Feb 17 |
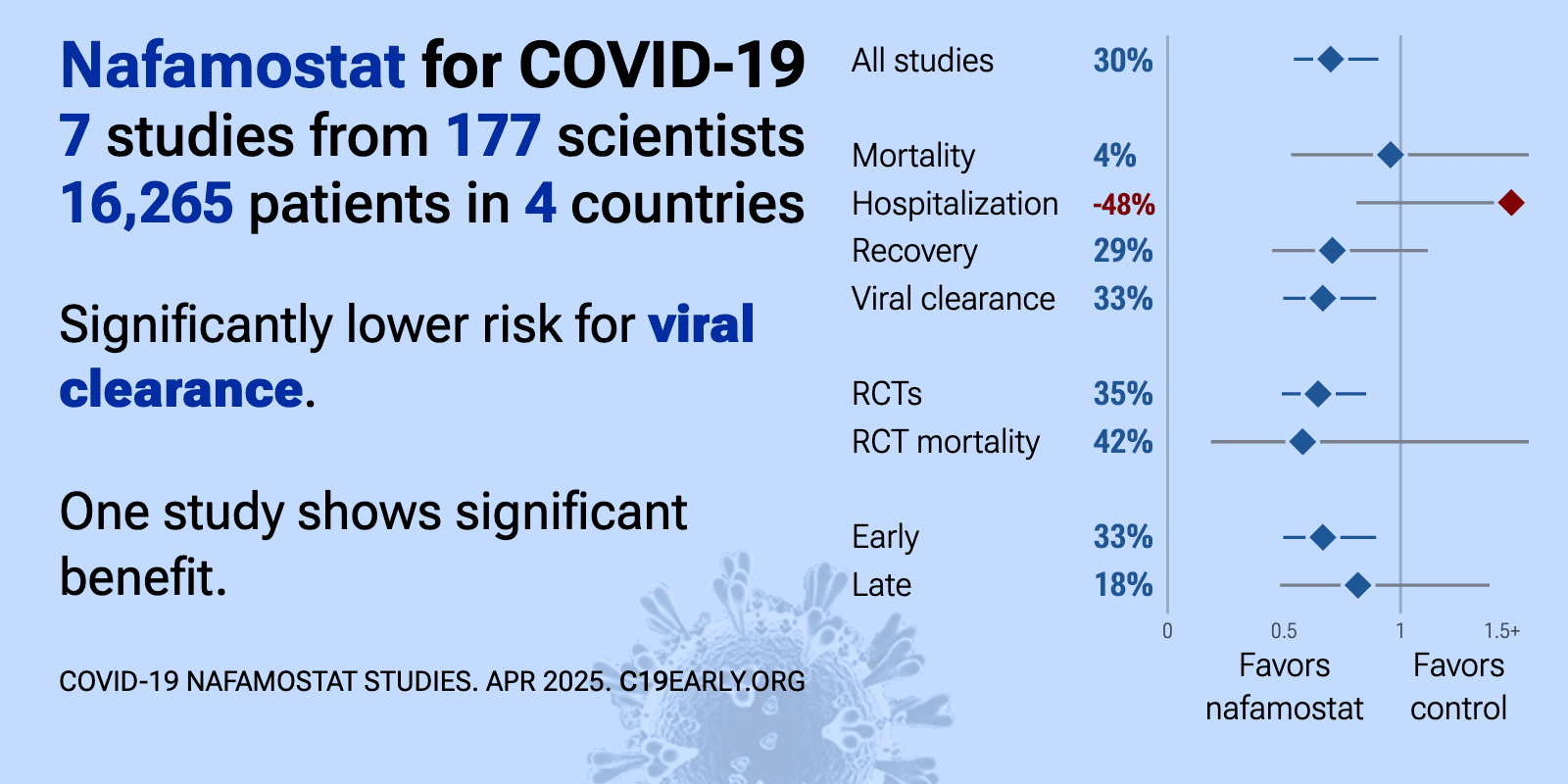
Nafamostat reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 7 studies | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for viral clearance. One study shows significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 30% [10‑46%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trial.. | ||
Jun 5 2025 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-6819274/v1 | INP-Guided Network Pharmacology Discloses Multi-Target Therapeutic Strategy Against Cytokine and IgE Storms in the SARS-CoV-2 NB.1.8.1 Variant |
| Computational modeling study presenting a multi-target therapeutic approach against the SARS-CoV-2 NB.1.8.1 variant using Intrinsic Network Pharmacology (INP) and network pharmacology tools. The researchers identified ZINC000014930714, a .. | ||
Feb 14 2024 |
et al., ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c06968 | Biophysical Analysis of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Recognition and Their Effect on Viral Dynamics in Different Cell Types: A Computational Prediction from In Vitro Experimental Data |
| In silico study showing that nafamostat, camostat, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, telmisartan, and captopril may be beneficial for COVID-19 by inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and replication in multiple cell types expressing ACE2 and T.. | ||
Oct 24 2023 |
et al., NEJM Evidence, doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2300132 | A Randomized Trial of Nafamostat for Covid-19 |
| 55% lower ventilation (p=0.23), 57% lower progression (p=0.14), and 28% improved recovery (p=0.36). RCT 160 hospitalized non-critically ill COVID-19 patients showing a 93% posterior probability that nafamostat reduced the odds of death or receipt of ventilatory or vasopressor support by day 28 compared to usual care. Nafamostat, a TMPRS.. | ||
Oct 19 2023 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm12206618 | RAndomized Clinical Trial Of NAfamostat Mesylate, A Potent Transmembrane Protease Serine 2 (TMPRSS2) Inhibitor, in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia |
| 67% lower mortality (p=1) and 20% improved recovery (p=1). RCT 15 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing a positive safety profile with nafamostat mesylate treatment. While the study was underpowered to detect differences in efficacy, Bayesian analysis suggested a signal for potential benefit (69.. | ||
Sep 30 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922 | Antiviral effect and safety of nafamostat mesilate in patients with mild early-onset COVID-19: An exploratory multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial |
| 33% improved viral clearance (p=0.007). RCT 30 early-onset COVID-19 patients showing significantly improved viral load reduction with nafamostat. | ||
Feb 8 2023 |
et al., NCT04390594 | Multicentre, Open Label, Randomised, Adaptative Clinical Trial of Efficacy and Safety of Treatment Regimens in Adult COVID-19 Patients in Senegal |
| 59 patient nafamostat late treatment RCT with results not reported over 3 years after completion. | ||
Sep 30 2022 |
et al., Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.7883/yoken.JJID.2021.699 | Nafamostat Mesylate Monotherapy in Patients with Moderate COVID-19: a Single-Center, Retrospective Study |
| 80% lower mortality (p=0.49) and 6% higher severe cases (p=1). Retrospective 64 hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes with nafamostat mesylate. | ||
Aug 1 2022 |
et al., NCT04871646 | A Double-blind, Multi-center, Multi-regional, Randomized Controlled, Phase 3 Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of CKD-314 in Hospitalized Adult Patients Diagnosed With COVID-19 |
| Estimated 586 patient nafamostat late treatment RCT with results not reported over 3 years after estimated completion. | ||
Jun 30 2022 |
et al., Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344 | Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach |
| In silico study of ivermectin, camostat, and nafamostat, showing that ivermectin had the best inhibitory action on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and Nsp10, while nafamostat had the best results for the other non-structural proteins. Author.. | ||
Feb 28 2022 |
et al., eBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103856 | Randomised controlled trial of intravenous nafamostat mesylate in COVID pneumonitis: Phase 1b/2a experimental study to investigate safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics |
| 48% longer hospitalization (p=0.21). RCT 42 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonitis showing no benefit with intravenous nafamostat mesylate. | ||
Feb 7 2022 |
et al., Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x | Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2 |
| In vitro and mouse study showing synergistic antiviral effects when combining pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors with antiviral nucleoside analogues against SARS-CoV-2. Authors screened 18 thousand drugs and validated 122 with antiviral a.. | ||
Dec 31 2021 |
et al., Chemical Science, doi:10.1039/D1SC01494C | Synergistic inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry by otamixaban and covalent protease inhibitors: pre-clinical assessment of pharmacological and molecular properties |
| In vitro study showing that otamixaban inhibits SARS-CoV-2 cell entry through TMPRSS2 inhibition. Authors found otamixaban to be a weak TMPRSS2 inhibitor in cell culture (IC50 of 18.7 μM) compared to camostat (IC50 of 151.1 nM) and nafamo.. | ||
Dec 26 2021 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11010116 | Association between Nafamostat Mesylate and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Multicenter Observational Study |
| 27% higher mortality (p=0.52). Retrospective multicenter observational study of 15,859 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Japan showing no significant difference in in-hospital mortality with nafamostat mesylate. Very few patients received treatment and they had more se.. | ||
Nov 30 2021 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101169 | Nafamostat in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomised Phase II clinical trial |
| 76% lower mortality (p=0.2), 42% greater improvement (p=0.28), and 42% improved recovery (p=0.28). RCT 104 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia showing no significant difference in the primary endpoint of time to clinical improvement with nafamostat. However, in patients with baseline National Early Warning .. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626 | Computational Identification of a Putative Allosteric Binding Pocket in TMPRSS2 |
| In silico study of TMPRSS2 inhibition by camostat, nafamostat, and bromhexine, suggesting allosteric binding for bromhexine, compared to camostat and nafamostat which bind to the active site of TMPRSS2 forming covalent adducts. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., NCT04418128 | Treatment Effect of Nafamostat Mesylate in Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia: Open Labelled Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial |
| Estimated 84 patient nafamostat late treatment RCT with results not reported over 4 years after estimated completion. | ||
Apr 5 2021 |
et al., NCT04628143 | Open-label, Multi-center, Randomized Controlled, Phase 2 Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of CKD-314 in Hospitalized Adult Patients Diagnosed With COVID-19 |
| 13 patient nafamostat late treatment RCT with results not reported over 4 years after completion. | ||