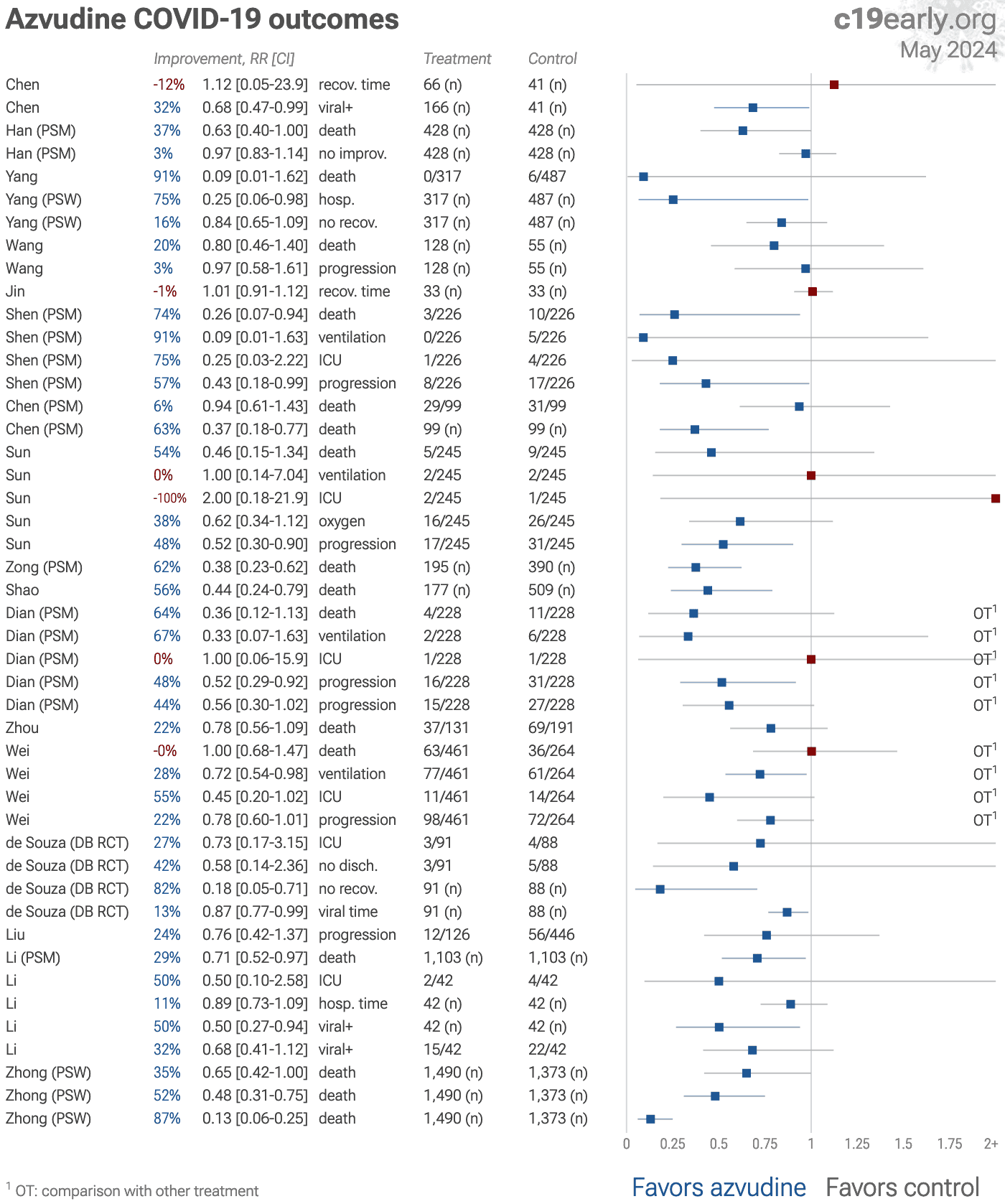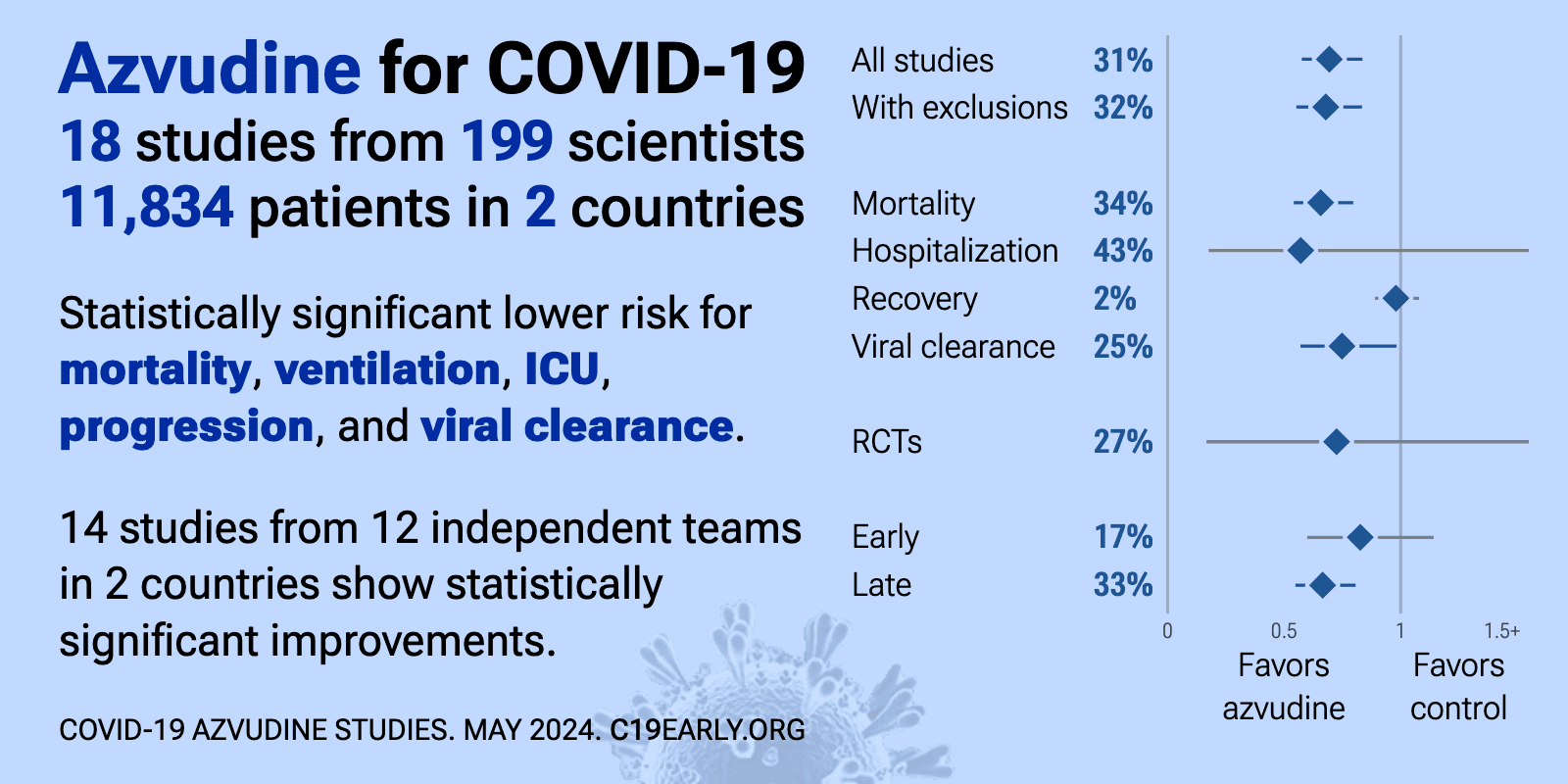
Azvudine is a nucleoside analog with potential host cell and organ toxicity. Studies to date highlight liver, reproductive, and hematologic toxicity - there is not the same volume of evidence for harm as there is with remdesivir, but there is also less data overall. Therefore, results may be less favorable with longer follow-up, and long-term morbidity could be an issue. COVID-19 studies show significantly increased risk of liver injury1,2.
Azvudine was adopted
in 1 country.
Recent:Chen.
Mar 1 |
Azvudine reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 40 studies (Version 41) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ICU admission, hospitalization, progression, and viral clearance. 31 studies from 22 independent teams in 2 countries show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome r.. | ||
Feb 26 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-34514-1 | Evaluating the effectiveness and safety of Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and hypertension: a multicenter retrospective cohort study |
| 36% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 16% lower progression (p=0.03). PSM retrospective 4,868 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension showing reduced mortality with azvudine. For composite disease progression, the azvudine group had more raw events (330) than the control group (320) out of identica.. | ||
Oct 14 2025 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-11625-8 | Association of Azvudine with severe outcomes among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during an omicron-dominance period in Wuhan, China: a single-center, retrospective, matched cohort study |
| 56% lower mortality (p=0.005), 62% lower progression (p<0.0001), and 34% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). Retrospective 1,406 hospitalized COVID-19 patients (703 matched pairs) in China showing significantly lower mortality and mechanical ventilation/ICU admission, and faster viral clearance with azvudine. | ||
Oct 8 2025 |
et al., Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2025.102987 | Real-world efficacy of oral azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective cohort study |
| 27% lower mortality (p=0.02), 18% lower ventilation (p=0.06), 21% lower ICU admission (p=0.03), and 20% lower progression (p=0.01). Retrospective 7,216 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing reduced mortality and composite outcomes with azvudine treatment. | ||
Jul 1 2025 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-05381-7 | Impact of early and delayed azvudine administration on COVID-19 mortality: a retrospective study |
| 45% lower mortality (p=0.05). PSM retrospective 604 COVID-19 patients (302 receiving azvudine, 302 controls) showing reduced mortality with azvudine treatment when administered within 8 days of symptom onset. | ||
Jun 18 2025 |
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2025.1584261 | Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in the treatment of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study using propensity score matching |
| 20% shorter hospitalization (p=0.001) and no change in viral clearance (p=1). Retrospective 192 COVID-19 patients in China showing significantly shorter hospitalization with azvudine treatment, but no significant difference for viral clearance. | ||
Jun 4 2025 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054 | Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study |
| Retrospective case-control study of 669 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing significant hepatotoxicity associated with azvudine treatment. | ||
May 7 2025 |
et al., American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.2025.211.Abstracts.A3027 | Early and Delayed Administration of Azvudine on Mortality of Adult Patients With COVID-19: A Retrospective Study |
| PSM retrospective 604 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with azvudine. Detailed results are only provided for the subgroup of non-mild patients. | ||
Apr 25 2025 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072 | Advances in the effectiveness and safety of azvudine treatment: a comprehensive review |
| Review of azvudine as a treatment for COVID-19, highlighting its pharmacological properties, clinical effectiveness, and safety profile. Azvudine, a dual-target nucleoside drug initially developed for HIV, received conditional approval fr.. | ||
Apr 9 2025 |
et al., VIEW, doi:10.1002/VIW.20240075 | The effectiveness and safety of azvudine treatment in COVID‐19 patients with kidney disease based on a multicenter retrospective cohort study |
| 38% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 21% lower progression (p=0.03). PSM retrospective 4,192 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with kidney disease showing significantly reduced all-cause mortality and disease progression with azvudine. | ||
Mar 31 2025 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-85677-w | Efficacy and safety of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in cancer patients with COVID-19 |
| PSM retrospective 596 cancer patients with COVID-19 showing that azvudine significantly reduced all-cause mortality and composite disease progression compared to paxlovid. | ||
Mar 15 2025 |
et al., BMC Pulmonary Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12890-025-03524-0 | Risk prediction and early intervention strategies for persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a retrospective cohort study |
| 9% improved viral clearance (p=0.88). Retrospective 660 patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and SARS-CoV-2 infection, identifying risk factors for persistent COVID-19. There was no significant difference in persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection with paxlovid, molnupiravir, or .. | ||
Mar 10 2025 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1 | Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU |
| 40% worse results (p<0.0001). Retrospective 286 critically ill COVID-19 ICU patients developing a predictive model for liver dysfunction, showing significantly higher risk with azvudine and paxlovid use. | ||
Mar 3 2025 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10666-3 | Prognostic factors in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and effectiveness of prophylactic anticoagulant therapy: a single-center retrospective study |
| 48% higher mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective 2,520 hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients focusing on prophylactic anticoagulation but also reporting results for azvudine and paxlovid. | ||
Feb 25 2025 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10643-w | Real-world effectiveness and safety of oral Azvudine versus Paxlovid for COVID-19 in patients with kidney disease: a multicenter, retrospective, cohort study |
| Retrospective 657 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with kidney disease showing no significant difference in all-cause mortality or disease progression between azvudine and paxlovid. Subgroup analysis showed lower disease progression with az.. | ||
Feb 18 2025 |
et al., Frontiers in Endocrinology, doi:10.3389/fendo.2025.1467303 | A multicenter, real-world cohort study: effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pre-existing diabetes |
| 26% lower mortality (p=0.02) and 9% lower progression (p=0.36). PSM retrospective 2,834 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pre-existing diabetes in China showing lower all-cause mortality with azvudine, but no significant difference in composite disease progression. | ||
Feb 5 2025 |
et al., VIEW, doi:10.1002/VIW.20240133 | Antiviral effectiveness and safety of azvudine in hospitalized SARS‐CoV‐2 patients with pre‐existing chronic respiratory diseases: A multicenter, retrospective cohort study |
| 27% lower mortality (p=0.02) and 15% higher progression (p=0.16). Retrospective 2,924 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with chronic respiratory diseases in China, showing lower all-cause mortality with azvudine, but no significant difference in composite disease progression. | ||
Jan 31 2025 |
et al., Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, doi:10.1155/cjid/3645253 | Real‐World Evaluation Study of Azvudine for the Treatment of Patients With COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis |
| 51% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 52% lower progression (p=0.002). Systematic review and meta-analysis of 19 studies (5 RCTs with 1,142 patients and 14 retrospective studies with 6,602 patients) showing significantly lower mortality and progression with azvudine treatment for COVID-19. | ||
Jan 27 2025 |
et al., iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2025.111907 | Real-world effectiveness of azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes |
| Retrospective 954 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing diabetes showing lower mortality with azvudine compared to paxlovid, but no significant difference for composite disease progression. | ||
Dec 31 2024 |
et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.032 | A retrospective cohort study of the efficacy and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients aged over 60 years |
| Retrospective 5,131 elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower mortality with azvudine compared to paxlovid. There was no significant difference in composite disease progression. Safety analysis showed azvudine had a lo.. | ||
Dec 26 2024 |
et al., European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-024-02220-9 | Azvudine efficacy in reducing mortality in COVID-19 patients |
| 35% lower mortality (p=0.05). Retrospective 2,862 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower mortality with azvudine treatment, with greater efficacy for severe and critical patients. | ||
Dec 18 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1511227 | Characteristics of patients with non-severe infections of different SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants in China |
| 9% faster viral clearance (p=0.03). Retrospective 244 non-severe COVID-19 patients in China infected with Omicron BA.2.76 or BA.5.1 subvariants, showing improved viral clearance with azvudine. | ||
Dec 12 2024 |
et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.004 | Real-world efficacy and safety of azvudine in hospitalized older patients with COVID-19 during the omicron wave in China: A retrospective cohort study |
| 22% lower mortality (p=0.001), 13% higher hospital discharge (p=0.05), 1% shorter hospitalization (p=0.43), and 10% faster viral clearance (p<0.0001). PSM retrospective 3,998 hospitalized COVID-19 patients aged 60 years and older in China showing lower all-cause mortality, higher rate of discharge, and shorter time to viral clearance with azvudine treatment. | ||
Nov 22 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390098 | Efficacy of azvudine plus dexamethasone in severe hospitalized patients with Omicron infection: a prospective multicenter study |
| 43% lower progression (p=0.03) and 14% faster viral clearance (p=0.02). Prospective multicenter study of 209 severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing improved 28-day composite outcomes, faster viral clearance, and higher PaO2/FiO2 levels with azvudine plus dexamethasone compared to dexamethasone.. | ||
Nov 17 2024 |
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106355 | Real-world effectiveness and safety of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study |
| 32% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 12% lower progression (p=0.01). PSM retrospective 32,864 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower all-cause mortality and disease progression with azvudine treatment. | ||
Nov 7 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1453234 | Systematic evaluation of therapeutic effectiveness of Azvudine in treating COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort study |
| 75% lower mortality (p=0.02) and 63% lower progression (p=0.02). Retrospective 264 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower risk of composite disease progression and all-cause mortality with azvudine treatment. | ||
Oct 7 2024 |
et al., Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S481591 | Efficacy of Azvudine Therapy in Patients with Severe and Non-Severe COVID‐19: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis |
| 32% higher mortality (p=0.2), 62% higher ventilation (p=0.22), 7% higher ICU admission (p=0.89), and 9% shorter hospitalization (p=0.05). PSM retrospective 303 hospitalized patients treated with azvudine and 303 matched controls in China, showing shorter hospital stay and higher lymphocyte improvement rate, particularly for non-severe patients, however there were no signifi.. | ||
Jul 31 2024 |
et al., Chinese Chemical Letters, doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110238 | Azvudine alleviates SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammation by targeting myeloperoxidase in NETosis |
| In silico, in vitro, and rhesus macaque study showing that azvudine (FNC) alleviates SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammation by targeting myeloperoxidase (MPO) and reducing neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation. Authors demonstrated FNC's.. | ||
Jul 12 2024 |
et al., The Clinical Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1111/crj.13798 | Efficacy and Safety of Azvudine in Patients With COVID‐19 in China: A Meta‐Analysis of Observational Studies |
| 39% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 33% lower progression (p=0.009). Meta analysis of 24 studies with 11,830 COVID-19 patients in China, showing significantly lower mortality, lower combined mortality/ventilation/ICU admission, and faster viral clearance with azvudine compared to SOC. In studies comparing .. | ||
Jun 24 2024 |
et al., Journal of Zhejiang University - SCIENCE B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology, doi:10.1631/jzus.B2300538 | Clinical characteristics and outcomes of hospitalized kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 infection in China during the Omicron wave: a single-center cohort study |
| 42% higher mortality (p=0.64). Retrospective 324 hospitalized kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 showing no significant benefit with molnupiravir, paxlovid, or azvudine. The study was conducted during the omicron wave in China between December 2022 and January .. | ||
Jun 13 2024 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0298772 | Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis |
| 52% lower mortality (p<0.0001), 10% lower ventilation (p=0.71), and 31% lower ICU admission (p=0.51). Meta analysis of 21 studies (7 studies have no control, comparing with paxlovid) with 10,011 COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality and faster viral clearance with azvudine treatment compared to standard of care or placebo, while there.. | ||
Apr 30 2024 |
et al., Infections in the immunosuppressed and immunocompromised host, doi:10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2024.209.1_MeetingAbstracts.A2917 | Effectiveness of Azvudine and Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in Kidney Transplant Recipients With COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 45% lower progression (p=0.36). Retrospective 148 hospitalized kidney transplant patients with COVID-19 in China showing lower risk of disease progression with azvudine treatment compared, and higher risk with paxlovid treatment. | ||
Apr 1 2024 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4157424/v1 | Azvudine reduces the mortality rate of patients with Coronavirus disease 2019: a single-center retrospective analysis study |
| 35% lower mortality (p=0.05). Retrospective 2,862 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower mortality with azvudine treatment. | ||
Mar 27 2024 |
et al., Advanced Science, doi:10.1002/advs.202306050 | Azvudine for the Treatment of COVID‐19 in Pre‐Existing Cardiovascular Diseases: A Single‐Center, Real‐World Experience |
| 81% lower mortality (p=0.0008). Retrospective 351 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pre-existing cardiovascular diseases in China, showing lower mortality with azvudine treatment. | ||
Mar 4 2024 |
et al., Journal of Cancer, doi:10.7150/jca.91530 | A Retrospective Analysis of Azvudine in Patients with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Cancer |
| 11% shorter hospitalization (p=0.26) and 50% improved viral clearance (p=0.03). PSM retrospective 84 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pre-existing cancer in China, showing faster viral clearance with azvudine. There was no significant difference in length of hospital stay or ICU admission. | ||
Feb 23 2024 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-024-02316-y | Effectiveness of azvudine in reducing mortality of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis |
| Systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 studies showing significantly lower mortality with azvudine compared to no antiviral treatment in COVID-19 patients. The mortality benefit was seen in both mild/moderate and severe disease, as wel.. | ||
Feb 12 2024 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 5:1 | Effects of Azvudine on the Low-Risk Patients Infected with COVID-19 Omicron Variants: A Retrospective Case-Control Study |
| 1% slower recovery (p=0.9). Retrospective 481 low-risk COVID-19 patients in China showing no significant difference in recovery or symptomatic severity with azvudine, but slightly lower total viral load. | ||
Feb 9 2024 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-53862-y | Comparison of azvudine, molnupiravir, and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in adult patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study |
| Retrospective 157 hospitalized mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients showing no significant differences between azvudine, molnupiravir, and paxlovid for time to viral clearance and length of hospitalization. | ||
Feb 9 2024 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468 | Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study |
| 20% lower mortality (p=0.44) and 3% lower progression (p=0.91). Retrospective 249 elderly patients with severe COVID-19, 128 treated with azvudine, 66 treated with paxlovid, and 55 receiving neither treatment, showing no significant differences for Ct value changes, progression, or survival for either.. | ||
Jan 31 2024 |
et al., Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, doi:10.1177/15330338241248573 | Impact of Anti-angiogenic Drugs on Severity of COVID-19 in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| 13% higher mortality (p=0.85). Retrospective 166 hospitalized NSCLC patients with COVID-19 showing no significant difference in mortality with paxlovid or azvudine in univariate analysis. | ||
Jan 18 2024 |
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107096 | Small-molecule antivirals treatment for COVID-19: A systematic review and network meta-analysis |
| Systematic review and network meta-analysis of 160 studies involving over 900,000 COVID-19 patients assessing the efficacy and safety of small-molecule antivirals. For azvudine, significant benefits were found for mortality, mechanical ve.. | ||
Jan 5 2024 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3707560/v1 | Risk of severe case in COVID-19 patients and Azvudine: A Retrospective cohort study after exit from ‘zero-COVID’ policy |
| 29% lower mortality (p=0.03). Retrospective 4,201 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China, showing lower mortality with azvudine. | ||
Nov 7 2023 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21941 | Inflammatory predictors (eosinophil, C-RP and IL-6) and effectiveness of oral Azvudine tablets treatment in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: A retrospective, self-controlled study |
| Retrospective 60 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China, 32 treated with azvudine for 7-14 days. The azvudine group had impoved eosinophil counts, CRP, IL-6, fibrinogen, NT-proBNP, and improved lung CT findings, suggesting reduced inflam.. | ||
Oct 21 2023 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387 | Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among 572 fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) hospitalized patients |
| 24% lower progression (p=0.44). Retrospective 572 fully vaccinated hospitalized patients in China, showing lower risk with azvudine treatment, without statistical significance. The composite outcome included intubation, non-invasive respiratory support, ICU admission, a.. | ||
Oct 19 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916 | Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients |
| 82% improved recovery (p=0.01) and 13% faster viral clearance (p=0.03). RCT 179 hospitalized patients in Brazil, showing improved recovery with azvudine treatment. | ||
Oct 13 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294 | Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching |
| no change in mortality (p=1), 28% lower ventilation (p=0.04), 55% lower ICU admission (p=0.05), and 22% lower progression (p=0.07). PSM retrospective 725 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China compared the effectiveness and safety of the oral antivirals azvudine and paxlovid. There was no significant difference in the risk of disease progression between groups, but a.. | ||
Oct 12 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1280026 | Secondary pulmonary infection and co-infection in elderly COVID-19 patients during the pandemics in a tertiary general hospital in Beijing, China |
| 22% lower mortality (p=0.15). Retrospective 322 hospitalized patients ≥65 in China, showing lower mortality with azvudine treatment, without statistical significance. | ||
Sep 30 2023 |
et al., Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S423725 | Efficacy of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir versus Azvudine for COVID-19 Treatment in Tibet: A Retrospective Study |
| Retrospective propensity-matched analysis of 227 COVID-19 patients in Tibet, China comparing azvudine to paxlovid. Overall, azvudine had comparable viral clearance time and clinical outcomes to paxlovid. However, for mild COVID-19 cases, .. | ||
Sep 30 2023 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153 | Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis |
| Systematic review and meta analysis of 5 RCTs showing improved clinical recovery and faster viral clearance with azvudine treatment. | ||
Aug 31 2023 |
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012 | Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities |
| 64% lower mortality (p=0.11), 67% lower ventilation (p=0.28), and 48% lower progression (p=0.03). Retrospective 2,118 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China, showing improved results with azvudine vs. paxlovid. | ||
Aug 24 2023 |
, K., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1228548 | Efficacy and safety evaluation of Azvudine in the prospective treatment of COVID-19 based on four phase III clinical trials |
| Review of four phase III clinical trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of azvudine, a nucleoside analog, for the treatment of COVID-19. The trials were conducted in China, Russia, and Brazil on patients with mild to moderate disease... | ||
Jul 23 2023 |
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11071859 | Composite Interventions on Outcomes of Severely and Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China |
| 56% lower mortality (p=0.007). Retrospective 1,082 severely and critically ill COVID-19 patients in China showing lower 60 day mortality with azvudine. Mortality was also lower with paxlovid, but without statistical significance, and health related quality of life was.. | ||
Jul 20 2023 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28947 | Oral azvudine for mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 in high risk, nonhospitalized adults: Results of a real‐world study |
| 91% lower mortality (p=0.09), 75% lower hospitalization (p=0.05), and 16% improved recovery (p=0.19). PSM retrospective 804 high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 in China. The study compared outcomes between 317 patients who received azvudine with 487 patients who received standard supportive treatment only. The.. | ||
Jul 14 2023 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3145554/v1 | Effectiveness and Optimal Timing of Azvudine in COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-center Retrospective Study in Beijing, China |
| 37% lower mortality (p=0.05) and 3% greater improvement (p=0.73). PSM retrospective 6,218 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower 28-day all-cause mortality with azvudine treatment compared to controls (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.40-1.00). Subgroup analysis found significantly faster clinical impro.. | ||
Jul 13 2023 |
et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007 | Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study |
| 62% lower mortality (p=0.0002). PSM retrospective 1072 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in China, showing lower mortality with azvudine treatment. | ||
May 5 2023 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981 | Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study |
| 54% lower mortality (p=0.16), 38% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.15), and 48% lower progression (p=0.02). PSM retrospective 490 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pre-existing conditions in China showing that azvudine was associated with a significantly lower risk of the composite outcome of disease progression, driven largely by lower rates.. | ||
Apr 30 2023 |
et al., Cardiology Plus, doi:10.1097/CP9.0000000000000049 | All-cause mortality in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury receiving versus not receiving azvudine: a propensity score-matched analysis |
| 6% lower mortality (p=0.88). PSM retrospective 332 hospitalized moderate to critically ill COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury in China, showing improved 14 day mortality but no difference in overall in-hospital mortality with azvudine treatment. | ||
Jan 23 2023 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899 | Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study |
| 74% lower mortality (p=0.04), 91% lower ventilation (p=0.06), 75% lower ICU admission (p=0.37), and 57% lower progression (p=0.05). PSM retrospective 900 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower risk of disease progression and death with azvudine treatment. | ||
Jan 6 2023 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.05.23284180 | Oral Azvudine (FNC) Tablets in Patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: A Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 12% slower recovery (p=0.95) and 32% improved viral clearance (p=0.04). Retrospective 207 COVID-19 patients in China, showing azvudine associated with faster viral clearance, with azvudine-treated patients obtaining a negative PCR test result 1.7 days faster on average compared to supportive care alone after .. | ||
Dec 6 2021 |
et al., Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6 | Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients |
| Analysis of azvudine (FNC) as a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients. Authors found that FNC inhibited SARS-CoV-2 and HCoV-OC43 coronavirus replication in vitro with EC50 between 1.2 and 4.3 μM. Oral .. | ||
Aug 13 2020 |
et al., Advanced Science, doi:10.1002/advs.202001435 | A Randomized, Open‐Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID‐19, a Pilot Study |
| 38% faster recovery (p=0.04) and 54% faster viral clearance (p=0.008). RCT 20 mild COVID-19 patients showing faster viral clearance and pneumonia improvement in chest CT images with azvudine treatment. | ||
References