Lactoferrin was adopted
in 1 country.
Recent:Palacios-Rosas.
Mar 1 |
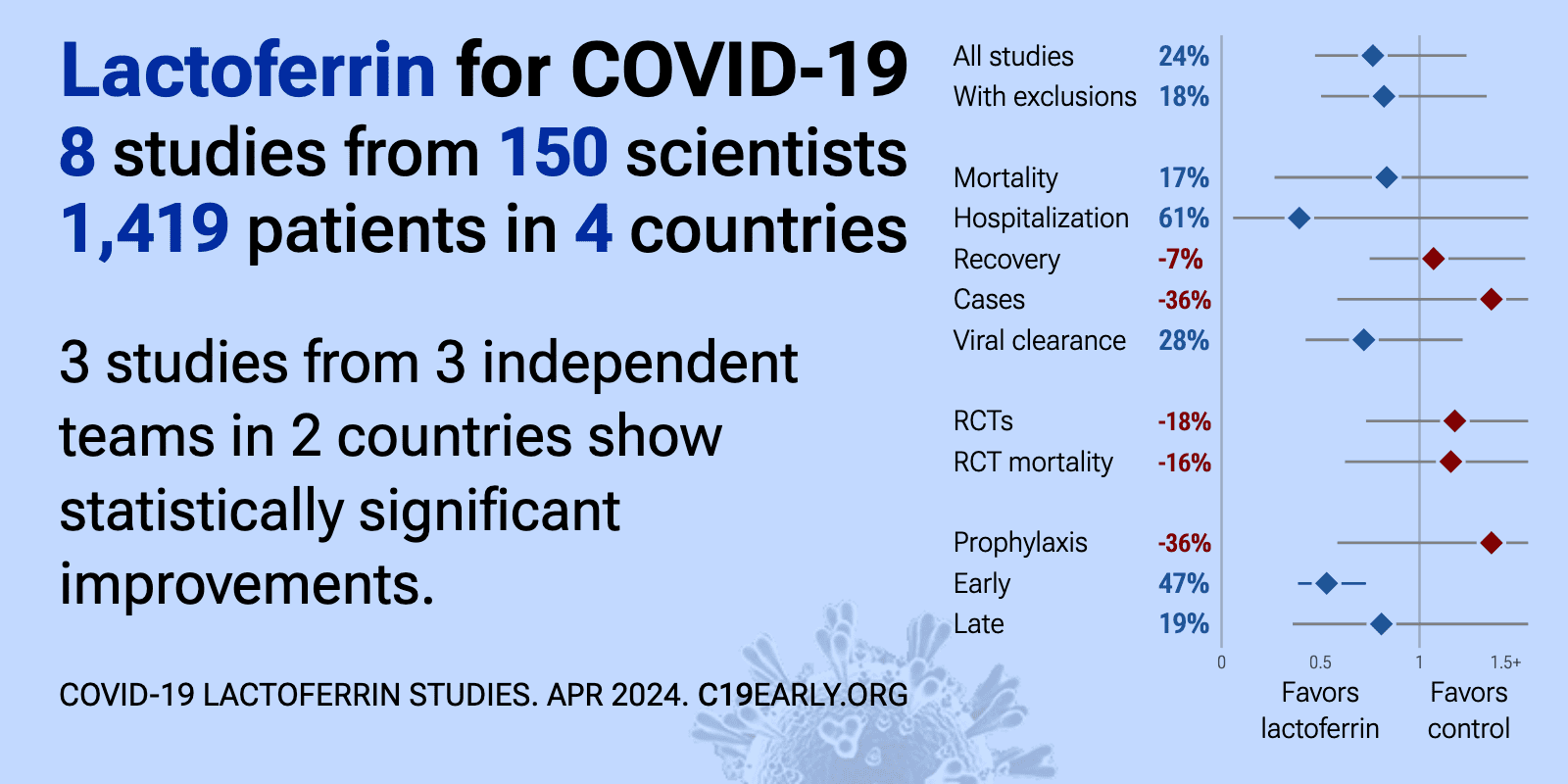
Lactoferrin for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 8 studies (Version 15) | |
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 24% [-24‑53%] lower risk, without reaching statistical significance. Results are worse for Randomized Controlled Trials and higher quality studies. Early treatment is .. | ||
Oct 16 2025 |
et al., COVID, doi:10.3390/covid5100176 | COVID-19 and Lactoferrin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |
| Systematic review and meta-analysis of lactoferrin studies for COVID-19. Authors found that lactoferrin demonstrated a significant effect in reducing fatigue among COVID-19 patients. While trends toward improvement were observed for other.. | ||
Apr 16 2025 |
et al., Italian Journal of Pediatrics, doi:10.1186/s13052-025-01961-5 | Role of nutrient supplements in children with post-COVID condition: a retrospective preliminary observation and narrative review |
| Retrospective 1,243 children with COVID-19 showing lower risk of long COVID at 6 months when treated with a Multi-Element Product (MEP) containing antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds (magnesium 200 mg, quercetin 150 mg, curcumin .. | ||
Nov 15 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1402135 | The potential of lactoferrin as antiviral and immune-modulating agent in viral infectious diseases |
| Review of the potential of lactoferrin as an antiviral and immune-modulating agent against various viruses, with a focus on SARS-CoV-2. Authors highlight lactoferrin's ability to interfere with virus-host cell interactions by binding to c.. | ||
Nov 1 2024 |
et al., NCT05783180 | A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Sesderma LACTYFERRIN™ Forte and Sesderma ZINC Defense™ (Liposomal Bovine Lactoferrin (LbLf) and Liposomal Zn (LZn)) and Standard of Care (SOC) vs SOC in the Treatment of Non-hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 |
| Estimated 40 patient lactoferrin early treatment RCT with results not reported over 1 year after estimated completion. | ||
Oct 17 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456634 | Immunomodulatory effect of bovine lactoferrin during SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| In silico, in vitro, and mouse study showing immunomodulatory effects of bovine lactoferrin (bLf) during SARS-CoV-2 infection. In silico analysis showed bLf strongly binds to TLR4 and NF-kB. In vitro, bLf modulated frequencies of NK and T.. | ||
Sep 24 2024 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms251910248 | Lactoferrin Supplementation in Preventing and Protecting from SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Is There Any Role in General and Special Populations? An Updated Review of Literature |
| Review of lactoferrin supplementation for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2. Authors summarize in vitro evidence showing lactoferrin can inhibit viral entry and replication through multiple mechanisms. Clinical trials in adults have .. | ||
Aug 4 2024 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17081021 | Lactoferrin Binds through Its N-Terminus to the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein |
| In vitro study showing that lactoferrin directly binds to the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, potentially explaining lactoferrin's observed protective effects against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Authors found that.. | ||
Jun 30 2024 |
et al., Sexually Transmitted Infections, doi:10.1136/sextrans-ICAR-2024.256 | Lactoferrin assumption in vaccinated subjects infected by SARS-CoV-2 may influence time length of negativization |
| 12% faster viral clearance. RCT 120 patients showing faster viral clearance with lactoferrin treatment. The currently available abstract has minimal details and does not report the confidence interval of the result. | ||
May 17 2024 |
et al., Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12051120 | Colostrum Lactoferrin Following Active and Recovered SARS-CoV-2 Infections during Pregnancy |
| Analysis of 69 lactating mothers showing higher colostrum lactoferrin concentrations in mothers with a history of COVID-19 infection during pregnancy or delivery compared to pre-pandemic controls. The highest lactoferrin concentrations we.. | ||
Mar 28 2024 |
et al., International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S448005 | Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Host Cell Infection |
| In vitro study showing that lactoferrin, camostat mesylate, and carrageenan inhibit SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection in airway epithelial Calu-3 cells. All show dose-dependent inhibition. The study focuses on novel LNP formulations and t.. | ||
Mar 28 2024 |
et al., ERJ Open Research, doi:10.1183/23120541.00031-2024 | Effect of lactoferrin treatment on symptoms and physical performance in long COVID patients: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial |
| RCT 72 long COVID outpatients showing no significant difference in fatigue, anxiety, depression, or cognitive failure with 6 weeks of lactoferrin treatment compared to placebo. | ||
Feb 15 2024 |
et al., Children, doi:10.3390/children11020249 | Lactoferrin in the Prevention of Recurrent Respiratory Infections in Preschool Children: A Prospective Randomized Study |
| 50% fewer cases (p=1). RCT 50 preschool children, 25 treated with bovine lactoferrin (bLf) prophylaxis, showing significantly lower frequency and duration of respiratory infections during the active phase with treatment. The only COVID-19 specific results repor.. | ||
Oct 29 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms242115718 | Sigma Receptor Ligands Prevent COVID Mortality In Vivo: Implications for Future Therapeutics |
| Mouse study showing the combination of lactoferrin and diphenhydramine resulted in slower weight loss, improved survival, and faster weight recovery in SARS-CoV-2 infected animals compared to controls. The study authors propose the.. | ||
Sep 25 2023 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16101352 | Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vero Cells by Bovine Lactoferrin under Different Iron-Saturation States |
| In vitro study showing that iron-free and iron-saturated bovine lactoferrin inhibited SARS-CoV-2 ancestral and omicron Vero cell infection. Treatment before or during infection was effective, while treatment after infection showed no sign.. | ||
Sep 21 2023 |
et al., International Dairy Journal, doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2023.105805 | Bovine lactoferrin suppresses the cathepsin-dependent pathway of SARS-CoV-2 entry in vitro |
| In vitro study showing variant dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with bovine lactoferrin (bLF). Authors found that bLF did not suppress entry of wild-type pseudoviruses into cells that express both ACE2 and TMPRSS2, but did suppress entr.. | ||
Jul 20 2023 |
et al., Future Science OA, doi:10.2144/fsoa-2023-0024 | Hen egg white bovine colostrum supplement reduces symptoms of mild/moderate COVID-19: a randomized control trial |
| 26% improved recovery (p=0.24), 11% worse viral clearance (p=0.36), and 8% lower long COVID (p=0.84). RCT 156 mild/moderate COVID-19 patients, 77 treated with hen egg white and bovine colostrum, showing faster recovery of severe symptoms with treatment. There were no significant differences in overall symptom duration, viral clearance, or.. | ||
Jun 30 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125552 | Inhibitory effect of lactoferrin-coated zinc nanoparticles on SARS-CoV-2 replication and entry along with improvement of lung fibrosis induced in adult male albino rats |
| In vitro and rat study showing lactoferrin-coated zinc nanoparticles (Lf-Zn-NPs) inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication and entry while improving lung fibrosis in rats. | ||
Apr 15 2023 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15040972 | Liposomal Lactoferrin Exerts Antiviral Activity against HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses In Vitro |
| In vitro study showing more potent antiviral activity for SARS-CoV-2 and HCoV229E with liposomal lactoferrin compared with free lactoferrin. Authors note that liposomal encapsulation has been shown to increase permeability, bioavailabilit.. | ||
Mar 31 2023 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2676422/v1 | Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 isolation in cell culture from nasal/nasopharyngeal swabs or saliva specimens of patients with COVID-19 |
| Analysis of nasal/nasopharyngeal swabs and saliva specimens, showing significantly lower isolation efficiency of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva specimens. In vitro study showing that lactoferrin and amylase, components of saliva, were found to inhi.. | ||
Mar 4 2023 |
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15051285 | Effect of Lactoferrin on Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: The LAC Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 12% higher mortality (p=0.85), 45% higher ventilation (p=0.39), 6% higher combined mortality/ICU admission (p=0.87), and 34% worse recovery (p=0.12). RCT 218 hospitalized patients in Italy, showing no significant differences with lactoferrin treatment. Authors note that in several previous studies showing clinical improvement, lactoferrin was given at an earlier stage of disease. Autho.. | ||
Dec 7 2022 |
et al., BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-022-00477-3 | Bovine lactoferrin for the prevention of COVID-19 infection in health care personnel: a double-blinded randomized clinical trial (LF-COVID) |
| 59% more symptomatic cases (p=0.34) and 23% more cases (p=0.65). Early terminated low-risk patient prophylaxis RCT in Peru, showing no significant difference in cases with lactoferrin. There were no moderate or severe cases. | ||
Aug 3 2022 |
et al., BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-022-00427-z | An overview on in vitro and in vivo antiviral activity of lactoferrin: its efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| Review of the antiviral activity of lactoferrin and efficacy for SARS-CoV-2. | ||
May 17 2022 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1605740/v1 | Lactoferrin binding to Sars-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein protects host from infection, inflammation and iron dysregulation. |
| Vero E6, Caco-2, and THP-1 in vitro study showing lactoferrin inhibited SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudovirus. Nutraceutically available bovine lactoferrin was more effective than human lactoferrin. | ||
May 13 2022 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23105436 | Lactoferrin Inhibition of the Complex Formation between ACE2 Receptor and SARS CoV-2 Recognition Binding Domain |
| Biolayer interferometry and turbidimetry study showing lactoferrin inhibits ACE2 - SARS-CoV-2 RBD binding. | ||
Nov 20 2021 |
et al., Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10111514 | Highly Specific Sigma Receptor Ligands Exhibit Anti-Viral Properties in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Cells |
| Vero E6 and H23 in vitro study finding SARS-CoV-2 antiviral activity associated with agonism of the sigma-1 receptor, ligation of the sigma-2 receptor, and a combination of the two. Authors identify synergistic effects with the combinatio.. | ||
Oct 28 2021 |
et al., World Journal of Gastroenterology, doi:10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6951 | Hepatic and gastrointestinal disturbances in Egyptian patients infected with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicentre cohort study |
| 79% lower mortality (p=0.11). Retrospective 547 hospitalized COVID+ patients in Egypt, showing lower mortality with lactoferrin treatment (without statistical significance). | ||
Oct 19 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph182010985 | Lactoferrin as Antiviral Treatment in COVID-19 Management: Preliminary Evidence |
| 47% faster viral clearance (p=0.0001). Small prospective study in Italy with 32 lactoferrin patients, 32 SOC, and 28 patients with no treatment, showing significantly faster viral clearance and improved recovery with treatment in unadjusted results. Oral and intranasal lactofe.. | ||
Sep 21 2021 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10184276 | Ambulatory COVID-19 Patients Treated with Lactoferrin as a Supplementary Antiviral Agent: A Preliminary Study |
| 76% lower hospitalization (p=0.32), 40% slower recovery (p=0.5), and 39% faster viral clearance (p=0.02). Retrospective survey based study in Italy with 82 patients treated with lactoferrin, and 39 control patients, showing significantly faster viral clearance with treatment. There was no significant difference in recovery time overall, howev.. | ||
Sep 3 2021 |
et al., Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.08.019 | Lactoferrin reduces the risk of respiratory tract infections: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials |
| Meta analysis of 6 RCTs, showing significantly lower risk of respiratory tract infections with lactoferrin. | ||
Aug 19 2021 |
et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2105815118 | Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 |
| In vitro study testing 1,425 compounds for SARS-CoV-2 antiviral activity, identifying 17 dose-responsive compounds with IC50 values <1μM. Lactoferrin inhibited SARS-CoV-2 in the nanomolar range in all cell models with multiple modes of ac.. | ||
Aug 19 2021 |
et al., Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina57080842 | The Prospect of Lactoferrin Use as Adjunctive Agent in Management of SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Randomized Pilot Study |
| 25% improved recovery (p=1). RCT 54 hospitalized patients in Egypt, showing no significant differences in recovery with lactoferrin treatment. 200mg lactoferrin orally once daily (group 1) or 200mg lactoferrin orally twice daily (group 2). | ||
Apr 14 2021 |
et al., PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.11303 | Natural resources to control COVID-19: could lactoferrin amend SARS-CoV-2 infectivity? |
| Review of the mechanisms of action and evidence for beneficial effects of lactoferrin for COVID-19. | ||
Feb 15 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.607443 | Molecular Mechanisms Behind Anti SARS-CoV-2 Action of Lactoferrin |
| In silico study of possible molecular mechanisms for anti-SARS-CoV-2 action of lactoferrin. | ||
Jan 23 2021 |
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020328 | Protective Effects of Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro |
| Caco-2 and Vero E6 in vitro study showing lactoferrin enhances the antiviral immune response, partially inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells, and modulates cytokine production. | ||
Sep 30 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106118 | Lactoferrin as potential preventative and adjunct treatment for COVID-19 |
| Review of lactoferrin for COVID-19. Authors propose that lactoferrin, a naturally occurring glycoprotein, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 cell entry by binding to cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and viral particles, similar to lactoferr.. | ||
Jul 11 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms21144903 | Lactoferrin as Protective Natural Barrier of Respiratory and Intestinal Mucosa against Coronavirus Infection and Inflammation |
| Review of the mechanisms of action and potential benefits of lactoferrin for COVID-19. Authors propose designing a trial combining an intranasal spray and oral administration (which they later performed). | ||
Apr 1 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Research in Health Sciences, doi:10.5530/ijrhs.8.1.3 | Liposomal Lactoferrin as Potential Preventative and Cure for COVID-19 |
| Prospective study of treatment with lactoferrin, vitamin C, and zinc, reporting recovery for all patients within 5 days. Depending on symptoms, lactoferrin nasal drops, mouth spray, or nebulization was also used. | ||