Feb 19 |
Dexamethasone for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 12 studies (Version 13) | |
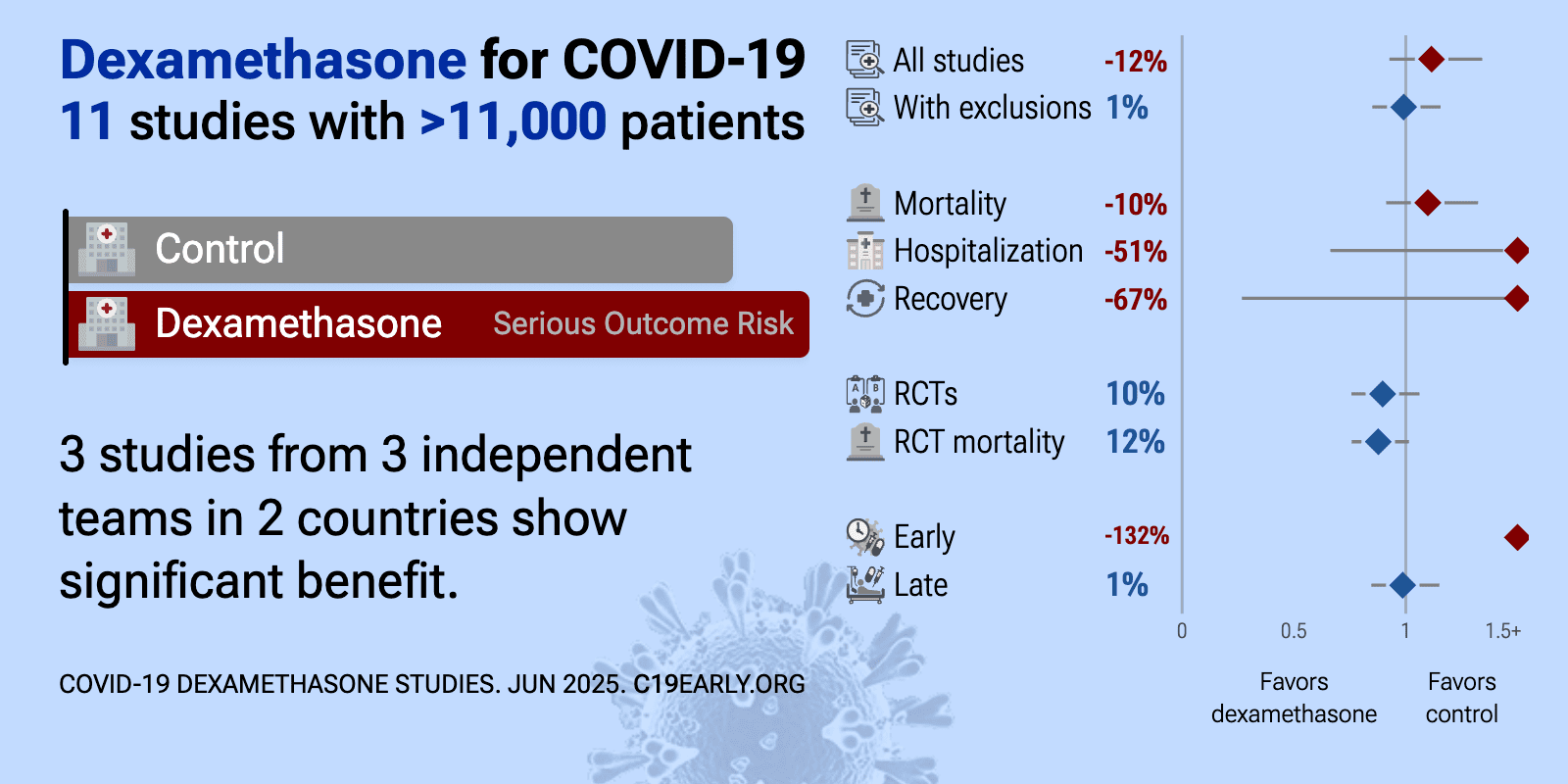
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 17% [-2‑40%] higher risk, without reaching statistical significance. Mortality results are negative, however all results to date are from late treatment trials. Contro.. | ||
Jan 14 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4 | Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats |
| Animal study analyzing potential cardiopulmonary harm with molnupiravir (MOL), favipiravir (FAVI), hydroxychloroquine (HCQL), and dexamethasone (DEX) in healthy Wistar albino rats. In summary: Data suggests molnupiravir may have the highe.. | ||
Oct 27 2025 |
et al., Journal of the Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada, doi:10.3138/jammi-2025-0010 | Extended-duration dexamethasone for the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Canada: A randomized clinical trial |
| Early-terminated open-label RCT of 11 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Canada, who still required oxygen after 10 days of dexamethasone, showing no benefit with an extended 20-day course versus stopping at 10 days. The extended dexametha.. | ||
Sep 2 2025 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.08.29.25334732 | Long-term follow-up of treatment comparisons in RECOVERY: a randomised, open-label, platform trial for patients hospitalised with COVID-19 |
| 6-month followup of RECOVERY patients. Results are reported within the respective trials for each treatment. | ||
May 14 2025 |
et al., Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S499371 | Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Trends Among COVID-19 Patients During the First Four Waves in Ngaliema Clinic, Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| 104% higher mortality (p=0.55). Retrospective 410 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the Democratic Republic of Congo showing significantly lower mortality with vitamin C treatment. | ||
Nov 26 2024 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0313289 | Clinical effects of dexamethasone among patients with sickle cell disease hospitalized with COVID-19: Outcomes from a single academic health system |
| 423% higher ICU admission (p=0.14) and 155% longer hospitalization (p=0.06). Retrospective 30 hospitalized patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) showing increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) with dexamethasone treatment for COVID-19. There were also trends towards increased ICU admission and longer hosp.. | ||
Nov 25 2024 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-10216-3 | The impact of dexamethasone on short- and long-term mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study |
| 34% lower mortality (p=0.01). Retrospective 576 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with dexamethasone treatment. Results are pending author clarification/correction due to critical internal inconsistencies. The respiratory support subgroup counts i.. | ||
Oct 22 2024 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-76871-3 | One-year mortality and associated factors in older hospitalized COVID-19 survivors: a Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea |
| 29% higher mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective 63,369 hospitalized COVID-19 survivors aged 60 years or older in Korea, showing lower 1-year mortality with macrolides (including azithromycin), higher 1-year mortality with corticosteroids (including dexamethasone and.. | ||
Oct 17 2024 |
et al., The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgae734 | Effectiveness of Dexamethasone for COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 35% higher mortality (p=0.2) and 46% worse improvement (p=0.02). Retrospective propensity score matched study of 529 hospitalized diabetic COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in mortality or clinical improvement with dexamethasone treatment. | ||
Oct 16 2024 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-75926-9 | Corticosteroids for hospitalized patients with severe/critical COVID-19: a retrospective study in Chongqing, China |
| 5% higher mortality (p=0.86). Retrospective 406 hospitalized severe/critical COVID-19 patients in China showing no significant difference in 28-day mortality with corticosteroid treatment (methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, or both). Corticosteroids were associated wi.. | ||
Sep 17 2024 |
et al., The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.23-0710 | Circulation of COVID-19-Related Medicines on Japanese Websites during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Their Quality and Authenticity |
| Investigation of the circulation and quality of COVID-19-related medicines sold online in Japan showing poor-quality ivermectin and dexamethasone. Four dexamethasone samples and two ivermectin samples failed quantitative analysis, and thr.. | ||
Aug 24 2024 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm13175013 | Prevalence and Risk Factors of Headache Associated with COVID-19 |
| 42% lower long COVID (p=0.08) and 3% improvement (p=0.9). Retrospective 295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Slovakia showing 35% prevalence of headache, of which 41% of patients had persistent headache 12-15 months after infection. Authors' analysis of long COVID headache is only for the subgr.. | ||
Aug 22 2024 |
et al., ERJ Open Research, doi:10.1183/23120541.00474-2024 | 1-year health outcomes associated with systemic corticosteroids for COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study |
| Retrospective 1,888 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the UK showing no significant difference in health-related quality of life or other patient reported outcomes, physical and mental health outcomes, and organ function one year aft.. | ||
Aug 20 2024 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09654-w | Predictors for cause-specific and timing of deaths in patients with COVID-19: a cohort study in Taiwan |
| 103% higher mortality (p=0.0002). Retrospective 2,196 COVID-19 patients in Taiwan (49% mild cases, 44% moderate, 7% severe) showing significantly higher mortality with dexamethasone. | ||
Aug 9 2024 |
et al., Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01520-0 | Impact of corticosteroid doses on prognosis of severe and critical COVID-19 patients with Omicron variant infection: a propensity score matching study |
| 23% higher mortality (p=0.03). Retrospective 1,167 severe/critical COVID-19 patients in China showing higher 28-day mortality with higher doses of corticosteroids (>50mg/day prednisone equivalent) compared to usual doses (30-50mg/day). The type of corticosteroid used d.. | ||
Jul 17 2024 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1385833 | Effect of early administration of dexamethasone in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia without acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and risk of development of acute respiratory distress syndrome: EARLY-DEX COVID-19 trial |
| 134% higher ventilation (p=0.41), 217% higher ICU admission (p=0.46), 17% higher ARDS (p=0.81), and 3% shorter hospitalization (p=0.88). RCT 126 hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients not requiring oxygen at admission, showing no significant difference in outcomes with dexamethasone treatment. | ||
May 31 2023 |
et al., The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00510-X | Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial |
| 15% higher mortality (p=0.15) and 46% higher ventilation (p=0.27). RCT 1,272 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypoxia receiving no oxygen or simple oxygen only, showing significantly increased mortality with higher dose dexamethasone compared to usual care (which included low-dose dexamethasone). 6-mo.. | ||
Apr 17 2023 |
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.8516 | Dexamethasone for Inpatients With COVID-19 in a National Cohort |
| 10% lower mortality (p=0.0002). PSM retrospective 80,699 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing reduced mortality or discharge to hospice with dexamethasone in patients requiring supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation/ECMO, but no significant difference in patien.. | ||
Mar 21 2023 |
et al., Pan African Medical Journal, doi:10.11604/pamj.2023.44.142.37858 | Factors associated with COVID-19 fatality among patients admitted in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe 2020-2022: a secondary data analysis |
| 130% higher mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective 672 COVID-19 patients in Zimbabwe, showing lower mortality with vitamin C and azithromycin treatment, and higher mortality with dexamethasone treatment. Results are pending author clarification/correction due to internal.. | ||
Apr 30 2022 |
et al., ERJ Open Research, doi:10.1183/23120541.00129-2022 | A potential harmful effect of dexamethasone in non-severe COVID-19: results from the COPPER-pilot study |
| 600% worse recovery (p=0.07). Pilot RCT of 7 outpatients with non-severe COVID-19 suggesting potential harmful effects of dexamethasone treatment. Time to recovery was significantly longer in the dexamethasone group compared to controls (p=0.03). Authors note that sys.. | ||
Jan 13 2022 |
et al., Journal of Independent Medicine, doi:10.71189/JIM/2025/V01N02A06 (date from preprint) | Low Rates of Hospitalization and Death in 4376 COVID-19 Patients Treated With Early Ambulatory Medical and Supportive Care: A Case Series and Observational Study |
| 100% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 100% lower hospitalization (p<0.0001). Retrospective 4,376 patients with mild/moderate COVID-19 in the USA treated with multiple medications including HCQ/ivermectin, zinc, azithromycin, budesonide, and dexamethasone (exact treatments specific to each patient), showing signifi.. | ||
Nov 25 2021 |
et al., European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.02532-2021 | Dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients not on intensive respiratory support |
| 59% higher mortality (p<0.0001). IPTW retrospective 19,973 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing increased 90-day mortality with dexamethasone in patients not on oxygen and no mortality benefit in patients on low-flow nasal cannula. Authors found consistent results acro.. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., European Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173947 | No clinical benefit of high dose corticosteroid administration in patients with COVID-19: A preliminary report of a randomized clinical trial |
| 7% higher mortality (p=1) and 18% higher ventilation (p=0.78). RCT 50 hospitalized COVID-19 ARDS patients showing no clinical benefit with high-dose dexamethasone. | ||
Mar 8 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.05.21251351 | A single-center retrospective cohort study of Covid-19 medications: Remdesivir, Favipiravir, Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone, and Interferon β1a and their combinations |
| Retrospective 324 hospitalized patients in Iran reporting on the use remdesivir, favipiravir, methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, and Interferon β1a and their combinations. There is no control group in this study. | ||
Feb 25 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436 | Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19 |
| 13% lower mortality (p=0.005), 21% lower ventilation (p=0.03), and 9% higher hospital discharge (p=0.003). RCT 6,425 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower 28-day mortality with dexamethasone treatment. The benefit was most pronounced in patients who had symptoms for more than 7 days at randomization, suggesting dexamethasone is most eff.. | ||
Oct 6 2020 |
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17021 | Effect of Dexamethasone on Days Alive and Ventilator-Free in Patients With Moderate or Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19 |
| 3% lower mortality (p=0.85) and 34% improvement (p=0.07). RCT 299 patients with moderate or severe COVID-19-related ARDS showing increased ventilator-free days with dexamethasone treatment. There was no significant difference in 28-day mortality (56.3% vs 61.5%), ICU-free days, or mechanical ven.. | ||
Mar 31 2020 |
et al., The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30417-5 | Dexamethasone treatment for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial |
| Non-COVID-19 RCT 277 hospitalized mechanically ventilated ARDS patients showing lower mortality with dexamethasone treatment. | ||
Dec 31 2012 |
et al., Veterinary Parasitology, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.07.011 | Dexamethasone treatment interferes with the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin in young cattle |
| Analysis of ivermectin and dexamethasone treatment in cattle, showing that dexamethasone interfered with the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin and reduced the efficacy of ivermectin. | ||