Famotidine was adopted
in 2 countries.
Recent:McLindon Ricke Alizadeh Saghati.
Mar 2 |
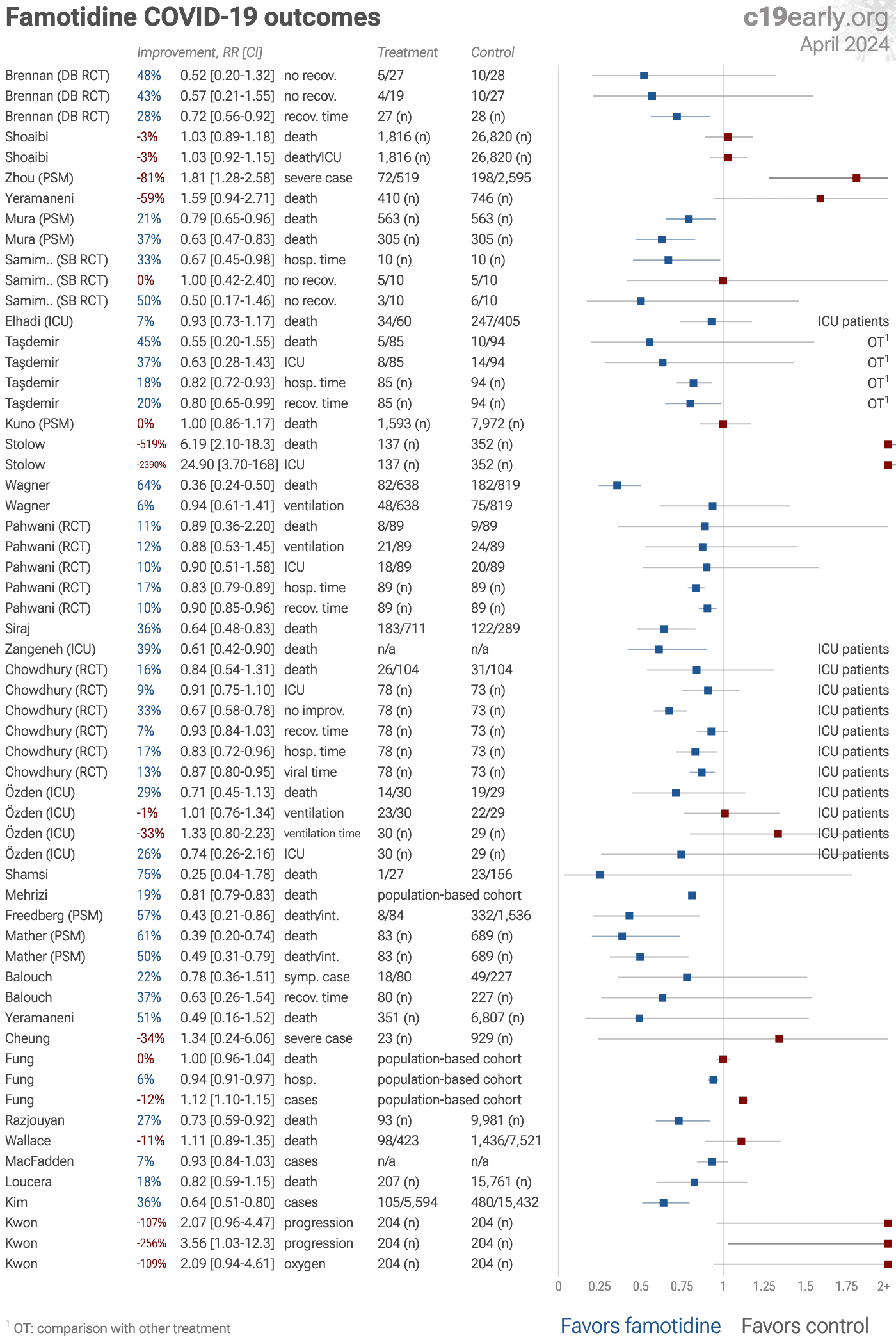
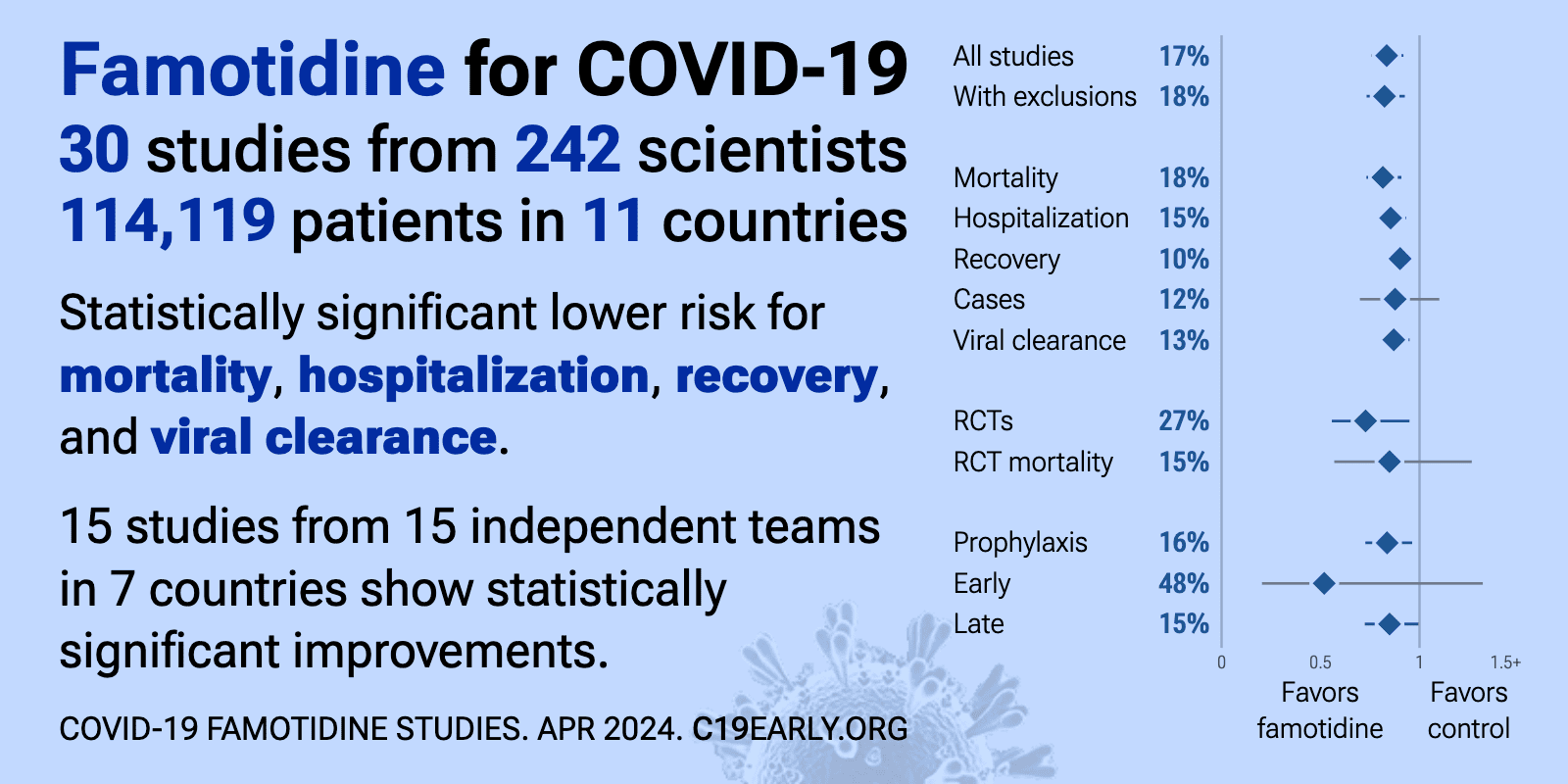
Famotidine reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 30 studies (Version 23) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, hospitalization, recovery, and viral clearance. 15 studies from 15 independent teams in 7 countries show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows.. | ||
Feb 16 |
et al., American Journal of Therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000002118 | Safety and Tolerability of Multimodal Therapy (Ivermectin, Doxycycline, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, and Zinc) With or Without Famotidine in Australian Patients With COVID-19 Infection: A Pilot Cohort Trial |
| RCT 275 outpatients showing very low hospitalization with combination therapy including ivermectin, doxycycline, vitamin C, vitamin D3, and zinc, with or without famotidine. There was no control group. Only 4 patients were hospitalized wi.. | ||
Feb 4 |
, D., Innovative Medicines & Omics, doi:10.36922/IMO025440058 | Mast cells and histamine receptor-targeted adjunctive treatments for COVID-19: A literature review |
| Review of clinical studies on antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers, and leukotriene receptor antagonists for COVID-19 treatment. Author finds that several mast cell-targeting agents show clinical benefits, with quercetin emerging as one .. | ||
Sep 30 2024 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36567 | Unraveling the relevance of SARS-Cov-2 infection and ferroptosis within the heart of COVID-19 patients |
| In silico study showing that ferroptosis-related genes are significantly altered in COVID-19 patients' hearts and identifying potential therapeutic compounds including famotidine, pyrvinium, astemizole, and thioridazine. | ||
Aug 5 2024 |
et al., Viral Immunology, doi:10.1089/vim.2024.0034 | Effective Treatment of COVID-19 Infection with Repurposed Drugs: Case Reports |
| Review of the successful treatment of COVID-19 using existing medications including HCQ, AZ, ivermectin, famotidine, monoclonal antibodies, and others. Authors note that the typical treatment of severe viral infections with multiple thera.. | ||
Dec 18 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1280434 | Drug prescription patterns and their association with mortality and hospitalization duration in COVID-19 patients: insights from big data |
| 19% lower mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective study of 917,198 hospitalized COVID-19 cases covered by the Iran Health Insurance Organization over 26 months showing that antithrombotics, corticosteroids, and antivirals reduced mortality while diuretics, antibiotics, and.. | ||
Nov 1 2023 |
, Famotidine Arm, NCT04727424 | Repurposed Approved and Under Development Therapies for Patients With Early-Onset COVID-19 and Mild Symptoms |
| 528 patient famotidine early treatment RCT with results not reported over 2 years after completion. | ||
Jul 17 2023 |
et al., Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, doi:10.1155/2023/5205188 | Survival and Mortality in Hospitalized Children with COVID-19: A Referral Center Experience in Yazd, Iran |
| 75% lower mortality (p=0.21). Retrospective 183 hospitalized pediatric COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing no significant difference in mortality with in unadjusted results. | ||
Jul 1 2023 |
et al., International Journal of Gerontology, doi:10.6890/IJGE.202307_17(3).0008 | Impact of Famotidine Use on Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Taiwan: A Retrospective Study |
| Retrospective 171 hospitalized patients in Taiwan, showing no signficant differences with famotidine, but a trend towards lower ICU admission. However, authors present only unadjusted results with groups that are not very comparable for I.. | ||
May 31 2023 |
et al., Journal of Psychosomatic Research, doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2023.111389 | Effect of famotidine on cognitive and behavioral dysfunctions induced in post-COVID-19 infection: A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study |
| RCT 50 recovered COVID-19 patients evaluating the efficacy of famotidine for improving cognitive impairment, depression and anxiety. At 6 and 12 weeks, the famotidine group had significantly greater improvements in MMSE (Mini-Mental State.. | ||
May 31 2023 |
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16171 | Effectiveness of famotidine on the risk of poor prognosis in patients with COVID-19: A nationwide cohort study in Korea |
| 107% higher progression (p=0.06) and 109% higher need for oxygen therapy (p=0.07). PSM retrospective 6,556 COVID-19 patients in South Korea, showing higher risk of poor outcomes with famotidine vs. other H2-blocker use. | ||
Mar 21 2023 |
et al., Journal of Korean Medical Science, doi:10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e99 | Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists and Proton Pump Inhibitors Are Associated With Reduced Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Without Comorbidities Including Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia: A Propensity Score-Matched Nationwide Cohort Study |
| 36% fewer cases (p<0.0001). PSM retrospective in South Korea, showing lower risk of COVID-19 cases with H2RA (including famotidine) and PPI use, but no significant difference in severe outcomes (results provided for the combined groups only). | ||
Mar 3 2023 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101889 | Report of the first seven agents in the I-SPY COVID trial: a phase 2, open label, adaptive platform randomised controlled trial |
| 67% higher mortality (p=0.18) and 100% worse recovery (p=0.02). RCT severe COVID-19 patients requiring ≥6 L/min oxygen, showing worse recovery with the addition of celecoxib and famotidine to remdesivir and dexamethasone. The treatment group mean age was 9 years older, and the treatment group had more.. | ||
Feb 28 2023 |
et al., Boğazi̇çi̇ Tip Dergi̇si̇, doi:10.14744/bmj.2023.77044 | Effects of Famotidine on COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Clinical Trial |
| 29% lower mortality (p=0.19), 1% higher ventilation (p=1), and 26% shorter ICU admission (p=0.6). Retrospective 59 ICU patients in Turkey, showing no significant difference in 30-day mortality or invasive mechanical ventilation with 160mg/day famotidine treatment. However, the famotidine group had lower fibrinogen and procalcitonin, s.. | ||
Aug 16 2022 |
et al., World Journal of Clinical Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8170 | Role of H2 receptor blocker famotidine over the clinical recovery of COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial |
| 16% lower mortality (p=0.53), 9% shorter ICU admission (p=0.33), 33% faster improvement (p<0.0001), and 7% faster recovery (p=0.14). RCT 208 ICU patients in Bangladesh, showing improved recovery with famotidine. Famotidine 40mg (<60kg) or 60mg every 8 hours. | ||
Aug 16 2022 |
et al., Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02195-9 (date from preprint) | Real-world evidence with a retrospective cohort of 15,968 COVID-19 hospitalized patients suggests 21 new effective treatments |
| 18% lower mortality (p=0.25). Retrospective 15,968 COVID-19 hospitalized patients in Spain, showing lower mortality with existing use of several medications including metformin, HCQ, azithromycin, aspirin, vitamin D, vitamin C, and budesonide. Since only hospitalized .. | ||
May 13 2022 |
et al., Obesity Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2022.100420 | Survival analysis based on body mass index in patients with Covid-19 admitted to the intensive care unit of Amir Al-Momenin Hospital in Arak – 2021 |
| 39% lower mortality (p=0.01). Retrospective 193 ICU patients in Iran, showing lower mortality with famotidine treatment. This study has multiple data issues: The text states that 134 people died and 59 were discharged. However, in Table 1, the column labeled 'Expired'.. | ||
Mar 29 2022 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac156 | Screening Large Population Health Databases for Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics: A Pharmacopeia-Wide Association Study (PWAS) of Commonly Prescribed Medications |
| 7% fewer cases (p=0.16). Retrospective 26,121 cases and 2,369,020 controls ≥65yo in Canada, showing no significant difference in cases with chronic use of famotidine. | ||
Feb 28 2022 |
et al., Indian Journal of Clinical Practice, 32:9 | Efficacy of Various Treatment Modalities on Patient-related Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients – A Retrospective Study |
| 36% lower mortality (p=0.002). Retrospective 1,000 COVID+ hospitalized patients in India, showing lower mortality with famotidine and remdesivir in multivariable logistic regression. | ||
Feb 24 2022 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, doi:10.14740/jocmr4658 | “MATH+” Multi-Modal Hospital Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 Infection: Clinical and Scientific Rationale |
| Review of the data supporting the MATH+ hospital treatment protocol for COVID-19. | ||
Feb 20 2022 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.22404 | Efficacy of Oral Famotidine in Patients Hospitalized With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| 11% lower mortality (p=1), 12% lower ventilation (p=0.73), 10% lower ICU admission (p=0.86), and 17% shorter hospitalization (p<0.0001). RCT with 89 famotidine and 89 control patients in Pakistan, showing faster recovery but no significant difference in mortality. 40mg oral famotidine daily. | ||
Feb 10 2022 |
et al., Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-326952 | Oral famotidine versus placebo in non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, data-intense, phase 2 clinical trial |
| 48% improved recovery (p=0.23). Small RCT with 27 famotidine and 28 placebo patients, showing improved recovery with treatment. Recovery was faster with treatment for 14 of 16 symptoms. There was no mortality or hospitalization. NCT04724720. | ||
Dec 31 2021 |
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050051 | Association of the patterns of use of medications with mortality of COVID-19 infection: a hospital-based observational study |
| 11% higher mortality (p=0.33). Retrospective 9,532 hospitalized COVID+ veterans in the USA, showing no significant difference in mortality with famotidine use. The study provides results for use before, after, and before+after. Before+after should more accurately repre.. | ||
Oct 31 2021 |
et al., JGH Open, doi:10.1002/jgh3.12905 (abstract 10/31/2021) | A retrospective analysis of clinical outcomes between hospitalized patients with COVID‐19 who received famotidine or pantoprazole |
| 64% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 6% lower ventilation (p=0.77). Retrospective 2,184 hospitalized patients in the USA, 638 treated with famotidine, showing lower mortality with treatment. | ||
Oct 31 2021 |
et al., American Journal of Gastroenterology, doi:10.14309/01.ajg.0000778736.01714.cd | A Retrospective Review: Famotidine Use Is Not Associated With Improved Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 |
| 519% higher mortality (p=0.001) and 2390% higher ICU admission (p=0.001). Retrospective 489 COVID+ hospitalized patients in the USA, showing higher mortality with famotidine treatment. | ||
Oct 25 2021 |
et al., Nicotine & Tobacco Research, doi:10.1093/ntr/ntab223 | Smoking Status and Factors associated with COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality among US Veterans |
| 27% lower mortality (p=0.006). Retrospective 10,074 hospitalized veterans with COVID-19 in the USA, showing lower mortality with existing famotidine use. | ||
Oct 11 2021 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27375 | The association between famotidine and in-hospital mortality of patients with COVID-19 |
| no change in mortality (p=0.97). PSM retrospective 9,565 COVID-19 hospitalized patients in the USA, 1,593 receiving famotidine, showing no significant difference in mortality. | ||
Oct 1 2021 |
et al., PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0266922 (date from preprint) | Effect of common maintenance drugs on the risk and severity of COVID-19 in elderly patients |
| no change in mortality (p=1), 6% lower hospitalization (p=0.0002), and 12% more cases (p<0.0001). Retrospective database analysis of 374,229 patients in the USA, showing higher cases, lower hospitalizations, and no change in mortality with famotidine use. | ||
Jul 12 2021 |
et al., Konuralp Tıp Dergisi, doi:10.18521/ktd.935888 | Famotidine in COVID-19 treatment |
| 45% lower mortality (p=0.29), 37% lower ICU admission (p=0.36), 18% shorter hospitalization (p=0.003), and 20% faster recovery (p=0.04). Retrospective 179 hospitalized patients in Turkey, 85 treated with famotidine and 94 treated with pantoprazole, showing faster recovery with famotidine in unadjusted results. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0251085 | Epidemiology, outcomes, and utilization of intensive care unit resources for critically ill COVID-19 patients in Libya: A prospective multi-center cohort study |
| 7% lower mortality (p=0.57). Prospective study of 465 COVID-19 ICU patients in Libya showing no significant differences with treatment. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.098 | Association Between Famotidine Use and COVID-19 Severity in Hong Kong: A Territory-wide Study |
| 34% higher severe cases (p=0.72). Retrospective 952 COVID-19 patients in Hong Kong, showing no significant difference in severe disease with famotidine use or PPI use. | ||
Apr 27 2021 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-462937/v1 | The Efficacy of Famotidine in improvement of outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A phase III randomised clinical trial |
| 33% shorter hospitalization (p=0.04) and no change in recovery (p=1). Very small RCT with 20 patients in Iran, showing shorter hospitalization time with famotidine treatment. There was no mortality or ICU admission. Famotidine 160mg four times a day. IRCT20200509047364N2. | ||
Mar 31 2021 |
et al., Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00689-y (date from preprint) | Real-world evidence for improved outcomes with histamine antagonists and aspirin in 22,560 COVID-19 patients |
| 21% lower mortality (p=0.02). PSM retrospective TriNetX database analysis of 1,379 severe COVID-19 patients requiring respiratory support, showing lower mortality with aspirin (not reaching statistical significance) and famotidine, and improved results from the combin.. | ||
Mar 23 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.633680 | COVID-19: Famotidine, Histamine, Mast Cells, and Mechanisms |
| Review of the potential mechanisms of action of famotidine, an over-the-counter histamine-2 receptor antagonist, for treating COVID-19. Authors propose that famotidine's principal mechanism of action involves on-target histamine receptor .. | ||
Mar 8 2021 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-84782-w | The in-vitro effect of famotidine on SARS-CoV-2 proteases and virus replication |
| In vitro study showing that famotidine does not bind or inhibit 3CLpro and PLpro, and no direct antiviral activity was observed with concentrations up to 200µM in Vero E6 and A549 cells. | ||
Feb 28 2021 |
et al., Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.011 | Famotidine Use Is Not Associated With 30-day Mortality: A Coarsened Exact Match Study in 7158 Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 From a Large Healthcare System |
| 51% lower mortality (p=0.22). Retrospective 7,158 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the USA, showing higher risk or mortality with in-hospital famotidine use, but lower risk when there was pre-existing at-home use, without statistical significance in both cases. | ||
Jan 20 2021 |
et al., Journal of Voice, doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2021.01.007 | Role of Famotidine and Other Acid Reflux Medications for SARS-CoV-2: A Pilot Study |
| 22% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.49) and 37% faster recovery (p=0.32). Survey of 307 patients in the USA, showing no significant difference in COVID-19 cases with famotidine use. | ||
Dec 4 2020 |
et al., Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323668 | Proton pump inhibitor or famotidine use and severe COVID-19 disease: a propensity score-matched territory-wide study |
| 84% higher severe cases (p=0.0001). Retrospective 4,445 COVID+ patients in China, showing higher risk of combined death/intubation/ICU with famotidine and with PPIs. | ||
Sep 24 2020 |
et al., American Journal of Gastroenterology, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001153 (date from preprint) | Comparative Effectiveness of Famotidine in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients |
| 3% higher mortality (p=0.67) and 3% higher combined mortality/ICU admission (p=0.62). Retrospective 1,816 famotidine users and 26,820 non-users hospitalized for COVID-19 in the USA, showing no significant differences with treatment. | ||
Aug 26 2020 |
et al., American Journal of Gastroenterology, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000832 | Impact of Famotidine Use on Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 |
| 61% lower mortality (p=0.004) and 50% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.003). PSM retrospective 878 hospitalized patients in the USA, 83 with existing famotidine use, showing significantly lower mortality with treatment. | ||
May 21 2020 |
et al., Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053 | Famotidine Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Cohort Study |
| 57% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.02). PSM retrospective 1,620 hospitalized patients in the USA, 84 with existing famotidine use, showing lower risk of combined death/intubation with treatment. | ||