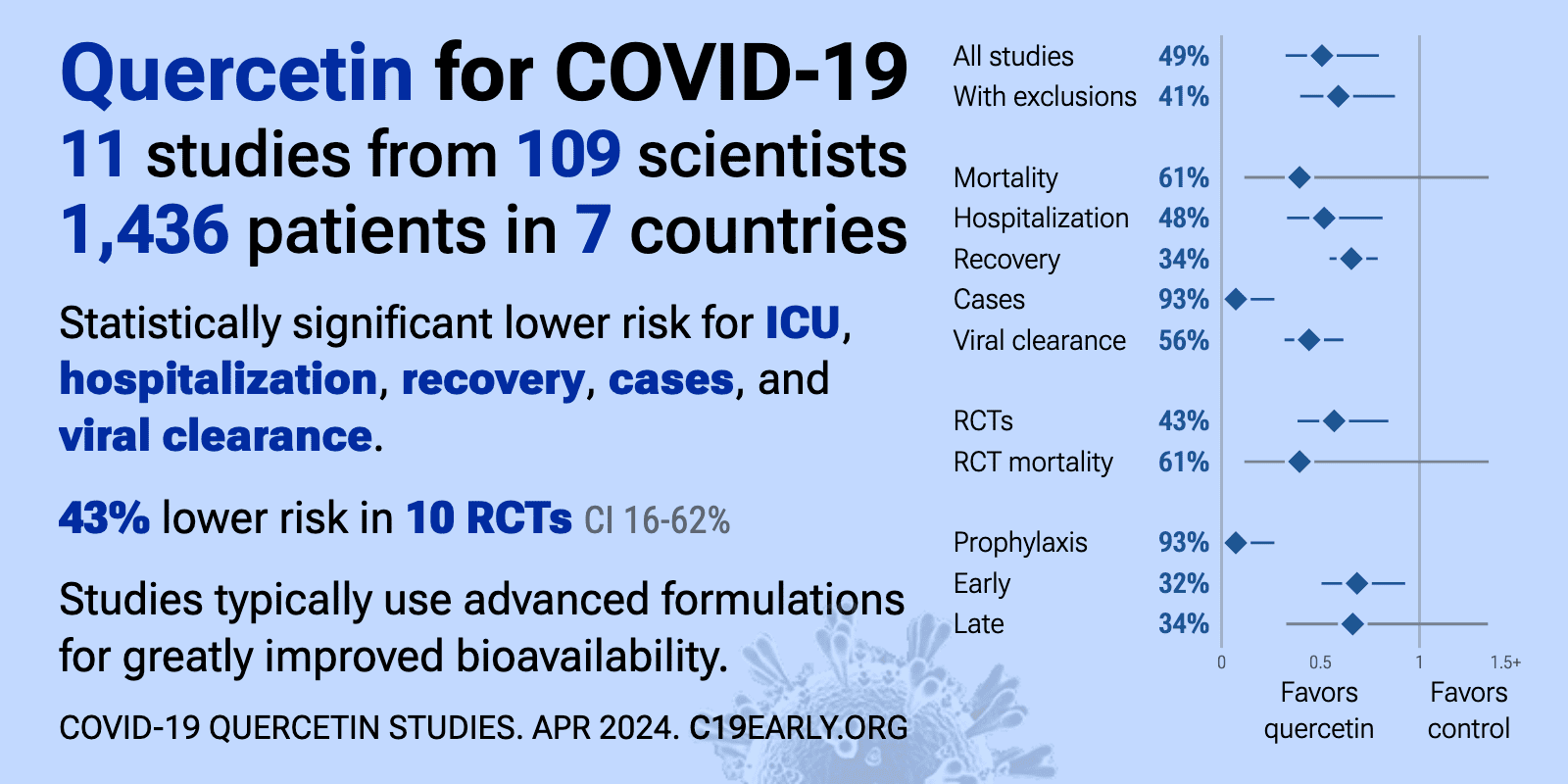
Mar 1 |
Quercetin reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 9 studies (Version 23) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ICU admission, hospitalization, recovery, cases, and viral clearance. 9 studies from 7 independent teams in 5 countries show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome.. | ||
Feb 26 |
et al., Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2026.199707 | Identification of key genes modules linking brain aging signatures and COVID-19-associated cognitive impairment |
| In silico study suggesting that seven compounds (fulvestrant, bucladesine, S-adenosylmethionine, valproic acid, folic acid, kaempferol, and quercetin) may be beneficial for COVID-19-associated cognitive impairment through targeting key ag.. | ||
Feb 4 |
, D., Innovative Medicines & Omics, doi:10.36922/IMO025440058 | Mast cells and histamine receptor-targeted adjunctive treatments for COVID-19: A literature review |
| Review of clinical studies on antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers, and leukotriene receptor antagonists for COVID-19 treatment. Author finds that several mast cell-targeting agents show clinical benefits, with quercetin emerging as one .. | ||
Jan 14 |
et al., Phytochemistry Letters, doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2025.104105 | Harnessing phytoconstituents to treat COVID-19 triggered acute respiratory distress syndrome: Insights from network pharmacology, and molecular modeling |
| In silico study showing that phytoconstituents apigenin-7-glucoside and quercetin bind strongly to inflammatory targets EGFR, JAK2, and RELA associated with COVID-19-triggered acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). | ||
Dec 17 2025 |
et al., BioMed Research International, doi:10.1155/bmri/9507417 | Targeting SIRT1: A Potential Strategy for Combating Severe COVID‐19 |
| Review showing that SIRT1 activation may benefit COVID-19 treatment through multiple anti-inflammatory and antiviral mechanisms. | ||
Nov 28 2025 |
et al., Journal of Molecular Modeling, doi:10.1007/s00894-025-06541-2 | Feasibility of the inhibitor development for SARS-CoV-2: a systematic approach for drug design |
| In silico analysis identifying quercetin as a potent Mpro inhibitor through multi-stage virtual screening. | ||
Nov 27 2025 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-27374-2 | Improving quercetin solubility via structural modification enhances dual-target coronavirus entry: an integrated in-vitro and in-silico study |
| In vitro and in silico study showing that quercetin derivatives QPABA and QPP inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV spike protein binding to host receptors. Authors synthesized quercetin para-aminobenzoic acid (QPABA) and quercetin penta-phosph.. | ||
Oct 30 2025 |
et al., Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-025-00907-2 | Phytochemical and antiviral investigation of Cynanchum acutum L. extract and derived semi-synthetic analogs targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease |
| In vitro study showing that Cynanchum acutum extract and its quercetin-3-O-β-galactoside derivatives inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero E6 cells. LC-MS/MS analysis identified 46 phytochemicals in the extract, with 20 being flavonoids in.. | ||
Aug 27 2025 |
et al., Applied and Environmental Microbiology, doi:10.1128/aem.00774-25 | Evaluation of respiratory virus transmissibility and resilience from fomites: the case of 11 SARS-CoV-2 clinical isolates |
| In vitro study showing that quercetin, tea tree oil, and daptomycin demonstrate significant antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants with >95% viral load reduction within minutes on environmental surfaces. Authors evaluated 11 SARS-.. | ||
Jun 5 2025 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-6819274/v1 | INP-Guided Network Pharmacology Discloses Multi-Target Therapeutic Strategy Against Cytokine and IgE Storms in the SARS-CoV-2 NB.1.8.1 Variant |
| Computational modeling study presenting a multi-target therapeutic approach against the SARS-CoV-2 NB.1.8.1 variant using Intrinsic Network Pharmacology (INP) and network pharmacology tools. The researchers identified ZINC000014930714, a .. | ||
Apr 16 2025 |
et al., Italian Journal of Pediatrics, doi:10.1186/s13052-025-01961-5 | Role of nutrient supplements in children with post-COVID condition: a retrospective preliminary observation and narrative review |
| Retrospective 1,243 children with COVID-19 showing lower risk of long COVID at 6 months when treated with a Multi-Element Product (MEP) containing antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds (magnesium 200 mg, quercetin 150 mg, curcumin .. | ||
Mar 26 2025 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0320415 | Integration of metabolomics and chemometrics with in-silico and in-vitro approaches to unravel SARS-Cov-2 inhibitors from South African plants |
| In silico and in vitro study showing that quercetin derivatives from South African plants effectively inhibit SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro). Authors integrated metabolomics and chemometrics with computational approaches to identify bi.. | ||
Mar 12 2025 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17030402 | Biochemical Screening of Phytochemicals and Identification of Scopoletin as a Potential Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, Revealing Its Biophysical Impact on Structural Stability |
| In vitro study showing that scopoletin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) with an IC50 of 15.75 μM. Authors employed virtual screening to identify scopoletin among five phytochemicals as a potential Mpro inhibitor, which was confirm.. | ||
Feb 20 2025 |
et al., Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105 | Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention |
| In silico computational docking study of phytochemicals from MilagaiKudineer, showing potential inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 targets. Authors evaluated binding affinities for the spike glycoprotein receptor-binding domain, RNA-d.. | ||
Feb 11 2025 |
et al., International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140920 | Green antiseptic for hand hygiene with high activity against SARS-CoV-2: Iota-carrageenan, quercetin, and Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil based nanoemulsion |
| In vitro study showing that a nanoemulsion combining quercetin, iota-carrageenan, and Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) essential oil inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication by 100% in epithelial cells, with no cytotoxicity observed. Authors dev.. | ||
Jan 24 2025 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0313616 | Secondary metabolites of Alternaria alternate appraisal of their SARS-CoV-2 inhibitory and anti-inflammatory potentials |
| In silico and in vitro study showing that compounds isolated from the fungus Alternaria alternate inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking the ACE2-Spike protein interaction and reducing ACE2 expression and inflammatory cytokines. Quercet.. | ||
Jan 24 2025 |
et al., Chemistry & Biodiversity, doi:10.1002/cbdv.202403202 | Amphibian‐Derived Peptides as Natural Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Main Protease (Mpro): A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Approach |
| In vitro and in silico study showing that amphibian-derived peptides inhibit SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Authors tested 23 peptides from Hylidae and Leptodactylidae amphibians and found five with significant Mpro inhibition, with IC5.. | ||
Jan 16 2025 |
et al., Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113 | Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective |
| Review of immune-boosting and antiviral effects of antioxidants in COVID-19 pneumonia. Authors provide an overview of the literature on the use of antioxidants, including vitamins, trace elements, ozone, glutathione, L-carnitine, melatoni.. | ||
Dec 31 2024 |
et al., Trends in Food Science & Technology, doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104864 | Bioactive compounds,quercetin, curcumin and β-glucan,regulate innate immunity via the gut-liver-brain axis |
| Review of how bioactive compounds quercetin, curcumin, and β-glucan regulate innate immunity through the gut-liver-brain axis, with focus on COVID-19. Authors describe how SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers excessive immune activation and cyto.. | ||
Dec 6 2024 |
et al., Wiadomości Lekarskie, doi:10.36740/WLek/191875 | Effectiveness of the quercetin use in patients with COVID-19 with concomitant type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| 15% shorter hospitalization (p<0.0001). RCT 60 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes showing quercetin treatment decreased levels of inflammatory markers (interleukin-6, CRP, ferritin), reduced length of hospital stay, and improved capillaroscopy measures compared.. | ||
Dec 3 2024 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0312866 | Integrated study of Quercetin as a potent SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibitor: Binding interactions, MD simulations, and In vitro assays |
| In silico and in vitro study showing quercetin as a potent inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Computational analyses reveal quercetin binds similarly to remdesivir in the RdRp active site and outperforms it i.. | ||
Nov 27 2024 |
et al., Bioresources and Bioprocessing, doi:10.1186/s40643-024-00822-z | Assessing multi-target antiviral and antioxidant activities of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2: an integrated in vitro and in silico study |
| In vitro and in silico study showing that propolis, curcumin, quercetin, and ginseng compounds inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection and bind to key viral proteins. In Vero CCL-81 cells, propolis and curcumin significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2 viral.. | ||
Nov 21 2024 |
et al., Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5 | Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study |
| In silico study showing potential inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 proteins by various compounds including dactinomycin, itraconazole, ivermectin, vitamin D, quercetin, curcumin, montelukast, bromhexine, hesperidin, EGCG and raloxifene. Authors p.. | ||
Nov 5 2024 |
et al., Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, doi:10.7324/JAPS.2024.177392 | Flavonoid compound of red fruit papua and its derivatives against sars-cov-2 mpro: An in silico approach |
| In silico study showing that flavonoid compounds from red fruit, especially quercetin 3'-glucoside derivatives, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Authors used molecular docking to identify quercetin 3'-glucoside as the best bin.. | ||
Oct 11 2024 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39167 | Decoding the mechanism of Qingjie formula in the prevention of COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking |
| In silico study showing potential benefits of quercetin for COVID-19 prevention through network pharmacology and molecular docking. Authors identified quercetin as one of the key active ingredients in Qingjie formula (QJF). Quercetin was .. | ||
Sep 16 2024 |
et al., RSC Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1039/D4MD00289J | Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro by chemically modified tyrosinase from Agaricus bisporus |
| In vitro study showing that a purified tyrosinase enzyme from the mushroom Agaricus bisporus, chemically modified with polymers, inhibited SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro protease activity and viral replication in Vero E6 cells. The tyrosinase bioconju.. | ||
Sep 16 2024 |
et al., AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01739-8 | Establishment of in-house assay for screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 protein inhibitors |
| In vitro study showing that curcumin, quercetin, gallic acid, and silymarin inhibit SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binding to the ACE2 receptor. Authors developed a novel immunofluorescent assay to screen potential inhibitors of the spike-ACE2 .. | ||
Sep 13 2024 |
et al., Food Bioscience, doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2024.105095 | Viola stocksii: A rich source of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory flavonoid glycosides with converged therapeutic potential against SARS-CoV-2 MPro, spike trimer, and surface glycoproteins |
| In silico and in vitro study showing that flavonoid glycosides from Viola stocksii exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antiviral properties against SARS-CoV-2 proteins. In silico analysis revealed strong binding .. | ||
Sep 8 2024 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-71569-y | Quercetin inhibited LPS-induced cytokine storm by interacting with the AKT1-FoxO1 and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in macrophages |
| In silico, in vitro, and mouse study showing that quercetin inhibits LPS-induced cytokine storm by interacting with the AKT1-FoxO1 and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathways in macrophages. Authors found quercetin effectively suppressed the overex.. | ||
Aug 29 2024 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.68098 | Computational Investigations to Identify Potent Natural Flavonoid Inhibitors of the Nonstructural Protein (NSP) 16/10 Complex Against Coronavirus |
| In silico study showing that the flavonoid compounds hesperidin, narirutin, and isoquercetin may have potential as antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the NSP16/10 protein complex. Authors performed molecular docking and mole.. | ||
Aug 16 2024 |
et al., RSC Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1039/d4md00286e | Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 viral entry by targeting spike:ACE2 interaction with O-modified quercetin derivatives |
| In vitro study showing that O-modified quercetin derivatives inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein:ACE2 interaction at low micromolar concentrations. Five derivatives (2e, 3a, 3b, 3c, 4b) displayed dose-dependent inhibition with IC50 value.. | ||
Aug 1 2024 |
et al., Asian Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, doi:10.56557/ajmab/2024/v9i28800 | Characterization of Phytochemical Inhibitors of the COVID-19 Primary Protease Using Molecular Modelling Approach |
| In silico study showing that quercetin, gallic acid, lactucin, and rutin may inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Quercetin and rutin demonstrated strong binding affinity to Mpro and favorable drug-likeness, bioactivity scores, an.. | ||
Jul 18 2024 |
et al., Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4897774 | Biomarkers Prediction and Immune Landscape in Covid-19 and “Brain Fog” |
| In silico study identifying key genes and potential therapeutic agents related to brain fog in COVID-19 patients. Authors analyzed frontal cortex transcriptome data and found upregulated genes involved in immune-related pathways and downr.. | ||
Jun 21 2024 |
et al., ChemistryOpen, doi:10.1002/open.202300198 | Phytoconstituents of Citrus limon (Lemon) as Potential Inhibitors Against Multi Targets of SARS‐CoV‐2 by Use of Molecular Modelling and In Vitro Determination Approaches |
| In silico study showing potential benefits of quercetin for COVID-19. Authors found that quercetin exhibited significant binding affinity to three SARS-CoV-2 targets: main protease (Mpro), spike glycoprotein, and RNA-dependent RNA polymer.. | ||
Jun 17 2024 |
et al., BioFactors, doi:10.1002/biof.2084 | The flavonoid quercetin decreases ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression but not SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in cultured human lung cells |
| In vitro study showing that quercetin acutely decreases expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 mRNA and protein in Calu-3 lung epithelial cells cultured at an air-liquid interface. Longer-term lower dose treatment decreased TMPRSS2 but not ACE2 e.. | ||
May 31 2024 |
et al., Archives of Medical Reports, 1:1 | Exploring the antiviral activity of Adhatoda beddomei bioactive compounds in interaction with coronavirus spike protein |
| In silico study showing potential benefits of bioactive compounds from Adhatoda beddomei against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Authors performed pharmacokinetic evaluations and molecular docking of naringenin, epicatechin, morin, querceti.. | ||
May 25 2024 |
et al., Clinical Science of Nutrition, doi:10.62210/ClinSciNutr.2024.86 | Investigation of potential effects of quercetin on COVID-19 treatment: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials |
| Systematic review of RCTs investigating quercetin for COVID-19. Five studies with a total of 803 participants were included. Authors found that quercetin treatment led to reductions in cases, viral persistence, hospitalization, oxygen req.. | ||
May 15 2024 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09387-w | Phytoconstituents of Artemisia Annua as potential inhibitors of SARS CoV2 main protease: an in silico study |
| In silico study showing that quercetin binds strongly to the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) and may be a potential inhibitor of viral replication. Authors screened 25 compounds from Artemisia annua and found that quercetin had one of the.. | ||
May 5 2024 |
et al., Review of Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics - International Edition, doi:10.61873/DTFA3974 | Network pharmacology and molecular docking reveal the mechanisms of action of Panax notoginseng against post-COVID-19 thromboembolism |
| In silico study showing potential benefits of quercetin and ginsenosides from Panax notoginseng (PNGS) for post-COVID-19 thromboembolism. Authors used network pharmacology and molecular docking to analyze PNGS mechanisms against COVID-19-.. | ||
Apr 30 2024 |
et al., Bulletin of Problems Biology and Medicine, doi:10.29254/2077-4214-2024-2-173-274-280 | Efficiency of quercetin and trimetasidine in patients with COVID-19 and concomitant chronic coronary syndrome: effect on systemic inflammation |
| Prospective study of 92 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and chronic coronary syndrome showing potential benefit with quercetin and trimetazidine. The quercetin group showed a 35% decrease in the SIRI inflammatory index (p=0.007), whil.. | ||
Apr 30 2024 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30080 | Therapeutic Implications of Quercetin and its Derived-products in COVID-19 Protection and Prophylactic |
| Review of quercetin and its derivatives for prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Authors discuss molecular docking evidence showing quercetin and its derivatives can bind to multiple SARS-CoV-2 proteins including the main protease, spike.. | ||
Apr 26 2024 |
et al., Journal of Proteins and Proteomics, doi:10.1007/s42485-024-00136-w | Targeting COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) main protease through phytochemicals of Albizia lebbeck: molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, MM–PBSA free energy calculations, and DFT analysis |
| In silico study showing potential benefits of quercetin and other phytochemicals from Albizia lebbeck as SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitors. Using molecular docking, the authors identified four promising compounds: vicenin 2, myri.. | ||
Apr 24 2024 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16050665 | Exploring the Antiviral Potential of Esters of Cinnamic Acids with Quercetin |
| In vitro study showing that esters of cinnamic acids with quercetin, particularly ester 7, inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and hCoV-OC43 coronavirus infection in Vero-76 and Vero E6 cells. Mechanism of action studies suggest ester 7 may inhibit corona.. | ||
Apr 22 2024 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0300441 | Bioinformatics and system biology approaches to determine the connection of SARS-CoV-2 infection and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma |
| In silico study suggesting that quercetin and tetrandrine are potential treatments for COVID-19 and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). Authors identify 70 shared differentially expressed genes between COVID-19 and ICC, indicating simi.. | ||
Apr 16 2024 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298201 | In silico study of alkaloids with quercetin nucleus for inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 protease and receptor cell protease |
| In silico study showing that the alkaloids with a quercetin nucleus may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection by binding to the main protease (Mpro) and the host cell protease TMPRSS2. Molecular docking analysis found three compounds, Phyllospadin.. | ||
Apr 13 2024 |
et al., European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106766 | Curcumin and quercetin co-encapsulated in nanoemulsions for nasal administration: a promising therapeutic and prophylactic treatment for viral respiratory infections |
| In vitro and ex vivo study showing that curcumin and quercetin co-encapsulated in nanoemulsions (NEs) for nasal administration inhibited murine β-coronavirus (MHV-3) infection. MHV-3 belongs to the same family as SARS-CoV-2. Authors found.. | ||
Apr 12 2024 |
et al., Journal of Nanobiotechnology, doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02435-2 | Development of nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin and ACE2-membrane as a novel therapy for COVID-19 |
| In vitro study showing that nanoparticles coated with both ACE2-containing cell membranes and quercetin (CM-NP-Q) inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lung cells. Authors developed nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin (NP-Q), ACE2-c.. | ||
Apr 5 2024 |
et al., Current Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/0109298673292839240329081008 | Discovery of Novel Natural Inhibitors Against SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Rational Approach to Antiviral Therapeutics |
| In silico and in vitro study showing potential inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) by quercetin and four other natural compounds isolated from medicinal plants. Authors used molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and.. | ||
Mar 18 2024 |
et al., Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-024-00585-6 | Effect of polyphenols against complications of COVID-19: current evidence and potential efficacy |
| Review of polyphenols for COVID-19. Authors note that polyphenols can inhibit key SARS-CoV-2 enzymes involved in viral replication and infection, and that many polyphenols have well-established safety profiles. Authors recommend additiona.. | ||
Mar 13 2024 |
et al., Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.8175 | Effect and mechanism of quercetin or quercetin‐containing formulas against COVID‐19: From bench to bedside |
| Review of quercetin and quercetin-containing formulas for COVID-19. Quercetin exhibits antiviral, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antioxidative, and antithrombotic effects relevant to COVID-19, with strong preclinical evidence. Autho.. | ||
Mar 7 2024 |
et al., International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics, doi:10.22159/ijap.2024v16i2.50128 | Decoding the therapeutic potential of empon-empon: a bioinformatics expedition unraveling mechanisms against COVID-19 and atherosclerosis |
| In silico study of compounds in empon-empon showing that quercetin may be beneficial for treating COVID-19 and atherosclerosis by inhibiting key signaling targets. Authors found that quercetin exhibits strong binding affinity to EP300 and.. | ||
Feb 29 2024 |
et al., International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/ijn.s451206 | Natural Products-Based Inhaled Formulations for Treating Pulmonary Diseases |
| Review of nanoformulations for inhaled therapeutics for respiratory diseases including potential for COVID-19. Inhaled formulations deliver treatment directly to both the upper and lower respiratory tract, enabling higher local concentrat.. | ||
Feb 28 2024 |
et al., Indian Drugs, doi:10.53879/id.61.02.13859 | Computational identification of selected bioactive compounds from Cedrus deodara as inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 main protease: a pharmacoinformatics study |
| In silico study showing that quercetin binds strongly to the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Authors found that out of 49 phytoconstituents from Cedrus deodara, quercetin exhibited the lowest binding energy of approximately -7.2 kcal/mol.. | ||
Feb 2 2024 |
et al., World Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, doi:10.4103/2311-8571.395061 | Investigating the Mechanism of Qu Du Qiang Fei 1 Hao Fang Formula against Coronavirus Disease 2019 Based on Network Pharmacology Method |
| In silico study showing that Qu Du Qiang Fei 1 Hao Fang (QDQF1), a traditional Chinese medicine formula, may benefit COVID-19 treatment through multi-target mechanisms involving ACE2, inflammatory cytokines, and MAPK signaling pathways. N.. | ||
Jan 29 2024 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3888947/v1 | Unlocking the potential of phytochemicals in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 M Pro protein - An in-silico and cell-based approach |
| In silico and in vitro study including quercetin and curcumin derivatives as potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitors. Molecular dynamics simulations and virtual screening identified quercetin and curcumin derivatives demethox.. | ||
Jan 26 2024 |
et al., Observatório de la Economía Latinoamericana, doi:10.55905/oelv22n1-192 | Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of quercetin in the treatment of Covid-19: a systematic review |
| Systematic review of 8 RCTs showing faster recovery, faster viral clearance, and fewer COVID-19 cases with quercetin. Quercetin was well tolerated with no significant adverse events. | ||
Jan 25 2024 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02299-w | Quercetin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection and prevents syncytium formation by cells co-expressing the viral spike protein and human ACE2 |
| In vitro study showing inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection and syncytium formation by quercetin in Vero E6 and Caco-2 cells at 100-400μM concentrations. Authors found that quercetin prevented the proteolytic processing of the SARS-CoV-2 sp.. | ||
Jan 9 2024 |
et al., Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X231219560 | Antiviral Significance of Isoquercetin (Quercetin-3-O-Glucoside) With Special Reference to its Anti-Coronaviral Potential |
| Review of the broad-spectrum antiviral significance of isoquercetin (quercetin-3-O-glucoside), focusing on SARS-CoV-2. Authors describe evidence from many studies showing inhibitory effects of isoquercetin on several stages of the viral l.. | ||
Jan 2 2024 |
et al., PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638 | Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats |
| In vitro and animal study showing that a novel artemisinin/quercetin/zinc (Art/Q/Zn) complex exhibits potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity (IC50 = 10.14 μg/ml) without cytotoxicity (CC50 = 208.5 μg/ml). The complex alleviates acrylamide-induce.. | ||
Dec 26 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1278039 | Relationship of quercetin intake and oxidative stress in persistent Covid |
| Discussion of the potential of quercetin for persistent COVID-19 symptoms resulting from oxidative stress. Authors explain how COVID-19 leads to oxidative stress through inflammation, cytokine storms, and coagulation abnormalities. Querce.. | ||
Dec 17 2023 |
et al., Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28248141 | Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug |
| Review of the biological and medicinal properties of quercetin, particularly its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, and antiviral effects. Quercetin demonstrates promise against SARS-CoV-2 as evidenced by its binding interactions.. | ||
Dec 15 2023 |
, A., MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1 | Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review |
| Review of a group of compounds with efficacy shown in RCTs, safety, favorable opportunity costs, biological plausibility, and accessibility without major conflicts of interest. The compounds include curcumin, nigella sativa (black seed), .. | ||
Dec 12 2023 |
et al., European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports, doi:10.1016/j.ejmcr.2023.100125 | Anti-SARS-CoV-2, antioxidant and immunomodulatory potential of dietary flavonol quercetin: Focus on molecular targets and clinical efficacy |
| Review of the antiviral, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties of the flavonoid quercetin and its glycosides. Authors review their ability to inhibit infections of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses by interfering with viral entry.. | ||
Dec 11 2023 |
et al., Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, doi:10.1186/s43042-023-00456-4 | Evaluation of therapeutic potentials of some bioactive compounds in selected African plants targeting main protease (Mpro) in SARS-CoV-2: a molecular docking study |
| In silico study showing potential antiviral benefits of quercetin, catechin, epicatechin, vitexin, kaempferol, gamma-sitosterol, and kaur-16-ene against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Molecular docking analysis showed that these com.. | ||
Dec 1 2023 |
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036238 | Active ingredient and mechanistic analysis of traditional Chinese medicine formulas for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: Insights from bioinformatics and in vitro experiments |
| Analysis of TCM treatments for COVID-19 including in silico and in vitro analysis of quercetin, a common ingredient in TCM treatments. Results suggest that quercetin may help alleviate COVID-19-associated inflammation by reducing levels o.. | ||
Nov 30 2023 |
et al., Bioinformation, doi:10.6026/973206300191081 | Molecular docking analysis of quercetin with known CoVid-19 targets |
| In silico analysis of quercetin for COVID-19. Molecular docking simulations suggest quercetin may bind more strongly than remdesivir to SARS-CoV-2 targets including ACE2, the spike protein, and some host proteins involved in viral entry. .. | ||
Nov 30 2023 |
et al., Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115453 | Two-month period of 500 mg lecithin-based delivery form of quercetin daily dietary supplementation counterbalances chronic fatigue symptoms: A double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Double-blind placebo-controlled RCT of 78 subjects with chronic fatigue (27% due to long COVID) showing significant improvement in fatigue symptoms, sleep quality, physical activity, and short physical performance battery scores with 500 .. | ||
Nov 28 2023 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02144-6 | Effects of Lianhuaqingwen Capsules in adults with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019: an international, multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial |
| 39% improved recovery (p<0.0001) and 11% improved viral clearance (p=0.21). RCT 815 mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients in China, 410 treated with Lianhuaqingwen (LHQW) for 14 days, showing improved recovery with treatment. 86.8% of the LHQW group achieved symptom resolution by day 14 compared to 71.9% for placebo.. | ||
Nov 23 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1271201 | Quercetin improves and protects Calu-3 airway epithelial barrier function |
| In vitro analysis of quercetin on airway epithelial barrier function using the Calu-3 cell culture model. Results show that quercetin increases transepithelial electrical resistance and decreases transepithelial leaks, indicating improved.. | ||
Nov 20 2023 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16111631 | Quercetin as a Therapeutic Product: Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Action and Clinical Applications—A Review |
| Review of the pharmacological actions, clinical trials, patents, marketed products, and approaches to improving the bioavailability of the flavonoid quercetin. Quercetin has shown therapeutic potential as an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory.. | ||
Nov 11 2023 |
et al., Medical Data Mining, doi:10.53388/MDM202407003 | Exploring the bioactive compounds of Feiduqing formula for the prevention and management of COVID-19 through network pharmacology and molecular docking |
| In silico study of components of Feiduqing finding that quercetin, among other compounds, has significant binding affinity to PTGS2, HSP90AA1, SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, and ACE2, suggesting that quercetin may have therapeutic potential for COVID-1.. | ||
Nov 10 2023 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29208 | Discovery of the covalent SARS‐CoV‐2 Mpro inhibitors from antiviral herbs via integrating target‐based high‐throughput screening and chemoproteomic approaches |
| In vitro study showing that quercetin can potently inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Mpro activity. Screening of 60 antiviral herbs showed Lonicera japonica extract inhibited Mpro in a time-dependent manner, indicating the presence of covalent cysteine-.. | ||
Nov 3 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264447 | SARS-CoV-2 N protein induced acute kidney injury in diabetic db/db mice is associated with a Mincle-dependent M1 macrophage activation |
| In vitro and mouse study showing that quercetin may ameliorate COVID-19 associated acute kidney injury through modulation of macrophage polarization by blocking the Mincle/Syk/NF-kB pathway. Authors suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 N protein c.. | ||
Nov 2 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115894 | Exploring the Binding Effects of Natural Products and Antihypertensive Drugs on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Investigation of Main Protease and Spike Protein |
| In silico molecular docking and molecular dynamics analysis identifying curcumin, quercetin, rosmarinic acid, and salvianolic acid B as having favorable binding to Mpro and three distinct sites on the S protein. Molecular dynamics simulat.. | ||
Oct 17 2023 |
et al., Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2023.10.029 | Quercetin: A promising drug candidate against the potential SARS-CoV-2-Spike mutants with high viral infectivity |
| In silico and in vitro study of quercetin showing inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 for wildtype and 6 different variants. Molecular docking and dynamics simulation analyses showed that quercetin binds in a cavity at the spike-ACE2 interface, sugg.. | ||
Oct 6 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Diabetes Management, doi:10.61797/ijdm.v2i2.259 | Evaluation of the Effect of Zinc, Quercetin, Bromelain and Vitamin C on COVID-19 Patients |
| Case series of 22 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing that a combination of quercetin 800mg, bromelain 165mg, zinc acetate 50mg and vitamin C 1g daily for 3-5 days was safe when given with other treatments. Authors include in silico mo.. | ||
Sep 26 2023 |
et al., Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3715 | The effect of quercetin supplementation on clinical outcomes in COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis |
| Systematic review and meta analysis of 5 studies, showing significantly lower mortality, ICU admission, and hospitalization with quercetin treatment. | ||
Sep 19 2023 |
et al., Makara Journal of Science, doi:10.7454/mss.v27i3.1609 | In-silico Approach for Predicting the Inhibitory Effect of Home Remedies on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 |
| In silico analysis showing that curcumin and quercetin may be beneficial for COVID-19 by binding to the main protease (Mpro), spike protein, and ACE2 receptor. Both compounds had suitable ADME properties and minimal predicted toxicity. | ||
Sep 5 2023 |
et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2309870120 | Reply to Yan et al.: Quercetin possesses a fluorescence quenching effect but is a weak inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2 main protease |
| In vitro study [Yan] and associated response from the original authors [Xu], collectively showing that quercetin and echinatin had weak SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibition in SDS-PAGE assays [Xu], despite false positive FRET results from MCA-A.. | ||
Sep 5 2023 |
et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2309289120 | Reframing quercetin as a promiscuous inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2 main protease |
| In vitro study [Yan] and associated response from the original authors [Xu], collectively showing that quercetin and echinatin had weak SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibition in SDS-PAGE assays [Xu], despite false positive FRET results from MCA-A.. | ||
Sep 1 2023 |
et al., Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.30476/ijms.2023.98947.3102 | Anti-cytokine Storm Activity of Fraxin, Quercetin, and their Combination on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cytokine Storm in Mice: Implications in COVID-19 |
| Mouse study showing benefit with quercetin for COVID-19 treatment by reducing proinflammatory cytokines and protecting lung and kidney tissues against lipopolysaccharide-induced damage. Lipopolysaccharide is used to induce cytokine storm .. | ||
Aug 25 2023 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6 | A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron |
| Review of natural products for SARS-CoV-2 omicron including an in silico study showing quercetin, curcumin, ascorbic acid, nigellidine, and chloroquine among many compounds docked to the ACE2 metallopeptidase domain. Quercetin, curcumin, .. | ||
Aug 25 2023 |
et al., Middle East Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.36348/merjps.2023.v03i04.001 | Flavonoids as Potent Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 Helicase: Grid Based Docking Approach |
| In silico analysis molecular docking analysis predicting that quercetin, rutin, isorhamnetin, and tamarixetin bind well with SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 helicase enzyme. The proposed mechanism of action is that these flavonoids can inhibit the ATPas.. | ||
Aug 3 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016 | Association of dietary intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols with immune-stimulating microbiota and COVID-19 risk in a group of Polish men and women |
| Dietary analysis of 95 adults in Poland, showing lower risk of COVID-19 with higher intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols. Results were statistically significant for total phytosterols, secoisolariciresinol, β-sitosterol, matai.. | ||
Jul 13 2023 |
et al., Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.07.004 | In silico anti-viral assessment of phytoconstituents in a traditional (Siddha Medicine) polyherbal formulation – Targeting Mpro and pan-coronavirus post-fusion Spike protein |
| In silico analysis of phytoconstituents of Kabasura Kudineer against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and Mpro, showing that quercetin (Mpro) and gallic acid (spike) had the highest binding affinity and stability. | ||
Jun 30 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125553 | Computational analysis of the phytocompounds of Mimusops elengi against spike protein of SARS CoV2 – An Insilico model |
| In silico study finding that quercetin and hederagenin showed very high binding affinities for COVID-19 associated receptors MMP9 and IL6. | ||
Jun 22 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1137407 | NASAFYTOL® supplementation in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 infection: results from an exploratory open-label randomized controlled trial |
| 91% lower combined mortality/ICU admission (p=0.02), 89% lower ventilation (p=0.05), 89% lower ICU admission (p=0.05), and 73% higher hospital discharge (p=0.07). RCT 49 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, 25 treated with curcumin and quercetin, shower lower mortality/ICU admission and improved recovery with treatment. All patients received vitamin D. 336mg curcumin, 520mg quercetin, and 18μg vitamin D.. | ||
Jun 3 2023 |
et al., Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, doi:10.1080/13102818.2023.2222196 | Inhibitory potential of phytochemicals on five SARS-CoV-2 proteins: in silico evaluation of endemic plants of Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| In silico study of phytochemicals from 28 plants identifying hesperidin and quercetin as having the highest binding affinity for SARS-CoV-2 RdRp. The highest affinity for Mpro was observed for genistein and hesperidin, with both compounds.. | ||
Jun 2 2023 |
et al., 11th International Seminar on New Paradigm and Innovation on Natural Sciences and its Application, doi:10.1063/5.0140285 | Utilization of quercetin flavonoid compounds in onion (Allium cepa L.) as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein against ACE2 receptors |
| In silico study showing high affinity binding between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and quercetin, and analysis of the quercetin content of onion. | ||
Jun 1 2023 |
et al., Future Virology, doi:10.2217/fvl-2022-0184 | Structure-based virtual identification of natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 and its Delta and Omicron variant proteins |
| In silico study showing the flavonoid quercetin and its derivative quercetin-3-acetyl-glucoside exhibit potential inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 main protease, helicase, and spike proteins. Related flavonoids like rutin and kaempf.. | ||
May 18 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1188086 | In silico evidence implicating novel mechanisms of Prunella vulgaris L. as a potential botanical drug against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury |
| In silico study identifying quercetin, luteolin and kaempferol as potentially protective for COVID-19 acute kidney injury. | ||
May 15 2023 |
et al., Journal of Modern Biology and Drug Discovery, doi:10.53964/jmbdd.2023004 | Use of Quercetin for Therapeutic Purposes in COVID-19 Infections: The Opinion of the Geriatrician Doctor |
| Review of the antiviral properties and potential benefits of quercetin for COVID-19. | ||
Apr 24 2023 |
et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2301775120 | Bioactive compounds from Huashi Baidu decoction possess both antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects against COVID-19 |
| In vitro study of compounds from Huashi Baidu (Q-14), showing dose-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with quercetin. Authors also perform a mouse study showing that Q-14 decreases SARS-CoV-2 viral load and reduces pulmonary inflammation... | ||
Apr 1 2023 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31764-9 | Channel activity of SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a inhibited by adamantanes and phenolic plant metabolites |
| In vitro study showing that adamantane derivatives and six out of ten tested polyphenols including curcumin and quercetin inhibited the SARS-CoV-2 viroporin ORF3a, which contributes to viral pathogenicity and cytotoxicity. Authors used ce.. | ||
Mar 31 2023 |
et al., Society of Toxicology Conference, 2023 | Computational Analysis of Lianhua Qingwen as an Adjuvant Treatment in Patients with COVID-19 |
| In silico analysis of components of Lianhua Qingwen, identifying quercetin, luteolin, wogonin, and phillyrin as potentially beneficial for COVID-19. Authors note that quercetin bound to Mpro at the same inhibitory pocket as nirmatrelvir (.. | ||
Mar 22 2023 |
et al., Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2023.101230 | Computational studies of potential antiviral compounds from some selected Nigerian medicinal plants against SARS-CoV-2 proteins |
| In silico study identifying quercetin and naringenin as potent multitarget-directed ligands for 3CLpro, PLpro, and ACE2 with favorable ADME properties. | ||
Feb 13 2023 |
et al., Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2427 | Quercetin for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis |
| Systematic review and meta analysis of 6 quercetin RCTs, showing significantly lower hospitalization and ICU admission. Differences for mortality and recovery were not statistically significant. | ||
Jan 26 2023 |
et al., Aging Cell, doi:10.1111/acel.13771 | Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces SARS-CoV-2 related mortality in mice |
| K18-hACE2 mouse study showing reduced COVID-19 severity with quercetin and dasatinib, for both prophylaxis and early treatment. | ||
Jan 25 2023 |
et al., Emergent: Journal of Educational Discoveries and Lifelong Learning, doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/NSJ6B | Applications of quercetin for the prevention of COVID-19 in healthcare workers |
| 96% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 98% fewer symptomatic cases (p<0.0001). Prospective study of healthcare workers in Uzbekistan showing lower mortality and cases with quercetin prophylaxis. Very minimal details are provided, there is no baseline information, and control mortality is very high. | ||
Jan 18 2023 |
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.17.524329 | Senolytic therapy alleviates physiological human brain aging and COVID-19 neuropathology |
| In vitro and animal study showing that senolytics including dasatinib + quercetin improve survival and mitigate neuropathological sequelae of SARS-CoV-2. Authors show that SARS-CoV-2 can initiate cellular senescence in the brains of COVID.. | ||
Jan 18 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1023997 | The possible therapeutic role of curcumin and quercetin in the early-stage of COVID-19—Results from a pragmatic randomized clinical trial |
| 29% improved recovery (p=0.11) and 91% improved viral clearance (p=0.05). Small RCT with 50 outpatients, 25 treated with curcumin, quercetin, and vitamin D, showing improved recovery and viral clearance with treatment. 168mg curcumin, 260mg, 360IU vitamin D3 daily for 14 days. Unadjusted baseline differences: t.. | ||
Jan 17 2023 |
et al., Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules28030938 | Quercetin: A Functional Food-Flavonoid Incredibly Attenuates Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections through Immunomodulatory Actions |
| Review of the antiviral properties of quercetin and derivatives, and potential mechanisms of action. | ||
Jan 16 2023 |
et al., The Gazette of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46766/thegms.pubheal.22120905 | Intravenous high dose vitamin C and ozonated saline effective treatment for Covid-19: The Evolution of Local Standard of Care |
| Retrospective 479 high risk outpatients in the USA treated with a protocol including intravenous vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, quercetin, bromelain, lactoferrin, HCQ, ivermectin, ozonated saline, azithromycin, ceftriaxone, methylprednisolon.. | ||
Jan 13 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1096853 | Quercetin as a possible complementary agent for early-stage COVID-19: Concluding results of a randomized clinical trial |
| 37% improved recovery (p=0.007) and 58% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). RCT 100 outpatients in Pakistan, 50 treated with quercetin phytosome, showing faster viral clearance and improved recovery with treatment. Patients in the treatment group were significantly younger (41 vs. 54). Authors report performing a.. | ||
Jan 12 2023 |
et al., Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, doi:10.1177/11779322221149622 | The Potential of Ameliorating COVID-19 and Sequelae From Andrographis paniculata via Bioinformatics |
| In silico study identifying multiple compounds including andrographolide, quercetin, and hydroxychloroquine (used as a reference) as promising inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. Authors note the potential synergistic effect of multiple compounds. | ||
Dec 12 2022 |
et al., Molecular Therapy, doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.12.002 | Treatment with Quercetin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 N protein-induced acute kidney injury by blocking Smad3-dependent G1 cell cycle arrest |
| Mouse study showing quercetin can significantly inhibit SARS-CoV-2 induced acute kidney injury via blocking of SARS-CoV-2 N-Smad3-mediated cell death. | ||
Nov 29 2022 |
et al., Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123074 | Interaction of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Quercetin with Spike Glycoprotein (S-Glycoprotein) of SARS-CoV-2: In Silico Study |
| In silico study suggesting efficacy of epigallocatechin gallate and quercetin for SARS-CoV-2. | ||
Oct 18 2022 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11206138 | Early Outpatient Treatment of COVID-19: A Retrospective Analysis of 392 Cases in Italy |
| Retrospective 392 outpatients in Italy showing 0.2% mortality with early treatment, compared with >3% in Italy at the time. Treatment varied for individual patients and included HCQ, vitamin D, vitamin C, vitamin A, zinc, quercetin, bromh.. | ||
Aug 25 2022 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15091049 | Quercetin in the Prevention and Treatment of Coronavirus Infections: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2 |
| Review of the potential benefits of quercetin for COVID-19, including inhibitory effects on several stages of the viral life cycle, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects, and synergistic effects with other treatments. | ||
Aug 10 2022 |
et al., Journal of King Saud University - Science, doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102277 | Docking and molecular dynamics studies of human ezrin protein with a modelled SARS-CoV-2 endodomain and their interaction with potential invasion inhibitors |
| In silico study of SARS-CoV-1&2 endodomains and ezrin docking, identifying ivermectin, quercetin, calcifediol, calcitriol, selamectin, and minocycline as potential therapeutic drugs with strong ezrin binding which may restrict viral endod.. | ||
Jun 16 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.3390/ijtm2020022 | Evaluation of the Clinical Effects of an Antiviral, Immunostimulant and Antioxidant Phytotherapy in Patients Suffering from COVID-19 Infection: An Observational Pilot Study |
| Retrospective case series of 240 patients in Italy in 2020, up to 96 years old, showing no mortality and 1.6% hospitalization with early treatment including vitamin C, quercetin, and green tea and red wine polyphenols. The formulation was.. | ||
May 20 2022 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074 | Jinhua Qinggan Granules for Nonhospitalized COVID-19 Patients: a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Controlled Trial |
| 81% greater improvement (p<0.0001) and 8% worse viral clearance (p=0.48). RCT 300 outpatients in China, showing improved recovery with Jinhua Qinggan treatment, but no significant difference in viral clearance or radiographic findings. Jinhua Qinggan includes quercetin, rutin, luteolin, wogonin, myricetin, urso.. | ||
May 15 2022 |
et al., Life Research, doi:10.53388/life2022-0205-302 | The pharmacological mechanism of quercetin as adjuvant therapy of COVID-19 |
| Review of the pharmacological mechanism of quercetin as adjuvant therapy for COVID-19. Authors discuss how quercetin and its metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication through various mechanisms, including interfering with t.. | ||
May 1 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.898062 | Oral Co-Supplementation of Curcumin, Quercetin, and Vitamin D3 as an Adjuvant Therapy for Mild to Moderate Symptoms of COVID-19—Results From a Pilot Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Trial |
| 33% improved recovery (p=0.15) and 50% improved viral clearance (p=0.009). RCT 50 COVID+ outpatients in Pakistan, 25 treated with curcumin, quercetin, and vitamin D, showing significantly faster viral clearance, significantly improved CRP, and faster resolution of acute symptoms (p=0.154). 168mg curcumin, 260mg .. | ||
Apr 29 2022 |
et al., Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11050876 | The Therapeutic and Prophylactic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19: An Outlook on the Clinical Studies, Inventive Compositions, and Patent Literature |
| Review of the evidence supporting the use of quercetin for COVID-19 from clinical studies and patents. | ||
Jan 21 2022 |
et al., European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022 | Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants |
| In vitro study testing combinations of plant extracts and micronutrients with several variants of SARS-CoV-2. A combination of vitamin C, N-acetylcysteine, curcumin, quercetin, resveratrol, theaflavin, naringenin, baicalin, and broccoli e.. | ||
Jan 4 2022 |
et al., Life, doi:10.3390/life12010066 | Promising Effects of 3-Month Period of Quercetin Phytosome® Supplementation in the Prevention of Symptomatic COVID-19 Disease in Healthcare Workers: A Pilot Study |
| 93% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.04). RCT 120 healthcare workers, 60 treated with quercetin phytosome, showing lower risk of cases with treatment. Quercetin phytosome 250mg twice a day. Section 2.1 states: 'A maximal follow-up period was determined to be at 3 months.' However.. | ||
Dec 28 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1149846/v1 | Quercetin and Luteolin Are Single-digit Micromolar Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase |
| In vitro and in silico study showing quercetin and luteolin inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). | ||
Dec 14 2021 |
et al., Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166322 | The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 virus induces heme oxygenase-1: Pathophysiologic implications |
| In vitro study transfecting SARS-CoV-2 viral spike protein in kidney cell lines, showing syncytia formation and upregulation of the cytoprotective gene HO-1, and that quercetin, which induces HO-1, can reduce syncytia formation. Authors c.. | ||
Dec 8 2021 |
et al., Medical Science Monitor, doi:10.12659/MSM.935379 | Retrospective Study of Outcomes and Hospitalization Rates of Patients in Italy with a Confirmed Diagnosis of Early COVID-19 and Treated at Home Within 3 Days or After 3 Days of Symptom Onset with Prescribed and Non-Prescribed Treatments Between November 2020 and August 2021 |
| Retrospective 158 COVID-19 patients in Italy treated with hesperidin, quercetin, indomethacin, aspirin, omeprazole, azithromycin, LMWH, and betamethasone (treatment specific for each patient), showing significantly lower hospitalization a.. | ||
Dec 2 2021 |
et al., European Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.1746158 | The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial |
| 86% lower mortality (p=0.24) and 32% faster recovery (p=0.04). Small RCT with 60 severe hospitalized patients in Iran, 30 treated with quercetin, showing shorter time until discharge. All patients received remdesivir or favipiravir, and vitamin C, vitamin D, famotidine, zinc, dexamethasone, and magne.. | ||
Nov 14 2021 |
et al., Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594 | Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols |
| In silico and in vitro study of plant polyphenols identifying quercetin, curcumin, ellagic acid, epigallocatechin gallate, and resveratrol as SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors with IC50 between 11.8µM and 23.4µM. Real-time binding was analyzed.. | ||
Sep 29 2021 |
et al., Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2021.108038 | In silico identification of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry inhibitors from selected natural antivirals |
| In silico study identifying quercetin derivatives as SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, ACE2, and neuropilin inhibitors. | ||
Sep 1 2021 |
et al., Zaporozhye Med. J., doi:10.14739/2310-1210.2021.5.231714 | Quercetin effectiveness in patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia |
| 29% improved recovery (p=0.5). RCT 200 patients in Ukraine, 99 treated with IV quercetin/polyvinylirolidone followed by oral quercetin/pectin, showing improved recovery with treatment. The paper states 'authors have no conflict of interest to declare.' However, author .. | ||
Jul 6 2021 |
et al., Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1177/2515690X211026193 | 20-Week Study of Clinical Outcomes of Over-the-Counter COVID-19 Prophylaxis and Treatment |
| 94% fewer cases (p=0.003). Retrospective 113 outpatients, 53 (patient choice) treated with zinc, quercetin, vitamin C/D/E, l-lysine, and quina, showing lower cases with treatment. Results are subject to selection bias and limited information on the groups is provid.. | ||
Jun 24 2021 |
et al., International Journal of General Medicine, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S318949 | Potential Clinical Benefits of Quercetin in the Early Stage of COVID-19: Results of a Second, Pilot, Randomized, Controlled and Open-Label Clinical Trial |
| 74% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). RCT 42 outpatients in Pakistan, 21 treated with quercetin phytosome, showing faster viral clearance and lower symptom severity with treatment. Patients in the treatment group were younger (43 vs. 56). | ||
Jun 15 2021 |
et al., Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758 | Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| Vero E6 in vitro study showing curcumin, hesperidin, and quercetin significantly inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication, and in silico analysis with promising Mpro and spike docking results. | ||
Jun 8 2021 |
et al., International Journal of General Medicine, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S318720 | Possible Therapeutic Effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early-Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study |
| 86% lower mortality (p=0.25), 94% lower ICU admission (p=0.006), and 68% lower hospitalization (p=0.003). RCT 152 outpatients in Pakistan, 76 treated with quercetin phytosome, showing lower mortality, ICU admission, and hospitalization with treatment. Potential data issues include: Table 5 hospitalization frequency mismatch: Table 5 reports 7.. | ||
Apr 8 2021 |
et al., Journal of Advances in Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.9734/jamps/2021/v23i330222 | Oral Quercetin in Adult Patients as a Potential Nutraceutical against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) |
| Prospective study of 52 patients treated with quercetin. There was no control group. | ||
Jan 19 2021 |
et al., Turk. J. Biol., 45:518-529 (date from preprint) | Treatment of COVID-19 patients with quercetin: a prospective, single center, randomized, controlled trial |
| 94% lower ICU admission (p=0.39) and 78% higher hospital discharge (p=0.1). RCT 447 moderate-to-severe hospitalized patients in Turkey, 52 treated with quercetin, bromelain, and vitamin C, showing no statistically significant difference in clinical outcomes. Authors claim computer-generated random numbers were us.. | ||
Dec 31 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.235 | Structural stability of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and identification of quercetin as an inhibitor by experimental screening |
| In vitro study showing that quercetin inhibits the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro). Authors performed biophysical characterization of 3CLpro structural stability and catalytic activity, designed a molecular screening procedure, and iden.. | ||
Nov 16 2020 |
et al., Current Pharmaceutical Design, doi:10.2174/1381612826999201116195851 | Natural Compounds as Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (3CLpro): A Molecular Docking and Simulation Approach to Combat COVID-19 |
| In silico study showing that the natural compounds kaempferol, quercetin, and rutin bind to the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2, also known as 3CLpro, with high affinity. Authors find these flavonoids interact with active site residues.. | ||
Nov 16 2020 |
et al., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3682517 | Synergistic Effect of Quercetin and Vitamin C Against COVID-19: Is a Possible Guard for Front Liners |
| 92% fewer cases (p=0.03). Small prophylaxis RCT with 113 patients showing fewer cases with quercetin + vitamin C + bromelain prophylaxis. Note that this paper disappeared from SSRN without explanation. This paper has multiple data issues: Impossible follow-up dura.. | ||
Oct 9 2020 |
et al., Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.6887 | A role for quercetin in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) |
| Review noting that quercetin has a theoretical, but significant, capability to interfere with SARS-CoV-2 replication, with results showing this to be the fifth best compound out of 18 candidates. | ||
Jun 19 2020 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01451 | Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19) |
| Review of the evidence for the use of vitamin C and quercetin both for prophylaxis in high-risk populations and for the treatment of COVID-19 patients. | ||
Apr 24 2020 |
et al., ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1 | In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2 |
| In silico study of natural compounds identifying quercetin, curcumin, hispidulin, cirsimaritin, sulfasalazine, and artemisin as potential compounds that inhibit SARS-CoV-2. | ||
Mar 31 2020 |
et al., Journal of Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.joim.2020.02.005 | In silico screening of Chinese herbal medicines with the potential to directly inhibit 2019 novel coronavirus |
| In silico study showing that 13 natural compounds from Chinese herbal medicines have potential anti-2019-nCoV activity by binding to viral proteins such as papain-like protease (PLpro), 3C-like protease (3CLpro), and the spike protein. Au.. | ||