Recent:Tran.
Feb 27 |
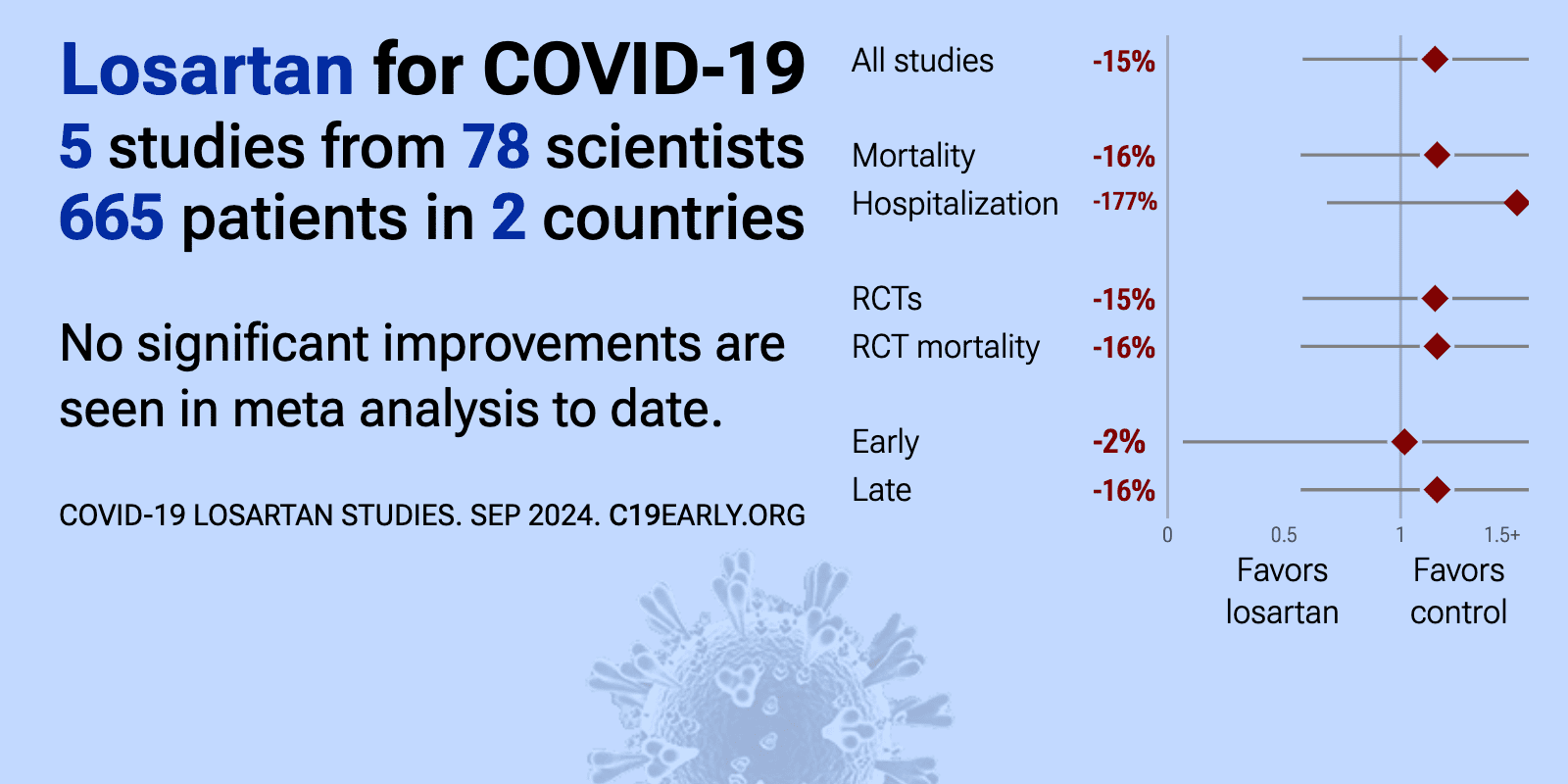
Losartan for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 6 studies (Version 3) | |
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 15% [-29‑84%] higher risk, without reaching statistical significance. Currently all studies are RCTs. Control Losartan Currently there is limited data, with only 30 co.. | ||
Jul 10 2024 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciae306 | Effects of Losartan on Patients Hospitalized for Acute COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial |
| 14% higher mortality (p=0.69), 1% higher ventilation (p=0.96), 3% higher need for oxygen therapy (p=0.43), and 75% higher ICU admission (p=0.21). RCT 341 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significant harm with losartan treatment. The trial was stopped early due to safety concerns after losartan patients experienced significantly higher rates of serious adverse events (39.8% vs.. | ||
Dec 31 2022 |
et al., SSRN Electronic Journal, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4278529 | Effect of Adding Losartan to Standard of Care Treatment on the Risk of Death and Icu Admission Among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Trial |
| 77% lower ventilation (p=0.01) and 36% lower ICU admission (p=0.24). RCT 302 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mechanical ventilation but no significant difference in ICU admission or mortality with losartan treatment. | ||
Oct 31 2022 |
et al., Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications, doi:10.1016/j.conctc.2022.100968 | COVIDMED – An early pandemic randomized clinical trial of losartan treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients |
| 533% higher mortality (p=0.49) and 160% longer hospitalization (p=0.3). RCT 15 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant differences with losartan treatment. The study was terminated early due to low enrollment. | ||
Mar 19 2022 |
et al., BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, doi:10.1186/s12872-022-02548-2 | Does Losartan reduce the severity of COVID-19 in hypertensive patients? |
| 81% lower mortality (p=0.003) and 3% fewer cases (p=0.86). Retrospective study of 280 hypertensive patients in Iran showing lower mortality with losartan use in COVID-19 patients, however data is contradictory and unclear. The text and Figure 1 indicate that 179 of 280 patients were PCR+, however.. | ||
Mar 16 2022 |
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.2735 | Efficacy of Losartan in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19–Induced Lung Injury |
| 3% higher mortality (p=1), 27% higher ventilation (p=0.47), and 3% lower need for oxygen therapy (p=0.66). RCT 205 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in lung injury (PaO2:FiO2 ratio) at day 7 with losartan treatment, and no difference in clinical outcomes including mortality. Losartan was associated with more adve.. | ||
Jul 31 2021 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100957 | A multi-center phase II randomized clinical trial of losartan on symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 |
| 2% higher ICU admission (p=1), 205% higher hospitalization (p=0.36), and 27% higher progression (p=0.74). RCT 117 symptomatic outpatients showing no significant difference in hospitalization, functional status, dyspnea, or viral load with losartan treatment. The trial was terminated early due to low event rates. Losartan 25mg twice daily for .. | ||
May 11 2021 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3 | Randomized Prospective Open Label Study Shows No Impact on Clinical Outcome of Adding Losartan to Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Mild Hypoxemia |
| 6% lower mortality (p=1), 53% lower ICU admission (p=0.6), 53% higher hospital discharge (p=0.6), and 10% shorter hospitalization. RCT 31 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with mild hypoxemia showing no significant difference in mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, or mortality with addition of losartan to standard care. | ||