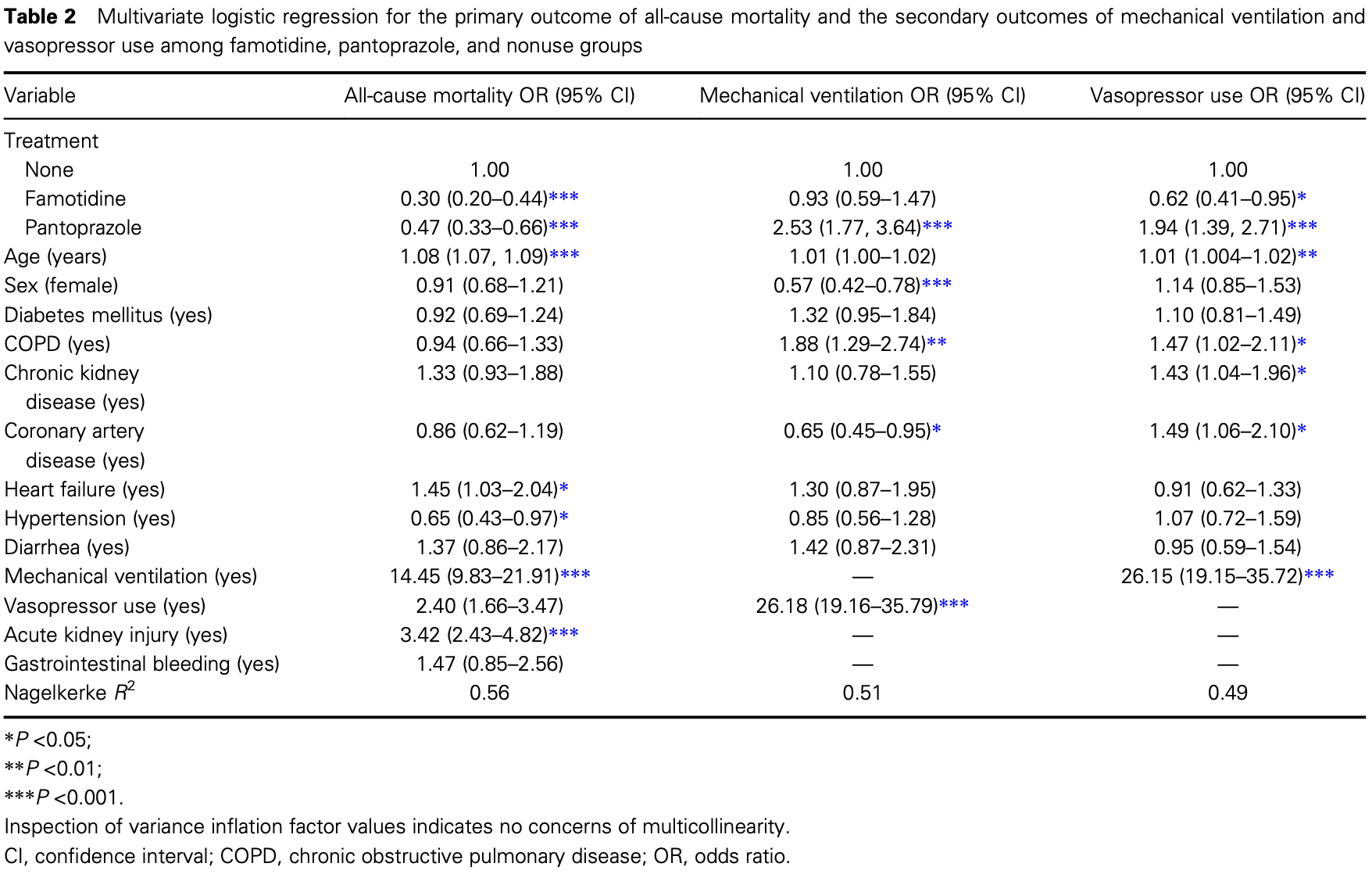
A retrospective analysis of clinical outcomes between hospitalized patients with COVID‐19 who received famotidine or pantoprazole
et al., JGH Open, doi:10.1002/jgh3.12905 (abstract 10/31/2021), Oct 2021
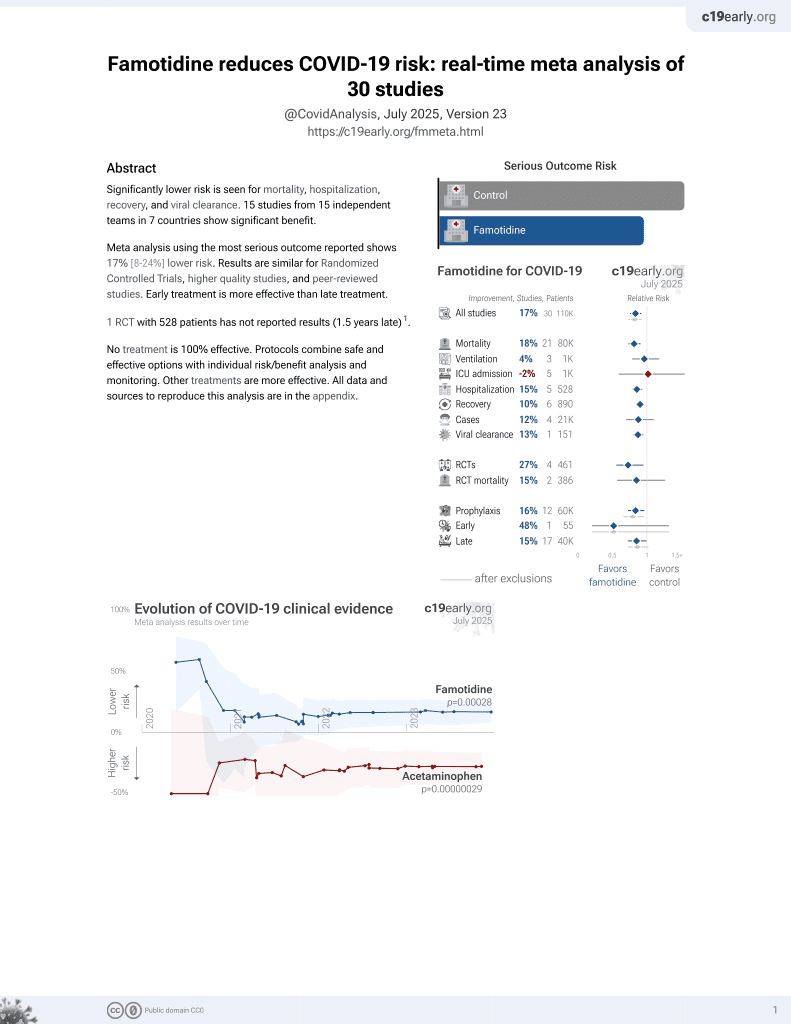
Famotidine for COVID-19
28th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2021, now with p = 0.00028 from 30 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 2,184 hospitalized patients in the USA, 638 treated with famotidine, showing lower mortality with treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
risk of death, 64.5% lower, RR 0.36, p < 0.001, treatment 82 of 638 (12.9%), control 182 of 819 (22.2%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 6.4% lower, RR 0.94, p = 0.77, treatment 48 of 638 (7.5%), control 75 of 819 (9.2%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wagner et al., 31 Oct 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 1 March, 2021.
Contact: jj.wagner5492@gmail.com.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Association With Respiratory Symptoms in Patients Diagnosed With SARS-CoV 2 (COVID-19)
Figure 1. Panel a: Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with GI Symptoms on Admission demographic characteristics and ICU or non ICU admissions comparing with presence or no of respiratory symptoms. Panel b: Odds Ratio Estimates for ICU Admission in Patients with COVID-19 presenting with GI symptoms.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jgh3.12905",
"ISSN": [
"2397-9070",
"2397-9070"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jgh3.12905",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jgh3.12905"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9519-4834",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine South Brooklyn Health Brooklyn New York USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wagner",
"given": "Justin J.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine South Brooklyn Health Brooklyn New York USA"
}
],
"family": "St. Cyr",
"given": "Nikolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine South Brooklyn Health Brooklyn New York USA"
}
],
"family": "Douen",
"given": "Aaron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Business Management Brooklyn New York USA"
}
],
"family": "Fogel",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine South Brooklyn Health Brooklyn New York USA"
}
],
"family": "Trillo",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JGH Open",
"container-title-short": "JGH Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-11T04:44:46Z",
"timestamp": 1689050686000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-11T04:45:09Z",
"timestamp": 1689050709000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-12T04:27:09Z",
"timestamp": 1689136029379
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688947200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jgh3.12905",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_6_2_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. (2023).WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID‐19) dashboard. Available from:https://covid19.who.int/Accessed 16 Jan 2023."
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID‐19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China",
"author": "Pan L",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_3_1",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2020.02.008",
"article-title": "Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS‐CoV‐2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods",
"author": "Wu C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin. B.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_4_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Mast cells contribute to coronavirus‐induced inflammation: new anti‐inflammatory strategy",
"author": "Kritas SK",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents",
"key": "e_1_2_6_5_1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Broad‐spectrum inhibition of coronavirus main and papain‐like proteases by HCV drugs",
"author": "Anson BJ",
"first-page": "10.21203/rs.3.r",
"journal-title": "Res. Sq.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_6_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc4739",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_6_7_1",
"unstructured": "BorrellB.New York clinical trial quietly tests heartburn remedy against coronavirus. Available from:https://www.science.org/content/article/new-york-clinical-trial-quietly-tests-heartburn-remedy-against-coronavirus. Accessed 7 Nov 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Freedberg DE",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "e_1_2_6_8_1",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000832",
"article-title": "Impact of famotidine use on clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID‐19",
"author": "Mather JF",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1617",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_9_1",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Association between famotidine use and COVID‐19 severity in Hong Kong: a territory‐wide study",
"author": "Cheung KS",
"first-page": "34940",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "e_1_2_6_10_1",
"volume": "0016",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000001153",
"article-title": "Comparative effectiveness of famotidine in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Shoaibi A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_11_1",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.011",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is not associated with 30‐day mortality: a coarsened exact match study in 7158 hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 from a large healthcare system",
"author": "Yeramaneni S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "919",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "e_1_2_6_12_1",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-021-06872-z",
"article-title": "Does famotidine reduce the risk of progression to severe disease, death, and intubation for COVID‐19 patients? A systemic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Sun C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3929",
"journal-title": "Dig. Dis. Sci.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_13_1",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cddis.2016.218",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors protect mice from acute systemic inflammation and induce long‐term cross‐tolerance",
"author": "Balza E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_14_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.092129",
"article-title": "Use of acid‐suppressive drugs and risk of pneumonia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Eom CS",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "310",
"journal-title": "CMAJ",
"key": "e_1_2_6_15_1",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-021-01907-8",
"article-title": "Relation of severe COVID‐19 to polypharmacy and prescribing of psychotropic drugs: the REACT‐SCOT case‐control study",
"author": "McKeigue PM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "BMC Med.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_16_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013",
"article-title": "Pre‐hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID‐19",
"author": "Ramachandran P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_17_1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID‐19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Lee SW",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "e_1_2_6_18_1",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13183",
"article-title": "Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of adverse clinical outcomes from COVID‐19: a meta‐analysis",
"author": "Kow CS",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_19_1",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2022-326952",
"article-title": "Oral famotidine versus placebo in non‐hospitalised patients with COVID‐19: a randomised, double‐blind, data‐intense, phase 2 clinical trial",
"author": "Brennan CM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "879",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "e_1_2_6_20_1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.633680",
"article-title": "COVID‐19: famotidine, histamine, mast cells, and mechanisms",
"author": "Malone RW",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_21_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinte.158.1.54",
"article-title": "A prospective randomized comparative trial showing that omeprazole prevents rebleeding in patients with bleeding peptic ulcer after successful endoscopic therapy",
"author": "Lin HJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "Arch. Intern. Med.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_22_1",
"volume": "158",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.38356.641134.8F",
"article-title": "Systematic review and meta‐analysis of proton pump inhibitor therapy in peptic ulcer bleeding",
"author": "Leontiadis GI",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "568",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "e_1_2_6_23_1",
"volume": "330",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2020.102926",
"article-title": "Anemia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Transfus. Apher. Sci.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_24_1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.22190",
"article-title": "Effect of stress ulcer prophylaxis with proton pump inhibitors vs histamine‐2 receptor blockers on in‐hospital mortality among ICU patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation",
"author": "PEPTIC Investigators for the Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials Group, Alberta Health Services Critical Care Strategic Clinical Network, and the Irish Critical Care Trials Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "e_1_2_6_25_1",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5414/CNP68065",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors and the kidney: critical review",
"author": "Brewster UC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nephrol.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_26_1",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000514940",
"article-title": "Incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury in COVID‐19: a systematic review",
"author": "Raina R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "199",
"journal-title": "Blood Purif.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_27_1",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/01.ajg.0000715272.88349.c2",
"article-title": "H2‐blocker use is associated with acute kidney injury among COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Trieu JA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S1723",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenter.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_28_1",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-015-3725-1",
"article-title": "Prevalence and outcome of gastrointestinal bleeding and use of acid suppressants in acutely ill adult intensive care patients",
"author": "Krag M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "833",
"journal-title": "Intens. Care Med.",
"key": "e_1_2_6_29_1",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jgh3.12905"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Gastroenterology",
"Hepatology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A retrospective analysis of clinical outcomes between hospitalized patients with <scp>COVID</scp>‐19 who received famotidine or pantoprazole",
"type": "journal-article"
}