The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial
et al., European Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.1746158, IRCT20200419047128N2, Dec 2021
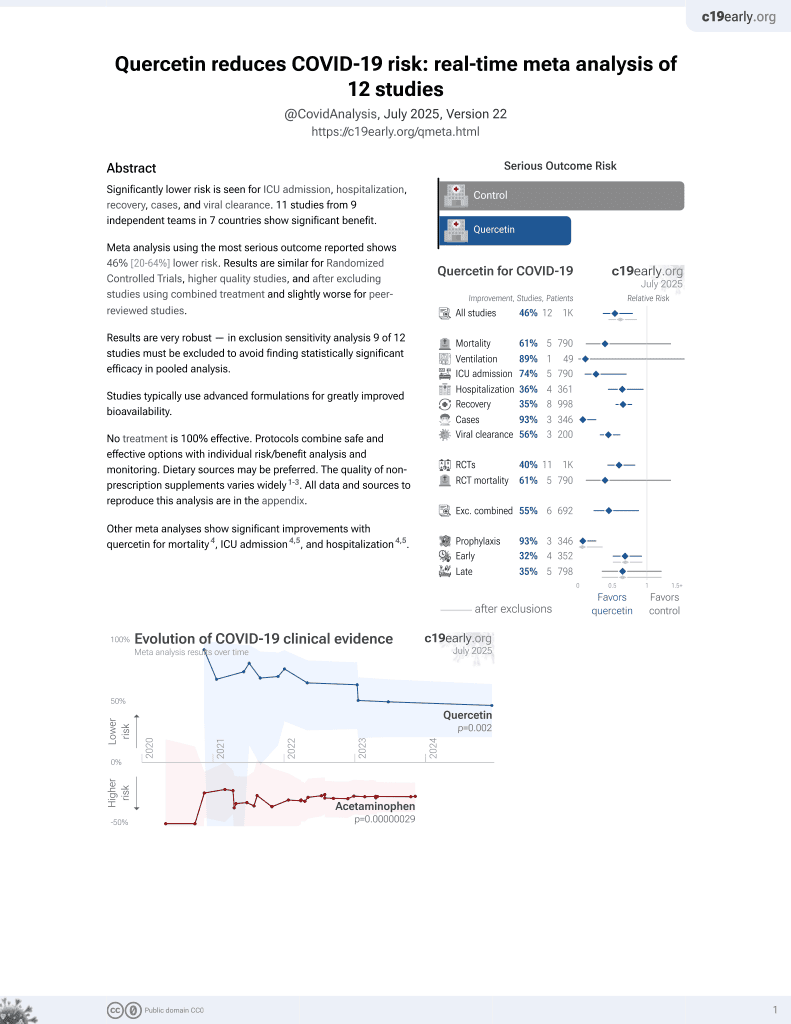
Quercetin for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2022, now with p = 0.0018 from 9 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
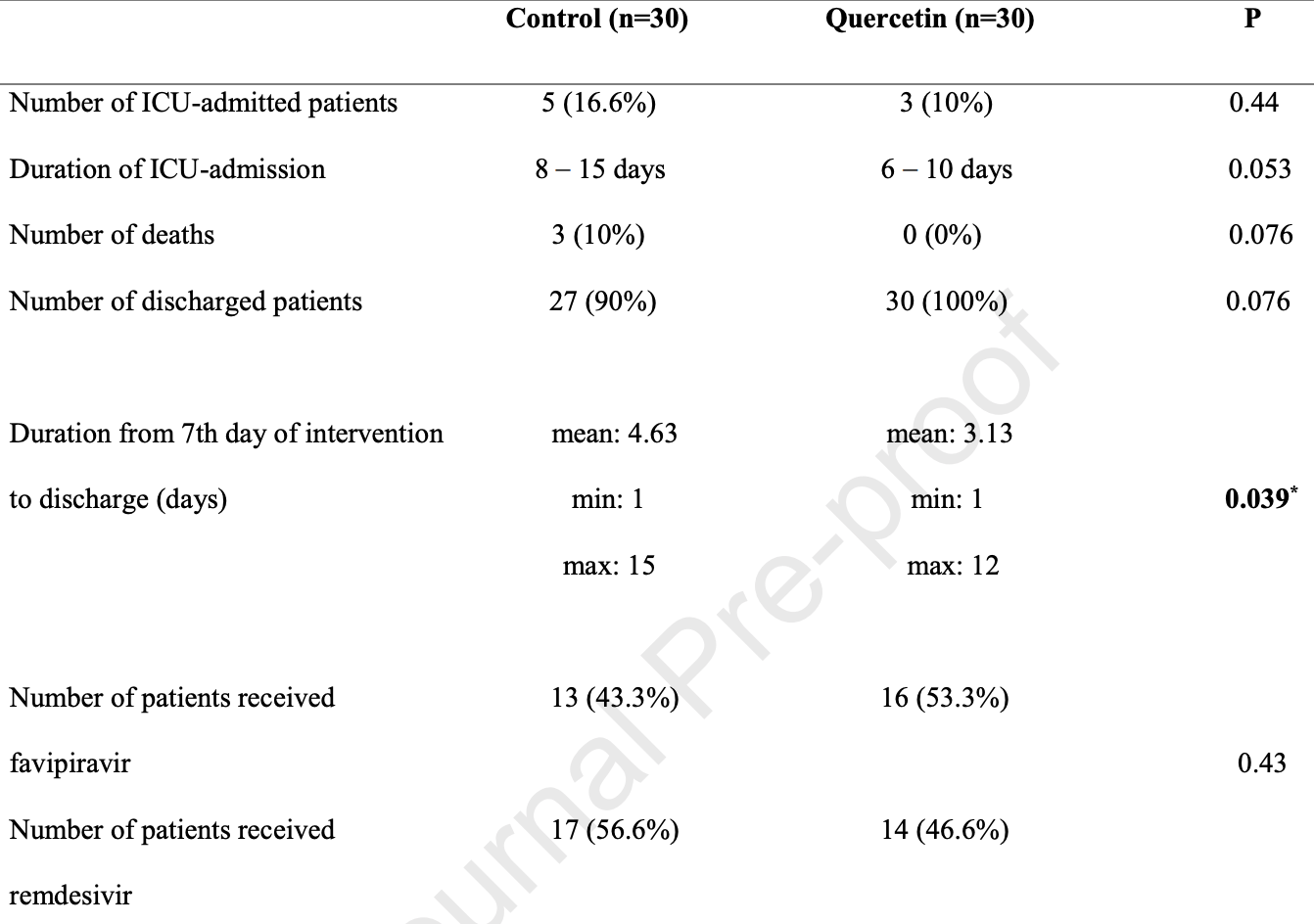
Small RCT with 60 severe hospitalized patients in Iran, 30 treated with quercetin, showing shorter time until discharge. All patients received remdesivir or favipiravir, and vitamin C, vitamin D, famotidine, zinc, dexamethasone, and magnesium (depending on serum levels). Quercetin 1000mg daily for 7 days.
Table 1 shows the duration of symptoms before randomization was 9.43 days in the Control group and 7.77 days in the quercetin group (P=0.043). Table 1 also shows that fever at baseline was present in 50% of the control group but 80% of the quercetin group (P=0.015).
The study was unblinded, and one of the primary endpoints that achieved significance was 'time to discharge'. Hospital discharge is a subjective clinical decision.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
This is the 3rd of 9 COVID-19 RCTs for quercetin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0018.
|
risk of death, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.24, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 3 of 30 (10.0%), NNT 10.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.71, treatment 3 of 30 (10.0%), control 5 of 30 (16.7%), NNT 15.
|
|
time to discharge from end of intervention, 32.4% lower, relative time 0.68, p = 0.04, treatment 30, control 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Shohan et al., 2 Dec 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 50.9 (treatment) 52.7 (control), 8 authors, study period December 2020 - January 2021, average treatment delay 7.8 days, trial IRCT20200419047128N2.
Contact: akhodadadi2@gmail.com, akhodadadi@ajums.ac.ir.
The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial
European Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174615
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Authorship contribution statement Mojtaba Shohan: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing original draft, Writingreview and editing.
Roohangiz
Declarations of interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Agrawal, Agrawal, Blunden, Quercetin: Antiviral Significance and Possible COVID -19 Integrative Considerations, Natural Product Communications
Ahmed, Abdelseed, Albalawi, Almutairi, Alsalameen et al., Evaluation of the Effect of Zinc, Quercetin, Bromelain and Vitamin C on COVID-19 Patients
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine
Biancatelli, Berrill, Catravas, Marik, Dabbous et al., Quercetin and vitamin C: an experimental, synergistic therapy for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 related disease (COVID-19), Frontiers in immunology
Carpinteiro, Edwards, Hoffmann, Kochs, Gripp et al., Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS -CoV-2 by epithelial cells, Cell Reports Medicine
Carpinteiro, Gripp, Hoffmann, Pöhlmann, Hoertel et al., Inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase by ambroxol prevents SARS -CoV-2 entry into epithelial cells, Journal of Biological Chemistry
Chamorro, Pandolfi, Moreno, Barreira, Martínez-Ramas et al., Effects of quercetin in a rat model of hemorrhagic traumatic shock and reperfusion, Molecules
Dabbous, El-Sayed, El Assal, Elghazaly, Ebeid et al., Safety and efficacy of favipiravir versus hydroxychloroquine in man agement of COVID-19: A randomised controlled trial, Scientific reports
Derosa, Maffioli, D'angelo, Di Pierro, A role for quercetin in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Phytotherapy Research
Di Pierro, Derosa, Maffioli, Bertuccioli, Togni et al., Possible Therapeutic Effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early -Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study
Glinsky, Tripartite combination of candidate pandemic mitigation agents: vitamin D, quercetin, and estradiol manifest properties of medicinal agents for targeted mitigation of the COVID-19 pandemic defined by genomics-guided tracing of SARS-CoV-2 targets in human cells, Biomedicines
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Diaz, Asperges et al., Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, New England Journal of Medicine
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Kornhuber, Carpinteiro et al., Association between FIASMAs and Reduced Risk of Intubation or Death in Individuals Hospitalized for Severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study, Clinical Pharmacology & Thera peutics
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patien ts infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The lancet
Jo, Kim, Shin, Kim, Inhibition of SARS-CoV 3CL protease by flavonoids, Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry
Kaka, Macdonald, Greer, Vela, Duan-Porter et al., Major update: remdesivir for adults with COVID-19: a living systematic review and meta -analysis for the American College of Physicians Practice Points, Annals of internal medicine
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID -19: a randomized clinical trial, Jama
Li, Yao, Han, Yang, Chaudhry et al., Metabolic Signatures Associated with Severity in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Moon, Barritt, Mortaz, Tabarsi, Varahram et al., Elevated Liver Enzymes in Patients with COVID-19: Look, but Not Too Hard, Frontiers in Immunology
Murohashi, Hagiwara, Kitayama, Yamaya, Higa et al., Outcome of early-stage combination treatment with favipiravir and methylprednisolone for severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 11 cases, Respiratory investigation
Nile, Nile, Qiu, Li, Jia et al., COVID-19: Pathogenesis, cytokine storm and therapeutic potential of interferons, Cytokine & growth factor reviews
Onal, Arslan, Ergun, Topuz, Semerci et al., Treatment of COVID-19 Patients with Quercetin: A Prospective, Single-Centre, Randomized, Controlled Trial
Ros, Pedrera, Garcia-Saez, Saeedi-Boroujeni, Mahmoudian-Sani, Partners in crime: the interplay of proteins and membranes in regulated necrosis, International journal of molecular sciences
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19
Shinkai, Tsushima, Tanaka, Hagiwara, Tarumoto et al., Efficacy and Safety of Favipiravir in Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia Patients without Oxygen Therapy: A Randomized, Phase III Clinical Trial, Infectious Diseases and Therapy
Singh, Khera, Chugh, Khera, Chugh, Efficacy and safety of remdesivir in COVID -19 caused by SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ open
Ucan, Cerci, Efe, Akgun, Ozmen et al., Benefits of treatment with favipiravir in hospitalized patients for COVID-19: a retrospective observational case-control study, Frontiers in immunology
Zhao, Di, Xu, The NLRP3 inflammasome and COVID-19: Activation, pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews