Feb 23 |
Meta-analysis of vitamin K studies | |
| Meta-analysis of vitamin K studies | ||
Jul 15 2025 |
et al., Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346 | Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain? |
| Review of vitamin supplementation for COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in neuropathic pain development. Authors examine how certain vitamins may help prevent post-COVID neuropathic pain by modulating pro-inflammatory cy.. | ||
Apr 7 2025 |
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1476622 | Low vitamin K status is a potential risk factor for COVID-19 infected patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis |
| Meta-analysis of 6 studies examining vitamin K status in COVID-19 patients showing that infected patients have significantly higher levels of dephosphorylated-uncarboxylated Matrix Gla Protein (dp-ucMGP), indicating lower vitamin K status.. | ||
Jan 16 2025 |
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17020304 | Vitamins K2 and D3 Improve Long COVID, Fungal Translocation, and Inflammation: Randomized Controlled Trial |
| RCT 151 long COVID outpatients showing improved long COVID Research Index, number of symptoms, inflammatory markers, and fungal translocation with vitamins D3 and K2 over 24 weeks. D3 2000IU daily and K2 240µg. Markers of inflammation (ox.. | ||
Jun 14 2024 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm13123476 | Vitamin K2 Supplementation in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients: A Randomised Controlled Trial |
| 200% higher mortality (p=1), 200% higher ICU admission (p=0.6), and 17% shorter hospitalization (p=0.52). RCT 40 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing vitamin K2 supplementation was well-tolerated and reduced dp-ucMGP levels, reflecting improved vitamin K status, but did not affect desmosine, a marker of elastic fiber degradation. The study .. | ||
Mar 24 2024 |
et al., AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-024-01690-8 | NBS superfood: a promising adjunctive therapy in critically ill ICU patients with omicron variant of COVID-19 |
| RCT 400 critically ill ICU patients with omicron-related ARDS showing significantly reduced mortality and inflammatory markers with a nutritional supplement containing vitamins A, B1-B3, B5, B6, B9, C, D, K, and zinc, potassium, manganese.. | ||
Sep 22 2023 |
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073761 | Dietary supplements to reduce symptom severity and duration in people with SARS-CoV-2: a double-blind randomised controlled trial |
| 14% improved recovery (p=0.41). Early terminated low-risk population (no hospitalization) very late treatment (mean 8 days) RCT with 44 patients treated with vitamin C, D, K, and zinc, and 46 control patients, showing no significant differences. Authors acknowledge that.. | ||
Sep 19 2022 |
et al., Microbial Pathogenesis, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792 | The effect of Nutrition Bio-shield superfood (NBS) on disease severity and laboratory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial |
| 61% lower mortality (p=0.002) and 28% shorter hospitalization (p=0.001). RCT 70 hospitalized severe COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing lower mortality and improved clinical markers with treatment combining vitamins A, B1-B3, B5, B6, B9, C, D, K, and magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, manganese, calcium,.. | ||
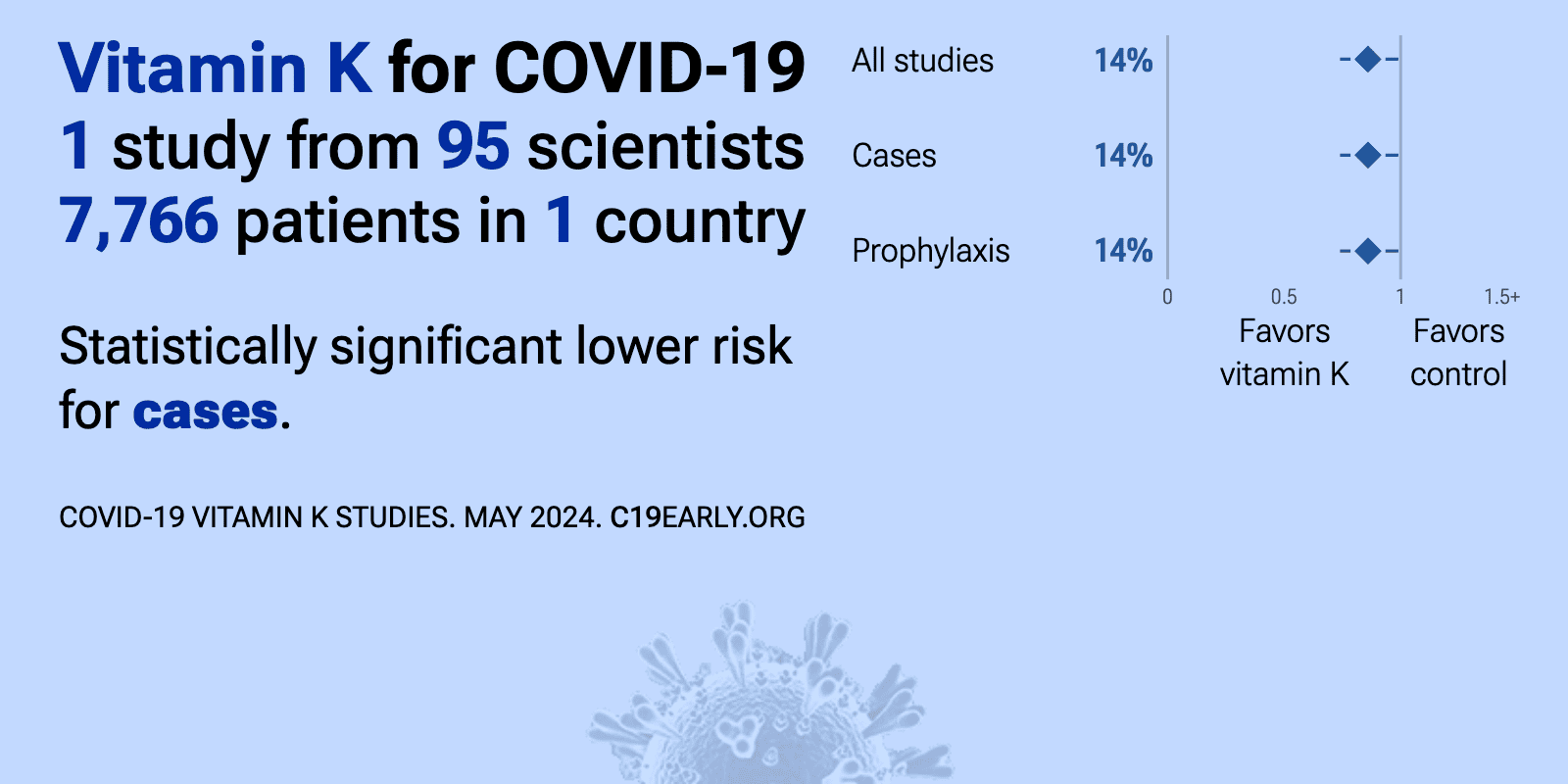
Nov 30 2021 |
et al., BMC Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12916-021-02168-1 | Nutritional risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective study within the NutriNet-Santé cohort |
| 14% fewer cases (p=0.04). Analysis of 7,766 adults in France, showing higher intakes of vitamin C, folate, vitamin K, dietary fibre, and fruit and vegetables associated with lower seropositivity. | ||
Jul 29 2021 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab408 | Vitamin K & D Deficiencies Are Independently Associated With COVID-19 Disease Severity |
| Case control study with 100 COVID-19+ patients and 50 age and gender matched controls, showing vitamin K and vitamin D levels independently associated with COVID-19 severity. | ||
Jun 9 2021 |
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061985 | The Association of Low Vitamin K Status with Mortality in a Cohort of 138 Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 |
| Retrospective 138 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower vitamin K status was associated with higher mortality, which remained significant after adjusting for age and sex, but not after further adjusting for comorbidities. Vitamin K.. | ||
Nov 16 2020 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Trials, S3:004 | A Randomized, Comparative Clinical Study to Evaluate the Activity of CurvicTM Formulation for Management of SARS-COV-2 Infection (COVID-19) |
| 75% improved recovery (p=0.001) and 100% improved 7-point scale results (p=0.0001). RCT 200 COVID-19 positive patients in India, 100 treated with curcumin, vitamin C, vitamin K2-7, and selenomethionine, showing faster recovery with treatment. | ||
Nov 9 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.11.07.20227512 | Vitamin D - contrary to vitamin K - does not associate with clinical outcome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients |
| Small retrospective study of 135 patients not finding a significant difference in vitamin D status. Patients with good outcomes had a median of 45.0 nmol/L versus 37.7 nmol/L for bad outcomes, p = 0.85. Authors found that vitamin D suffic.. | ||
Aug 27 2020 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1258 | Reduced Vitamin K Status as a Potentially Modifiable Risk Factor of Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| Retrospective 135 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing low vitamin K status was associated with poor outcomes, elastic fiber degradation, and thrombosis risk. Dp-ucMGP, an inverse marker of extrahepatic vitamin K status, was severely el.. | ||