Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899, Jan 2023
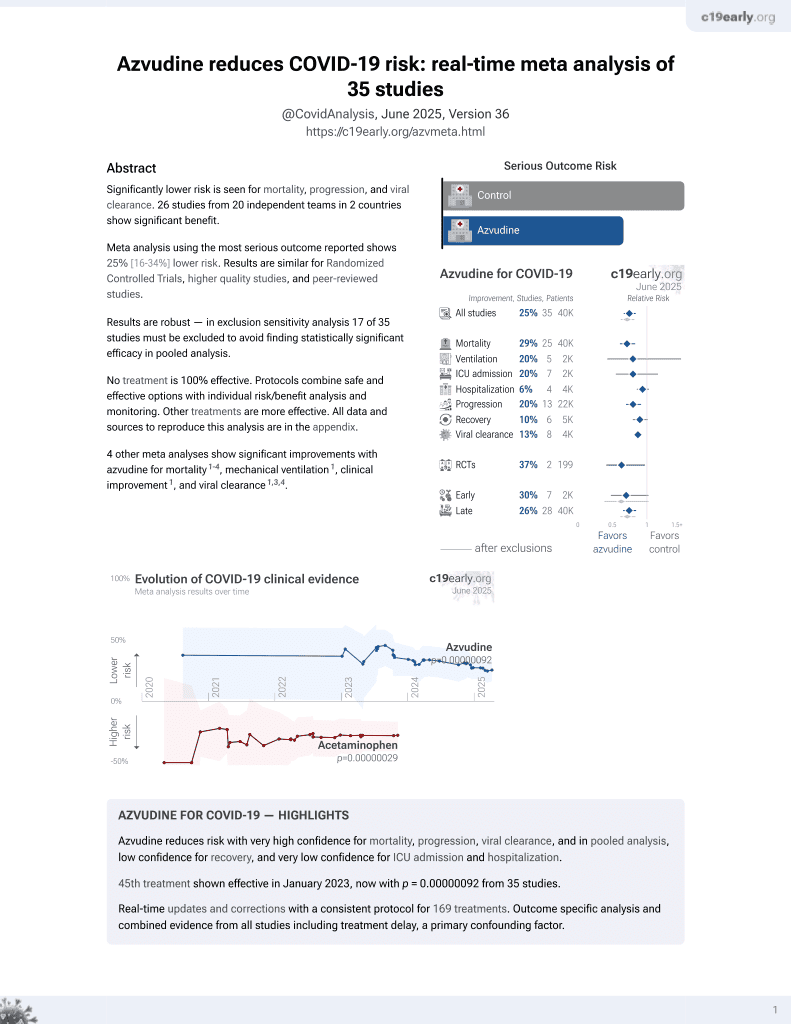
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
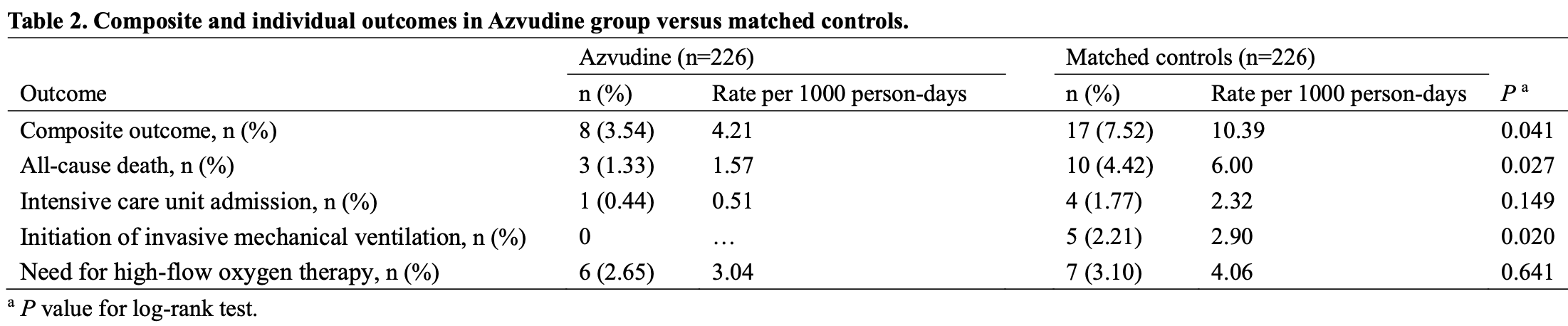
PSM retrospective 900 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing lower risk of disease progression and death with azvudine treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments3.
|
risk of death, 74.0% lower, HR 0.26, p = 0.04, treatment 3 of 226 (1.3%), control 10 of 226 (4.4%), NNT 32, propensity score matching, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 90.9% lower, RR 0.09, p = 0.06, treatment 0 of 226 (0.0%), control 5 of 226 (2.2%), NNT 45, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 75.0% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.37, treatment 1 of 226 (0.4%), control 4 of 226 (1.8%), NNT 75, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of progression, 57.0% lower, HR 0.43, p = 0.048, treatment 8 of 226 (3.5%), control 17 of 226 (7.5%), NNT 25, all-cause death, intensive care unit admission, initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation, and need for high-flow oxygen therapy, propensity score matching, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Xiong et al., Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054.
Shen et al., 23 Jan 2023, retrospective, China, preprint, 12 authors, average treatment delay 8.2 days.
Contact: dengguangtong@outlook.com, chenxiangck@126.com, shenmx1988@csu.edu.cn, zengflorachn@hotmail.com.
Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
doi:10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899
Current guidelines prioritize the use of the Azvudine in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. However, the clinical effectiveness of Azvudine in real-world studies was lacking, despite the clinical trials showed shorter time of nucleic acid negative conversion. To evaluate the clinical effectiveness following Azvudine treatment in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, we identified 1505 hospitalized COVID-19 patients during the study period, with a follow-up of up to 29 days. After exclusions and propensity score matching, we included 226 Azvudine recipients and 226 matched controls. The lower crude incidence rate of composite disease progression outcome (4.21 vs. 10.39 per 1000 person-days, P=0.041) and all-cause mortality (1.57 vs. 6.00 per 1000 person-days, P=0.027) were observed among Azvudine recipients compared with matched controls. The incidence rates of initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation were also statistically different between the groups according to the log-rank tests (P=0.020). Azvudine treatment was associated with significantly lower risks of composite disease progression outcome (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.43; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.18 to 0.99) and all-cause death (HR: 0.26; 95% CI: 0.07 to 0.94) compared with matched controls. Subgroup analyses indicated robustness of the point estimates of HRs (ranged from 0.14 to 0.84). Notably, male Azvudine recipients had a stronger effectiveness than female recipients with respect to both composite outcome and all-cause death. These findings suggest that Azvudine treatment showed substantial clinical benefits in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, and should be considered for use in this population of patients.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work.
CONTRIBUTIONS Conception and design: Guangtong, Xiang Chen, Furong Zeng, and Minxue Shen. Acquisition of data: Furong Zeng, Chenggen Xiao, Yuming Sun, Daishi Li, Ping Wu. Interpretation of data, statistical analysis and manuscript writing: Guangtong Deng, Furong Zeng, and Minxue Shen.
References
Amani, Amani, Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID-19 : a rapid review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28441
Austin, Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations, Biom J, doi:10.1002/bimj.200810488
Chang, 4'-Modified Nucleosides for Antiviral Drug Discovery: Achievements and Perspectives, Acc Chem Res, doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00697
Cheema, Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28471
Lieber, SARS-CoV-2 VOC type and biological sex affect molnupiravir efficacy in severe COVID-19 dwarf hamster model, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1
Murakami, Therapeutic advances in COVID-19, Nat Rev Nephrol, doi:10.1038/s41581-022-00642-4
Ren, A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study, Adv Sci (Weinh), doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Ye, China approves first homegrown COVID antiviral, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-022-02050-x
Yu, Chang, Azvudine, FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched, Innovation (Camb), doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Zhang, Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zheng, Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid for COVID-19:a meta-analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.09.027
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Current guidelines prioritize the use of the Azvudine in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. However, the clinical effectiveness of Azvudine in real-world studies was lacking, despite the clinical trials showed shorter time of nucleic acid negative conversion. To evaluate the clinical effectiveness following Azvudine treatment in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, we identified 1505 hospitalized COVID-19 patients during the study period, with a follow-up of up to 29 days. After exclusions and propensity score matching, we included 226 Azvudine recipients and 226 matched controls. The lower crude incidence rate of composite disease progression outcome (4.21 vs. 10.39 per 1000 person-days, P=0.041) and all-cause mortality (1.57 vs. 6.00 per 1000 person-days, P=0.027) were observed among Azvudine recipients compared with matched controls. The incidence rates of initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation were also statistically different between the groups according to the log-rank tests (P=0.020). Azvudine treatment was associated with significantly lower risks of composite disease progression outcome (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.43; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.18 to 0.99) and all-cause death (HR: 0.26; 95% CI: 0.07 to 0.94) compared with matched controls. Subgroup analyses indicated robustness of the point estimates of HRs (ranged from 0.14 to 0.84). Notably, male Azvudine recipients had a stronger effectiveness than female recipients with respect to both composite outcome and all-cause death. These findings suggest that Azvudine treatment showed substantial clinical benefits in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, and should be considered for use in this population of patients.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
23
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shen",
"given": "Minxue",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xiao",
"given": "Chenggen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Yuming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Daishi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Liping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Qingrong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dian",
"given": "Yating",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meng",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Furong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Xiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Guangtong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-24T01:55:17Z",
"timestamp": 1674525317000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-24T01:55:17Z",
"timestamp": 1674525317000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-24T05:56:24Z",
"timestamp": 1674539784550
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
23
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
23
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2023.01.23.23284899"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "posted-content"
}