Recent:Shokri-Afra.
Feb 23 |
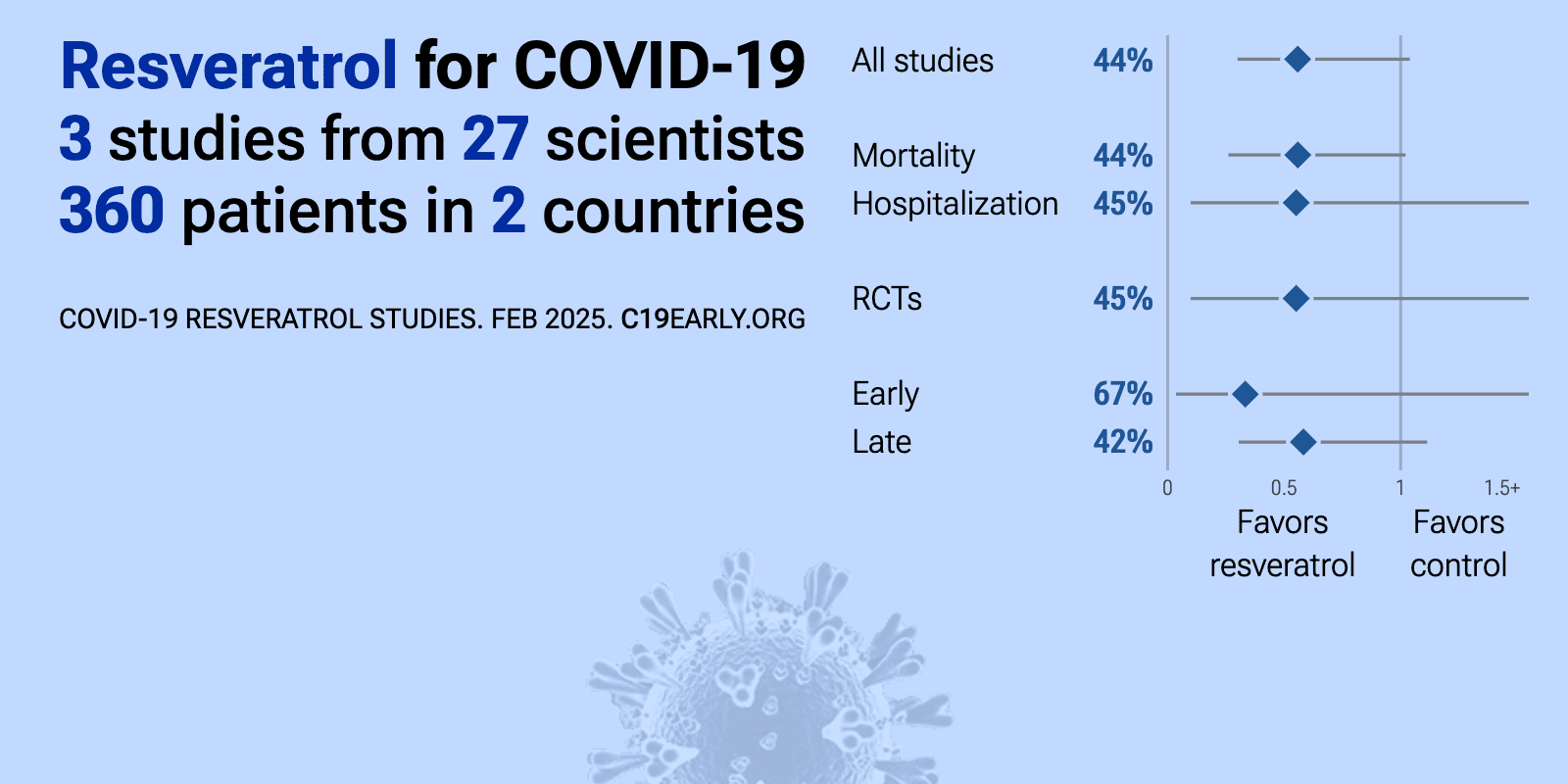
Resveratrol for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 3 studies | |
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 44% [-4‑70%] lower risk, without reaching statistical significance. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials and better for peer-reviewed studies. Results .. | ||
Dec 17 2025 |
et al., BioMed Research International, doi:10.1155/bmri/9507417 | Targeting SIRT1: A Potential Strategy for Combating Severe COVID‐19 |
| Review showing that SIRT1 activation may benefit COVID-19 treatment through multiple anti-inflammatory and antiviral mechanisms. | ||
Jun 12 2025 |
et al., Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2025.110607 | SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactome: insights into more players during pathogenesis |
| Review of SARS-CoV-2 host-pathogen interactions during viral pathogenesis, focusing on protein-protein interactions that facilitate viral entry, replication, immune evasion, assembly, and release. Authors comprehensively analyze how SARS-.. | ||
Aug 3 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016 | Association of dietary intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols with immune-stimulating microbiota and COVID-19 risk in a group of Polish men and women |
| Dietary analysis of 95 adults in Poland, showing lower risk of COVID-19 with higher intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols. Results were statistically significant for total phytosterols, secoisolariciresinol, β-sitosterol, matai.. | ||
Jun 29 2022 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9 | Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled proof-of-concept trial of resveratrol for outpatient treatment of mild coronavirus disease (COVID-19) |
| 67% lower hospitalization (p=0.62) and 43% lower progression (p=0.52). RCT 100 outpatients in the USA, showing lower hospitalization and progression with resveratrol, without statistical significance. | ||
Mar 22 2022 |
et al., COVID, doi:10.3390/covid2040031 | A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Evaluating Concentrated Phytochemical-Rich Nutritional Capsule in Addition to a Probiotic Capsule on Clinical Outcomes among Individuals with COVID-19—The UK Phyto-V Study |
| 44% greater improvement (p=0.02). RCT 147 long COVID patients in the UK, 56 treated with a phytochemical-rich concentrated food capsule, showing improved recovery with treatment. Treatment included curcumin, bioflavonoids, chamomile, ellagic acid, and resveratrol. | ||
Jan 21 2022 |
et al., European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022 | Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants |
| In vitro study testing combinations of plant extracts and micronutrients with several variants of SARS-CoV-2. A combination of vitamin C, N-acetylcysteine, curcumin, quercetin, resveratrol, theaflavin, naringenin, baicalin, and broccoli e.. | ||
Nov 14 2021 |
et al., Food Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131594 | Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro main protease by plant polyphenols |
| In silico and in vitro study of plant polyphenols identifying quercetin, curcumin, ellagic acid, epigallocatechin gallate, and resveratrol as SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors with IC50 between 11.8µM and 23.4µM. Real-time binding was analyzed.. | ||
Oct 25 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19031172 (date from preprint) | Effect of a Nutritional Support System to Increase Survival and Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Stage III and Comorbidities: A Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial |
| 86% lower mortality (p=0.03) and 57% lower ventilation (p=0.31). 80 patient RCT with 40 patients treated with a comprehensive regimen of nutritional support, showing significantly lower mortality with treatment. Treatment contained cholecalciferol, vitamin C, zinc, spirulina maxima, folic acid, glutami.. | ||
Oct 11 2021 |
et al., Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2021/8447545 | A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of a Nutritional Supplement (ImmuActive) for COVID-19 Patients |
| 43% improved recovery (p=0.004) and 6% faster viral clearance (p=0.47). RCT 100 patients in India, 50 treated with ImmuActive (curcumin, andrographolides, resveratrol, zinc, selenium, and piperine), showing improved recovery with treatment. | ||
Oct 1 2021 |
et al., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3934228 | Resveratrol and Zinc in the Treatment of Outpatients With COVID-19 – The Reszinate Study - A Phase 1/2 Randomized Clinical Trial Utilizing Home Patient-Obtained Nasal and Saliva Viral Sampling |
| 14% higher ventilation (p=1), 14% higher ICU admission (p=1), and 14% higher hospitalization (p=1). Small RCT of zinc plus resveratrol in COVID-19+ outpatients, showing no significant differences in viral clearance or symptoms. Although the treatment group was older (46.3 vs. 38.5) and had more severe baseline symptoms, they had similar.. | ||
Jul 10 2021 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13071335 | Resveratrol and Pterostilbene Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Air–Liquid Interface Cultured Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells |
| In vitro study showing resveratrol and pterostilbene inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero E6 cells and human bronchial epithelial cells. Both compounds had an antiviral effect when added post-infection, suggesting they interfere with vi.. | ||
Jul 29 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.21.20151423 | Resveratrol and Copper for treatment of severe COVID-19: an observational study (RESCU 002) |
| 44% lower mortality (p=0.06). Retrospective 230 severe COVID-19 patients in India, showing lower mortality with resveratrol + copper, without statistical significance. This study followed preclinical data showing that sepsis-related cytokine storm and fatality in mice.. | ||
Jun 4 2020 |
, P., Cell Stress and Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9 | COVID-19 and heme oxygenase: novel insight into the disease and potential therapies |
| Proposal that COVID-19 risk is related to low intracellular heme oxygenase (HO-1), and that therapies that raise HO-1 may be beneficial, which includes fluvoxamine, certain anesthetics (sevoflurane or isoflurane), hemin, estrogen, statins.. | ||