Effect of 8.4% Soda-Bicarbonate Steam Inhalation on the Course of Disease in Mild to Moderate Cases of Covid-19
, K., Acta Scientific Orthopaedics, 4:4, CTRI/2020/07/026535, Mar 2021
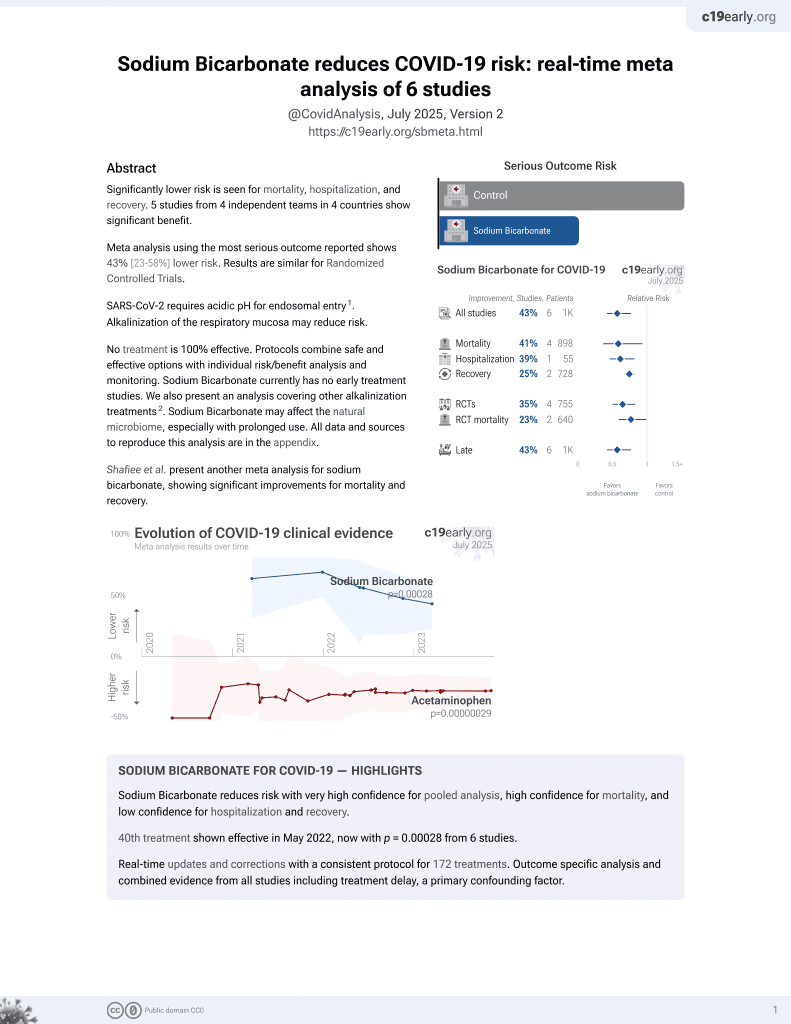
41st treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2022, now with p = 0.00028 from 6 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 60 hospitalized patients in India, showing significantly greater clinical improvement with inhaled sodium bicarbonate.
Nasal and oral inhalation of nebulized 50ml 8.4% sodium bicarbonate for 5 minutes twice daily for 5 days.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
|
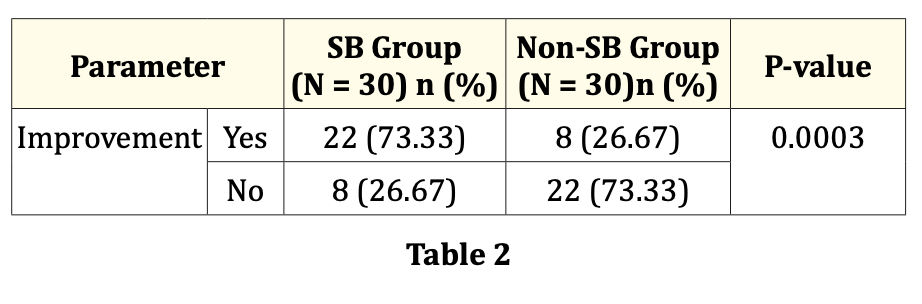
risk of no improvement, 63.6% lower, RR 0.36, p < 0.001, treatment 8 of 30 (26.7%), control 22 of 30 (73.3%), NNT 2.1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Wang et al., Efficacy of nasal irrigation and oral rinse with sodium bicarbonate solution on virus clearance for COVID-19 patients, Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145669.
2.
El-Badrawy et al., Efficacy and safety of nebulized Sodium Bicarbonate in adults with COVID-19 (SODIC): a randomized, single center, double-blinded, controlled trial, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2025.100801.
3.
Baxter et al., Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients, Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/01455613221123737.
4.
El-Badrawy (B) et al., Role of Sodium Bicarbonate as Adjuvant Treatment of Nonsevere Computed Tomography-identified COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Preliminary Report, Indian Journal of Respiratory Care, doi:10.4103/ijrc.ijrc_48_21.
Mody et al., 19 Mar 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, 1 author, study period July 2020 - September 2020, trial CTRI/2020/07/026535.
Effect of 8.4% Soda-Bicarbonate Steam Inhalation on the Course of Disease in Mild to Moderate Cases of Covid-19
Background: A prospective, randomized open label parallel group trial was carried out to evaluate the effect of 8.4% soda-bicarbonate steam inhalation on the course of covid-19 infection in mild to moderate confirmed cases of covid-19. Methods: 30 patients were enrolled and compared with 30 patients in a control group, giving a total sample size of 60 patients. Randomisation was achieved by sealed envelope technique. The 30 patients in the SB group received SB inhalation in addition to all other therapeutic measures as part of covid-19 treatment protocol. The control group was treated according to same treatment protocol, but without SB inhalation therapy. Clinical symptoms and lab markers were recorded on Day 1 and Day 5 of patients' stay at hospital.
Results: Patients receiving 8.4% SB inhalation as part of their treatment showed faster improvement in symptomatology and quicker normalization of inflammatory lab markers.
Conclusion: The results of this study show a highly significant improvement in the clinical picture of covid-19 affected patients treated with inhalations of steam impregnated with 8.4% sodium bicarbonate.
Proportion of subjects showing clinical symptomatic improvement was statistically significantly higher in the SB group as compared to the non-SB group. Proportion of improvement was found to be 73.33 and 26.67 in the SB and non-SB groups respectively (p-value 0.0003). Further studies with a larger patient population can establish further proof for the application of sodium bicarbonate as a useful agent to combat the covid-19 infection.
References
Alaiwa, pH modulates the activity and synergism of the airway surface liquid antimicrobials defensin-3 and LL-37, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Ashfaq, Lysosomotropic agents as HCV entry inhibitors, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/1743-422X-8-163
Aslan, The effect of nebulized sodium bicarbonate treatment on RADS patients due to chlorine gas inhalation, Inhalation Toxicology
Badrawy, Effect of sodium bicarbonate 8.4% on respiratory tract pathogens, The Journal of Chest and Lung Research
Chu V Mcelroy, The Avian Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis undergoes direct low PH dependent Fusion activation during entry into the host cells, Journal of Virology
Gomez, Safety, tolerability and effects of sodium bicarbonate inhalation in cystic fi brosis, Clinical Drug Investigation
Herrera, Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?, Clinical Oral Investigations
Mudasir A Mir, A review on probable Lysosomotropic properties of Sodium bicarbonate to restrain viral entry of Coronavirus 2, SARS
Pezzulo, Reduced airway surface pH impairs bacterial killing in the porcine cystic fibrosis lung, Nature
Prajapat, Drug targets for corona virus: A systematic review, Indian Journal of Pharmacology
Slonczewski, Cytoplasmic pH measurement and homeostasis in bacteria and archaea, Advances in Microbial Physiology
Vincent, Hydroxychloroquine reduces viral load in COVID-19 patients
Wang, SARS coronavirus entry into host cells through a novel clathrin-and caveolae-independent endocytic pathway, Cell Research
Yang, pH-Dependent Entry of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Is Mediated by the Spike Glycoprotein and Enhanced by Dendritic Cell Transfer through DC-SIGN, Journal of Virology
Yang, pH-dependent entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus is mediated by the spike glycoprotein and enhanced by dendritic cell transfer through DC-SIGN, Journal of Virology
mody2