Combination of Tocilizumab and Steroids to Improve Mortality in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Spanish, Multicenter, Cohort Study
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8, TOCICOV, EUPAS34415, Dec 2020
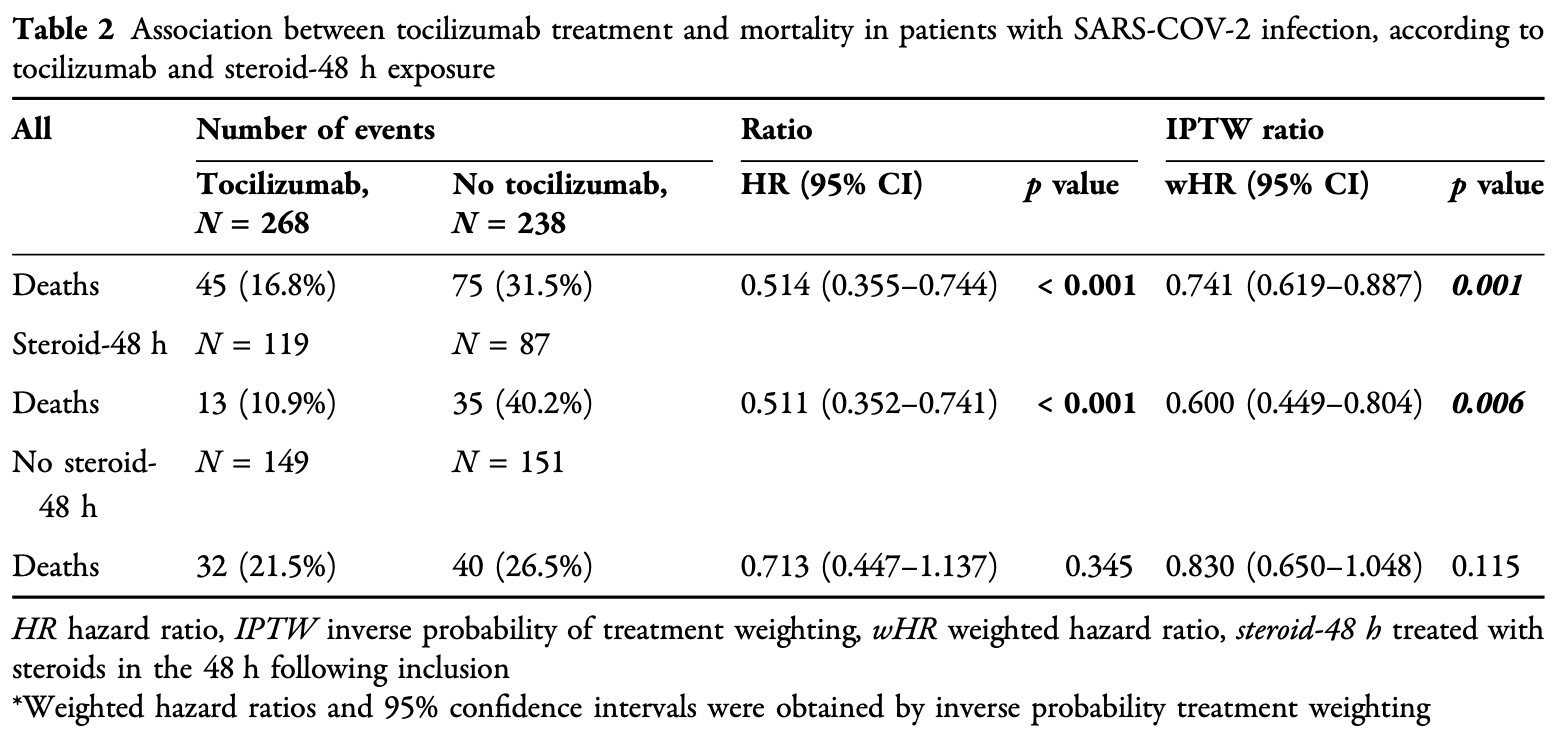
Retrospective 506 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Spain showing lower mortality with tocilizumab.
|
risk of death, 25.9% lower, HR 0.74, p = 0.001, treatment 268, control 238, propensity score weighting.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ruiz-Antorán et al., 6 Dec 2020, retrospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, 25 authors, study period 3 March, 2020 - 20 April, 2020, trial EUPAS34415 (TOCICOV).
Contact: bruizantoran@gmail.com, anafcruz999@gmail.com.
Combination of Tocilizumab and Steroids to Improve Mortality in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Spanish, Multicenter, Cohort Study
doi:10.1007/s40121-020
Background: We aimed to determine the impact of tocilizumab use on severe COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 19) pneumonia mortality. Methods: We performed a multicentre retrospective cohort study in 18 tertiary hospitals in Spain from March to April 2020. Consecutive patients admitted with severe COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab were compared to patients not treated with tocilizumab, adjusting by inverse probability of the treatment weights (IPTW). Tocilizumab's effect in patients receiving steroids during the 48 h following inclusion was analysed. Results: During the study period, 506 patients with severe COVID-19 fulfilled the inclusion Bele ´n Ruiz-Antora ´n and Ara ´nzazu Sancho-Lo ´pez contributed equally to this work.
Authorship Contribution. Conceptualization and study design: ASL, BRA, AFC. Methodology: BRA, AFC, ASL, F-T. Data collection: all authors. Data interpretation: ASL, BRA, AFC, FT. Writing first draft: ASL, BRA, AFC. Critical revision for important intellectual content: all authors. Final approval: All authors. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work by ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work will be appropriately investigated and resolved. AFC and BRA had full access to all the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Prior Presentation. This manuscript is based on work that has been previously presented at medRxiv, posted 10 September 2020 ( https:// www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.09 .
07.20189357v2). Disclosures. Bele ´n Ruiz-Antora ´n, Ara ´nzazu Sancho-Lo ´pez, Ferra ´n Torres, Vı ´ctor Moreno-Torres, Itziar de Pablo-Lo ´pez, Paulina Garcı ´a-Lo ´pez, Francisco Abad-Santos, Clara M. Rosso-Ferna ´ndez, Ana Aldea-Perona, Eva Montane ´, Ruth M. Aparicio-Herna ´ndez, Roser Llop-Rius, Consuelo Pedro ´s, Paloma Gijo ´n, Carolina Herna ´ndez-Carballo, Marı ´a J Pedrosa-Martı ´nez, Consuelo Rodrı ´guez-Jime ´nez, Guillermo Prada-Ramallal, Lourdes Cabrera-Garcı ´a, Josefa A. Aguilar-Garcı ´a, Rocı ´o Sanjuan-Jimenez, Evelyn I. Ortiz-Barraza, Enrique Sa ´nchez-Chica and Ana Ferna ´ndez-Cruz declare no conflicts of interest...
References
Agostino, Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non-randomized control group, Stat Med
Austin, An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies, Multivariate Behav Res
Austin, Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples, Stat Med
Campins, Boixeda, Perez-Cordon, Aranega, Lopera et al., Early tocilizumab treatment could improve survival among COVID-19 patients, Clin Exp Rheumatol
Cascella, Rajnik, Cuomo, Dulebohn, Napoli, Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19)
Cohen, Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, doi:10.4324/9780203771587
Fadel, Morrison, Vahia, Smith, Chaudhry et al., Early short course corticosteroids in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa601
Ferna ´ndez-Cruz, Ruiz-Antora ´n, ˜oz-Go ´mez, ´pez, Mills-Sa ´nchez et al., A retrospective controlled cohort study of the impact of glucocorticoid treatment in SARS-CoV-2 infection mortality, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.01168-20
Foca, Linee guida sulla gestione terapeutica e di supporto per pazienti con infezione da coronavirus COVID-19
Fu, Xu, Wei, Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19?, J Transl Med
Gorgolas, Cabello, Perez, Alvarez, Alvarez et al., Compassionate use of tocilizumab in severe SARS-CoV2 pneumonia. When late administration is too late, medRxiv
Guaraldi, Meschiari, Cozzi-Lepri, Milic, Tonelli et al., Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
Herrero, Gimeno, Garcı ´a, Go ´mez, Mocho ´n et al., Methylprednisolone added to tocilizumab reduces mortality in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: an observational study, J Internal Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13145
Li, Fan, Lai, Han, Li et al., Coronavirus infections and immune responses, J Med Virol
Martı ´nez-Sanz, Ron, Herrera, Pe ´rez-Molina, Moreno, Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicentre cohort study, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021
Mcgonagle, Sharif, 'regan, Bridgewood, The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease, Autoimmun Rev
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Mikulska, Nicolini, Signori, Biagio, Sepulcri et al., Tocilizumab and steroid treatment in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, PLoS ONE
Narain, Stefanov, Chau, Weber, Marder et al., Comparative survival analysis of immunomodulatory therapy for coronavirus disease 2019 cytokine storm, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.275
Rodrı ´guez-Ban ˜o, Pacho ´n, Carratala, Ryan, Jarrı ´n I et al., Treatment with tocilizumab or corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients with hyperinflammatory state: a multicentre cohort study (SAM-COVID-19), Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.010
Rosenbaum, The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects, Biometrika
Salvarani, Dolci, Massari, Merlo, Cavuto et al., Effect of tocilizumab vs standard care on clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615
Somers, Eschenauer, Troost, Golob, Gandhi et al., Tocilizumab for treatment of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1101/2020.05.29.20117358
Who, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation Report-164
Xu, Han, Li, Sun, Wang et al., Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8",
"ISSN": [
"2193-8229",
"2193-6382"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8",
"alternative-id": [
"373"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "7 October 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "16 November 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "6 December 2020"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "the TOCICOV-study group",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2020-9077",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ruiz-Antorán",
"given": "Belén",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sancho-López",
"given": "Aránzazu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torres",
"given": "Ferrán",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moreno-Torres",
"given": "Víctor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Pablo-López",
"given": "Itziar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-López",
"given": "Paulina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abad-Santos",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosso-Fernández",
"given": "Clara M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldea-Perona",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montané",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aparicio-Hernández",
"given": "Ruth M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Llop-Rius",
"given": "Roser",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pedrós",
"given": "Consuelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gijón",
"given": "Paloma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hernández-Carballo",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pedrosa-Martínez",
"given": "María J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodríguez-Jiménez",
"given": "Consuelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prada-Ramallal",
"given": "Guillermo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cabrera-García",
"given": "Lourdes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aguilar-García",
"given": "Josefa A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanjuan-Jimenez",
"given": "Rocío",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ortiz-Barraza",
"given": "Evelyn I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sánchez-Chica",
"given": "Enrique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernández-Cruz",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-06T03:02:19Z",
"timestamp": 1607223739000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-12T06:41:31Z",
"timestamp": 1615531291000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-19T12:33:53Z",
"timestamp": 1747658033841,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 42,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1607212800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1607212800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "347-362",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "373_CR1",
"unstructured": "WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation Report—164 [Internet]. 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200702-covid-19-sitrep-164.pdf?sfvrsn=ac074f58_2. Accessed 4 Jul 2020."
},
{
"key": "373_CR2",
"unstructured": "Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England).",
"key": "373_CR3",
"unstructured": "Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395:1033–4.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537",
"author": "D McGonagle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102537",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "373_CR4",
"unstructured": "McGonagle D, Sharif K, O’Regan A, Bridgewood C. The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19(6):102537.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25685",
"author": "G Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "424",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "373_CR5",
"unstructured": "Li G, Fan Y, Lai Y, Han T, Li Z, Zhou P, et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J Med Virol. 2020;92(4):424–32.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02339-3",
"author": "B Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med.",
"key": "373_CR6",
"unstructured": "Fu B, Xu X, Wei H. Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19? J Transl Med. 2020;18:164.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"author": "X Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10970",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "373_CR7",
"unstructured": "Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, Fu B, et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(20):10970–5.",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "373_CR8",
"unstructured": "Foca E. Linee guida sulla gestione terapeutica e di supporto per pazienti con infezione da coronavirus COVID-19. 2020; Marzo. http://www.fvcalabria.unicz.it/COVID-19/LINEE-GUIDA/linee-guida-SIMIT-marzo-2020.pdf. Accessed 1 Oct 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19981015)17:19<2265::AID-SIM918>3.0.CO;2-B",
"author": "RBJ D’Agostino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2265",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "373_CR9",
"unstructured": "D’Agostino RBJ. Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non-randomized control group. Stat Med. 1998;17(19):2265–81.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/biomet/70.1.41",
"author": "PR Rosenbaum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Biometrika",
"key": "373_CR10",
"unstructured": "Rosenbaum PR, RDTcro. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika. 1983;70:41–55.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00273171.2011.568786",
"author": "PC Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "399",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Multivariate Behav Res",
"key": "373_CR11",
"unstructured": "Austin PC. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivariate Behav Res. 2011;46(3):399–424.",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4324/9780203771587",
"author": "DJ Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR12",
"unstructured": "Cohen DJ. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Routledge; 2013. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203771587.",
"volume-title": "Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3697",
"author": "PC Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3083",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "373_CR13",
"unstructured": "Austin PC. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat Med. 2009;28(25):3083–107.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9",
"author": "G Guaraldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e474",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "373_CR14",
"unstructured": "Guaraldi G, Meschiari M, Cozzi-Lepri A, Milic J, Tonelli R, Menozzi M, et al. Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(8):e474–84.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR15",
"unstructured": "Martínez-Sanz J, Muriel A, Ron R, Herrera S, Pérez-Molina JA, Moreno S, et al. Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicentre cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR16",
"unstructured": "Rodríguez-Baño J, Pachón J, Carratalá J, Ryan P, Jarrín I, Yllescas M, et al. Treatment with tocilizumab or corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients with hyperinflammatory state: a multicentre cohort study (SAM-COVID-19). Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.010."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR17",
"unstructured": "Salvarani C, Dolci G, Massari M, Merlo DF, Cavuto S, Savoldi L, et al. Effect of tocilizumab vs standard care on clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa601",
"author": "R Fadel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2114",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis.",
"key": "373_CR18",
"unstructured": "Fadel R, Morrison AR, Vahia A, Smith ZR, Chaudhry Z, Bhargava P, et al. Early short course corticosteroids in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(16):2114–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa601.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01168-20",
"author": "A Fernández-Cruz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e01168",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother.",
"key": "373_CR19",
"unstructured": "Fernández-Cruz A, Ruiz-Antorán B, Muñoz-Gómez A, Sancho-López A, Mills-Sánchez P, Centeno-Soto GA, et al. A retrospective controlled cohort study of the impact of glucocorticoid treatment in SARSCoV-2 infection mortality. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64(9):e01168. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01168-20.",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "L Campins",
"first-page": "578",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Rheumatol.",
"key": "373_CR20",
"unstructured": "Campins L, Boixeda R, Perez-Cordon L, Aranega R, Lopera C, Force L. Early tocilizumab treatment could improve survival among COVID-19 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38:578.",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "373_CR21",
"unstructured": "Gorgolas M, Cabello A, Prieto Perez L, Villar Alvarez F, Alvarez Alvarez B, Rodriguez Nieto MJ, et al. Compassionate use of tocilizumab in severe SARS-CoV2 pneumonia. When late administration is too late. medRxiv [Internet]. 2020;2020.06.13.20130088. http://medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/06/16/2020.06.13.20130088.abstract. Accessed 5 Oct 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0237831",
"author": "M Mikulska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0237831",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "373_CR22",
"unstructured": "Mikulska M, Nicolini LA, Signori A, Di Biagio A, Sepulcri C, Russo C, et al. Tocilizumab and steroid treatment in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(8):e0237831.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.275",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR23",
"unstructured": "Narain S, Stefanov DG, Chau AS,Weber AG, Marder G, Kaplan B, et al. Comparative survival analysis of immunomodulatory therapy for coronavirus disease 2019 cytokine storm. Chest. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.275."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR24",
"unstructured": "Sanz Herrero F, Puchades Gimeno F, Ortega García P, Ferrer Gómez C, Ocete Mochón MD, García Deltoro M. Methylprednisolone added to tocilizumab reduces mortality in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: an observational study. J Internal Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13145."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.29.20117358",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "373_CR25",
"unstructured": "Somers EC, Eschenauer GA, Troost JP, Golob JL, Gandhi TN, Wang L, et al. Tocilizumab for treatment of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19. MedRxiv. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.29.20117358. Update in: Clin Infect Dis. 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.09.07.20189357",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40121-020-00373-8"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Combination of Tocilizumab and Steroids to Improve Mortality in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Spanish, Multicenter, Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}