Artemisinin was adopted
in 13 countries.
Feb 17 |
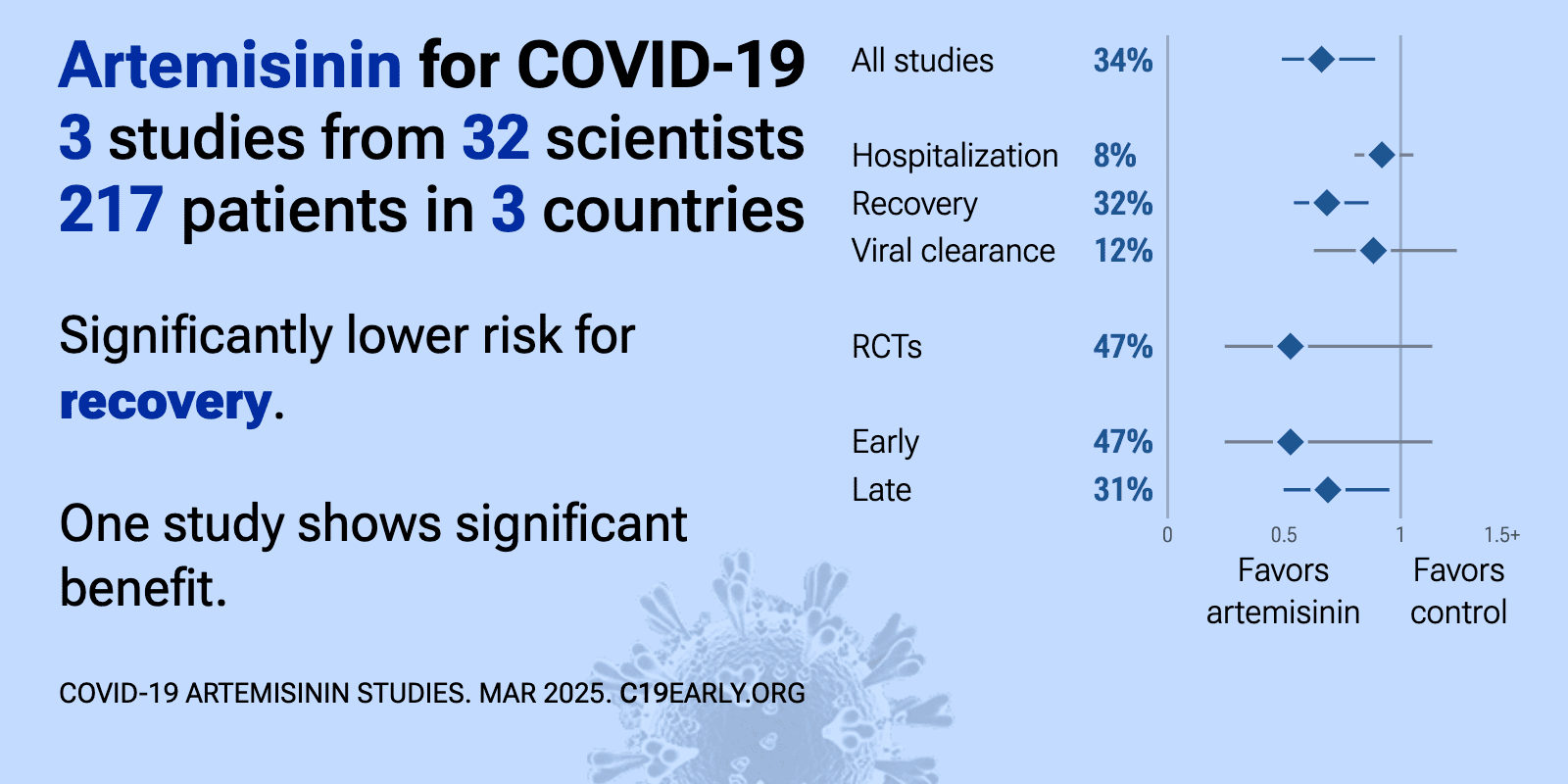
Artemisinin reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 3 studies | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for recovery. One study shows significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 34% [11‑51%] lower risk. Results are similar for peer-reviewed studies and better f.. | ||
Jul 31 2025 |
et al., Rwanda Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences, doi:10.4314/rjmhs.v8i2.2 | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF- α) and Antiviral Activities of Artemisia SPP. Extracts on SARS-COV2 |
| In vitro and cross-sectional study showing that Artemisia afra and Artemisia annua extracts inhibit TNF-α levels in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients by approximately 50-70% in severe cases. Authors analyzed the phytochemical composition of et.. | ||
Nov 15 2024 |
et al., Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules29225403 | Insights into SARS-CoV-2: Small-Molecule Hybrids for COVID-19 Treatment |
| Review of recent advances in small-molecule hybrid compounds as potential antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2. Authors provide an overview of hybrids, which are formed by covalently linking two or more pharmacophores, as a promising appro.. | ||
Oct 26 2024 |
et al., Molecular Biology Research Communications, doi:10.22099/mbrc.2024.50245.2001 | Non-spike protein inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by natural products through the key mediator protein ORF8 |
| In silico study showing that ivermectin, artemisinin, and DEG-168 may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the ORF8 protein's binding sites. Ivermectin showed the highest binding affinity. Authors identified two key binding regions on ORF8 - a.. | ||
May 18 2024 |
et al., NCT04330690 | A Multi-centre, Adaptive, Randomized, Open-label, Controlled Clinical Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of Investigational Therapeutics for the Treatment of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients (CATCO: Canadian Treatments for COVID-19), in Conjunction With the Public Health Emergency SOLIDARITY Trial (World Health Organization) |
| Estimated 966 patient artemisinin late treatment RCT with results not reported over 1.5 years after estimated completion. | ||
May 15 2024 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09387-w | Phytoconstituents of Artemisia Annua as potential inhibitors of SARS CoV2 main protease: an in silico study |
| In silico study showing that artemisinin and artesunate from Artemisia annua bind to the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), with artesunate exhibiting a binding score of -7.5 kcal/mol. Authors screened 25 phytoconstituents, identifying arte.. | ||
Jan 2 2024 |
et al., PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638 | Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats |
| In vitro and animal study showing that a novel artemisinin/quercetin/zinc (Art/Q/Zn) complex exhibits potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity (IC50 = 10.14 μg/ml) without cytotoxicity (CC50 = 208.5 μg/ml). The complex alleviates acrylamide-induce.. | ||
Dec 1 2022 |
et al., NCT05273242 | WHO Solidarity Trial Plus: An International Randomised Trial of Additional Treatments for COVID-19 in Hospitalised Patients Who Are All Receiving the Local Standard of Care in Nepal |
| Estimated 400 patient artemisinin late treatment RCT with results not reported over 3 years after estimated completion. | ||
Nov 1 2022 |
et al., eBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104322 | Safety and efficacy of four drug regimens versus standard-of-care for the treatment of symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19: A randomised, open-label, multi-arm, phase 2 clinical trial |
| 29% lower progression (p=0.66), 27% faster recovery (p=0.1), and 1% worse viral clearance (p=0.76). High COI low-risk patient RCT in South Africa, showing no significant differences with artesunate-amodiaquine or pyronaridine-artesunate. | ||
Feb 7 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Plant Science, doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.780257 | Artemisinins in Combating Viral Infections Like SARS-CoV-2, Inflammation and Cancers and Options to Meet Increased Global Demand |
| Review of artemisinin and related compounds (artemisinins) for their potential in combating viral infections, inflammation, and cancers, with a special focus on SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19. Authors explain that artemisinin, a sesquiterpene lacton.. | ||
Feb 7 2022 |
et al., Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x | Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2 |
| In vitro and mouse study showing synergistic antiviral effects when combining pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors with antiviral nucleoside analogues against SARS-CoV-2. Authors screened 18 thousand drugs and validated 122 with antiviral a.. | ||
Mar 19 2021 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.649532 | Repurposing Anti-Malaria Phytomedicine Artemisinin as a COVID-19 Drug |
| Review of artemisinin, an anti-malaria phytomedicine with anti-inflammatory properties, as a potential COVID-19 drug. Authors explain that artemisinin, discovered by Nobel laureate Tu Youyu, shows broad-spectrum antiviral activity and spe.. | ||
Feb 1 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418 | Targeting TGF-β pathway with COVID-19 Drug Candidate ARTIVeda/PulmoHeal Accelerates Recovery from Mild-Moderate COVID-19 |
| 52% improved recovery (p=0.08). RCT 60 mild-moderate COVID-19 patients showing faster recovery with artemisinin. | ||
Apr 28 2020 |
et al., China Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200312-00412 | Clinical study of artesunate in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 |
| 31% faster recovery (p=0.02), 8% shorter hospitalization (p=0.22), and 29% faster viral clearance (p=0.05). Prospective study of 43 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing faster symptom improvement and shorter hospitalization with artesunate. Artesunate 60 mg twice daily for 10 days. | ||
Apr 24 2020 |
et al., ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12181404.v1 | In-Silico Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) from Natural Products: Quercetin, Hispidulin, and Cirsimaritin Exhibited Better Potential Inhibition than Hydroxy-Chloroquine Against COVID-19 Main Protease Active Site and ACE2 |
| In silico study of natural compounds identifying quercetin, curcumin, hispidulin, cirsimaritin, sulfasalazine, and artemisin as potential compounds that inhibit SARS-CoV-2. | ||