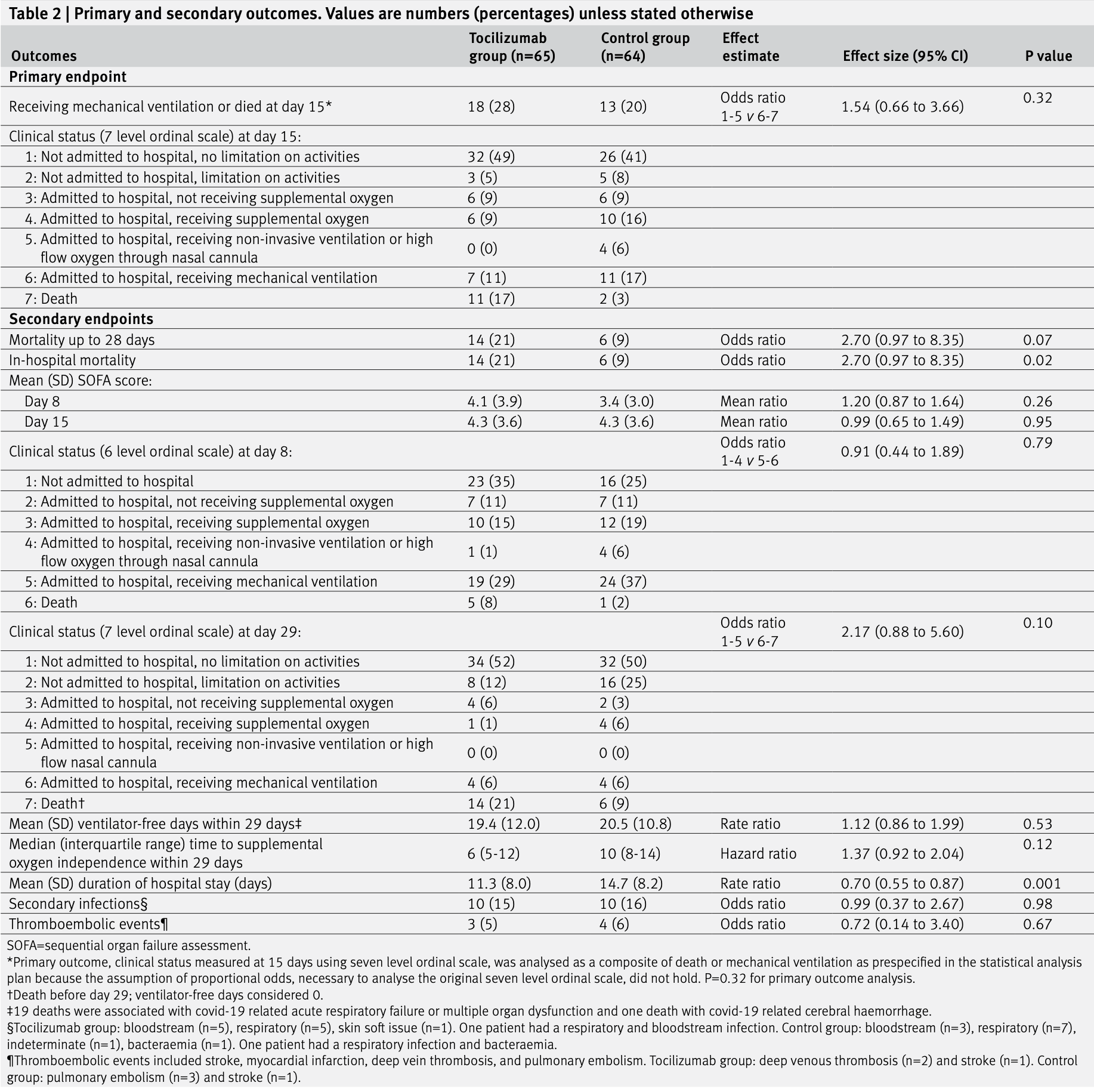
Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial
et al., BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n84, TOCIBRAS, NCT04403685, Jan 2021
RCT 129 hospitalized patients with severe or critical COVID-19 in Brazil showing no benefit and potential harm with tocilizumab treatment.
|
risk of death, 129.7% higher, RR 2.30, p = 0.09, treatment 14 of 65 (21.5%), control 6 of 64 (9.4%), day 28.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 1.0% lower, RR 0.99, p = 0.96, treatment 65, control 64, relative SOFA score, day 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Veiga et al., 20 Jan 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, mean age 57.0, 36 authors, study period 8 May, 2020 - 17 July, 2020, average treatment delay 10.0 days, trial NCT04403685 (history) (TOCIBRAS).
Contact: viviane.veiga@bp.org.br.
Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial
BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n84
Objective To determine whether tocilizumab improves clinical outcomes for patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19).
Design Randomised, open label trial. setting Nine hospitals in Brazil, 8 May to 17 July 2020. cOnclusiOns In patients with severe or critical covid-19, tocilizumab plus standard care was not superior to standard care alone in improving clinical outcomes at 15 days, and it might increase mortality. trial registratiOn ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04403685.
conclusions In this trial including patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical covid-19, the use of tocilizumab plus standard care was not superior to standard care alone in improving patients' clinical status at 15 days, and might have increased mortality. The collaborators are listed in the supplementary file. The trial was designed by the executive committee (see supplementary file). The executive committee vouches for the completeness and accuracy of the data and for the fidelity of the trial to the protocol. Contributors: ABC, DLCF, JP, PS, and VCV conceived the study, wrote the protocol, recruited patients, and drafted the manuscript. ABC, RGR, FRM, FGZ, OB, LCPA, RDL, AA, LKD, and CGC developed the protocol and approved the final version for the Coalition covid-19 Brazil Group, recruited patients, participated in interim discussions, and reviewed the manuscript. CZO developed the REDCap database and attended to all data collection related issues. LPD and LMI performed the statistical analysis. LECA, AFS, and MCP coordinated exploratory sample collection and will be performing the exploratory analysis, participated in the protocol development an interim discussion and reviewed the manuscript. VCV, ABC, DLCF, JP, and PS act as guarantors, accept full responsibility for the work, had access to the data, and controlled the decision to publish. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the..
References
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026
Campochiaro, Della-Torre, Cavalli, Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19 patients: a single-centre retrospective cohort study, Eur J Intern Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.021
Canziani, Trovati, Brunetta, -19 Task Forces. Interleukin-6 receptor blocking with intravenous tocilizumab in COVID-19 severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective case-control survival analysis of 128 patients, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102511
Capra, Rossi, Mattioli, Impact of low dose tocilizumab on mortality rate in patients with COVID-19 related pneumonia, Eur J Intern Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.009
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Coalition Covid-19 Brazil I Investigators. Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2019014
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI137244
Colaneri, Bogliolo, Valsecchi, The Covid Irccs San Matteo Pavia Task Force. Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE), Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8050695
Core, R: a language and environmnet for statistical computing
Farias, Prats, Cavalcanti, Rationale and design of tocilizumab in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: an open label multicentre randomised controlled trial (TOCIBRAS). Revista Brasileira de terapia intensiva, Rev Bras Ter Intensiva, doi:10.5935/0103-507X.20200060
Furtado, Berwanger, Fonseca, COALITION COVID-19 Brazil II Investigators. Azithromycin in addition to standard of care versus standard of care alone in the treatment of patients admitted to the hospital with severe COVID-19 in Brazil (COALITION II): a randomised clinical trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6
Gupta, Wang, Hayek, Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252
Hermine, Tharaux, Effect of Tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820
Herold, Jurinovic, Arnreich, Elevated levels of IL-6 and CRP predict the need for mechanical ventilation in COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.008
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in Hospitalised Patients with Covid-19 -Preliminary Report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Horby, Roddick, Spata, Azithromycin in hospitalized patients with covid-19 (RECOVERY): a randomized, controlled, openlabel, platform trial, doi:10.1101/2020.12.10.20245944
Jones, Palumbo, Brown, Coronavirus: A visual guide to the economic impact, BBC News
Kewan, Covut, Mj, Rose, Gopalakrishna et al., Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418
Klopfenstein, Zayet, Lohse, Tocilizumab multidisciplinary team. Tocilizumab therapy reduced intensive care unit admissions and/or mortality in COVID-19 patients, Med Mal Infect, doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2020.05.001
Laguna-Goya, Utrero-Rico, Talayero, IL-6-based mortality risk model for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.009
Langer-Gould, Smith, Gonzales, Early identification of COVID-19 cytokine storm and treatment with anakinra or tocilizumab, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.081
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Merad, Martin, Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4
Moore, June, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb8925
Moreno-Pérez, Andres, Experience with tocilizumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia after 80 days of followup: A retrospective cohort study, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102523
Nicola, Alsafi, Sohrabi, The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review, Int J Surg, doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018
Nishimoto, Terao, Mima, Nakahara, Takagi et al., Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2008-05-155846
Petrak, Van Hise, Skorodin, Early tocilizumab dosing is associated with improved survival in critically ill patients infected with SARS-COV-2, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.27.20211433
Quartuccio, Sonaglia, Pecori, Higher levels of IL-6 early after tocilizumab distinguish survivors from nonsurvivors in COVID-19 pneumonia: A possible indication for deeper targeting of IL-6, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26149
Rosas, Brau, Waters, Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.27.20183442
Rose-John, Winthrop, Calabrese, The role of IL-6 in host defence against infections: immunobiology and clinical implications, Nat Rev Rheumatol, doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2017.83
Rossotti, Travi, Ughi, Safety and efficacy of anti-il6-receptor tocilizumab use in severe and critical patients affected by coronavirus disease 2019: A comparative analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.07.008
Salvarani, Dolci, Massari, RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 Study Group. Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615
Scott, Tocilizumab: A review in rheumatoid arthritis, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-017-0829-7
Siemieniuk, Rochwerg, Agoritsas, A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
Somers, Eschenauer, Troost, Tocilizumab for treatment of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa954
Stone, Frigault, Nj, Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028836
Tanaka, Narazaki, Kishimoto, IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016295
Tomasiewicz, Piekarska, Stempkowska-Rejek, Tocilizumab for patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective, multi-center study, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2020.1800453
Vaninov, In the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0305-6
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n84",
"ISSN": [
"1756-1833"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n84",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To determine whether tocilizumab improves clinical outcomes for patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Design</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Randomised, open label trial.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Setting</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Nine hospitals in Brazil, 8 May to 17 July 2020.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Participants</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Adults with confirmed covid-19 who were receiving supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation and had abnormal levels of at least two serum biomarkers (C reactive protein, D dimer, lactate dehydrogenase, or ferritin). The data monitoring committee recommended stopping the trial early, after 129 patients had been enrolled, because of an increased number of deaths at 15 days in the tocilizumab group.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Interventions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Tocilizumab (single intravenous infusion of 8 mg/kg) plus standard care (n=65) versus standard care alone (n=64).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Main outcome measure</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The primary outcome, clinical status measured at 15 days using a seven level ordinal scale, was analysed as a composite of death or mechanical ventilation because the assumption of odds proportionality was not met.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 129 patients were enrolled (mean age 57 (SD 14) years; 68% men) and all completed follow-up. All patients in the tocilizumab group and two in the standard care group received tocilizumab. 18 of 65 (28%) patients in the tocilizumab group and 13 of 64 (20%) in the standard care group were receiving mechanical ventilation or died at day 15 (odds ratio 1.54, 95% confidence interval 0.66 to 3.66; P=0.32). Death at 15 days occurred in 11 (17%) patients in the tocilizumab group compared with 2 (3%) in the standard care group (odds ratio 6.42, 95% confidence interval 1.59 to 43.2). Adverse events were reported in 29 of 67 (43%) patients who received tocilizumab and 21 of 62 (34%) who did not receive tocilizumab.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In patients with severe or critical covid-19, tocilizumab plus standard care was not superior to standard care alone in improving clinical outcomes at 15 days, and it might increase mortality.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n ClinicalTrials.gov\n <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" xlink:href=\"NCT04403685\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\">NCT04403685</jats:ext-link>\n .\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/bmj.n84"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0287-3601",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Veiga",
"given": "Viviane C",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prats",
"given": "João A G G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farias",
"given": "Danielle L C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosa",
"given": "Regis G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dourado",
"given": "Leticia K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zampieri",
"given": "Fernando G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Machado",
"given": "Flávia R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopes",
"given": "Renato D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berwanger",
"given": "Otavio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azevedo",
"given": "Luciano C P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avezum",
"given": "Álvaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lisboa",
"given": "Thiago C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rojas",
"given": "Salomón S O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coelho",
"given": "Juliana C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leite",
"given": "Rodrigo T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carvalho",
"given": "Júlio C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andrade",
"given": "Luis E C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandes",
"given": "Alex F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pintão",
"given": "Maria C T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castro",
"given": "Claudio G",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "Jr"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Sueli V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Almeida",
"given": "Thiago M L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Costa",
"given": "André N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gebara",
"given": "Otávio C E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Freitas",
"given": "Flávio G Rezende",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pacheco",
"given": "Eduardo S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Machado",
"given": "David J B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Josiane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conceição",
"given": "Fábio G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siqueira",
"given": "Suellen R R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Damiani",
"given": "Lucas P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ishihara",
"given": "Luciana M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schneider",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Souza",
"given": "Denise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cavalcanti",
"given": "Alexandre B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scheinberg",
"given": "Phillip",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04403685",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "BMJ",
"container-title-short": "BMJ",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-21T01:00:23Z",
"timestamp": 1611190823000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-21T05:00:23Z",
"timestamp": 1611205223000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-05T13:42:30Z",
"timestamp": 1749130950764,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 286,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1611100800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://data.bmj.org/tdm/10.1136/bmj.n84",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/bmj.n84",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "n84",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.1",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. World Health Organization, 2020. https://Covid19.who.int/. [Accessed 19 October 2020.]"
},
{
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.2",
"unstructured": "Jones L, Palumbo D, Brown D. Coronavirus: A visual guide to the economic impact. BBC News: BBC; 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb8925",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-017-0829-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a016295",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2017.83",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5935/0103-507X.20200060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.15"
},
{
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.16",
"unstructured": "R Core Team . R: a language and environmnet for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0305-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.19"
},
{
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028836",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2008-05-155846",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa954",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1800453",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.07.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102523",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8050695",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medmal.2020.05.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102511",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.27.20211433",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.081",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.40"
},
{
"key": "2021012021000910000_372.jan19_15.n84.41"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmj.n84"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy"
}