Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac153, REGENERON P2, NCT04315298, Feb 2022
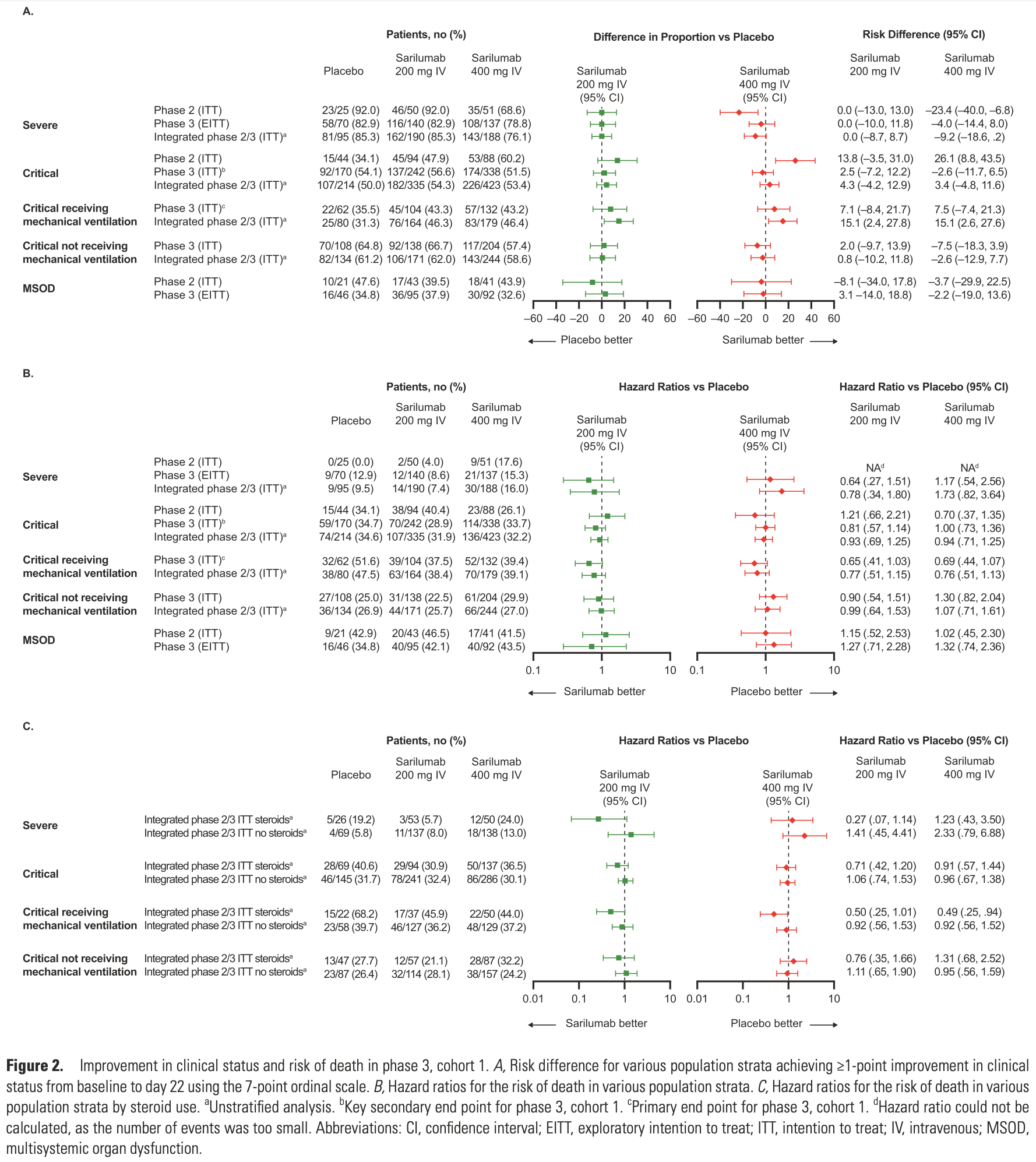
Phase 2 and phase 3 RCTs with 1,365 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant improvement with sarilumab vs placebo. Post-hoc analysis suggests a potential mortality benefit with sarilumab in mechanically ventilated patients receiving corticosteroids at baseline. Phase 2 and phase 3 results are listed separately1,2.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments3.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 6.8% higher, HR 1.07, p = 0.89, treatment 180, control 90, adjusted per study, all 400mg patients.
|
|
risk of death, 1341.2% higher, HR 14.41, p = 0.03, treatment 9 of 51 (17.6%), control 0 of 25 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 400mg, severe patients, phase 2, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 30.0% lower, HR 0.70, p = 0.28, treatment 23 of 88 (26.1%), control 15 of 44 (34.1%), NNT 13, adjusted per study, 400mg, critical patients, phase 2, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 2.0% higher, HR 1.02, p = 0.97, treatment 17 of 41 (41.5%), control 9 of 21 (42.9%), NNT 72, adjusted per study, 400mg, MSOD patients, phase 2, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 22.4% higher, HR 1.22, p = 0.41, treatment 187, control 90, adjusted per study, all 200mg patients.
|
|
risk of death, 300.0% higher, HR 4.00, p = 0.55, treatment 2 of 50 (4.0%), control 0 of 25 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 200mg, severe patients, phase 2, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 21.0% higher, HR 1.21, p = 0.55, treatment 38 of 94 (40.4%), control 15 of 44 (34.1%), adjusted per study, 200mg, critical patients, phase 2, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 15.0% higher, HR 1.15, p = 0.74, treatment 20 of 43 (46.5%), control 9 of 21 (42.9%), adjusted per study, 200mg, MSOD patients, phase 2, day 60.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 4.4% higher, RR 1.04, p = 0.91, treatment 180, control 90, all 400mg patients.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 292.2% higher, RR 3.92, p = 0.04, treatment 16 of 51 (31.4%), control 2 of 25 (8.0%), 400mg, severe patients, phase 2, day 22.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 39.7% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.006, treatment 35 of 88 (39.8%), control 29 of 44 (65.9%), NNT 3.8, 400mg, critical patients, phase 2, day 22.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 7.1% higher, RR 1.07, p = 0.79, treatment 23 of 41 (56.1%), control 11 of 21 (52.4%), 400mg, MSOD patients, phase 2, day 22.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 12.2% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.30, treatment 187, control 90, all 200mg patients.
|
|
risk of no improvement, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 4 of 50 (8.0%), control 2 of 25 (8.0%), 200mg, severe patients, phase 2, day 22.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 20.9% lower, RR 0.79, p = 0.14, treatment 49 of 94 (52.1%), control 29 of 44 (65.9%), NNT 7.3, 200mg, critical patients, phase 2, day 22.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 15.4% higher, RR 1.15, p = 0.60, treatment 26 of 43 (60.5%), control 11 of 21 (52.4%), 200mg, MSOD patients, phase 2, day 22.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Sivapalasingam et al., Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac153.
Sivapalasingam et al., 26 Feb 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 61.0, 40 authors, study period 18 March, 2020 - 2 July, 2020, trial NCT04315298 (history) (REGENERON P2).
Contact: david.lederer@regeneron.com.
Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac153
Background. Open-label platform trials and a prospective meta-analysis suggest efficacy of anti-interleukin (IL)-6R therapies in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) receiving corticosteroids. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of sarilumab, an anti-IL-6R monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Methods. In this adaptive, phase 2/3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, adults hospitalized with COVID-19 received intravenous sarilumab 400 mg or placebo. The phase 3 primary analysis population included patients with critical COVID-19 receiving mechanical ventilation (MV). The primary outcome was proportion of patients with ≥1-point improvement in clinical status from baseline to day 22. Results. There were 457 and 1365 patients randomized and treated in phases 2 and 3, respectively. In phase 3, patients with critical COVID-19 receiving MV (n = 298; 28.2% on corticosteroids), the proportion with ≥1-point improvement in clinical status (alive, not receiving MV) at day 22 was 43.2% for sarilumab and 35.5% for placebo (risk difference, +7.5%; 95% confidence interval [CI], -7.4 to 21.3; P =.3261), a relative risk improvement of 21.7%. In post hoc analyses pooling phase 2 and 3 critical patients receiving MV, the hazard ratio for death for sarilumab vs placebo was 0.76 (95% CI, .51 to 1.13) overall and 0.49 (95% CI, .25 to .94) in patients receiving corticosteroids at baseline. Conclusions. This study did not establish the efficacy of sarilumab in hospitalized patients with severe/critical COVID-19. Post hoc analyses were consistent with other studies that found a benefit of sarilumab in patients receiving corticosteroids. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04315298.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Clinical Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for COVID and non-COVID research that is not related to this article. S. Saggar reports grants from BARDA and fees from Allergan/AbbVie. S. J. S. reports grants from BARDA. V. M., M. E. S., and W. P. report grants from BARDA. D. K. S. has received support to conduct the study from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and reports grants from BARDA. J. A. A. has received support to conduct the study from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals; reports grants from BARDA, Atea, Emergent Biosolutions, Frontier Technologies, Gilead, Janssen, Pfizer, and ViiV; and reports grants and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Merck. S. M. B. reports grants from BARDA, Sedana, Janssen, NIH, and the Department of Defense; personal fees from Hamilton and New York University and other from Faron; and book fees from Oxford University and Brigham Young University. The remaining author: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been..
References
Benucci, Giannasi, Cecchini, COVID-19 pneumonia treated with sarilumab: a clinical series of eight patients, J Med Virol
Fleischmann, Genovese, Lin, Long-term safety of sarilumab in rheumatoid arthritis: an integrated analysis with up to 7 years' follow-up, Rheumatology
Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Horby, Pessoa-Amorim, Peto, Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): preliminary results of a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Luo, Liu, Qiu, Liu, Liu et al., Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience, J Med Virol
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Montesarchio, Parrela, Iommelli, Outcomes and biomarker analyses among patients with COVID-19 treated with interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist sarilumab at a single institution in Italy, J Immuno Ther Cancer
Morena, Milazzo, Oreni, Off-label use of tocilizumab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Milan, Italy, Eur J Intern Med
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19-interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Peterson, Vock, Powers, Analysis of an ordinal endpoint for use in evaluating treatments for severe influenza requiring hospitalization, Clin Trials
Price, Altice, Shyr, Tocilizumab treatment for cytokine release syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: survival and clinical outcomes, Chest
Remap-Cap, Gordon, Mouncey, Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Valle, Kim-Schulze, Hui, An inflammatory cytokine signature helps predict COVID-19 severity and death, Nat Med
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Zhang, Zhao, Zhang, The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): the perspectives of clinical immunologists from China, Clin Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac153",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac153",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Open-label platform trials and a prospective meta-analysis suggest efficacy of anti–interleukin (IL)-6R therapies in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) receiving corticosteroids. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of sarilumab, an anti–IL-6R monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this adaptive, phase 2/3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, adults hospitalized with COVID-19 received intravenous sarilumab 400 mg or placebo. The phase 3 primary analysis population included patients with critical COVID-19 receiving mechanical ventilation (MV). The primary outcome was proportion of patients with ≥1-point improvement in clinical status from baseline to day 22.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>There were 457 and 1365 patients randomized and treated in phases 2 and 3, respectively. In phase 3, patients with critical COVID-19 receiving MV (n = 298; 28.2% on corticosteroids), the proportion with ≥1-point improvement in clinical status (alive, not receiving MV) at day 22 was 43.2% for sarilumab and 35.5% for placebo (risk difference, +7.5%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –7.4 to 21.3; P =.3261), a relative risk improvement of 21.7%. In post hoc analyses pooling phase 2 and 3 critical patients receiving MV, the hazard ratio for death for sarilumab vs placebo was 0.76 (95% CI, .51 to 1.13) overall and 0.49 (95% CI, .25 to .94) in patients receiving corticosteroids at baseline.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This study did not establish the efficacy of sarilumab in hospitalized patients with severe/critical COVID-19. Post hoc analyses were consistent with other studies that found a benefit of sarilumab in patients receiving corticosteroids.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>NCT04315298.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sivapalasingam",
"given": "Sumathi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Lederer",
"given": "David J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bhore",
"given": "Rafia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Clinical Outcomes Research, Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Northwell Health, Manhasset, New York, New York, and Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Northwell Health , Hempstead, New York, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hajizadeh",
"given": "Negin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Thoracic Medicine and Surgery, Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University , Philadelphia, Pennsylvania , USA"
}
],
"family": "Criner",
"given": "Gerard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hosain",
"given": "Romana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "Adnan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Giannelou",
"given": "Angeliki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Somersan-Karakaya",
"given": "Selin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "O’Brien",
"given": "Meagan P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Boyapati",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Parrino",
"given": "Janie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Musser",
"given": "Bret J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Labriola-Tompkins",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ramesh",
"given": "Divya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Purcell",
"given": "Lisa A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gulabani",
"given": "Daya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kampman",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Waldron",
"given": "Alpana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Montefiore–Moses , Bronx, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ng Gong",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Holy Name Medical Center , Teaneck, New Jersey , USA"
}
],
"family": "Saggar",
"given": "Suraj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine and Hackensack University Medical Center , Hackensack, New Jersey , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sperber",
"given": "Steven J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, NYC Health + Hospitals/Lincoln , Bronx, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Menon",
"given": "Vidya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Jacobi Medical Center , Bronx, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Stein",
"given": "David K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Columbia University , New York, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sobieszczyk",
"given": "Magdalena E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pulmonary and Sleep Disorder Clinic, Valley Medical Center , Renton, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Park",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai , New York, New York , USA and"
}
],
"family": "Aberg",
"given": "Judith A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Intermountain Medical Center and University of Utah , Salt Lake City, Utah , USA"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Samuel M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kosmicki",
"given": "Jack A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Horowitz",
"given": "Julie E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Manuel A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Baras",
"given": "Aris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kowal",
"given": "Bari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Thomas DiCioccio",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Akinlade",
"given": "Bolanle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Nivens",
"given": "Michael C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Braunstein",
"given": "Ned",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Herman",
"given": "Gary A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Yancopoulos",
"given": "George D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc , Tarrytown, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Weinreich",
"given": "David M",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-17T20:11:37Z",
"timestamp": 1645128697000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-25T03:07:56Z",
"timestamp": 1661396876000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-22T13:53:53Z",
"timestamp": 1721656433769
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 23,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645833600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac153/43887701/ciac153.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/75/1/e380/45514220/ciac153.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/75/1/e380/45514220/ciac153.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e380-e388",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
26
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0001",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0002",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0003",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108393",
"article-title": "The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): the perspectives of clinical immunologists from China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108393",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0004",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"article-title": "An inflammatory cytokine signature helps predict COVID-19 severity and death",
"author": "Del Valle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1636",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0005",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0006",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25801",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "814",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0007",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.011",
"article-title": "Off-label use of tocilizumab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Milan, Italy",
"author": "Morena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0008",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26062",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pneumonia treated with sarilumab: a clinical series of eight patients",
"author": "Benucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2368",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0009",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jitc-2020-001089",
"article-title": "Outcomes and biomarker analyses among patients with COVID-19 treated with interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist sarilumab at a single institution in Italy",
"author": "Montesarchio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e001089",
"journal-title": "J Immuno Ther Cancer",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0010",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.006",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab treatment for cytokine release syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: survival and clinical outcomes",
"author": "Price",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0011",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19—preliminary report",
"author": "Gordon",
"first-page": "2021.2001.2007.21249390",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0012",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): preliminary results of a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0013",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1740774517697919",
"article-title": "Analysis of an ordinal endpoint for use in evaluating treatments for severe influenza requiring hospitalization",
"author": "Peterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "Clin Trials",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0015",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/kez265",
"article-title": "Long-term safety of sarilumab in rheumatoid arthritis: an integrated analysis with up to 7 years’ follow-up",
"author": "Fleischmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "292",
"journal-title": "Rheumatology (Oxford)",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0016",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Recovery Collaborative Group.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0017",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Remap-Cap",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1491",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0018",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Nuffield Department of Population Health.",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—interim WHO solidarity trial results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0020",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0021",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization.",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0022"
},
{
"author": "National Institutes of Health.",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0023"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization.",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.11330",
"article-title": "Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies Working Group.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022082503044331400_CIT0025",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2021.05.13.21256973",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/75/1/e380/6537638"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "75"
}
sivapalasingam