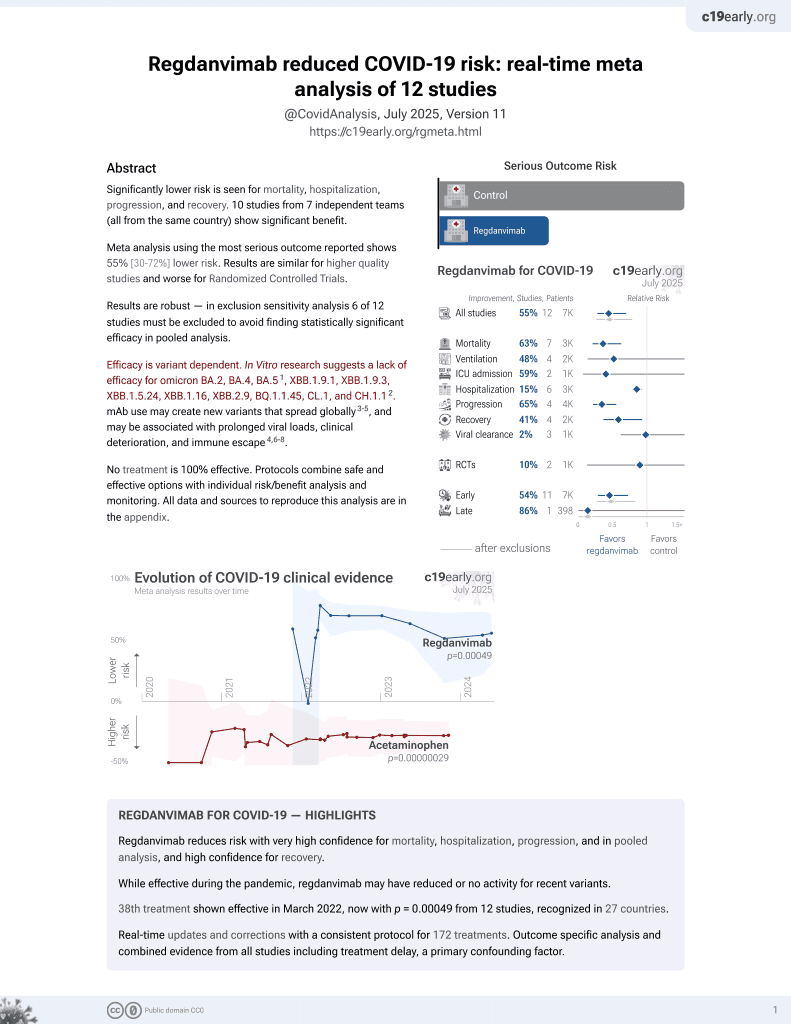
39th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2022, now with p = 0.00049 from 12 studies, recognized in 27 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
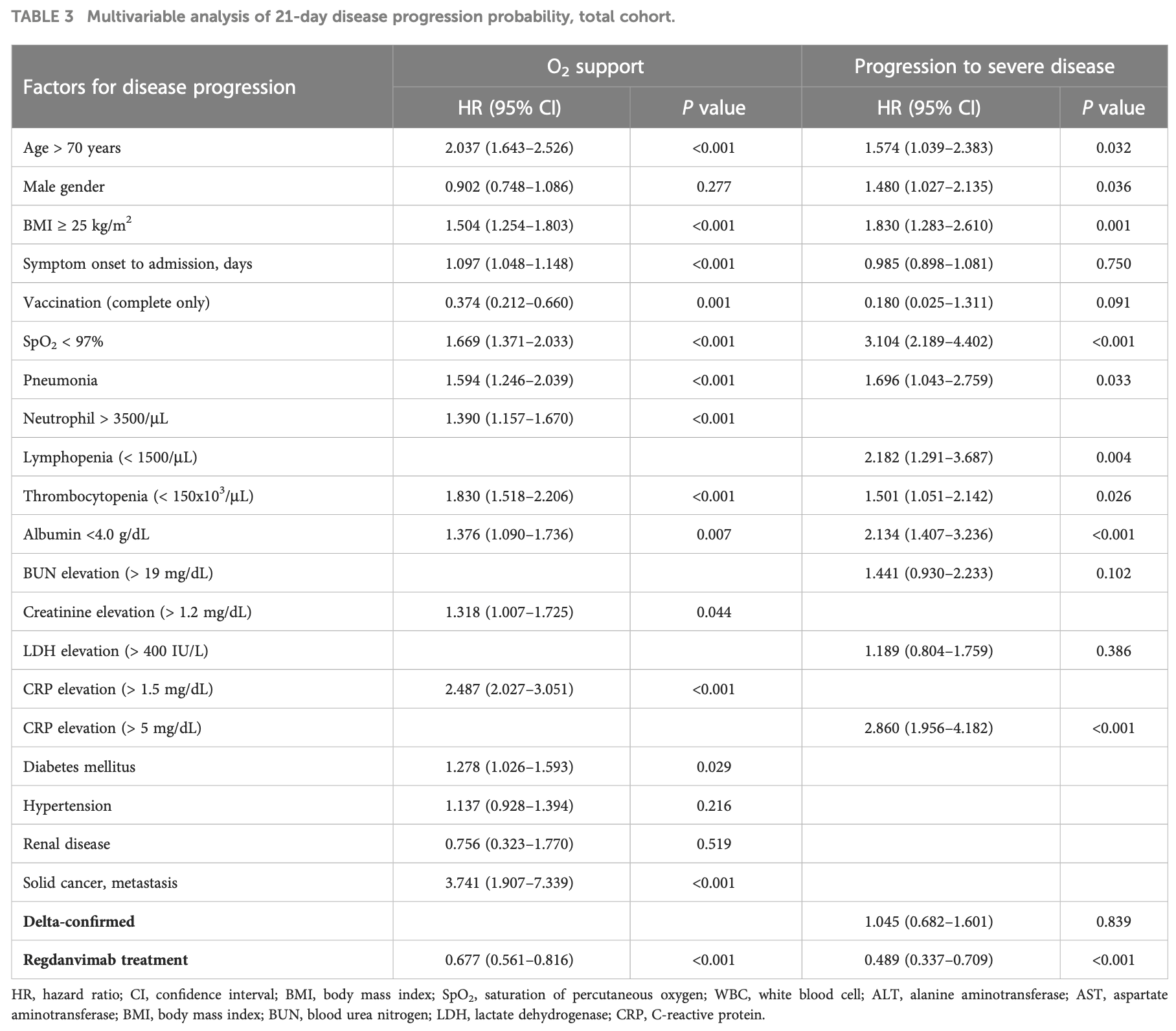
Retrospective 2,214 mild/moderate COVID-19 patients in South Korea, 1,095 treated with regdanivimab, showing lower oxygen requirements and lower progression to severe disease with treatment in the overall cohort, but not within the delta subset.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2, BA.4, BA.51, ХВВ.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.12.
|
risk of progression, 51.1% lower, HR 0.49, p < 0.001, treatment 1,095, control 1,119, adjusted per study, all, multivariable.
|
|
risk of progression, 33.5% lower, HR 0.67, p = 0.22, treatment 1,095, control 1,119, adjusted per study, delta, multivariable.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 32.3% lower, HR 0.68, p < 0.001, treatment 1,095, control 1,119, adjusted per study, all, multivariable.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 3.7% lower, HR 0.96, p = 0.83, treatment 1,095, control 1,119, adjusted per study, delta, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kim et al., 15 May 2023, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 20 authors, study period December 2020 - September 2021, average treatment delay 3.6 days.
Contact: sshhissh@gmail.com, ktkwon@knu.ac.kr, kjykey@gmail.com, krpeck@skku.edu.
Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment for SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, which exhibited decreased in vitro activity: a nationwide real-world multicenter cohort study
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512
Background: Immune-evading severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants are emerging continuously. The clinical effectiveness of monoclonal antibody agents that exhibit decreased in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants needs to be elucidated. Methods: A nationwide, multicenter, retrospective cohort study was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of regdanvimab, an anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody agent. Regdanvimab was prescribed in South Korea before and after the emergence of the delta variant, against which the in vitro activity of regdanvimab was decreased but present. Mild to moderate coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) patients with risk factors for disease progression who were admitted within seven days of symptom onset were screened in four designated hospitals between December 2020 and September 2021. The primary outcomes, O 2 requirements and progression to severe disease within 21 days of admission, were compared between the regdanvimab and supportive care groups, with a subgroup analysis of delta variant-confirmed patients. Results: A total of 2,214 mild to moderate COVID-19 patients were included, of whom 1,095 (49.5%) received regdanvimab treatment. In the analysis of the total Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology frontiersin.org 01
Ethics statement Review by the Institutional Review Board was exempted because the present investigation was conducted as part of a public health response, and minimal risk was expected to the participating patients.
Author contributions HK, YRJ, JYL, and J-HK have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship. SS, KTK, JYK, and KRP have contributed equally to this work and share corresponding authorship. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512/ full#supplementary-material
References
Bae, Ko, Choi, Park, Lim et al., Heterologous ChAdOx1 and Bnt162b2 vaccination induces strong neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 including delta variant with tolerable reactogenicity, Clin. Microbiol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.04.019
Bierle, Ganesh, Razonable, Breakthrough COVID-19 and casirivimab-imdevimab treatment during a SARS-CoV-2 B1. 617.2 (Delta) surge, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2021.105026
Cox, Peacock, Harvey, Hughes, Wright et al., SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102685
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Boscia, Heller et al., Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Crespo Casal, Moya et al., Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.2832
Jang, Oh, Kim, Regdanvimab for patients with mild-tomoderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the delta variant, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035
Joo, Ko, Kim, Kang, Baek et al., Clinical and virologic effectiveness of remdesivir treatment for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea: a nationwide multicenter retrospective cohort study, J. Korean Med. Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e83
Kim, Lee, Kim, Kim, Kim et al., COVID-19 special report] July 2021 status and characteristics of the COVID-19 variant virus outbreak in the republic of Korea
Kim, Ryu, Lee, Kim, Seo et al., A therapeutic neutralizing antibody targeting receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20602-5
Lee, Lee, Ko, Hyun, Kim et al., Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment in high-risk COVID-19 patients to prevent progression to severe disease, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.772320
Lee, Lee, Lee, Kim, Lee et al., Regdanvimab in patients with mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection: a propensity score-matched retrospective cohort study, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108570
Lee, Park, Lee, Early oxygen requirement in patients with mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 who received regdanvimab after delta-variant outbreak, Infect. Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2022.0011
Mayo, Error statistics, Philosophy of statistics
Nham, Ko, Song, Choi, Kim et al., Kinetics of vaccine-induced neutralizing antibody titers and estimated protective immunity against wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and the delta variant: a prospective nationwide cohort study comparing three COVID-19 vaccination protocols in south Korea, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.968105
Nham, Song, Noh, Cheong, Kim, National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 treatment guidelines, anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies, J. Korean Med. Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e351
Park, Lim, Kim, Park, Lim et al., Clinical and virological characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV
Planas, Veyer, Baidaliuk, Staropoli, Guivel-Benhassine et al., Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant delta to antibody neutralization, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9
Ryu, Kang, Noh, Woo, Lee et al., The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of CT-P59 against gamma, delta and its associated variants of SARS-CoV-2, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.023
Salleh, Derrick, Deris, Structural evaluation of the spike glycoprotein variants on SARS-CoV-2 transmission and immune evasion, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22147425
Streinu-Cercel, Sandulescu, Preotescu, Kim, Kim et al., Efficacy and safety of regdanvimab (CT-P59): a phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in outpatients with mild-to-Moderate coronavirus disease, Open Forum Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac053
Sung, Kim, Heo, Seo, Jang et al., Clinical course and outcomes of 3,060 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea, J. Korean Med. Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e280
Syed, Regdanvimab: first approval, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01626-7
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Sakai-Tagawa, Fujisaki et al., Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA
Twohig, Nyberg, Zaidi, Thelwall, Sinnathamby et al., Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8
Vanblargan, Errico, Halfmann, Zost, Crowe et al., None
Wen, Badgett, Cornell, Number needed to treat: a descriptor for weighing therapeutic options, Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm, doi:10.2146/ajhp040558
Yamasoba, Kosugi, Kimura, Fujita, Uriu et al., Neutralisation sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00365-6
Yang, Won, Baek, Lee, Kim et al., Neutralizing activity against omicron BA.5 after tixagevimab/cilgavimab administration comparable to those after omicron BA.1/BA.2 breakthrough infections, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139980
Zhou, Wang, Misasi, Pegu, Zhang et al., Structural basis for potent antibody neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants including B.1.1.529, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn8897
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512",
"ISSN": [
"2235-2988"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Immune-evading severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants are emerging continuously. The clinical effectiveness of monoclonal antibody agents that exhibit decreased <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic> activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants needs to be elucidated.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A nationwide, multicenter, retrospective cohort study was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of regdanvimab, an anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody agent. Regdanvimab was prescribed in South Korea before and after the emergence of the delta variant, against which the <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic> activity of regdanvimab was decreased but present. Mild to moderate coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) patients with risk factors for disease progression who were admitted within seven days of symptom onset were screened in four designated hospitals between December 2020 and September 2021. The primary outcomes, O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> requirements and progression to severe disease within 21 days of admission, were compared between the regdanvimab and supportive care groups, with a subgroup analysis of delta variant–confirmed patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 2,214 mild to moderate COVID-19 patients were included, of whom 1,095 (49.5%) received regdanvimab treatment. In the analysis of the total cohort, significantly fewer patients in the regdanvimab group than the supportive care group required O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> support (18.4% vs. 27.1%, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001) and progressed to severe disease (4.0% vs. 8.0%, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001). In the multivariable analysis, regdanvimab was significantly associated with a decreased risk for O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> support (HR 0.677, 95% CI 0.561–0.816) and progression to severe disease (HR 0.489, 95% CI 0.337–0.709). Among the 939 delta-confirmed patients, O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> support (21.5% vs. 23.5%, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.526) and progression to severe disease (4.2% vs. 7.3%, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.055) did not differ significantly between the regdanvimab and supportive care groups. In the multivariable analyses, regdanvimab treatment was not significantly associated with a decreased risk for O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub> support (HR 0.963, 95% CI 0.697–1.329) or progression to severe disease (HR 0.665, 95% CI 0.349–1.268) in delta-confirmed group.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Regdanvimab treatment effectively reduced progression to severe disease in the overall study population, but did not show significant effectiveness in the delta-confirmed patients. The effectiveness of dose increment of monoclonal antibody agents should be evaluated for variant strains exhibiting reduced susceptibility.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Haein",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jang",
"given": "Young Rock",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Ji Yeon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ko",
"given": "Jae-Hoon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Jee Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cho",
"given": "Seongcheol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Yong Dae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Junghoon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hyun",
"given": "Miri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Hyun Ah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hwang",
"given": "Soyoon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryou",
"given": "Sangmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Na",
"given": "Yoo Jin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Joo-Yeon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Changhee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Nan Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shin",
"given": "Seunghwan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kwon",
"given": "Ki Tae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Jin Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peck",
"given": "Kyong Ran",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-15T13:30:25Z",
"timestamp": 1684157425000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-15T13:30:33Z",
"timestamp": 1684157433000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100018688",
"award": [
"#2021-ER1907-00"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-16T04:42:19Z",
"timestamp": 1684212139788
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1684108800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.04.019",
"article-title": "Heterologous ChAdOx1 and Bnt162b2 vaccination induces strong neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 including delta variant with tolerable reactogenicity",
"author": "Bae",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1390.e1",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2021.105026",
"article-title": "Breakthrough COVID-19 and casirivimab-imdevimab treatment during a SARS-CoV-2 B1",
"author": "Bierle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105026",
"journal-title": "617.2 (Delta) surge. J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00809-7",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies",
"author": "Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate covid-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"article-title": "Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2832",
"article-title": "Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1236",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "B7",
"unstructured": "Il-Hwan KimA. K. P.\n LeeH.\n KimJ.\n KimD. H.\n KimJ.\n NoJ. S.\n COVID-19 special report] July 2021 status and characteristics of the COVID-19 variant virus outbreak in the republic of Korea2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.035",
"article-title": "Regdanvimab for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study and subgroup analysis of patients with the delta variant",
"author": "Jang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "94",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e83",
"article-title": "Clinical and virologic effectiveness of remdesivir treatment for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea: a nationwide multicenter retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Joo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Korean Med. Sci.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B10",
"unstructured": "Weakly briefing of COVID-19 and vaccination status2021"
},
{
"key": "B11",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 special report] outbreak report of COVID-19 during designation of class 1 infectious disease in the republic of Korea (January 20, 2020–April 24, 2022)2022"
},
{
"key": "B12",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 special report] epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 reinfection cases in the republic of Korea2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20602-5",
"article-title": "A therapeutic neutralizing antibody targeting receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "288",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.772320",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment in high-risk COVID-19 patients to prevent progression to severe disease",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108570",
"article-title": "Regdanvimab in patients with mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection: a propensity score-matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108570",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2022.0011",
"article-title": "Early oxygen requirement in patients with mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 who received regdanvimab after delta-variant outbreak",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "Infect. Chemother.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "SA. \"Error statistics\"",
"author": "Mayo",
"first-page": "152",
"key": "B17",
"volume-title": "Philosophy of statistics",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.968105",
"article-title": "Kinetics of vaccine-induced neutralizing antibody titers and estimated protective immunity against wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and the delta variant: a prospective nationwide cohort study comparing three COVID-19 vaccination protocols in south Korea",
"author": "Nham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e351",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccination in Korea: past, present, and the way forward",
"author": "Nham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Korean Med. Sci.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "B20",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 treatment guidelines, anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac239",
"article-title": "Clinical and virological characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e27",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9",
"article-title": "Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant delta to antibody neutralization",
"author": "Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.023",
"article-title": "The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of CT-P59 against gamma, delta and its associated variants of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Ryu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "578",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22147425",
"article-title": "Structural evaluation of the spike glycoprotein variants on SARS-CoV-2 transmission and immune evasion",
"author": "Salleh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7425",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac053",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of regdanvimab (CT-P59): a phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in outpatients with mild-to-Moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Streinu-Cercel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofac053",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e280",
"article-title": "Clinical course and outcomes of 3,060 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea, January-may 2020",
"author": "Sung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Korean Med. Sci.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-021-01626-7",
"article-title": "Regdanvimab: first approval",
"author": "Syed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2133",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "2. N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8",
"article-title": "Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study",
"author": "Twohig",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"article-title": "An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies",
"author": "VanBlargan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2146/ajhp040558",
"article-title": "Number needed to treat: a descriptor for weighing therapeutic options",
"author": "Wen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2031",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"key": "B33",
"unstructured": "WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard"
},
{
"key": "B34",
"unstructured": "Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00365-6",
"article-title": "Neutralisation sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies",
"author": "Yamasoba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "942",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139980",
"article-title": "Neutralizing activity against omicron BA.5 after tixagevimab/cilgavimab administration comparable to those after omicron BA.1/BA.2 breakthrough infections",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abn8897",
"article-title": "Structural basis for potent antibody neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants including B.1.1.529",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1192512/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Immunology",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment for SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, which exhibited decreased in vitro activity: a nationwide real-world multicenter cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "13"
}