Mar 1 |
Sarilumab for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 11 studies (Version 10) | |
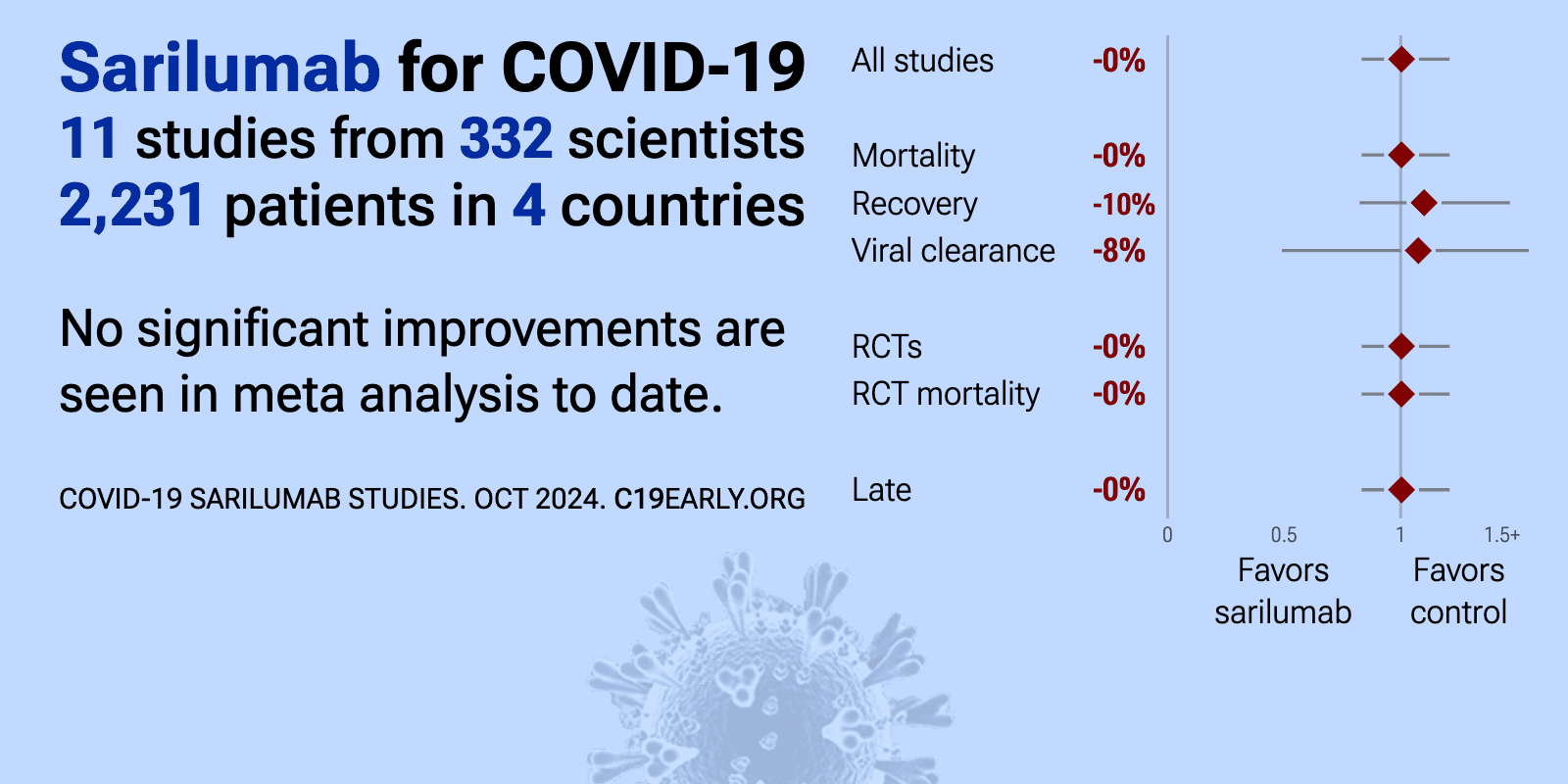
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 0% [-17‑21%] higher risk, without reaching statistical significance. Currently all studies are RCTs. Control Sarilumab All data and sources to reproduce this analysis .. | ||
Mar 6 2025 |
et al., British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1002/bcp.70025 | Adverse events associated with monoclonal antibodies used for treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis |
| Systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 RCTs with 19,797 COVID-19 patients, showing a statistically significant increased risk of hepatotoxicity and neutropenia associated with monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments compared to standard o.. | ||
Mar 31 2023 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101895 | Sarilumab plus standard of care vs standard of care for the treatment of severe COVID-19: a phase 3, randomized, open-labeled, multi-center study (ESCAPE study) |
| 30% higher mortality (p=0.67), 7% greater improvement (p=0.69), and 8% worse viral clearance (p=1). RCT with 176 severe COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in time to clinical improvement or 30 day mortality with sarilumab treatment. | ||
Feb 26 2022 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac153 | Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 7% higher mortality (p=0.89) and 4% worse improvement (p=0.91). Phase 2 and phase 3 RCTs with 1,365 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant improvement with sarilumab vs placebo. Post-hoc analysis suggests a potential mortality benefit with sarilumab in mechanically ventilated patients r.. | ||
Feb 26 2022 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac153 | Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 8% higher mortality (p=0.59) and 6% worse improvement (p=0.47). Phase 2 and phase 3 RCTs with 1,365 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant improvement with sarilumab vs placebo. Post-hoc analysis suggests a potential mortality benefit with sarilumab in mechanically ventilated patients r.. | ||
Feb 25 2022 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263591 | Subcutaneous sarilumab for the treatment of hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID19 disease: A pragmatic, embedded randomized clinical trial |
| 350% higher mortality (p=0.05), 650% higher combined mortality/intubation (p=0.03), and 500% higher ventilation (p=0.16). RCT 50 hospitalized moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients showing higher mortality with subcutaneous sarilumab compared to standard of care. The study was stopped early due to a high probability of futility and potential harm. | ||
Feb 23 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.819621 | Subcutaneous IL-6 Inhibitor Sarilumab vs. Standard Care in Hospitalized Patients With Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19: An Open Label Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 300% higher mortality (p=0.54), 450% higher ventilation (p=0.53), and 33% worse 7-point scale results (p=0.36). RCT 30 hospitalized moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in 30-day mortality, clinical improvement at day 7, or time to discharge with sarilumab compared to standard care. | ||
Feb 15 2022 |
et al., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/AAC.02107-21 | Early Use of Sarilumab in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Pneumonia and Features of Systemic Inflammation: the SARICOR Randomized Clinical Trial |
| 35% higher mortality (p=0.71), 22% higher ventilation (p=0.7), and 36% lower progression (p=0.23). RCT 115 hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients in Spain showing a trend towards reduced progression to severe respiratory failure requiring high-flow oxygen, non-invasive ventilation, or mechanical ventilation, and reduced mortality, wi.. | ||
Feb 3 2022 |
et al., European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.02523-2021 | Effect of interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: two randomised controlled trials of the CORIMUNO-19 Collaborative Group |
| 26% lower mortality (p=0.44). Two open-label RCTs of 97 and 91 critically ill COVID-19 patients in France showing no significant differences with tocilizumab or sarilumab. | ||
Jan 31 2022 |
et al., The Lancet Rheumatology, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00315-5 | Sarilumab in adults hospitalised with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 pneumonia (CORIMUNO-SARI-1): An open-label randomised controlled trial |
| 30% lower mortality (p=0.4), 1% worse recovery (p=1), and 10% higher progression (p=0.7). RCT 148 hospitalized patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 pneumonia in France showing no significant differences with sarilumab treatment. | ||
Nov 30 2021 |
et al., Current Medicine Research and Practice, doi:10.4103/cmrp.cmrp_71_21 | Tolerability of Sarilumab – An anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody is controversial for the management of COVID-19 |
| Review of sarilumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, for the management of COVID-19. Authors report that sarilumab was proposed as a potential treatment to reduce mortality by abating the inflammatory cytokine storm in.. | ||
Oct 17 2021 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00543-2 | Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in patients with COVID19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Phase III Clinical Trial (SARTRE Study) |
| 3% higher mortality (p=0.98), 30% lower ICU admission (p=0.5), and 14% worse recovery (p=0.66). RCT 201 hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients under standard oxygen therapy in Spain showing no significant difference with sarilumab treatment. | ||
May 31 2021 |
et al., The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0 | Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial |
| 2% lower mortality (p=0.96), 5% higher ICU admission (p=0.89), and 8% greater improvement (p=0.47). RCT 416 hospitalized severe or critical COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference with intravenous sarilumab compared to placebo for clinical improvement, survival at day 29, or other secondary outcomes. | ||
Apr 22 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433 | Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19 |
| 26% lower mortality (p=0.39). RCT 803 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing improved outcomes with tocilizumab and sarilumab. There was only 48 sarilumab patients and the model used shrinks the posterior distribution for each intervention effect toward the overall .. | ||