Montelukast has a boxed warning for neuropsychiatric side effects1.
Feb 11 |
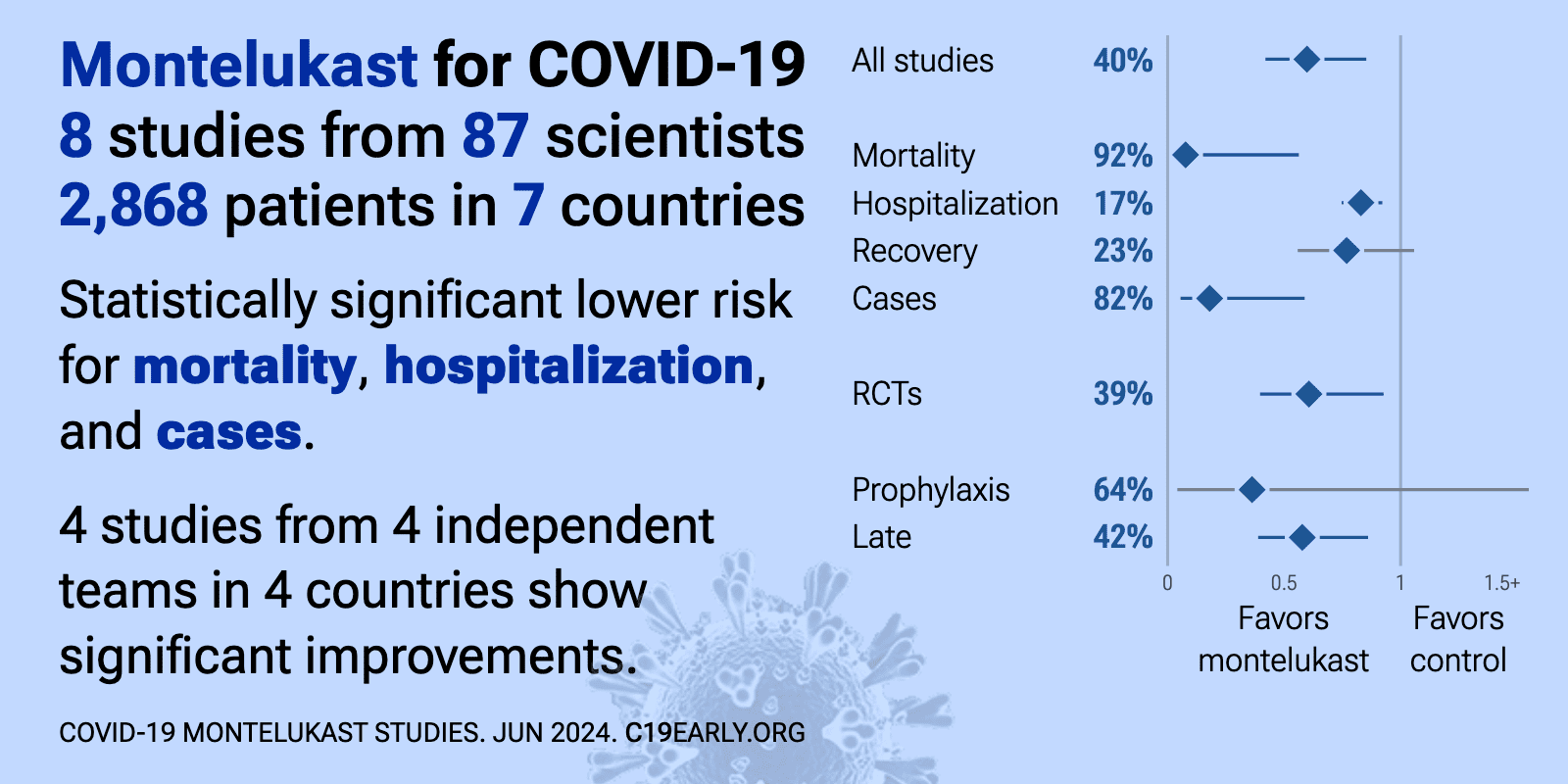
Montelukast reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 9 studies (Version 9) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for hospitalization and cases. 4 studies from 4 independent teams in 4 countries show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 39% [14‑56%] lower risk. Re.. | ||
Jan 10 2025 |
et al., Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.4274/tjps.galenos.2024.49768 | In silico Evaluation of H1-Antihistamine as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase: Repurposing Study of COVID-19 Therapy |
| In silico study showing that H1RA antihistamines, including bilastine, fexofenadine, mizolastine, rupatadine, terfenadine, and the leukotriene receptor antagonists montelukast and zafirlukast, may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA poly.. | ||
Nov 21 2024 |
et al., Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5 | Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study |
| In silico study showing potential inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 proteins by various compounds including dactinomycin, itraconazole, ivermectin, vitamin D, quercetin, curcumin, montelukast, bromhexine, hesperidin, EGCG and raloxifene. Authors p.. | ||
Aug 5 2024 |
et al., Genel Tıp Dergisi, doi:10.54005/geneltip.1352153 | The Effect of Montelukast Treatment on Elderly Patients Diagnosed with COVID-19 |
| 14% lower mortality (p=1), 90% higher ICU admission (p=0.46), and 3% shorter hospitalization (p=0.81). Retrospective 75 hospitalized COVID-19 patients over 60 in Turkey showing no significant differences with montelukast treatment. | ||
May 18 2024 |
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39332 (date from preprint) | Time to Sustained Recovery Among Outpatients With COVID-19 Receiving Montelukast vs Placebo |
| 1% fewer combined hospitalization/ER visits (p=1), 48% higher progression (p=0.29), and 2% improved recovery (p=0.72). RCT 1,250 outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 showing no significant difference in time to sustained recovery with montelukast treatment. There were no deaths and only 2 hospitalizations in each group. Notably, results were better .. | ||
Sep 23 2023 |
et al., Qatar Medical Journal, doi:10.5339/qmj.2023.15 | Characteristics and outcomes of adult patients with asthma presenting with COVID-19: A comparative cohort study |
| 13% lower hospitalization (p=0.61). Retrospective 616 COVID-19 patients with asthma in Qatar showing no significant difference in hospitalization risk with montelukast use. | ||
Aug 31 2023 |
et al., NCT04695704 | Double-blind Randomized Clinical Trial, Placebo-controlled to Assess the Efficacy of Montelukast in Mild-moderate Respiratory Symptoms in Patients With Long-COVID-19: E-SPERANZA COVID-19 PROJECT |
| Estimated 284 patient montelukast late treatment RCT with results not reported over 2 years after estimated completion. | ||
Jul 5 2023 |
et al., Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15071891 | Montelukast and Telmisartan as Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant |
| In silico and in vitro study showing that montelukast and telmisartan inhibit SARS-CoV-2 wild-type and the omicron variant. In silico analysis found montelukast and telmisartan bind to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain .. | ||
Mar 30 2023 |
et al., Biomedical Research Bulletin, doi:10.34172/biomedrb.2023.06 | Effect of Montelukast on Treatment of Coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19): A Systematic Review |
| Systematic review of 8 studies showing improved symptoms, clinical deterioration, hospitalization length, and mortality with montelukast treatment for COVID-19 patients. | ||
Mar 19 2023 |
, M., Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1080/14656566.2023.2192866 | Montelukast as a potential treatment for COVID-19 |
| Review of montelukast as a potential treatment for COVID-19. | ||
Sep 15 2022 |
et al., The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology, doi:10.1186/s43168-022-00154-6 | Value of montelukast as a potential treatment of post-COVID-19 persistent cough: a non-randomized controlled pilot study |
| 50% improved recovery (p<0.0001). RCT 68 post-COVID-19 outpatients showing improvement in cough severity measures with montelukast treatment. The montelukast group had a greater reduction in number of cough paroxysms per day, cough severity visual analog scale, cough seve.. | ||
Jul 31 2022 |
et al., The Clinical Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1111/crj.13529 | The effectiveness of gabapentin and gabapentin/montelukast combination compared with dextromethorphan in the improvement of COVID‐19‐ related cough: A randomized, controlled clinical trial |
| 20% shorter hospitalization (p=0.01) and 25% improved recovery (p=0.0006). RCT 180 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing improved cough symptoms and shorter hospitalization with montelukast/gabapentin compared to gabapentin. For gabapentin vs. dextromethorphan there was no significant difference in hospitalizat.. | ||
Jun 1 2022 |
et al., NCT04718285 | A National, Multi-Center, Open-Label, Three-Arm, Phase II Study to Investigate the Effect of Montelukast Between Emergency Room Visits and Hospitalizations in COVID-19 Pneumonia in Comparison With Standard Treatment |
| Estimated 380 patient montelukast early treatment RCT with results not reported over 3 years after estimated completion. | ||
Feb 28 2022 |
et al., International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108412 | Levocetirizine and montelukast in the COVID-19 treatment paradigm |
| Retrospective 53 patients reporting a potential benefit with levocetirizine and montelukast treatment for COVID-19. 51 of 53 patients were considered clinically cured on the combination therapy, with symptom resolution typically within 7 .. | ||
Feb 8 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.784214 | Montelukast Inhibits Platelet Activation Induced by Plasma From COVID-19 Patients |
| In vitro study showing that montelukast inhibits platelet activation induced by plasma from COVID-19 patients. Authors demonstrate that montelukast prevents the surface expression of tissue factor (TF) and P-selectin on platelets, reduces.. | ||
Jan 4 2022 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27552 | Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID‐19 |
| 92% lower mortality (p=0.01), 81% lower progression (p=0.007), and 15% shorter hospitalization (p=0.04). RCT 180 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Turkey showing faster reduction in inflammatory markers, improved pulmonary function, and lower rates of macrophage activation syndrome, respiratory failure and mortality with montelukast treatmen.. | ||
Nov 22 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20214502 | Efficacy of montelukast in the management of COVID-19: double blind randomized placebo controlled trial |
| 67% lower ICU admission (p=0.62), 25% higher progression (p=0.79), and no change in hospital discharge (p=1). RCT 90 mild to moderate COVID-19 patients showing no significant differences with montelukast treatment. | ||
Mar 4 2021 |
et al., Journal of Asthma, doi:10.1080/02770903.2021.1881967 | Montelukast in hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19 |
| 64% lower progression (p=0.09) and 12% shorter hospitalization (p=0.33). Retrospective 92 hospitalized patients showing lower clinical deterioration with montelukast treatment, without statistical significance in multivariable analysis. The treatment group was older. | ||
Feb 10 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.014 | Effectiveness of a multidrug therapy consisting of ivermectin, azithromycin, montelukast and acetylsalicylic acid to prevent hospitalization and death among ambulatory COVID-19 cases in Tlaxcala, Mexico |
| 78% lower mortality (p=0.001), 52% lower ventilation (p=0.15), 67% lower hospitalization (p=0.001), and 59% improved recovery (p=0.001). Prospective trial of 768 COVID-19 outpatients in Mexico, 481 treated with ivermectin, AZ, montelukast, and aspirin, and 287 control patients with various treatments, showing significantly lower mortality and hospitalization, and significa.. | ||
Sep 17 2020 |
et al., Journal of Asthma, doi:10.1080/02770903.2020.1786112 | Montelukast’s ability to fight COVID-19 infection |
| 91% lower hospitalization (p=0.02) and 82% fewer cases (p=0.004). Retrospective 445 elderly patients with severe asthma showing reduced risk of COVID-19 infection with montelukast treatment. | ||
Sep 4 2020 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01344 | Montelukast Drug May Improve COVID-19 Prognosis: A Review of Evidence |
| Review of evidence that montelukast may improve COVID-19 prognosis. Authors note ten experimentally supported properties of montelukast that could be beneficial, including antiviral effects, prevention of SARS-CoV-2-induced endotheliitis .. | ||
References