Dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients not on intensive respiratory support
et al., European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.02532-2021, Nov 2021
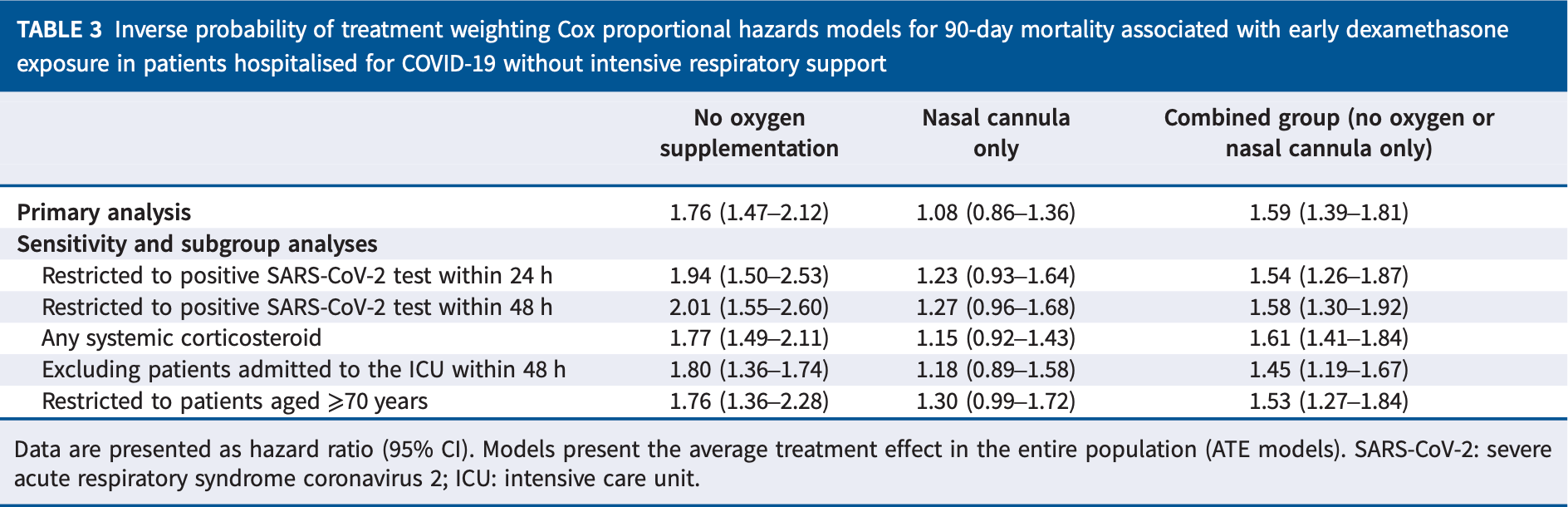
IPTW retrospective 19,973 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing increased 90-day mortality with dexamethasone in patients not on oxygen and no mortality benefit in patients on low-flow nasal cannula. Authors found consistent results across multiple sensitivity analyses. Authors suggest that widespread adoption of dexamethasone for less severely ill COVID-19 patients may cause unintended harm, hypothesizing that early corticosteroid use may impair viral clearance and immune responses important for infection resolution.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 59.0% higher, HR 1.59, p < 0.001, treatment 7,507, control 7,443, all patients, propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death, 76.0% higher, HR 1.76, p < 0.001, treatment 3,124, control 6,006, no oxygen, propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death, 8.0% higher, HR 1.08, p = 0.52, treatment 4,383, control 1,437, nasal cannula, propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Crothers et al., 25 Nov 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 71.0, 15 authors, study period 7 June, 2020 - 31 May, 2021.
Contact: crothk@uw.edu, permissions@ersnet.org.
Dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients not on intensive respiratory support
European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.02532-2021
Although commonly used, dexamethasone within 48 h of admission was associated with increased 90-day mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 not on oxygen and with no mortality benefit in patients on low-flow nasal cannula https://bit.ly/3l2aqjb
EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY JOURNAL ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE | K. CROTHERS ET AL. on February 8, 2026 by guest. Please see licensing information on first page for reuse rights. https://publications.ersnet.org
References
Akgun, Tate, Pisani, Medical ICU admission diagnoses and outcomes in human immunodeficiency virus-infected and virus-uninfected veterans in the combination antiretroviral era, Crit Care Med
Angus, Derde, Al-Beidh, Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Arabi, Mandourah, Hameed, Corticosteroid therapy for critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Austin, Stuart, Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies, Stat Med
Austin, The use of propensity score methods with survival or time-to-event outcomes: reporting measures of effect similar to those used in randomized experiments, Stat Med
Bartoletti, Marconi, Scudeller, Efficacy of corticosteroid treatment for hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a multicentre study, Clin Microbiol Infect
Chen, Tang, Tan, Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome with glucosteroids: the Guangzhou experience, Chest
Dequin, Heming, Meziani, Effect of hydrocortisone on 21-day mortality or respiratory support among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Ioannou, Locke, Green, Risk factors for hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, or death among 10131 US veterans with SARS-CoV-2 infection, JAMA Netw Open
Jeronimo, Farias, Val, Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): a randomized, double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial, Clin Infect Dis
Jung, Wernly, Fjolner, Steroid use in elderly critically ill COVID-19 patients, Eur Respir J
Kieszak, Flanders, Kosinski, A comparison of the Charlson comorbidity index derived from medical record data and administrative billing data, J Clin Epidemiol
King, Yoon, Rentsch, Development and validation of a 30-day mortality index based on pre-existing medical administrative data from 13,323 COVID-19 patients: the Veterans Health Administration COVID-19 (VACO) Index, PLoS One
Li, Liao, Zhou, Comparison of associations between glucocorticoids treatment and mortality in COVID-19 patients and SARS patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Shock, doi:10.1183/13993003.02532-202112
Liu, Li, Fan, Low-to-moderate dose corticosteroids treatment in hospitalized adults with COVID-19, Clin Microbiol Infect
Liu, Zhang, Dong, Corticosteroid treatment in severe COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, J Clin Invest
Matthay, Wick, Corticosteroids, COVID-19 pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome, J Clin Invest
Mehta, An, Andersen, Use of hydroxychloroquine, remdesivir, and dexamethasone among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 in the United States: a retrospective cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Metlay, Waterer, Long, Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Moreno, Rodriguez, Reyes, Corticosteroid treatment in critically ill patients with severe influenza pneumonia: a propensity score matching study, Intensive Care Med
Rentsch, Beckman, Tomlinson, Early initiation of prophylactic anticoagulation for prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 mortality in patients admitted to hospital in the United States: cohort study, BMJ
Rentsch, Kidwai-Khan, Tate, Patterns of COVID-19 testing and mortality by race and ethnicity among United States veterans: a nationwide cohort study, PLoS Med
Sinha, Furfaro, Cummings, Latent class analysis reveals COVID-19-related ARDS subgroups with differential responses to corticosteroids, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Steinberg, Hudson, Goodman, Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids for persistent acute respiratory distress syndrome, N Engl J Med
The, Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Tomazini, Maia, Cavalcanti, Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: the CoDEX randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Torres, Sibila, Ferrer, Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory response: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Villar, Ferrando, Martinez, Dexamethasone treatment for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Wagner, Griesel, Mikolajewska, Systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Xu, Shetterly, Powers, Extension of Kaplan-Meier methods in observational studies with time-varying treatment, Value Health
Yang, Liu, Zhou, The effect of corticosteroid treatment on patients with coronavirus infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Infect
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02532-2021",
"ISSN": [
"0903-1936",
"1399-3003"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/13993003.02532-2021",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Dexamethasone decreases mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients on intensive respiratory support (IRS) but is of uncertain benefit if less severely ill. We determined whether early (within 48 h) dexamethasone was associated with mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 not on IRS.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We included patients admitted to US Veterans Affairs hospitals between 7 June 2020 and 31 May 2021 within 14 days after a positive test for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Exclusions included recent prior corticosteroids and IRS within 48 h. We used inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) to balance exposed and unexposed groups, and Cox proportional hazards models to determine 90-day all-cause mortality.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Of 19 973 total patients (95% men, median age 71 years, 27% black), 15 404 (77%) were without IRS within 48 h. Of these, 3514 out of 9450 (34%) patients on no oxygen received dexamethasone and 1042 (11%) died; 4472 out of 5954 (75%) patients on low-flow nasal cannula (NC) only received dexamethasone and 857 (14%) died. In IPTW stratified models, patients on no oxygen who received dexamethasone experienced 76% increased risk for 90-day mortality (hazard ratio (HR) 1.76, 95% CI 1.47–2.12); there was no association with mortality among patients on NC only (HR 1.08, 95% CI 0.86–1.36).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In patients hospitalised with COVID-19, early initiation of dexamethasone was common and was associated with no mortality benefit among those on no oxygen or NC only in the first 48 h; instead, we found evidence of potential harm. These real-world findings do not support the use of early dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients without IRS.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
17
]
]
},
"alternative-id": [
"10.1183/13993003.02532-2021"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crothers",
"given": "Kristina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "DeFaccio",
"given": "Rian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tate",
"given": "Janet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alba",
"given": "Patrick R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goetz",
"given": "Matthew Bidwell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0971-6887",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "Joseph T.",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "Jr"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marconi",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ohl",
"given": "Michael E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rentsch",
"given": "Christopher T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodriguez-Barradas",
"given": "Maria C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahrir",
"given": "Shahida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Justice",
"given": "Amy C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akgün",
"given": "Kathleen M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "for the Veterans Aging Cohort Study Clinical COVID-19 Working Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Respiratory Journal",
"container-title-short": "Eur Respir J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"publications.ersnet.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-25T14:05:37Z",
"timestamp": 1637849137000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-24T01:18:37Z",
"timestamp": 1740359917000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"1I0IRX003666-01"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"1I0IRX003666-01"
]
}
],
"name": "Veterans Affairs Rehabilitation Research and Development"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007217",
"award": [
"13-457"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"13-457"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100007217",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Health Services Research and Development"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007217",
"award": [
"C19-20-406"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"C19-20-406"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100007217",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Health Services Research and Development"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007217",
"award": [
"MVP000"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"MVP000"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100007217",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Health Services Research and Development"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-09T01:59:25Z",
"timestamp": 1767923965917,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 77,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1637798400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1183/13993003.02532-2021",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "81",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2102532",
"prefix": "10.1183",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "European Respiratory Society (ERS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16761",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-0857",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci140617",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/SHK.0000000000001738",
"article-title": "Comparison of associations between glucocorticoids treatment and mortality in COVID-19 patients and SARS patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Shock",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.8",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1177",
"article-title": "Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): a randomized, double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Jeronimo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e373",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.9",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "Efficacy of corticosteroid treatment for hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a multicentre study",
"author": "Bartoletti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.10",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.045",
"article-title": "Low-to-moderate dose corticosteroids treatment in hospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.11",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Wagner",
"first-page": "CD014963",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.12",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n311",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0895-4356(98)00154-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241825",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.22310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827caa46",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.6607",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.5984",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jval.2011.07.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.21"
},
{
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.22",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. 2021. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov Date last accessed: 30 August 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-018-5332-4",
"article-title": "Corticosteroid treatment in critically ill patients with severe influenza pneumonia: a propensity score matching study",
"author": "Moreno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1470",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.23",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201706-1172OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.062",
"article-title": "The effect of corticosteroid treatment on patients with coronavirus infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.25",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.129.6.1441",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa051693",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30417-5",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone treatment for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Villar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.29",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.88",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00979-2021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI143331",
"article-title": "Corticosteroids, COVID-19 pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Matthay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6218",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.32",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202105-1302OC",
"article-title": "Latent class analysis reveals COVID-19-related ARDS subgroups with differential responses to corticosteroids",
"author": "Sinha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1274",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "2024102102464305000_60.1.2102532.33",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://publications.ersnet.org/lookup/doi/10.1183/13993003.02532-2021"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients not on intensive respiratory support",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1183/ers-crossmark-policy",
"volume": "60"
}