Antiviral effect and safety of nafamostat mesilate in patients with mild early-onset COVID-19: An exploratory multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922, Sep 2023
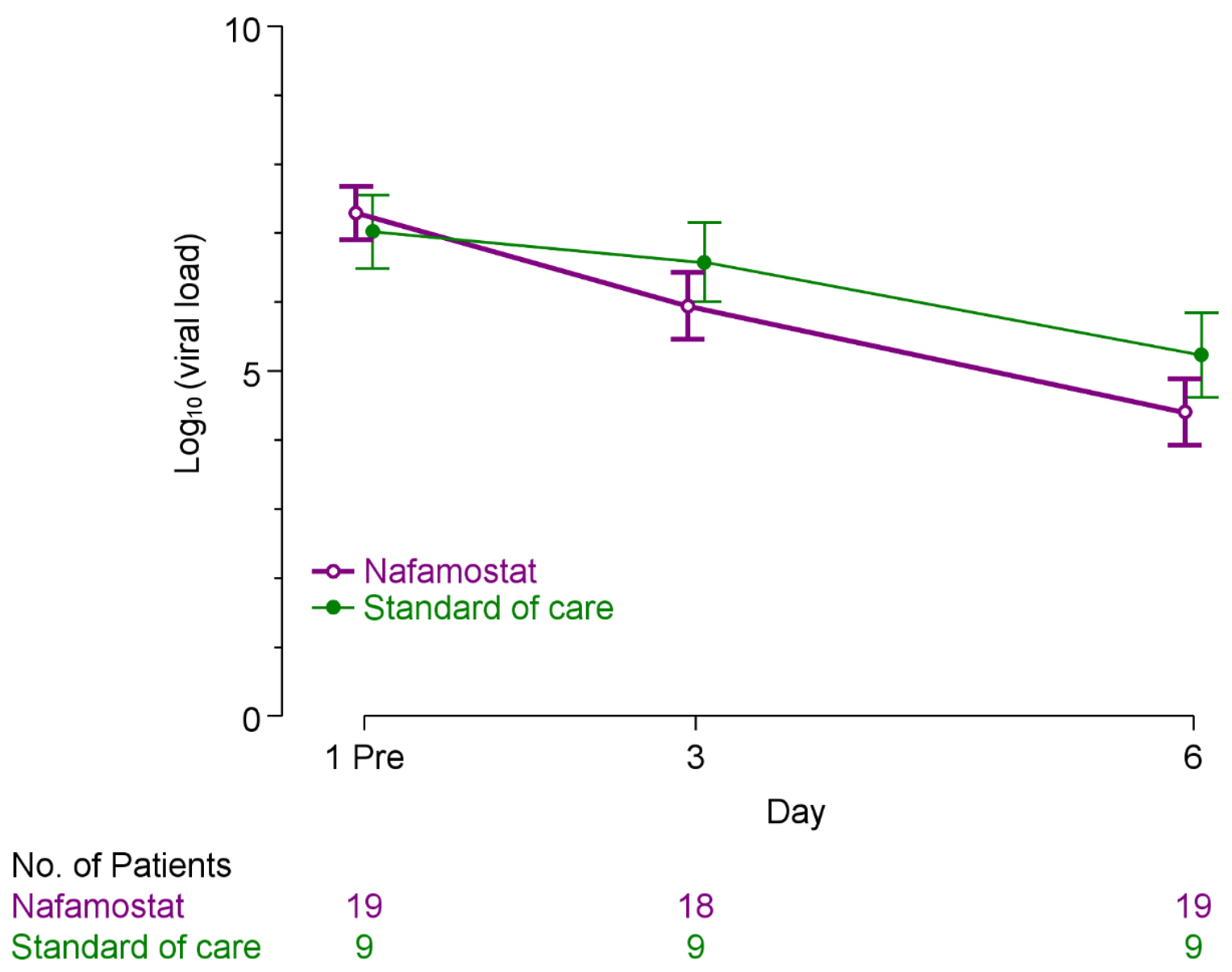
RCT 30 early-onset COVID-19 patients showing significantly improved viral load reduction with nafamostat.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
Japan, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers TMPRSS2 inhibitors and nafamostat.
|
viral load, 33.3% lower, relative load 0.67, p = 0.007, treatment mean 3.0 (±0.91) n=19, control mean 2.0 (±0.8) n=10, relative reduction in viral load, day 6.
|
|
viral load, 60.0% lower, relative load 0.40, p = 0.01, treatment mean 1.5 (±0.91) n=19, control mean 0.6 (±0.79) n=10, relative reduction in viral load, mid-recovery, day 3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Okugawa et al., 30 Sep 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, Japan, peer-reviewed, mean age 39.3, 22 authors, study period July 2021 - July 2022, average treatment delay 2.5 days.
Contact: moriyakyojl0720@gmail.com.
Antiviral effect and safety of nafamostat mesilate in patients with mild early-onset COVID-19: An exploratory multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the antiviral effects and safety of nafamostat in early-onset patients with coronavirus disease 2019 . Methods: In this exploratory multicentre randomized controlled trial, patients were assigned to three groups within 5 days of symptom onset, with 10 participants in each group: nafamostat at either 0.2 mg/kg/h or 0.1 mg/kg/h or a standard-of-care group. The primary endpoint was area under the curve for decrease in SARS-CoV-2 viral load in nasopharyngeal samples from baseline to day 6. Results: Of the 30 randomized patients, 19 received nafamostat. Overall, 10 patients received low-dose nafamostat, 9 patients received high-dose nafamostat, and 10 received standard-of-care. The detected viruses were Omicron strains. The regression coefficient for area under the curve for decrease in viral load as the response variable and nafamostat dose per body weight as the explanatory variable showed a significant relationship of -40.1 (95% confidence interval, -74.1 to -6.2; P = 0.022). Serious adverse events were not observed in either group. Phlebitis occurred in ca. 50% of patients treated with nafamostat. Conclusions: Nafamostat exerts virus load-reducing effects in patients with early-onset COVID-19.
Competing Interests: JI, YS, and KM are co-inventors on patent applications of nafamostat as an antiviral agent (PCT/JP2021/9968, patent applicant: the University of Tokyo). All other authors declare no competing interests. Towa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., supplied nafamostat mesilate. Ethical Approval: This study was approved by the Clinical Research Review Board of the University of Tokyo (approval number 2021501SP), and each participating hospital investigator received permission from their administrator to conduct the study. All participants provided written informed consent to participate in the study. The study was registered in the Japan Registry of Clinical Trials (jRCTs031210183).
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023. 106922 .
References
Aggarwal, Akerman, Milogiannakis, Silva, Walker et al., SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.5: evolving tropism and evasion of potent humoral responses and resistance to clinical immunotherapeutics relative to viral variants of concern, EBiomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.penalty-@M104270
Cao, Zhang, Yu, Shao, Chen et al., A method for quantifying the unstable and highly polar drug nafamostat mesilate in human plasma with optimized solid-phase extraction and ESI-MS detection: more accurate evaluation for pharmacokinetic study, Anal Bioanal Chem, doi:10.1007/s00216-008-2054-4
Chan, Hu, Chai, Shuai, Liu et al., Virological features and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, Cell Rep Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100743
Co, Ltd, Phermacutical interview form for FUTHAN for injection
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Wisemandle, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Hernández-Mitre, Tong, Denholm, Dore, Bowen et al., Nafamostat mesylate for treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: a structured, narrative review, Clin Pharmacokinet, doi:10.1007/s40262-022-01170-x
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Pöhlmann, A multibasic cleavage site in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for infection of human lung cells, Mol Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hoffmann, Schroeder, Kleine-Weber, Muller, Drosten et al., Nafamostat Mesylate Blocks Activation of SARS-CoV-2: New Treatment Option for COVID-19, doi:10.1128/AAC.00754-20
Hui, Ho, Cheung, Ng, Ching et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6
Ikeda, Okugawa, Kashiwabara, Moritoyo, Kanno et al., Multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled study of the efficacy and safety of favipiravir and nafamostat mesilate in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.039
Koch, Uckeley, Doldan, Stanifer, Boulant et al., TMPRSS2 expression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/embj.2021107821
Lingas, Néant, Gaymard, Belhadi, Peytavin et al., Effect of remdesivir on viral dynamics in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a modelling analysis of the randomized, controlled, open-label DisCoVeRy trial, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac048
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Goonawardane, Saito et al., Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x
Parienti, De Grooth, Clinical relevance of nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 viral load reduction in outpatients with COVID-19, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac104
Quinn, Gaughan, Bruce, Antonelli, Connor et al., Randomised controlled trial of intravenous nafamostat mesylate in COVID pneumonitis: Phase 1b/2a experimental study to investigate safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, EBiomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103856
Yamamoto, Kiso, Sakai-Tagawa, Iwatsuki-Horimoto, Imai et al., The anticoagulant nafamostat potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S proteinmediated fusion in a cell fusion assay system and viral infection in vitro in a cell-type-dependent manner, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12060629
Zhuravel, Khmelnitskiy, Burlaka, Gritsan, Goloshchekin et al., Nafamostat in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomised Phase II clinical trial, EClinicalmedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101169
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922",
"ISSN": [
"0924-8579"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922",
"alternative-id": [
"S0924857923002017"
],
"article-number": "106922",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Antiviral effect and safety of nafamostat mesilate in patients with mild early-onset COVID-19: An exploratory multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3455-8291",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Okugawa",
"given": "Shu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4732-3483",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ikeda",
"given": "Mahoko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kashiwabara",
"given": "Kosuke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moritoyo",
"given": "Takashi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kohsaka",
"given": "Takao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shimizu",
"given": "Toshio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5086-1891",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hagiya",
"given": "Hideharu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hasegawa",
"given": "Kou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7014-9095",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Otsuka",
"given": "Fumio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miwa",
"given": "Ayumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kisimoto",
"given": "Nobuhito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mizoguchi",
"given": "Ayako",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imamura",
"given": "Akira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1677-3369",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ikeuchi",
"given": "Kazuhiko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsutsumi",
"given": "Takeya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9080-0172",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jubishi",
"given": "Daisuke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3281-8400",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hashimoto",
"given": "Hideki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okamoto",
"given": "Koh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3073-6564",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Harada",
"given": "Sohei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inoue",
"given": "Jun-ichiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seto",
"given": "Yasuyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moriya",
"given": "Kyoji",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-08T06:08:02Z",
"timestamp": 1688796482000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-29T11:05:18Z",
"timestamp": 1706526318000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100009619",
"award": [
"JP20fk0108503"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100009619",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-19T14:48:51Z",
"timestamp": 1745074131976,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1693526400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688688000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0924857923002017?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0924857923002017?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "106922",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0001",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12060629",
"article-title": "The anticoagulant nafamostat potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated fusion in a cell fusion assay system and viral infection in vitro in a cell-type-dependent manner",
"author": "Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "629",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0002",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022",
"article-title": "A multibasic cleavage site in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for infection of human lung cells",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0003",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021107821",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 expression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells",
"author": "Koch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EMBO J",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0004",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40262-022-01170-x",
"article-title": "Nafamostat mesylate for treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: a structured, narrative review",
"author": "Hernández-Mitre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1331",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacokinet",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0005",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101169",
"article-title": "Nafamostat in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomised Phase II clinical trial",
"author": "Zhuravel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalmedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0006",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103856",
"article-title": "Randomised controlled trial of intravenous nafamostat mesylate in COVID pneumonitis: Phase 1b/2a experimental study to investigate safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics",
"author": "Quinn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBiomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0007",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.039",
"article-title": "Multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled study of the efficacy and safety of favipiravir and nafamostat mesilate in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Ikeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0008",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac048",
"article-title": "Effect of remdesivir on viral dynamics in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a modelling analysis of the randomized, controlled, open-label DisCoVeRy trial",
"author": "Lingas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1404",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0009",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac104",
"article-title": "Clinical relevance of nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 viral load reduction in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Parienti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2038",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0010",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0011",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00754-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0012",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Schroeder S, Kleine-Weber H, Muller MA, Drosten C, Pohlmann S. Nafamostat Mesylate Blocks Activation of SARS-CoV-2: New Treatment Option for COVID-19. 2020;64(6):e00754-20. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00754-20."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0013",
"unstructured": "Nichi-Iko Pharmacutical Co., Ltd. Phermacutical interview form for FUTHAN for injection. 2022. https://www.nichiiko.co.jp/medicine/file/31050/interview/31050_interview.pdf Access March 10, 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00216-008-2054-4",
"article-title": "A method for quantifying the unstable and highly polar drug nafamostat mesilate in human plasma with optimized solid-phase extraction and ESI-MS detection: more accurate evaluation for pharmacokinetic study",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1063",
"journal-title": "Anal Bioanal Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0014",
"volume": "391",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0015",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Virological features and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2",
"author": "Chan",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0016",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"article-title": "Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity",
"author": "Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0017",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104270",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.5: evolving tropism and evasion of potent humoral responses and resistance to clinical immunotherapeutics relative to viral variants of concern",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBiomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106922_bib0018",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0924857923002017"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral effect and safety of nafamostat mesilate in patients with mild early-onset COVID-19: An exploratory multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "62"
}
okugawa