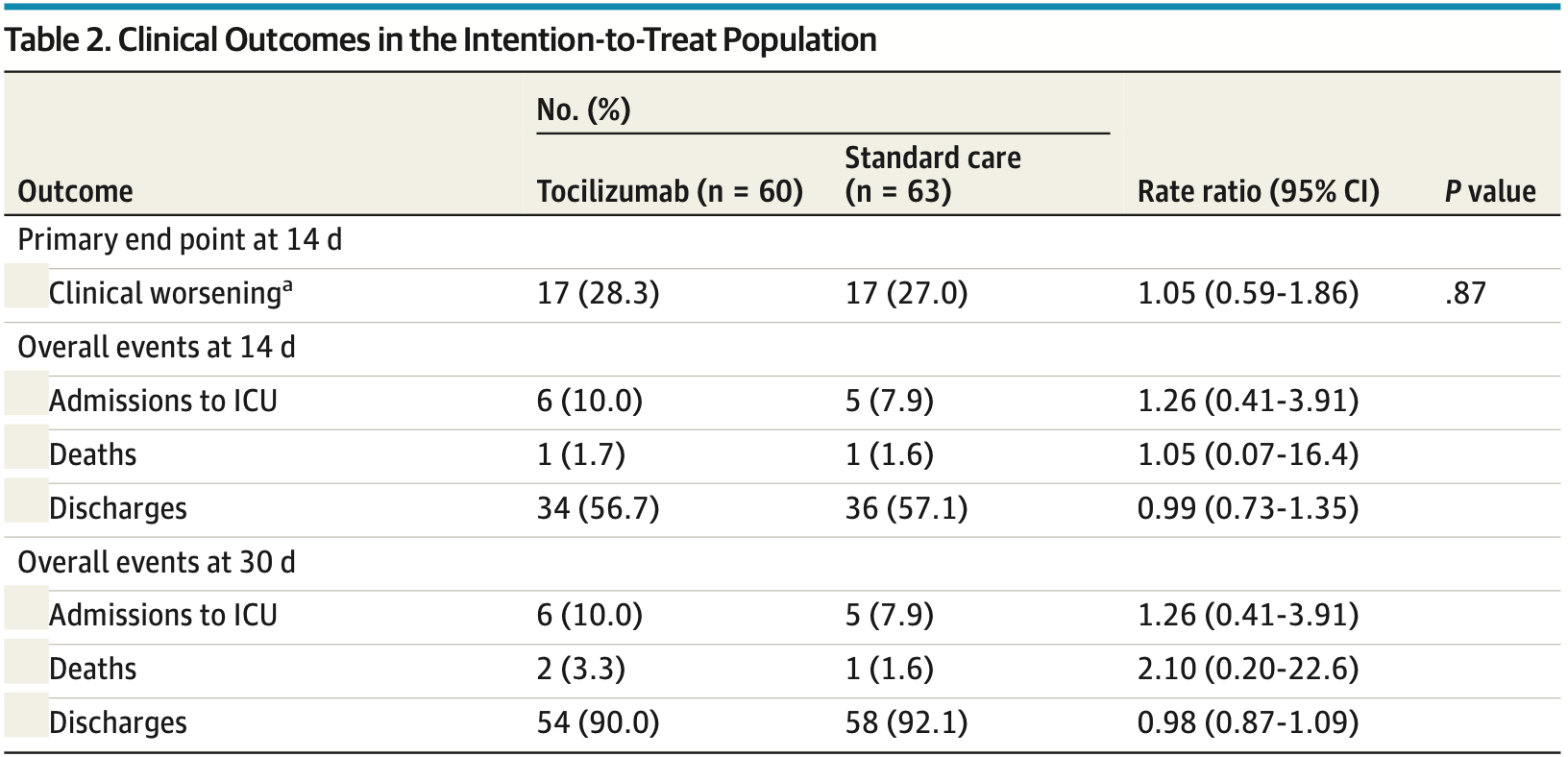
Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia
et al., JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615, RCT-TCZ-COVID-19, NCT04346355, Jan 2021
RCT 126 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with pneumonia showing no significant benefit of tocilizumab treatment.
|
risk of death, 110.0% higher, RR 2.10, p = 0.61, treatment 2 of 60 (3.3%), control 1 of 63 (1.6%), day 30.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 26.0% higher, RR 1.26, p = 0.76, treatment 6 of 60 (10.0%), control 5 of 63 (7.9%), day 30.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 26.0% higher, RR 1.26, p = 0.76, treatment 6 of 60 (10.0%), control 5 of 63 (7.9%), day 30.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 5.0% higher, RR 1.05, p = 1.00, treatment 17 of 60 (28.3%), control 17 of 63 (27.0%), day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Salvarani et al., 1 Jan 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Italy, peer-reviewed, median age 60.0, 39 authors, study period 31 March, 2020 - 11 June, 2020, average treatment delay 8.0 days, trial NCT04346355 (history) (RCT-TCZ-COVID-19).
Contact: salvarani@ausl.re.it.
Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia
JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615
IMPORTANCE The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is threatening billions of people worldwide. Tocilizumab has shown promising results in retrospective studies in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia with a good safety profile. OBJECTIVE To evaluate the effect of early tocilizumab administration vs standard therapy in preventing clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS Prospective, open-label, randomized clinical trial that randomized patients hospitalized between March 31 and June 11, 2020, with COVID-19 pneumonia to receive tocilizumab or standard of care in 24 hospitals in Italy. Cases of COVID-19 were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction method with nasopharyngeal swab. Eligibility criteria included COVID-19 pneumonia documented by radiologic imaging, partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO 2 /FIO 2 ) ratio between 200 and 300 mm Hg, and an inflammatory phenotype defined by fever and elevated C-reactive protein. INTERVENTIONS Patients in the experimental arm received intravenous tocilizumab within 8 hours from randomization (8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg), followed by a second dose after 12 hours. Patients in the control arm received supportive care following the protocols of each clinical center until clinical worsening and then could receive tocilizumab as a rescue therapy.
MAIN OUTCOME AND MEASURES The primary composite outcome was defined as entry into the intensive care unit with invasive mechanical ventilation, death from all causes, or clinical aggravation documented by the finding of a PaO 2 /FIO 2 ratio less than 150 mm Hg, whichever came first. RESULTS A total of 126 patients were randomized (60 to the tocilizumab group; 66 to the control group). The median (interquartile range) age was 60.0 (53.0-72.0) years, and the majority of patients were male (77 of 126, 61.1%). Three patients withdrew from the study, leaving 123 patients available for the intention-to-treat analyses. Seventeen patients of 60 (28.3%) in the tocilizumab arm and 17 of 63 (27.0%) in the standard care group showed clinical worsening within 14 days since randomization (rate ratio, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.59-1.86). Two patients in the experimental group and 1 in the control group died before 30 days from randomization, and 6 and 5 patients were intubated in the 2 groups, respectively. The trial was prematurely interrupted after an interim analysis for futility.
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE In this randomized clinical trial of hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and PaO 2 /FIO 2 ratio between 200 and 300 mm Hg who received tocilizumab, no benefit on disease progression was observed compared with standard care. Further blinded, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to confirm the results and to evaluate possible applications of tocilizumab in different stages of the disease.
Author Contributions: Drs Dolci and Costantini had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs Salvarani and Dolci contributed equally to this article and are co-first authors. Drs Facciolongo and Costantini contributed equally to this article and are co-last authors. Concept and design: Salvarani, Dolci, Massari, Cavuto, Bruzzi, Boni, Turrà, Colombelli,
References
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009575
Cao, COVID-19: immunopathology and its implications for therapy, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0308-3
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI137244
Guan, Ni, Hu, China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Guaraldi, Meschiari, Cozzi-Lepri, Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Infettive E Tropicali, Croce E Carle, Cuneo, Del Bono
Le, Li, Yuan, FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome, Oncologist, doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028
Liu, Li, Zhou, Guan, Xiang, Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)?, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102452
Manfredi, Cassone, Furini, Tocilizumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease: a multicenter retrospective study, Intern Med J, doi:10.1111/imj.14670
Mccarthy, Savinelli, Feeney, Tocilizumab therapy in individuals with COVID-19 infection and hyperinflammatory state, Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.13912
Merlo, Savoldi, Braglia, Emilia, Italy et al., SOC Internistica Multidisciplinare, Ospedale Civile Guastalla, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia
Price, Altice, Shyr, Tocilizumab treatment for cytokine release syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: survival and clinical outcomes, Chest. Published online, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.006
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Sc Medicina Interna, Ao, Mauriziano, SC Malattie dell'Apparato Respiratorio
Schirmer, Muratore, Salvarani, Tocilizumab for the treatment of giant cell arteritis, Expert Rev Clin Immunol, doi:10.1080/1744666X.2018.1468251
Sciascia, Aprà, Baffa, Pilot prospective open, single-arm multicentre study on off-label use of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19, Clin Exp Rheumatol
Ss Reumatologia, SC Medicina Interna, DIMET, Università del Piemonte Orientale e AOU Maggiore della Carità di Novara (Sainaghi); Reumatologia
Stone, Tuckwell, Dimonaco, Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1613849
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy, Autoimmun Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117
Zeng, Huang, Guo, Association of inflammatory markers with the severity of COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.055
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"ISSN": [
"2168-6106"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SOC Reumatologia, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Unità di Reumatologia, Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Salvarani",
"given": "Carlo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unità di Malattie Infettive, Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Dolci",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SOC Malattie Infettive, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Massari",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Infrastruttura Ricerca e Statistica, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Merlo",
"given": "Domenico Franco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Infrastruttura Ricerca e Statistica, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Cavuto",
"given": "Silvio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Infrastruttura Ricerca e Statistica, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Savoldi",
"given": "Luisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Epidemiologia Clinica, IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, Genova, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bruzzi",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SOC Internistica Multidisciplinare, Ospedale Civile Guastalla, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Boni",
"given": "Fabrizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Infrastruttura Ricerca e Statistica, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Braglia",
"given": "Luca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SOC Farmacia, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Turrà",
"given": "Caterina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOC Medicina Generale Ospedale di Vittorio Veneto, Treviso, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Ballerini",
"given": "Pier Ferruccio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOC Medicina Generale Ospedale di Vittorio Veneto, Treviso, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Sciascia",
"given": "Roberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dipartimento di Medicina Sperimentale e Clinica, Università degli Studi di Firenze, SOD Malattie infettive e tropicali, AOU Careggi, Firenze, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Zammarchi",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medicina Interna 1, Dipartimento Emergenza ed Accettazione, AOU Careggi, Firenze, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Para",
"given": "Ombretta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UO di Malattie Infettive, Ospedale Regionale Ca’ Foncello di Treviso, Treviso, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Scotton",
"given": "Pier Giorgio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UO di Malattie Infettive, Ospedale Regionale Ca’ Foncello di Treviso, Treviso, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Inojosa",
"given": "Walter Omar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SSD Centro DH Allergologia e Immunologia Clinica, ASST-Mantova, Mantva, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Ravagnani",
"given": "Viviana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOC Malattie Infettive e Tropicali, AOUI di Verona, Verona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Salerno",
"given": "Nicola Duccio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SS Reumatologia, SC Medicina Interna, DIMET, Università del Piemonte Orientale e AOU Maggiore della Carità di Novara"
}
],
"family": "Sainaghi",
"given": "Pier Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Reumatologia, Medicina Interna, Ospedale S. Andrea, La Spezia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Brignone",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOC Malattie Infettive, AUSL di Piacenza, Piacenza, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Codeluppi",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SOC Internistica Multidisciplinare, Ospedale Civile Guastalla, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Teopompi",
"given": "Elisabetta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unità di malattie Infettive, ASST di Cremona, Cremona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Milesi",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOC Medicina Generale, ULSS6 Euganea Ospedali Riuniti Padova Sud, Padova, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bertomoro",
"given": "Perla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Medicina Interna, AO Ordine Mauriziano, Torino, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Claudio",
"given": "Norbiato",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Malattie dell’Apparato Respiratorio, AO SS. Antonio e Biagio e C. Arrigo, Alessandria, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Salio",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unità di Malattie Infettive, Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica e Sperimentale, Università di Pisa, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Falcone",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SC Malattie Infettive, ASL1 Imperia, Impersia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Cenderello",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UO Malattie Infettive ed Epatologia, AOU Parma, Parma, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Donghi",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Malattie Infettive e Tropicali, AO S. Croce e Carle, Cuneo, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Del Bono",
"given": "Valerio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UO Medicina, Ospedale di Treviglio, ASST Bergamo Ovest, Bergamo, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Colombelli",
"given": "Paolo Luigi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dipartimento di Malattie Infettive, Tropicali e Microbiologia, IRCCS Ospedale Sacro Cuore-Don Calabria, Negrar di Valpolicella, Verona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Angheben",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medicina Interna Universitaria, AOU Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Passaro",
"given": "Angelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medicina Interna, Ospedale Evangelico, Genoa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Secondo",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UO Malattie Infettive, Dipartimento di scienze mediche e chirurgiche, Università di Bologna, Bologna, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pascale",
"given": "Renato",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOC Medicina Interna, AUSSS3 Serenissima, Dolo, Venezia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Piazza",
"given": "Ilaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "SOC Pneumologia, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Facciolongo",
"given": "Nicola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Costantini",
"given": "Massimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 Study Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Internal Medicine",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Intern Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-20T13:31:03Z",
"timestamp": 1603200663000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-04T13:30:55Z",
"timestamp": 1609767055000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-04T17:35:03Z",
"timestamp": 1749058503907
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 565,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/articlepdf/2772186/jamainternal_salvarani_2020_oi_200094_1609365347.37772.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "24",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China.",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi200094r1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ioi200094r2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "762",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi200094r3",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019.",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2620",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "ioi200094r4",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0308-3",
"article-title": "COVID-19: immunopathology and its implications for therapy.",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "ioi200094r5",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.055",
"article-title": "Association of inflammatory markers with the severity of COVID-19: a meta-analysis.",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi200094r6",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—preliminary report.",
"author": "Horby",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi200094r7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102452",
"article-title": "Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)?",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "ioi200094r8",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imj.v50.9",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease: a multicenter retrospective study.",
"author": "Manfredi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1085",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Intern Med J",
"key": "ioi200094r9",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1744666X.2018.1468251",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of giant cell arteritis.",
"author": "Schirmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "339",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Clin Immunol",
"key": "ioi200094r10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1613849",
"article-title": "Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis.",
"author": "Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "317",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi200094r11",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028",
"article-title": "FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome.",
"author": "Le",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "943",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Oncologist",
"key": "ioi200094r12",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab.",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10970",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "ioi200094r13",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy.",
"author": "Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "ioi200094r14",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Pilot prospective open, single-arm multicentre study on off-label use of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19.",
"author": "Sciascia",
"first-page": "529",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Rheumatol",
"key": "ioi200094r15",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Tocilizumab treatment for cytokine release syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: survival and clinical outcomes.",
"author": "Price",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ioi200094r16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study.",
"author": "Guaraldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e474",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "ioi200094r17",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Tocilizumab therapy in individuals with COVID-19 infection and hyperinflammatory state.",
"author": "McCarthy",
"journal-title": "Respirology",
"key": "ioi200094r18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ioi200094r19",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Severe Covid-19.",
"author": "Berlin",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi200094r20"
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2772186"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [
"A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "181"
}