Mar 1 |
Sodium Bicarbonate reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 6 studies (Version 2) | |
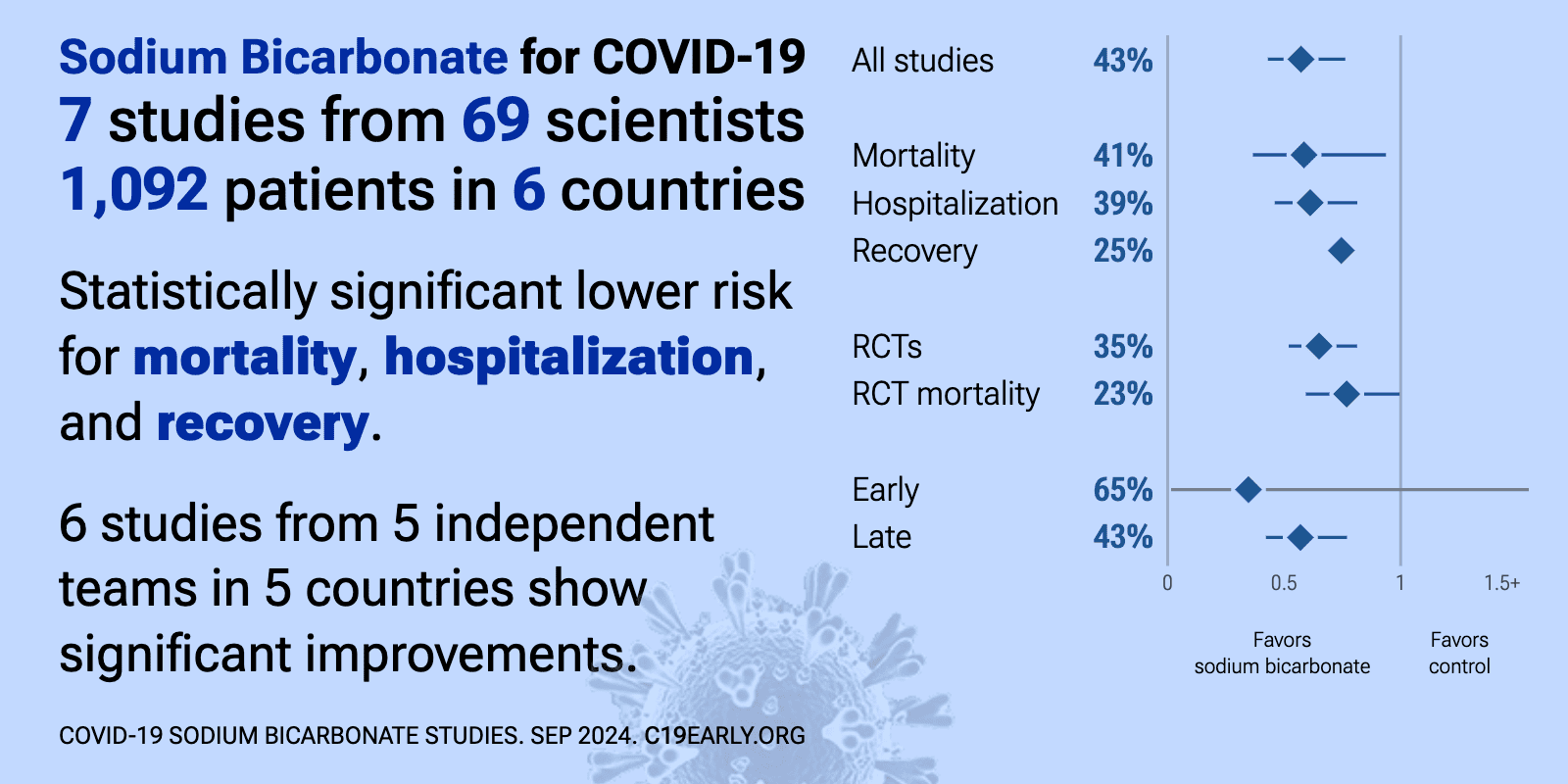
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, hospitalization, and recovery. 5 studies from 4 independent teams in 4 countries show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 43% [23‑58%].. | ||
Jun 3 2024 |
et al., Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1177/2515690x241258403 | Alkalinization Using Sodium Bicarbonate for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |
| 27% lower mortality (p=0.02), 39% lower hospitalization (p=0.3), and 53% improved recovery (p=0.0005). Meta analysis of 7 studies showing significantly lower mortality, shorter hospitalization, and higher recovery with alkalinization using sodium bicarbonate for COVID-19. | ||
Jan 9 2024 |
et al., Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research, doi:10.4103/ijnmr.ijnmr_38_23 | A Comparison of the Effects of Chlorhexidine and Sodium Bicarbonate Mouthwashes on COVID-19–Related Symptoms |
| RCT 116 healthcare workers comparing 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthwash (n=36), 7.5% sodium bicarbonate mouthwash (n=40), and placebo (n=40) twice daily for 2 weeks, with symptoms followed for 4 weeks. There were lower symtoms and cases in both.. | ||
Mar 15 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145669 | Efficacy of nasal irrigation and oral rinse with sodium bicarbonate solution on virus clearance for COVID-19 patients |
| 39% shorter hospitalization (p=0.0009). RCT 55 mild/moderate patients in China, showing shorter hospitalization with sodium bicarbonate nasal irrigation and oral rinsing. Oral rinse with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution three times daily. Nasal irrigation two times with the solut.. | ||
Nov 18 2022 |
et al., Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2025.100801 (date from preprint) | Efficacy and safety of nebulized Sodium Bicarbonate in adults with COVID-19 (SODIC): a randomized, single center, double-blinded, controlled trial |
| 23% lower mortality (p=0.26) and 28% faster recovery (p<0.0001). RCT 546 patients showing significantly faster recovery and lower mortality with sodium bicarbonate (inhaled and nasal drops). The reduction in mortality is only statistically significant when excluding baseline critical cases. Authors hyp.. | ||
Aug 25 2022 |
et al., Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/01455613221123737 | Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients |
| Small RCT 79 PCR+ patients 55+ comparing pressure-based nasal irrigation with povidone-iodine and sodium bicarbonate, showing significantly lower hospitalization when compared with CDC data. | ||
Jun 12 2022 |
et al., Indian Journal of Respiratory Care, doi:10.4103/ijrc.ijrc_48_21 | Role of Sodium Bicarbonate as Adjuvant Treatment of Nonsevere Computed Tomography-identified COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Preliminary Report |
| 57% lower mortality (p=0.37), 39% lower progression (p=0.52), and 19% improved recovery (p=0.03). Prospective study of 182 COVID-19 pneumonia patients, 127 treated with sodium bicarbonate inhalation and nasal drops, showing significantly faster recovery and improved CT scores with treatment. Authors note that contacts of index cases a.. | ||
May 28 2022 |
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms10061118 | Effects of Different Inhalation Therapy on Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Ventilated COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial |
| 23% lower mortality (p=0.13). RCT mechanically ventilated patients in Croatia, 42 treated with sodium bicarbonate inhalation, and 52 control patients, showing no significant difference in mortality with treatment. Treated patients showed a lower incidence of gram-posi.. | ||
Jan 28 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Drug Delivery, doi:10.3389/fddev.2023.1164671 (date from preprint) | On a model-based approach to improve intranasal spray targeting for respiratory viral infections |
| Computational fluid dynamics study of nasal spray administration in 2 subjects showing 100x improvement in nasopharyngeal drug delivery using a new spray placement protocol. The study also found the optimal droplet size range for nasophar.. | ||
Dec 29 2021 |
et al., Brazilian Journal of Development, doi:10.34117/bjdv7n12-039 | Preliminary observation of the use of sodium bicarbonate solution as an adjunct in the treatment of coronavirus 2019 disease (COVID-19): prognosis improvement in patients requiring intensive care |
| 76% lower mortality (p=0.0001). Analysis of 76 ICU patients in Brazil, 44 treated with bronchoalveolar lavage using 3% sodium bicarbonate, showing significantly lower mortality with treatment. Bronchoalveolar lavage with 10ml of sodium bicarbonate solution directly into.. | ||
Jul 7 2021 |
, M., Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23901 | Gargling with 7.5% Sodium Bicarbonate Solution for SARS-CoV-2 Viremia Clearance: Our Institutional Clinical Experience |
| Report on 10 patients treated with sodium bicarbonate gargling, suggesting no significant improvements. There was no control group and gargling only, without inhalation or nasal spray/rinse. | ||
Mar 19 2021 |
, K., Acta Scientific Orthopaedics, 4:4 | Effect of 8.4% Soda-Bicarbonate Steam Inhalation on the Course of Disease in Mild to Moderate Cases of Covid-19 |
| 64% greater improvement (p=0.0007). RCT 60 hospitalized patients in India, showing significantly greater clinical improvement with inhaled sodium bicarbonate. Nasal and oral inhalation of nebulized 50ml 8.4% sodium bicarbonate for 5 minutes twice daily for 5 days. | ||
Oct 27 2020 |
et al., Farmacia, doi:10.31925/farmacia.2020.5.1 | Lysosomotropic properties of sodium bicarbonate and COVID-19 |
| Review exploring the use of sodium bicarbonate as a lysosomotropic agent against SARS-CoV-2 based on its widespread use during the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic. Authors suggest that the careful use of sodium bicarbonate could help restrain S.. | ||
Oct 14 2020 |
et al., Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, doi:10.34172/apb.2021.047 | Sodium Bicarbonate Nebulized Therapy in Patients with Confirmed COVID-19 |
| Proposal for nebulized sodium bicarbonate therapy for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection by raising endosomal pH and inhibiting viral entry into cells. Author proposes that inhalation of nebulized sodium bicarbonate solution (<5%) several.. | ||
May 19 2020 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Intensive Care and Medicine, doi:10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029 | Case reports of observed significant improvement in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 and maximum ventilatory support after inhalation of sodium bicarbonate |
| Case series of four ventilated COVID-19 patients treated with sodium bicarbonate inhalation, all showing clinical and radiological improvement, with 2 patients extubated within 24-72 hours. | ||
References