Targeting TGF-β pathway with COVID-19 Drug Candidate ARTIVeda/PulmoHeal Accelerates Recovery from Mild-Moderate COVID-19
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418, ARTI-19, CTRI/2020/09/028044, Feb 2021
46th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 3 studies, recognized in 13 countries.
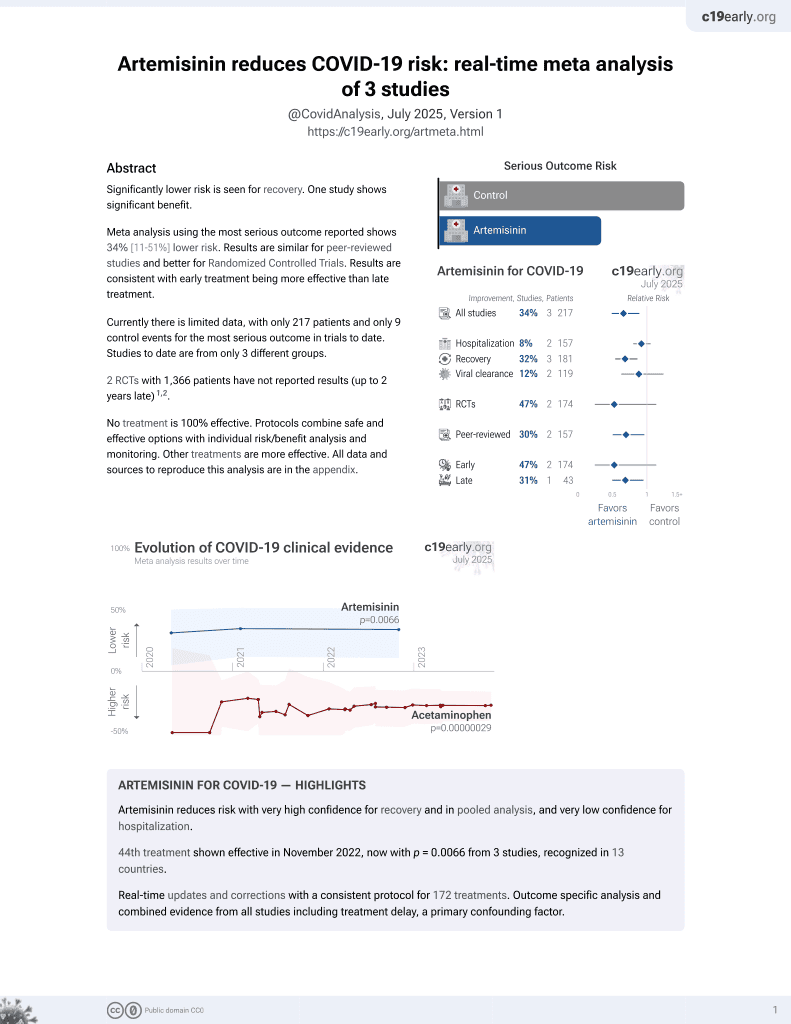
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
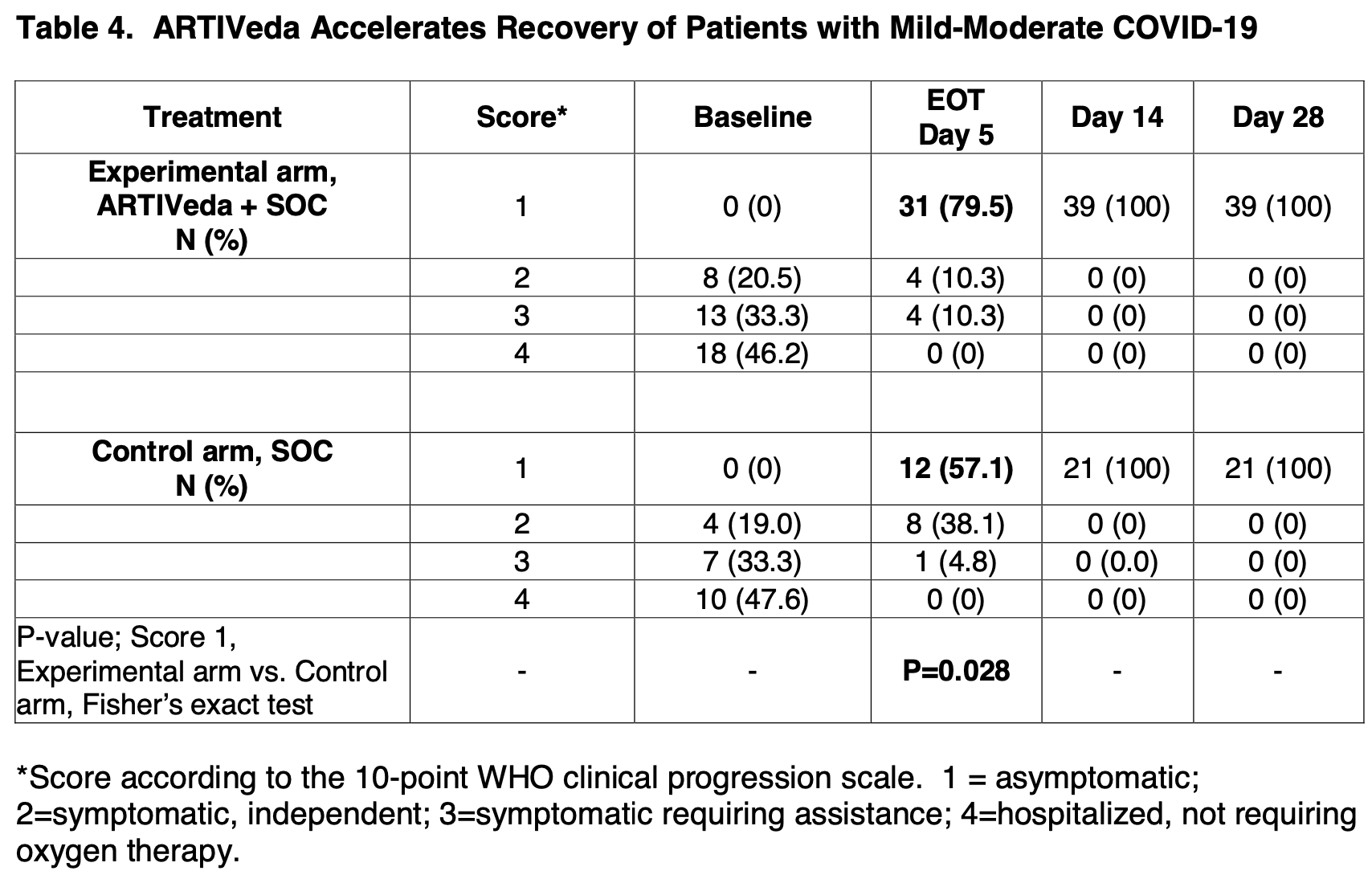
RCT 60 mild-moderate COVID-19 patients showing faster recovery with artemisinin.
|
risk of no recovery, 52.1% lower, RR 0.48, p = 0.08, treatment 8 of 39 (20.5%), control 9 of 21 (42.9%), NNT 4.5, day 5.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Trieu et al., 1 Feb 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, preprint, median age 44.5, 7 authors, study period 8 October, 2020 - 21 November, 2020, trial CTRI/2020/09/028044 (ARTI-19).
Contact: fatih.uckun@aresmit.com.
Targeting TGF-β pathway with COVID-19 Drug Candidate ARTIVeda/PulmoHeal Accelerates Recovery from Mild-Moderate COVID-19
doi:10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418
Our COVID-19 drug candidate ARTIVeda TM /PulmoHeal is a novel gelatin capsule formulation of the Artemisia extract Ayurveda for oral delivery of TGF-β targeting anti-malaria phytomedicine Artemisinin with documented anti-inflammatory and anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Here we report the safety and efficacy of ARTIVeda TM in adult COVID-19 patients with symptomatic mildmoderate COVID-19, who were treated in a randomized, open-label Phase IV study in Bangalore, Karnataka, India (Clinical Trials Registry India identifier: CTRI/2020/09/028044). ARTIVeda showed a very favorable safety profile, and the only ARTIVeda-related adverse events were transient mild rash and mild hypertension. Notably, ARTIVeda, when added to the SOC, accelerated the recovery of patients with mild-moderate COVID-19. While all patients were symptomatic at baseline (WHO score = 2-4), 31 of 39 (79.5%) of patients treated with ARTIVeda plus SOC became asymptomatic (WHO score = 1) by the end of the 5-day therapy, including 10 of 10 patients with severe dry cough 7 of 7 patients with severe fever. By comparison, 12 of 21 control patients (57.1%) treated with SOC alone became asymptomatic on day 5 (P=0.028, Fisher's exact test). This clinical benefit was particularly evident when the treatment outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients (WHO score = 4) treated with SOC
) 0 (0) 0 (0) Vertigo 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (2.6) 1 (2.6) 0 (0) 0 (0) Headache 1 (4.8) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Respiratory disorders 1 (4.8) 0 (0) 1 (4.8) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Dyspnea 1 (4.8) 0 (0) 1 (4.8) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Subjects reporting individual adverse events may not add up to the number of subjects within a System Organ Classification (SOC) because a subject may have reported more than one adverse event within an SOC term. For subjects reporting an adverse event with more than one severity assessment under the same MedDRA preferred term (PT), the highest severity is reported. System Organ Class (SOC) and preferred terms within each SOC were sorted alphabetically. The following COVID-19-related presenting signs and symptoms were not included as AEs in this table: Diarrhea, loss of taste/smell, cough, sore throat, conjunctivitis. Each of these have resolved in patients receiving ARTIVeda within 5 days.
References
Alhelfawi, Potential approach for fighting against corona virus disease, ASRJETS
Ashton, Gordi, Trinh, Artemisinin pharmacokinetics in healthy adults after 250, 500 and 1000 mg single oral doses, Biopharm Drug Dispos
Bossman, Ward, Protein-based Therapies for Acute Lung Injury: Targeting Neutrophil Extracellular Traps, Expert Opin Ther Targets, doi:10.1517/14728222.2014.902938
Budinger, Chandel, Donnelly, Eisenbart, Oberoi et al., Active transforming growth factor-b1 activates the procollagen I promoter in patients with acute lung injury, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-004-2503-2
Cao, Feng, Gao, Artemisinin enhances the anti-tumor immune response in 4T1 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, Int Immunopharmacol
Cao, Hu, Li, Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Potential of Artemisinins In Vitro, ACS Infect Dis
Duc, De Vries, Nguyen, Nguyen, Kager et al., The pharmacokinetics of a single dose of artemisinin in healthy Vietnamese subjects, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Faust, Krumholz, Du, All-Cause Excess Mortality and COVID-19-Related Mortality Among US Adults Aged 25-44 Years, March-July 2020, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24243
Fox, Akmatbekov, Harbert, Li, Brown et al., Pulmonary and cardiac Pathology in COVID -19; the first autopsy series from New Orleans, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.06.2
Frank, Matthay, TGF-β and lung fluid balance in ARDS, PNAS
Gilmore, Zhou, Ramirez, In vitro efficacy of Artemisinin-based treatments against SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.05.326637
Gordi, Huong, Hai, Nieu, Ashton, Artemisinin pharmacokinetics and efficacy in uncomplicated-malaria patients treated with two different dosage regimens, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
He, Ding, Zhang, He, Shen et al., Expression of elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in SARS-CoV infected ACE2+ cells in SARS patients: relation to the acute lung injury and pathogenesis of SARS, J. Pathol
Hien, Hanpithakpong, Truong, Orally formulated artemisinin in healthy fasting Vietnamese male subjects: a randomized, four-sequence, open-label, pharmacokinetic crossover study, Clin Ther
Hu, Huang, Alleviation of Inflammatory Response of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Puerarin via Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-b1), Med Sci Monit
Jenkins, Su, Su, Scotton, Camerer et al., Ligation of protease-activated receptor 1 enhances α(v)β6 integrin-dependent TGF-β activation and promotes acute lung injury, J Clin Invest
Kangbai, Babawo, Kaitibi, Sandi, George et al., Re-reading ACT, BCG, and Low COVID-19 in Africa, SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00704-3
Lev, Salim, Mela, Goette, Molinas, Platelets possess functional TGF-β receptors and Smad2 protein, Platelets, doi:10.1080/09537100600800743
Li, Li, Li, Zeng, Artemisinin-Based and Other Antimalarials: Detailed Account of Studies by Chinese Scientists Who Discovered and Developed Them
Li, Wang, Jou, Yang, Huang et al., SARS coronavirus papain-like protease induces Egr-1-dependent up-regulation of TGF-β1 via ROS/p38 MAPK/STAT3 pathway, Scientific Reports
Li, Yuan, Li, Safety and efficacy of artemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of COVID-19: an open-label, non-randomised and controlled trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Lin, Wu, Xie, Song, Zhu et al., Clinical study of Artesunate in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019, Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue, doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200312-00412
Nithiananthan, Crawford, Knock, Physiological fluid flow moderates fibroblast responses to TGF-beta1, J Cell Biochem
Peters, Vadasz, Wujak, TGF-β directs trafficking of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC which has implications for ion and fluid transport in acute lung injury, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.1306798111
Pittet, Griffiths, Geiser, Kaminski, Dalton et al., TGF-beta is a critical mediator of acute lung injury, J Clin Invest
Scaccabarozzi, Signorini, Perego, Dp, Ferrante et al., The Use Of Antimalarial Drugs Against Viral Infection, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/Microorganisms8010085
Sehailia, Chemat, In-silico Studies of Antimalarial-agent Artemisinin and Derivatives Portray More Potent Binding to Lys353 and Lys31-Binding Hotspots of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein than Hydroxychloroquine: Potential Repurposing of Artenimol for COVID-19, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12098652.v1
Shimbori, Bellaye, Xia, Fibroblast growth factor-1 attenuates TGF-beta1induced lung fibrosis, J Pathol
Stafford, Arnold, Jebakumar, Manglam, Sangwaiya et al., Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: New Insights Into The Value Of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGFβ) Antagonists Such As Imatinib and other Kinase Inhibitors, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1610
Uckun, Carlson, Orhan, Powell, Pizzimenti et al., Rejuveinix Shows a Favorable Clinical Safety Profile in Human Subjects and Exhibits Potent Preclinical Protective Activity in the Lipopolysaccharide-Galactosamine Mouse Model of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Multi-Organ Failure, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.594321
Uckun, Prognostic Factors Associated with High-Risk for Fatal ARDS in COVID-19 and Potential Role for Precision Medicines as Part of COVID-19 Supportive Care Algorithms, Ann Pulm Crit Care Med
Uckun, Reducing the Fatality Rate of COVID-19 by Applying Clinical Insights From Immuno-Oncology and Lung Transplantation, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00796
Uckun, Saund, Windlass, Trieu, Minireview] Repurposing Anti-Malaria Phytomedicine Artemisinin as a COVID-19 Drug, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Uckun, Trieu, Medical-Scientific Rationale for a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of Trabedersen/OT-101 in COVID-19 Patients with Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure, Annals Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
Vries, Tran, Nguyen, The pharmacokinetics of a single dose of artemisinin in patients with uncomplicated falciparum malaria, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Wang, Liu, Xie, Li, Yao et al., miR-425 reduction causes aberrant proliferation and collagen synthesis through modulating TGF-β/Smad signaling in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Int J Clin Exp Pathol
Wang, Lu, Li, Lai, Hua et al., SAR coronavirus papain-like protease up-regulates the collagen expression through non-Samd TGFβ1 signaling, Virus Research
Wang, Zou, Pan, Efficacy and Safety of Artemisinin-Piperaquine for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Malaria: A Systematic Review, Front Pharmacol
Woolf, Chapman, Lee, COVID-19 as the Leading Cause of Death in the United States, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24865
Woolf, Chapman, Sabo, Weinberger, Hill et al., Excess deaths from COVID-19 and other causes, March-July 2020, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.19545
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Internal Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Wu, Zhang, Shi, Sun, Wang, Therapeutic effect of artemisinin on lupus nephritis mice and its mechanisms, Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
Xiong, Liu, Cao, Wang, Guo et al., Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1747363
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Zhang, Qi, Song, Ling, Artemisinin attenuates early renal damage on diabetic nephropathy rats through suppressing TGF-β1 regulator and activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, Life Sci
Zhao, Nicholls, Chen, Severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus nucleocapsid protein interacts with Smad3 and modulates transforming growth factor-beta signalling, J. Biol. Chem
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Risk factors of critical and mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
Zhou, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140.6736(20)30566
Zuo, Yalavarthi, Shi, Gockman, Zuo et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.138999
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:p>Our COVID-19 drug candidate ARTIVeda™/PulmoHeal is a novel gelatin capsule formulation of the Artemisia extract Ayurveda for oral delivery of TGF-β targeting anti-malaria phytomedicine Artemisinin with documented anti-inflammatory and anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Here we report the safety and efficacy of ARTIVeda™ in adult COVID-19 patients with symptomatic mild-moderate COVID-19, who were treated in a randomized, open-label Phase IV study in Bangalore, Karnataka, India (Clinical Trials Registry India identifier: CTRI/2020/09/028044). ARTIVeda showed a very favorable safety profile, and the only ARTIVeda-related adverse events were transient mild rash and mild hypertension. Notably, ARTIVeda, when added to the SOC, accelerated the recovery of patients with mild-moderate COVID-19. While all patients were symptomatic at baseline (WHO score = 2-4), 31 of 39 (79.5%) of patients treated with ARTIVeda plus SOC became asymptomatic (WHO score = 1) by the end of the 5-day therapy, including 10 of 10 patients with severe dry cough 7 of 7 patients with severe fever. By comparison, 12 of 21 control patients (57.1%) treated with SOC alone became asymptomatic on day 5 (P=0.028, Fisher’s exact test). This clinical benefit was particularly evident when the treatment outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients (WHO score = 4) treated with SOC alone versus SOC plus ARTIVeda were compared. The median time to becoming asymptomatic was only 5 days for the SOC plus ARTIVeda group (N=18) but 14 days for the SOC alone group (N=10) (P=0.004, Log-rank test). These data provide clinical proof of concept that targeting the TGF-β pathway with ARTIVeda may contribute to a faster recovery of patients with mild-moderate COVID-19 when administered early in the course of their disease.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trieu",
"given": "Vuong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saund",
"given": "Saran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahate",
"given": "Prashant V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barge",
"given": "Viljay B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nalk",
"given": "K. Sunil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Windlass",
"given": "Hitesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9334-183X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uckun",
"given": "Fatih M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-01T16:37:51Z",
"timestamp": 1612197471000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-23T19:23:51Z",
"timestamp": 1619205831000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T16:47:07Z",
"timestamp": 1698770827169
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24865",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.19545",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24243",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.00796",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.7",
"unstructured": "Zheng Z , Peng F , Xu B et al. Risk factors of critical and mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Journal of Infection 2020; S0163-4453(20)30234-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prognostic Factors Associated with High-Risk for Fatal ARDS in COVID-19 and Potential Role for Precision Medicines as Part of COVID-19 Supportive Care Algorithms",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Ann Pulm Crit Care Med",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.8",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.594321",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-813133-6.00006-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.10",
"unstructured": "Li G , Li Y , Li Z , Zeng M. Chapter 6: Artemisinin and Derivatives: Clinical Studies. In Li G , Li Y , Li Z , Zeng M , eds. Artemisinin-Based and Other Antimalarials: Detailed Account of Studies by Chinese Scientists Who Discovered and Developed Them. Academic Press; 2018:353–413."
},
{
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "The Use Of Antimalarial Drugs Against Viral Infection Microorganisms",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.11",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.649532",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.12",
"unstructured": "Uckun FM , Saund S , Windlass H , Trieu V. [Minireview] Repurposing Anti-Malaria Phytomedicine Artemisinin as a COVID-19 Drug. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2021; submitted"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.12098652.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.14",
"unstructured": "Sehailia M , Chemat S. In-silico Studies of Antimalarial-agent Artemisinin and Derivatives Portray More Potent Binding to Lys353 and Lys31-Binding Hotspots of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein than Hydroxychloroquine: Potential Repurposing of Artenimol for COVID-19. ChemRxiv. 2020. Preprint. https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv.12098652.v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00522",
"article-title": "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Potential of Artemisinins In Vitro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2524",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect Dis",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.15",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.05.326637",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.16",
"unstructured": "Gilmore K , Zhou Y , Ramirez S , et al. In vitro efficacy of Artemisinin-based treatments against SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv. 2020. 10.05.326637; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.05.326637."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00704-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106216",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.18",
"unstructured": "Li G , Yuan M , Li H , et al. Safety and efficacy of artemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of COVID-19: an open-label, non-randomised and controlled trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;106216."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.1994.51.785",
"article-title": "The pharmacokinetics of a single dose of artemisinin in healthy Vietnamese subjects",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "785",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.19",
"volume": "51",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/(SICI)1099-081X(199805)19:4<245::AID-BDD99>3.0.CO;2-Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.04.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.1997.56.503",
"article-title": "The pharmacokinetics of a single dose of artemisinin in patients with uncomplicated falciparum malaria",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.22",
"volume": "56",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.46.4.1026-1031.2002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.562363",
"article-title": "Efficacy and Safety of Artemisinin-Piperaquine for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Malaria: A Systematic Review",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "562363",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.24",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.041",
"article-title": "Artemisinin enhances the anti-tumor immune response in 4T1 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.25",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117966",
"article-title": "Artemisinin attenuates early renal damage on diabetic nephropathy rats through suppressing TGF-β1 regulator and activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117966",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.26",
"volume": "256",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/abbs/gmq101",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.27"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential approach for fighting against corona virus disease",
"first-page": "127",
"journal-title": "ASRJETS",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.28",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.46891",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.29"
},
{
"article-title": "Medical-Scientific Rationale for a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of Trabedersen/OT-101 in COVID-19 Patients with Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure",
"first-page": "01",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Annals Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.30",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1747363",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.2067",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M708033200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2017.04.008",
"article-title": "SAR coronavirus papain-like protease up-regulates the collagen expression through non-Samd TGF-β1 signaling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Virus Research",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.34",
"volume": "235",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep25754",
"article-title": "SARS coronavirus papain-like protease induces Egr-1-dependent up-regulation of TGF-β1 via ROS/p38 MAPK/STAT3 pathway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25754",
"journal-title": "Scientific Reports",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.35",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI27183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI11963",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1322478111",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1306798111",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.39",
"unstructured": "Peters DM , Vadasz I , Wujak T et al., TGF-β directs trafficking of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC which has implications for ion and fluid transport in acute lung injury. PNAS 2013; E374–E383 www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1306798111"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-004-2503-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.138999",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/14728222.2014.902938",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/MSM.915570",
"article-title": "Alleviation of Inflammatory Response of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Puerarin via Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-b1)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6523",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Monit",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.43",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09537100600800743",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.06.2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1610",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.46",
"unstructured": "Stafford N , Arnold A , Jebakumar S , Manglam V , Sangwaiya A , Arnold J. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: New Insights Into The Value Of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGFβ) Antagonists Such As Imatinib and other Kinase Inhibitors. BMJ 2020; 369 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1610 (Published 22 April 2020)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.4768",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.25767",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.48"
},
{
"article-title": "miR-425 reduction causes aberrant proliferation and collagen synthesis through modulating TGF-β/Smad signaling in acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"first-page": "2604",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Exp Pathol",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.49",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.00",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200312-00412",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020314102350000_2021.01.24.21250418v1.51"
}
],
"reference-count": 51,
"references-count": 51,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.01.24.21250418"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Targeting TGF-β pathway with COVID-19 Drug Candidate ARTIVeda/PulmoHeal Accelerates Recovery from Mild-Moderate COVID-19",
"type": "posted-content"
}