Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients
et al., Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/01455613221123737, NCT04559035, Aug 2022
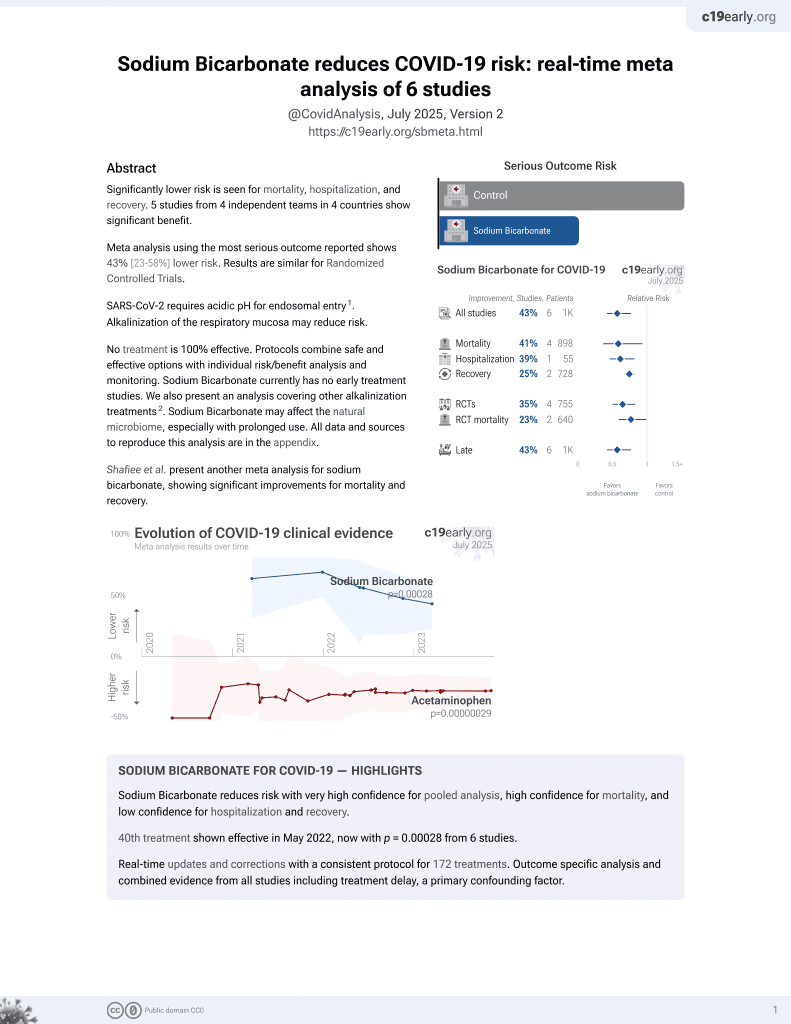
41st treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2022, now with p = 0.00028 from 6 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
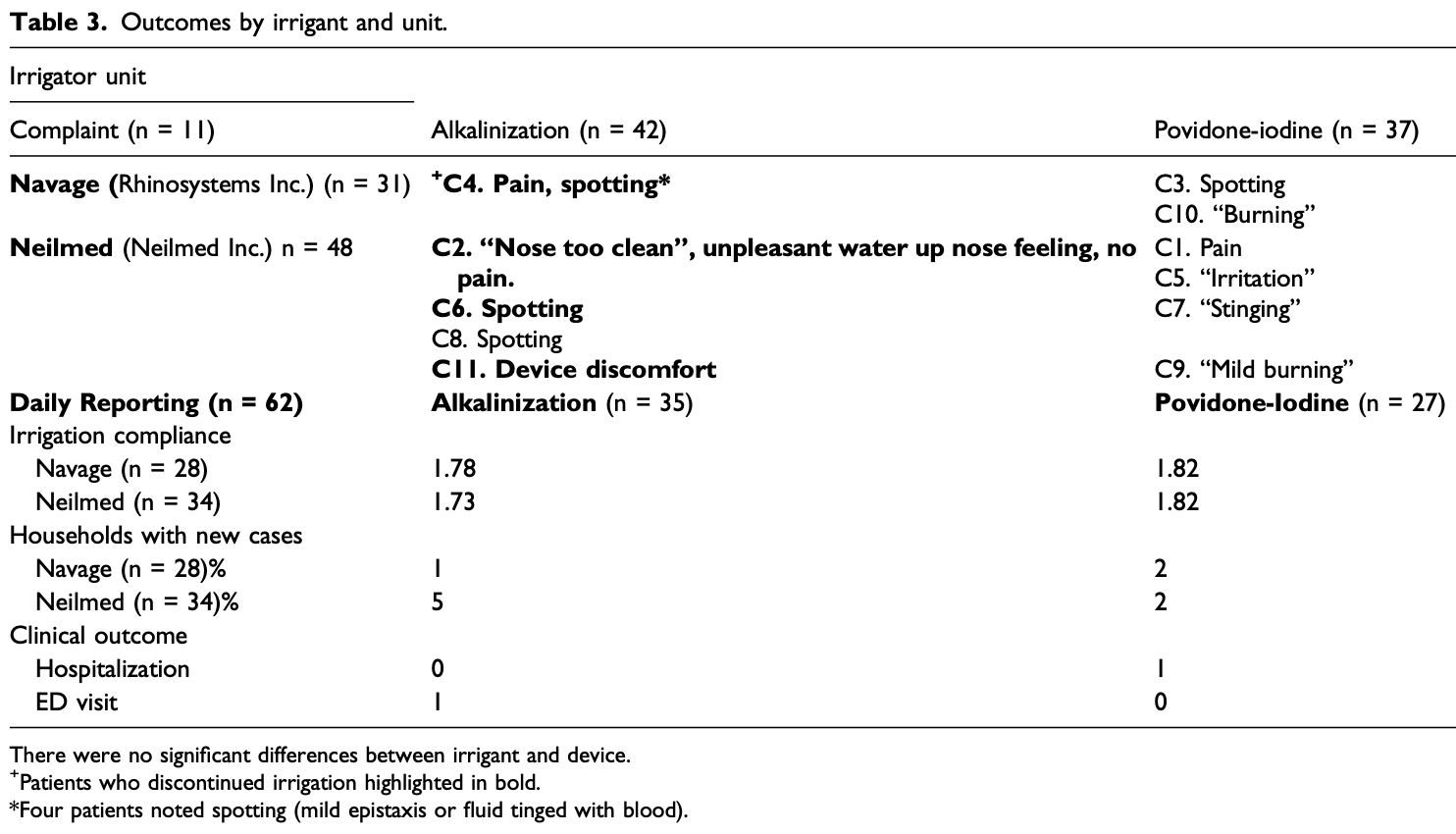
Small RCT 79 PCR+ patients 55+ comparing pressure-based nasal irrigation with povidone-iodine and sodium bicarbonate, showing significantly lower hospitalization when compared with CDC data.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments7.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers sodium bicarbonate and povidone-iodine.
|
risk of hospitalization, 65.3% lower, RR 0.35, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 37 (0.0%), control 1 of 42 (2.4%), NNT 42, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), vs. PVP-I.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 94.1% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.004, nasal irrigation vs. CDC data.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Wang et al., Efficacy of nasal irrigation and oral rinse with sodium bicarbonate solution on virus clearance for COVID-19 patients, Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145669.
2.
El-Badrawy et al., Efficacy and safety of nebulized Sodium Bicarbonate in adults with COVID-19 (SODIC): a randomized, single center, double-blinded, controlled trial, Current Therapeutic Research, doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2025.100801.
3.
Baxter et al., Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients, Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/01455613221123737.
4.
El-Badrawy (B) et al., Role of Sodium Bicarbonate as Adjuvant Treatment of Nonsevere Computed Tomography-identified COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Preliminary Report, Indian Journal of Respiratory Care, doi:10.4103/ijrc.ijrc_48_21.
5.
Delić et al., Effects of Different Inhalation Therapy on Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Ventilated COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms10061118.
Baxter et al., 25 Aug 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period 24 September, 2020 - 21 December, 2020, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo, trial NCT04559035 (history).
Contact: abaxter@augusta.edu, @AmyBaxterMD.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/01455613221123737",
"ISSN": [
"0145-5613",
"1942-7522"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/01455613221123737",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p> To determine whether initiating saline nasal irrigation after COVID-19 diagnosis reduces hospitalization and death in high-risk outpatients compared with observational controls, and if irrigant composition impacts severity. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p> Participants 55 and older were enrolled within 24 hours of a + PCR COVID-19 test between September 24 and December 21, 2020. Among 826 screened, 79 participants were enrolled and randomly assigned to add 2.5 mL povidone-iodine 10% or 2.5 mL sodium bicarbonate to 240 mL of isotonic nasal irrigation twice daily for 14 days. The primary outcome was hospitalization or death from COVID-19 within 28 days of enrollment by daily self-report confirmed with phone calls and hospital records, compared to the CDC Surveillance Dataset covering the same time. Secondary outcomes compared symptom resolution by irrigant additive. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p> Seventy-nine high-risk participants were enrolled (mean [SD] age, 64 [8] years; 36 [46%] women; 71% Non-Hispanic White), with mean BMI 30.3. Analyzed by intention-to-treat, by day 28, COVID-19 symptoms resulted in one ED visit and no hospitalizations in 42 irrigating with alkalinization, one hospitalization of 37 in the povidone-iodine group, (1.27%) and no deaths. Of nearly three million CDC cases, 9.47% were known to be hospitalized, with an additional 1.5% mortality in those without hospitalization data. Age, sex, and percentage with pre-existing conditions did not significantly differ by exact binomial test from the CDC dataset, while reported race and hospitalization rate did. The total risk of hospitalization or death (11%) was 8.57 times that of enrolled nasal irrigation participants (SE = 2.74; P = .006). Sixty-two participants completed daily surveys (78%), averaging 1.8 irrigations/day. Eleven reported irrigation-related complaints and four discontinued use. Symptom resolution was more likely for those reporting twice daily irrigation ( X<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 8.728, P = .0031) regardless of additive. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p> SARS-CoV-2+ participants initiating nasal irrigation were over 8 times less likely to be hospitalized than the national rate. </jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/01455613221123737"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7123-0733",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baxter",
"given": "Amy L",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, UK"
}
],
"family": "Schwartz",
"given": "Kyle R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Ryan W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kuchinski",
"given": "Ann-Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychology, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Swartout",
"given": "Kevin M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory for Theory and Mathematical Modeling, Department of Medicine-Division of Infectious Diseases, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Mathematics, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Srinivasa Rao",
"given": "Arni S R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gibson",
"given": "Robert W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Cherian",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0350-8243",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Giller",
"given": "Taylor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Boomer",
"given": "Houlton",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"family": "Lyon",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0947-3034",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schwartz",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Ear, Nose & Throat Journal",
"container-title-short": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-25T18:40:10Z",
"timestamp": 1661452810000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-25T18:40:36Z",
"timestamp": 1661452836000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Bernard and Anne Gray Donor Advised Fund"
},
{
"award": [
"Supplied Materials"
],
"name": "Neilmed Inc."
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100010716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Community Foundation for Greater Atlanta"
},
{
"award": [
"Supplied Materials"
],
"name": "Rhinosystems Inc."
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-25T19:12:04Z",
"timestamp": 1661454724062
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661385600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/01455613221123737",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/01455613221123737",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/01455613221123737",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "014556132211237",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr1-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-02039-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Li C",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "bibr3-01455613221123737",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-37703-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Burton MJ",
"first-page": "Cd013627",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "bibr5-01455613221123737",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1622",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0145561320932318",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-015-0091-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-018-0200-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Pelletier JS",
"first-page": "145561320957237",
"journal-title": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"key": "bibr10-01455613221123737",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.65.4.1916-1928.1991",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Madewell ZJ",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "bibr13-01455613221123737",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Control CfD",
"key": "bibr15-01455613221123737",
"volume-title": "CDC COVID-19 Case Surveillance Public Use Data"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7717/peerj.7000",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22703",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102581",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01948-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154262",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14429",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/lary.26064",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8707",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/125810",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2026913",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Viner RM",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "JAMA Pediatr",
"key": "bibr29-01455613221123737",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jamp.2014.1205",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-86494-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Sajuthi SP",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "bibr32-01455613221123737",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-019-05628-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0954",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-01455613221123737"
},
{
"author": "Goyal A",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "bibr36-01455613221123737",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102618",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr37-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0145561320950491",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr38-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.explore.2020.09.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr39-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr40-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22975",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr41-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-021-03102-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr42-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/br.2021.1494",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr43-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/ice.2020.116",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr44-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr45-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr46-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-6306",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr47-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsa2011686",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr48-01455613221123737"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cis626",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr49-01455613221123737"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/01455613221123737"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Otorhinolaryngology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID+ outpatients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy"
}
baxterph