Recent:Mahajan.
Feb 19 |
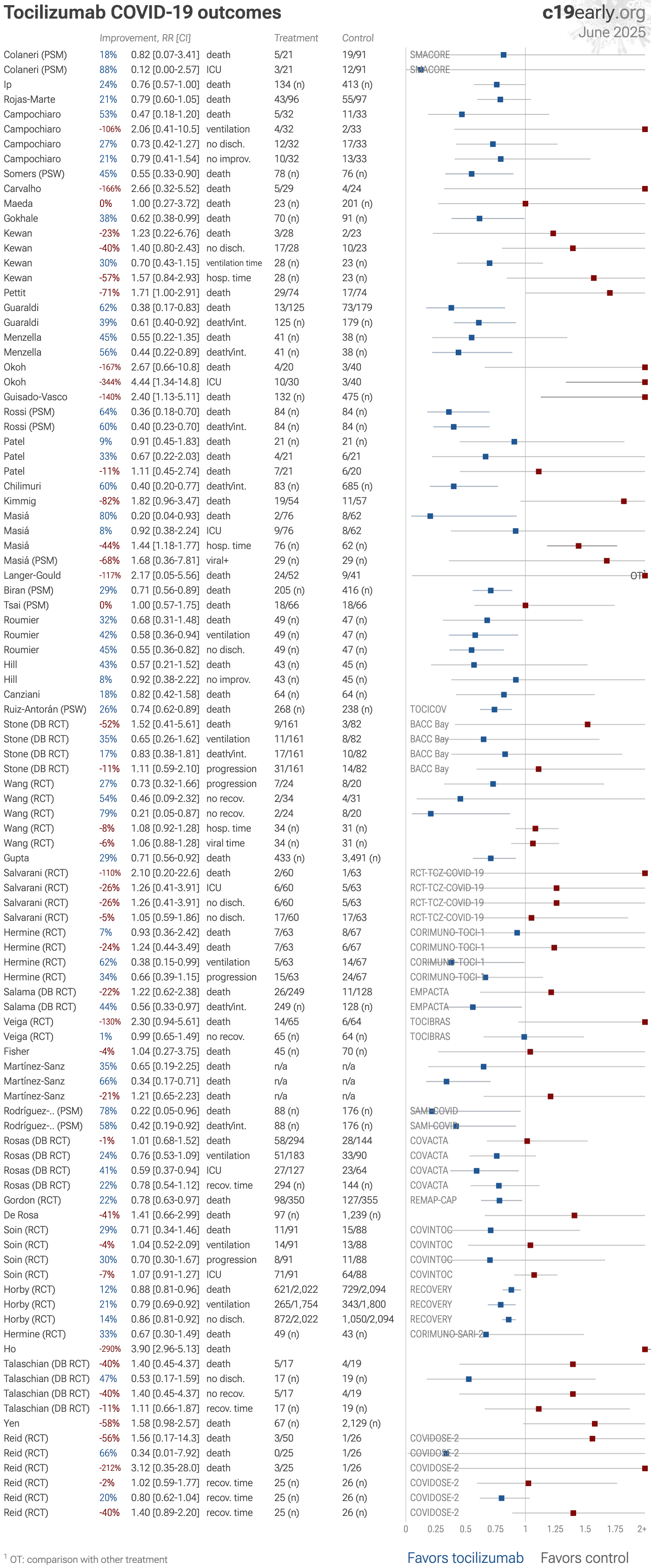
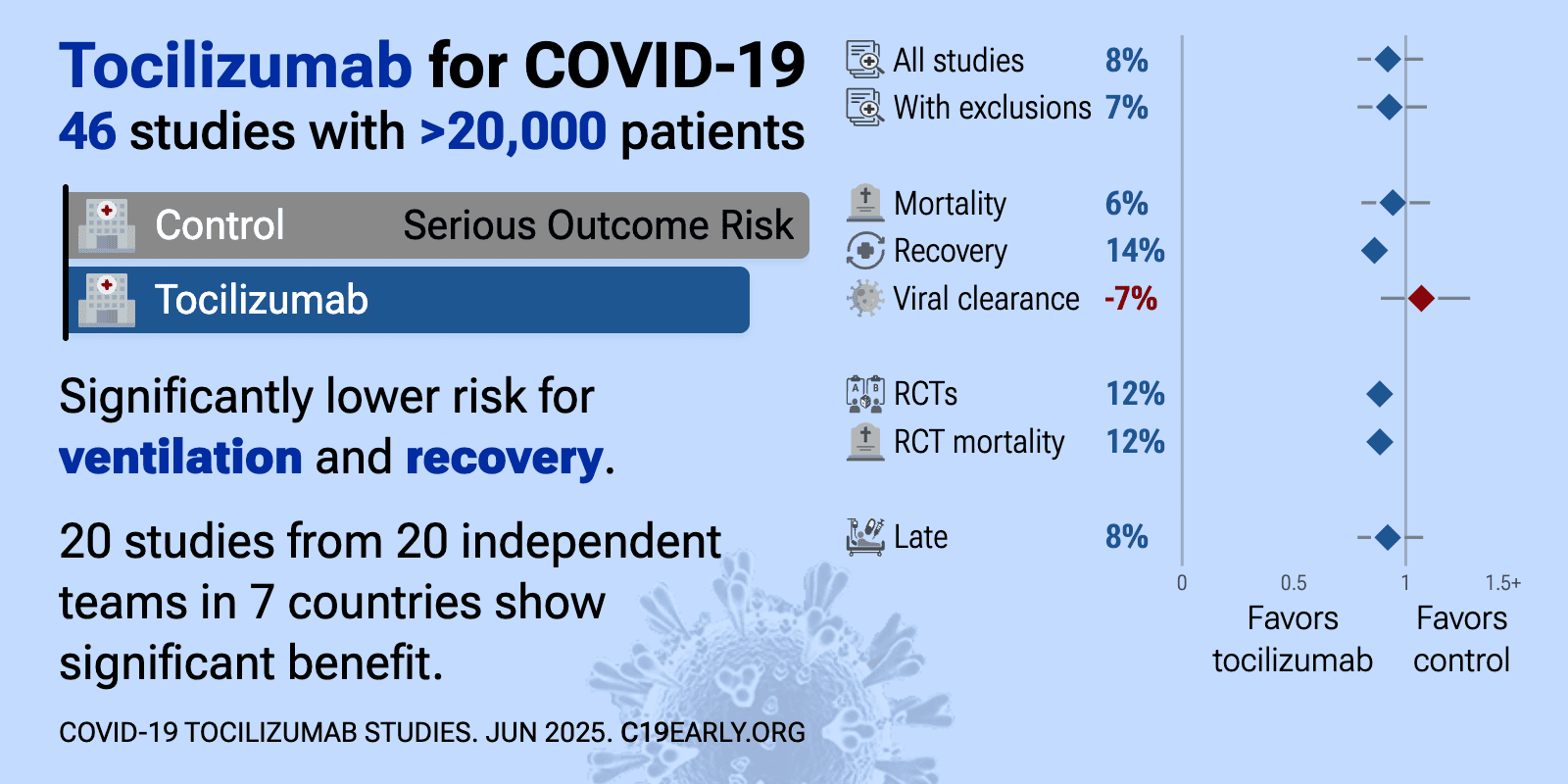
Tocilizumab for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 47 studies (Version 26) | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for ventilation and recovery. 21 studies from 21 independent teams in 8 countries show significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 8% [-6‑21%] lower risk, wi.. | ||
Jan 30 |
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms27031391 | Interleukins in COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Immunopathogenesis, Therapeutic Perspectives and Vaccine-Induced Immune Responses |
| Review of the role of interleukins in COVID-19 immunopathogenesis and therapeutic approaches. | ||
Sep 11 2025 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z | Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase |
| Retrospective disproportionality analysis of 276,631 COVID-19 adverse event reports from the WHO VigiBase database showing that remdesivir and baricitinib were associated with 2.4-fold and 2.3-fold increased odds of cardiovascular adverse.. | ||
Sep 2 2025 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.08.29.25334732 | Long-term follow-up of treatment comparisons in RECOVERY: a randomised, open-label, platform trial for patients hospitalised with COVID-19 |
| 6-month followup of RECOVERY patients. Results are reported within the respective trials for each treatment. | ||
Jul 6 2025 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-08638-3 | Tocilizumab as a targeted immunomodulatory therapy in the management of severe respiratory illnesses: a multicenter cohort study of COVID-19 patients |
| 16% lower mortality (p=0.002). Retrospective 1,470 critically ill COVID-19 patients in Saudi Arabia showing significantly lower mortality with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Mar 6 2025 |
et al., British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1002/bcp.70025 | Adverse events associated with monoclonal antibodies used for treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis |
| Systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 RCTs with 19,797 COVID-19 patients, showing a statistically significant increased risk of hepatotoxicity and neutropenia associated with monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments compared to standard o.. | ||
Feb 10 2025 |
et al., NCT04479358 | COVIDOSE-2: A Multi-center, Randomized, Controlled Phase 2 Trial Comparing Early Administration of Low-dose Tocilizumab to Standard of Care in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonitis Not Requiring Invasive Ventilation |
| 2% slower recovery (p=0.94). RCT 85 patients in the USA showing no significant differences with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Nov 8 2024 |
et al., Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6 | The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death |
| Review of the effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on cell death pathways in SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 induces oxidative stress and ROS generation which can lead to several types of regulated cell death including NETosis, ferro.. | ||
Aug 20 2024 |
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09654-w | Predictors for cause-specific and timing of deaths in patients with COVID-19: a cohort study in Taiwan |
| 58% higher mortality (p=0.06). Retrospective 2,196 COVID-19 patients in Taiwan (49% mild cases, 44% moderate, 7% severe) showing higher mortality with tocilizumab, without statistical significance. | ||
Feb 20 2024 |
et al., Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, doi:10.18502/ijaai.v23i1.14956 | Tocilizumab Failed to Reduce Mortality in Severe COVID-19 Patients: Results from a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial |
| 40% higher mortality (p=0.71), 47% higher hospital discharge (p=0.26), and 40% worse recovery (p=0.71). RCT 40 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran showing no significant improvement in mortality, clinical outcomes, or oxygen therapy requirements with tocilizumab treatment. The study found no significant differences between the tocilizuma.. | ||
Nov 20 2023 |
et al., Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice, doi:10.1186/s40545-023-00662-w | Does tocilizumab have an effect on the clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients? A meta-analysis of randomized control trials |
| Meta-analysis of 17 RCTs showing no significant differences with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Oct 31 2023 |
et al., HCA Healthcare Journal of Medicine, doi:10.36518/2689-0216.1546 | A Retrospective Cohort Study Assessing the Impact of Statin Therapy on Hospital Length of Stay and Inpatient Mortality in COVID-19 Patients |
| 290% higher mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective 26,445 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the USA, showing higher mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Feb 3 2022 |
et al., European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.02523-2021 | Effect of interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: two randomised controlled trials of the CORIMUNO-19 Collaborative Group |
| 33% lower mortality (p=0.33). Two open-label RCTs of 97 and 91 critically ill COVID-19 patients in France showing no significant differences with tocilizumab or sarilumab. | ||
May 31 2021 |
et al., The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0 | Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial |
| 13% lower mortality (p=0.008), 21% lower ventilation (p=0.002), and 14% higher hospital discharge (p<0.0001). RCT 4,116 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significantly lower mortality with tocilizumab. 6-month results are from [Horby] | ||
May 31 2021 |
et al., The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00081-3 | Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial |
| 29% lower mortality (p=0.4), 4% higher ventilation (p=1), 30% lower progression (p=0.47), and 7% higher ICU admission (p=0.49). RCT 180 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 in India showing no significant difference in disease progression with tocilizumab. | ||
May 1 2021 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10091951 | Risk Factors for Mortality in COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients in Piedmont, Italy: Results from the Multicenter, Regional, CORACLE Registry |
| 41% higher mortality (p=0.38). Retrospective 1,538 hospitalized patients in Italy, showing only HCQ associated with reduced mortality. Authors analyze mortality amongst those that were alive at day 7 to avoid survival time bias due to drug recording requiring a minimum.. | ||
Apr 30 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.057 | Tocilizumab treatment in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A retrospective observational study |
| Retrospective 96 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with tocilizumab in unadjusted results, however the groups are not comparable, for example the tocilizumab group was significantly more likely to be treated with HC.. | ||
Apr 26 2021 |
et al., Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100751 | Clinical review of COVID-19 patients presenting to a quaternary care private hospital in South India: A retrospective study |
| 429% higher mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective 3,345 hospitalized patients in India, showing higher mortality with remdesivir and tocilizumab in unadjusted results. Confounding by indication is likely. | ||
Apr 22 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433 | Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19 |
| 22% lower mortality (p=0.03). RCT 803 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing improved outcomes with tocilizumab and sarilumab. There was only 48 sarilumab patients and the model used shrinks the posterior distribution for each intervention effect toward the overall .. | ||
Apr 22 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028700 | Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia |
| 1% higher mortality (p=1), 24% lower ventilation (p=0.16), 41% lower ICU admission (p=0.04), and 22% faster recovery (p=0.18). RCT 452 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia showing no significant difference in clinical status or mortality at day 28 with tocilizumab. There was significantly lower ICU admission for patients not in the ICU at baseline. | ||
Feb 28 2021 |
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.010 | Treatment with tocilizumab or corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients with hyperinflammatory state: a multicentre cohort study (SAM-COVID-19) |
| 78% lower mortality (p=0.04) and 58% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.03). Retrospective 778 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hyperinflammatory state showing tocilizumab associated with lower mortality. The 1:2 PSM analysis may be the most accurate because it provides documented, tight covariate balance acros.. | ||
Feb 28 2021 |
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021 | Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicentre cohort study |
| 35% lower mortality (p=0.51). Retrospective 1,229 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Spain showing that tocilizumab was associated with decreased mortality in patients with high C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (>150 mg/L) but not in those with lower CRP levels. | ||
Feb 28 2021 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.021 | Tocilizumab in the treatment of critical COVID-19 pneumonia: A retrospective cohort study of mechanically ventilated patients |
| 4% higher mortality (p=0.96). Retrospective 115 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients showing no mortality benefit with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Jan 20 2021 |
et al., BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n84 | Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial |
| 130% higher mortality (p=0.09) and 1% improved recovery (p=0.96). RCT 129 hospitalized patients with severe or critical COVID-19 in Brazil showing no benefit and potential harm with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Jan 7 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2030340 | Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia |
| 22% higher mortality (p=0.72) and 44% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.03). RCT 377 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pneumonia showing that tocilizumab significantly reduced mechanical ventilation or death by day 28, however there was no difference in mortality alone. | ||
Jan 1 2021 |
et al., JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820 | Effect of Tocilizumab vs Usual Care in Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Moderate or Severe Pneumonia |
| 7% lower mortality (p=1), 62% lower ventilation (p=0.05), and 34% lower progression (p=0.18). RCT 130 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with moderate or severe pneumonia showing tocilizumab did not reduce WHO-CPS scores below 5 at day 4 (primary outcome), but reduced the proportion of patients needing noninvasive ventilation, high-fl.. | ||
Jan 1 2021 |
et al., JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615 | Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia |
| 110% higher mortality (p=0.61), 26% higher ICU admission (p=0.76), and 26% lower hospital discharge (p=0.76). RCT 126 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pneumonia showing no significant benefit of tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Jan 1 2021 |
et al., JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252 | Association Between Early Treatment With Tocilizumab and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 |
| 29% lower mortality (p=0.007). Retrospective 3,924 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Dec 31 2020 |
et al., SSRN Electronic Journal, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3667681 | Tocilizumab Ameliorates the Hypoxia in COVID-19 Moderate Patients with Bilateral Pulmonary Lesions: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Multicenter Trial |
| 27% lower progression (p=0.53), 8% longer hospitalization (p=0.35), and 6% slower viral clearance (p=0.54). RCT 65 COVID-19 patients in China showing improvement in hypoxia recovery with tocilizumab treatment, especially in moderate patients with bilateral pulmonary lesions. | ||
Dec 10 2020 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028836 | Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 |
| 52% higher mortality (p=0.54), 35% lower ventilation (p=0.36), 17% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.65), and 11% higher progression (p=0.76). RCT 243 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 showing no significant difference in intubation or death with tocilizumab compared to placebo. Authors hypothesize that elevated interleukin-6 levels may represent host responses to infection ra.. | ||
Dec 6 2020 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8 | Combination of Tocilizumab and Steroids to Improve Mortality in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Spanish, Multicenter, Cohort Study |
| 26% lower mortality (p=0.001). Retrospective 506 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Spain showing lower mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Nov 30 2020 |
et al., Journal of Autoimmunity, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102511 | Interleukin-6 receptor blocking with intravenous tocilizumab in COVID-19 severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective case-control survival analysis of 128 patients |
| 18% lower mortality (p=0.57). Retrospective case-control study of 128 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory impairment showing no significant difference in 30-day mortality with intravenous tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Nov 22 2020 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26674 | Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with COVID‐19: Clinical outcomes, inflammatory marker kinetics, and safety |
| 43% lower mortality (p=0.27) and 8% greater improvement (p=0.86). Retrospective 88 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in clinical improvement or mortality with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Nov 14 2020 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Immunology, doi:10.1007/s10875-020-00911-6 | Tocilizumab for Severe Worsening COVID-19 Pneumonia: a Propensity Score Analysis |
| 32% lower mortality (p=0.34), 42% lower ventilation (p=0.03), and 45% higher hospital discharge (p=0.03). Prospective analysis of 96 hospitalized patients with severe worsening COVID-19 pneumonia showing that tocilizumab treatment was associated with reduced need for ventilatory support and shorter time to oxygen withdrawal, however there wa.. | ||
Nov 5 2020 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-76187-y | Impact of tocilizumab administration on mortality in severe COVID-19 |
| no change in mortality (p=1). PSM retrospective 274 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no difference in mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Oct 31 2020 |
et al., The Lancet Rheumatology, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0 | Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study |
| 29% lower mortality (p=0.004). Retrospective 764 COVID-19 patients requiring ICU support showing lower mortality with tocilizumab. There was significantly higher use of HCQ+AZ in the treatment group, which was not adjusted for in the propensity score matching or Cox re.. | ||
Oct 31 2020 |
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.081 | Early identification of COVID-19 cytokine storm and treatment with anakinra or tocilizumab |
| 117% higher mortality (p=0.53). Retrospective 93 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with cytokine storm showing no significant difference between anakinra and tocilizumab treatment after adjusting for baseline characteristics. | ||
Oct 31 2020 |
et al., EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999 | Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study |
| 80% lower mortality (p=0.04), 8% lower ICU admission (p=1), 44% longer hospitalization (p=0.0004), and 68% worse viral clearance (p=0.51). Prospective cohort study of 138 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Oct 28 2020 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.583897 | IL-6 Inhibition in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients Is Associated With Increased Secondary Infections |
| 82% higher mortality (p=0.09). Retrospective 111 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing that tocilizumab treatment was associated with increased secondary bacterial infections, higher mortality (35.2% vs 19.3%, p=0.020), and a trend toward more fungal infections (5.6.. | ||
Oct 24 2020 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, doi:10.1111/jcpt.13303 | Tocilizumab use in patients with moderate to severe COVID‐19: A retrospective cohort study |
| 60% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.008). Retrospective 1,225 hospitalized patients showing lower mortality/intubation with tocilizumab. | ||
Oct 20 2020 |
et al., Journal of Internal Medicine, doi:10.1111/joim.13163 | Use of the IL‐6R antagonist tocilizumab in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients |
| 9% lower mortality (p=0.8). Retrospective 42 hospitalized COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab showing no significant differences in mortality compared to matched controls. | ||
Oct 17 2020 |
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph13100317 | Effect of Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case-Control Cohort Study |
| 64% lower mortality (p=0.003) and 60% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.001). Retrospective 246 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia showing significantly lower mortality with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Oct 15 2020 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100591 | Clinical characteristics and outcomes among hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19 admitted to a tertiary medical center and receiving antiviral, antimalarials, glucocorticoids, or immunomodulation with tocilizumab or cyclosporine: A retrospective observational study (COQUIMA cohort) |
| 140% higher mortality (p=0.02). Retrospective 607 patients showing higher mortality with tocilizumab use. | ||
Oct 5 2020 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26471 | Tocilizumab use in COVID‐19‐associated pneumonia |
| 167% higher mortality (p=0.21) and 344% higher ICU admission (p=0.01). PSM retrospective 77 hospitalized patients receiving tocilizumab treatment and matched controls, showing no significant difference in outcomes. | ||
Sep 29 2020 |
et al., Critical Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03306-6 | Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 ARDS undergoing noninvasive ventilation |
| 45% lower mortality (p=0.19) and 56% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.02). Retrospective 79 COVID-19 patients with ARDS undergoing noninvasive ventilation showing lower risk of intubation or death with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Aug 31 2020 |
et al., The Lancet Rheumatology, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9 | Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study |
| 62% lower mortality (p=0.02) and 39% lower combined mortality/intubation (p=0.02). Retrospective 544 patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia showing lower mechanical ventilation or death with tocilizumab. | ||
Aug 21 2020 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26429 | Late onset infectious complications and safety of tocilizumab in the management of COVID‐19 |
| 71% higher mortality (p=0.05). Retrospective 74 hospitalized COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab and 74 matched controls, showing higher mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418 | Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID–19: A retrospective cohort study |
| 40% lower hospital discharge (p=0.27), 30% shorter ventilation (p=0.16), and 57% longer hospitalization (p=0.16). Retrospective 51 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significant reduction in vasopressor support duration with tocilizumab treatment, but no significant difference in other outcomes. | ||
Jul 31 2020 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100467 | Tocilizumab improves survival in patients with persistent hypoxia in severe COVID-19 pneumonia |
| 38% lower mortality (p=0.05). Retrospective cohort study of 161 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and persistent hypoxia showing survival benefit with tocilizumab. | ||
Jul 28 2020 |
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26365 | The association of interleukin‐6 value, interleukin inhibitors, and outcomes of patients with COVID‐19 in New York City |
| no change in mortality (p=1). Retrospective 224 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the USA, showing no significant difference in mortality with tocilizumab. | ||
Jul 15 2020 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.13.20149328 | Effects of Tocilizumab in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Quasi-Experimental Study |
| 166% higher mortality (p=0.3). Retrospective 53 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing no difference in mortality, need for renal replacement therapy, use of antibiotics, or positive cultures with tocilizumab treatment. | ||
Jul 11 2020 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa954 | Tocilizumab for Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19 |
| 45% lower mortality (p=0.02). Retrospective 154 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients showing improved survival with tocilizumab. However, tocilizumab was associated with significantly higher rates of superinfection, particularly ventilator-associated pneumonia. | ||
Jun 30 2020 |
et al., European Journal of Internal Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.021 | Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19 patients: a single-centre retrospective cohort study |
| 53% lower mortality (p=0.15), 27% higher hospital discharge (p=0.32), and 21% greater improvement (p=0.61). \Retrospective 65 severe COVID-19 patients showing no statistically significant differences with tocilizumab. | ||
Jun 19 2020 |
et al., QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcaa206 | Outcomes in patients with severe COVID-19 disease treated with tocilizumab: a case–controlled study |
| 21% lower mortality (p=0.11). Retrospective case-control study of 193 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing a non-statistically significant trend toward lower mortality with tocilizumab treatment. When excluding intubated patients, tocilizumab was associated with sig.. | ||
May 25 2020 |
et al., PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0237693 | Hydroxychloroquine and Tocilizumab Therapy in COVID-19 Patients - An Observational Study |
| 24% lower mortality (p=0.06). Retrospective 2,512 hospitalized patients showing lower mortality with tocilizumab treatment within a subset of ICU patients, 143 treated with tocilizumab with adequate data, and 413 control patients. | ||
May 9 2020 |
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8050695 | Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE) |
| 18% lower mortality (p=0.85) and 88% lower ICU admission (p=0.43). PSM retrospective 112 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in ICU admission or mortality with tocilizumab. | ||