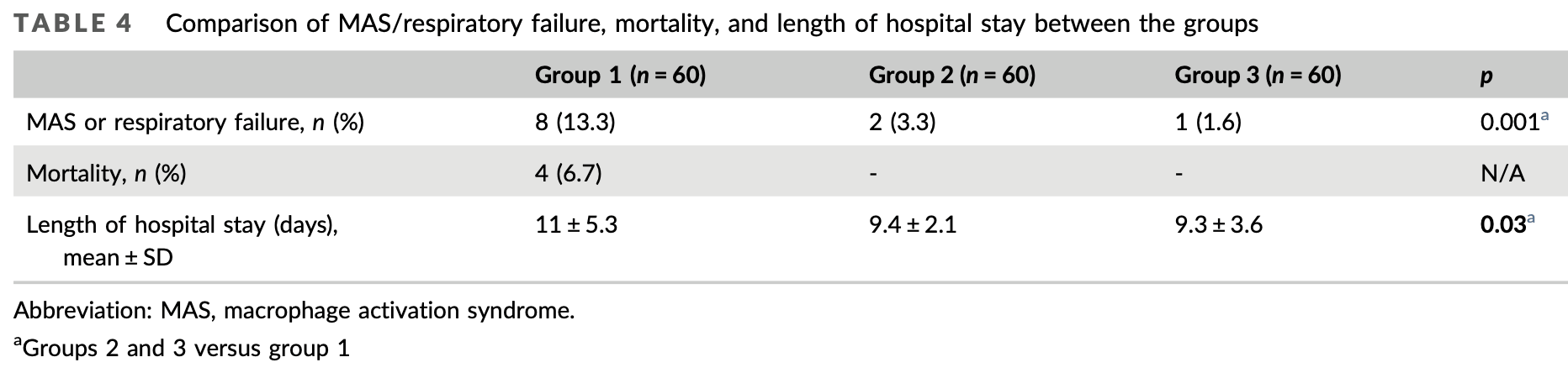
Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID‐19
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27552, NCT05094596, Jan 2022
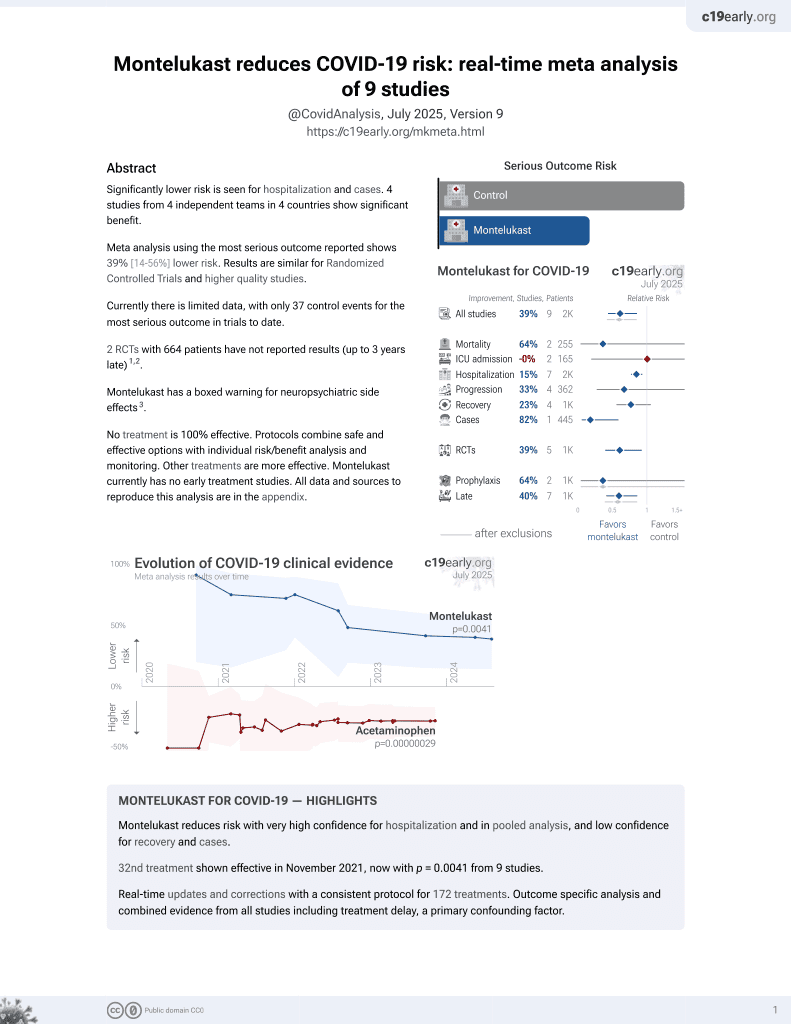
32nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0041 from 9 studies.
Lower risk for hospitalization and cases.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 180 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Turkey showing faster reduction in inflammatory markers, improved pulmonary function, and lower rates of macrophage activation syndrome, respiratory failure and mortality with montelukast treatment (10mg or 20mg daily) in addition to standard care. The higher dose of 20mg daily showed greater improvement in pulmonary function compared to 10mg daily. There was no mortality in the montelukast groups compared to 6.7% mortality with standard care alone.
|
risk of death, 92.3% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.01, treatment 0 of 120 (0.0%), control 4 of 60 (6.7%), NNT 15, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of death, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.12, treatment 0 of 60 (0.0%), control 4 of 60 (6.7%), NNT 15, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 20mg.
|
|
risk of death, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.12, treatment 0 of 60 (0.0%), control 4 of 60 (6.7%), NNT 15, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 10mg.
|
|
MAS or respiratory failure, 81.2% lower, RR 0.19, p = 0.007, treatment 3 of 120 (2.5%), control 8 of 60 (13.3%), NNT 9.2.
|
|
MAS or respiratory failure, 87.5% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.03, treatment 1 of 60 (1.7%), control 8 of 60 (13.3%), NNT 8.6, 20mg.
|
|
MAS or respiratory failure, 75.0% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.09, treatment 2 of 60 (3.3%), control 8 of 60 (13.3%), NNT 10.0, 10mg.
|
|
hospitalization time, 15.5% lower, relative time 0.85, p = 0.04, treatment mean 9.3 (±3.6) n=60, control mean 11.0 (±5.3) n=60, 20mg.
|
|
hospitalization time, 14.5% lower, relative time 0.85, p = 0.03, treatment mean 9.4 (±2.1) n=60, control mean 11.0 (±5.3) n=60, 10mg.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kerget et al., 4 Jan 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Turkey, peer-reviewed, mean age 54.6, 4 authors, study period May 2021 - July 2021, trial NCT05094596 (history).
Contact: bjkerget1903@gmail.com.
Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID‐19
Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27552
The inflammatory/anti-inflammatory balance has an important role in the clinical course of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) infection, which has affected over 200 million people since it first appeared in China in December 2019. This study aimed to determine the effectiveness of montelukast, which has known anti-inflammatory and bronchodilatory effects, in these patients. The prospective randomized controlled study included 180 patients who were hospitalized in the infectious diseases department of our hospital between May and July 2021 and were diagnosed with the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 by real-time polymerase chain reaction of nasopharyngeal swabs. The patients were divided into three groups and received only standard treatment according to national guidelines (Group 1) or standard treatment plus 10 mg/day montelukast (Group 2) or 20 mg/day montelukast (Group 3). Laboratory parameters and pulmonary function tests (PFTs) at admission and on Day 5 of treatment were compared. Comparison of laboratory parameters on Day 5 showed that Groups 2 and 3 had significantly lower levels of lactate dehydrogenase, fibrinogen, D-dimer, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin compared with Group 1 (p = 0.04, 0.002, 0.05, 0.03, and 0.04, respectively). In the comparison between Groups 2 and 3, only fibrinogen was significantly lower in Group 3 (p = 0.02). PFT results did not differ between the groups at admission, while on Day 5, only Group 3 showed significant improvements in forced expiratory volume in 1 s, forced vital capacity, and peak expiratory flow 25-75 compared with admission (p = 0.001 for all). Montelukast may be beneficial in COVID-19 patients to maintain the inflammatory/anti-inflammatory balance, prevent respiratory failure through its bronchodilator activity, and reduce mortality.
T A B L E 3 Regression analysis of laboratory and pulmonary function parameters in Group 2 (10 mg montelukast) and Group 3 (20 mg montelukast)
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
References
Bisgaard, Kerget, Aydın, Karaşahin, Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID-19, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Brodeur, Gray, Islam, Bhuiyan, A literature review of the economics of COVID-19, J Econ Surv
Chen, Li, Wang, Zou, Montelukast, an anti-asthmatic drug, inhibits zika virus infection by disrupting viral integrity, Front Microbiol
Davidson, Wysocki, Batlle, Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronavirus with ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme)-2 as their main receptor: therapeutic implications, Hypertension
Fidan, Aydoğdu, As a potential treatment of COVID-19: montelukast, Med Hypotheses
Graham, Steenbruggen, Miller, Standardization of spirometry 2019 update. An official American thoracic society and European respiratory society technical statement, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
He, Lu, Zhang, The clinical course and its correlated immune status in COVID-19 pneumonia, J Clin Virol
Kerget, Kerget, Aksakal, Aşkın, Sağlam et al., Evaluation of alpha defensin, IL-1 receptor antagonist, and IL-18 levels in COVID-19 patients with macrophage activation syndrome and acute respiratory distress syndrome, J Med Virol
Kerget, Kerget, Koçak, Are serum interleukin 6 and surfactant protein D levels associated with the clinical course of COVID-19?, Lung
Kircheis, Haasbach, Lueftenegger, Heyken, Ocker et al., NF-κB pathway as a potential target for treatment of critical stage COVID-19 patients, Front Immunol
Lee, Nguyen, Myoung, Zika virus-encoded NS2A and NS4A strongly downregulate NF-κB promoter activity, J Microbiol Biotechnol
Pizzichini, Leff, Reiss, Montelukast reduces airway eosinophilic inflammation in asthma: a randomized, controlled trial, Eur Respir J
Sanghai, Tranmer, Taming the cytokine storm: repurposing montelukast for the attenuation and prophylaxis of severe COVID-19 symptoms, Drug Discovery Today
Vaninov, In the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm, Nat Rev Immunol
Wisastra, Dekker, Inflammation, cancer and oxidative lipoxygenase activity are intimately linked, Cancers
Wu, Chik, Li, Tsang, Li, Anti-inflammatory effects of high-dose montelukast in an animal model of acute asthma, Clin Exp Allergy
Yu, Wei, Zhang, Montelukast, a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-1 antagonist, dose-and time-dependently protects against focal cerebral ischemia in mice, Pharmacology
Yuki, Fujiogi, Koutsogiannaki, COVID-19 pathophysiology: a review, Clin Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27552",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.27552",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.27552"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-10-09"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-12-23"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-01-04"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6048-1462",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Diseases Ataturk University School of Medicine Erzurum Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kerget",
"given": "Buğra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5160-4854",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infection Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Health Sciences University Erzurum Regional Education and Research Hospital Erzurum Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kerget",
"given": "Ferhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0167-0802",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infection Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Health Sciences University Erzurum Regional Education and Research Hospital Erzurum Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aydın",
"given": "Murat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4245-1534",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infection Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Health Sciences University Erzurum Regional Education and Research Hospital Erzurum Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Karaşahin",
"given": "Ömer",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-27T14:52:11Z",
"timestamp": 1640616731000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-05T15:44:32Z",
"timestamp": 1657035872000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-07T13:40:04Z",
"timestamp": 1657201204436
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1641254400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1641254400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.27552",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/jmv.27552",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.27552",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1950-1958",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26589",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00408-020-00393-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01615.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.14a04.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201908-1590ST",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joes.12423",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104361",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0305-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.598444",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2020.09.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers6031500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000081072",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15256",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109828",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4014/jmb.2011.11003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.03079",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.200207-747OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.27552"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID‐19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "94"
}