Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE)
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8050695, SMACORE, May 2020
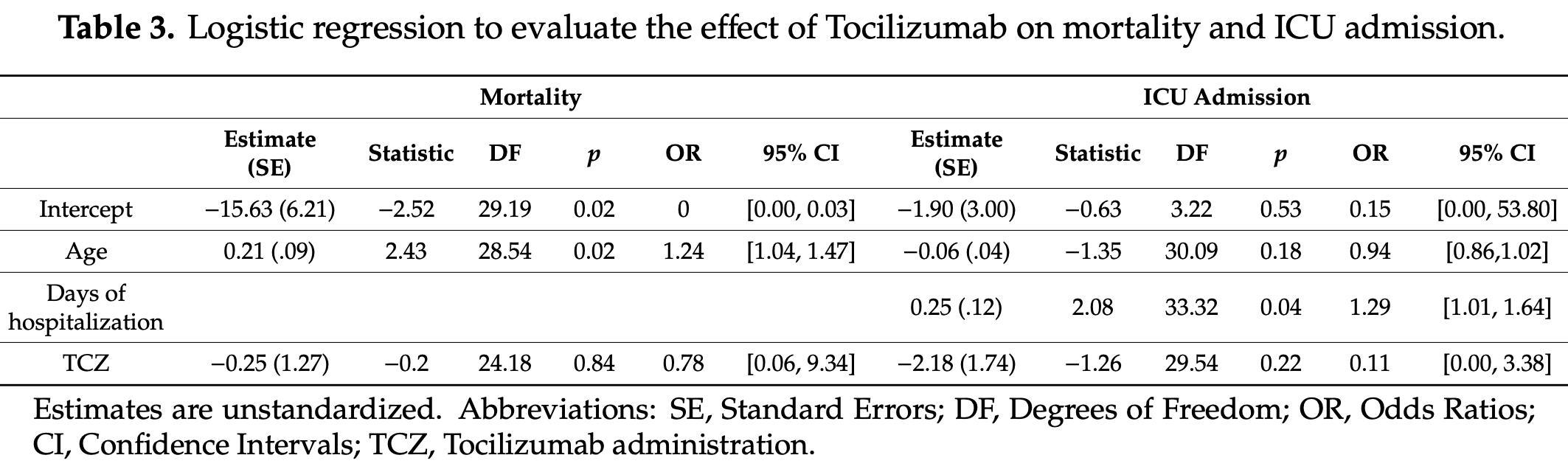
PSM retrospective 112 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in ICU admission or mortality with tocilizumab.
|
risk of death, 18.2% lower, RR 0.82, p = 0.85, treatment 5 of 21 (23.8%), control 19 of 91 (20.9%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 87.5% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.43, treatment 3 of 21 (14.3%), control 12 of 91 (13.2%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Colaneri et al., 9 May 2020, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, median age 63.5, 11 authors, study period 14 March, 2020 - 27 March, 2020, SMACORE trial.
Contact: raffaele.bruno@unipv.it (corresponding author), marta.colaneri01@universitadipavia.it, pietro.valsecchi01@universitadipavia.it, p.sacchi@smatteo.pv.it, v.zuccaro@smatteo.pv.it, l.bogliolo@smatteo.pv.it, carlomaurizio.montecucco@unipv.it, fabio.brandolino01@universitadipavia.it, francesco.mojoli@unipv.it, e.giusti@auxologico.it.
Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE)
Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8050695
Objective: This study aimed to assess the role of Tocilizumab therapy (TCZ) in terms of ICU admission and mortality rate of critically ill patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Design: Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia were prospectively enrolled in SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE). A retrospective analysis of patients treated with TCZ matched using propensity score to patients treated with Standard Of Care (SOC) was conducted. Setting: The study was conducted at IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Hospital, Pavia, Italy, from March 14, 2020 to March 27, 2020. Participants: Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 hospitalized in our institution at the time of TCZ availability. Interventions: TCZ was administered to 21 patients. The first administration was 8 mg/kg (up to a maximum 800 mg per dose) of Tocilizumab intravenously, repeated after 12 h if no side effects were reported after the first dose. Main Outcomes and Measures: ICU admission and 7-day mortality rate. Secondary outcomes included clinical and laboratory data. Results: There were 112 patients evaluated (82 were male and 30 were female, with a median age of 63.55 years). Using propensity scores, the 21 patients who received TCZ were matched to 21 patients who received SOC (a combination of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin and prophylactic dose of low weight heparin). No adverse event was detected following TCZ administration. This study found that treatment with TCZ did not significantly affect ICU admission (OR 0.11; 95% CI between 0.00 and 3.38; p = 0.22) or 7-day mortality rate (OR 0.78; 95% CI between 0.06 and 9.34; p = 0.84) when compared with SOC. Analysis of laboratory measures showed significant interactions between time and treatment regarding C-Reactive Protein (CRP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), platelets and international normalized ratio (INR) levels. Variation in lymphocytes count was observed over time, irrespective of treatment. Conclusions: TCZ administration did not reduce ICU admission or Microorganisms 2020, 8, 695; doi:10.3390/microorganisms8050695 www.mdpi.com/journal/microorganisms mortality rate in a cohort of 21 patients. Additional data are needed to understand the effect(s) of TCZ in treating patients diagnosed with COVID-19.
Author Contributions: M.C. conceived the presented idea and wrote the final manuscript. L.B., P.V., P.S. and V.Z. encouraged to investigate and supervised the findings of this work. F.B., C.M. and F.M. contributed to the design and implementation of the research, E.M.G. analyzed the results and R.B. contributed to the final version of the manuscript and supervised the project. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding:
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Annane, Bellissant, Bollaert, Briegel, Keh et al., Corticosteroids for treating sepsis, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002243.pub3
Austin, An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies, Multivar. Behav. Res, doi:10.1080/00273171.2011.568786
Bates, Mächler, Bolker, Walker, Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using {lme4}, J. Stat. Softw, doi:10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Coomes, Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Fujiwara, Nishimoto, Hamano, Asanuma, Miki et al., Masked early symptoms of pneumonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis during tocilizumab treatment: A report of two cases, Mod. Rheumatol, doi:10.3109/s10165-008-0111-7
Genovese, Kremer, Van Vollenhoven, Alten, Scali et al., Transaminase Levels and Hepatic Events During Tocilizumab Treatment: Pooled Analysis of Long-Term Clinical Trial Safety Data in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Arthritis Rheumatol, doi:10.1002/art.40176
Ghebreyesus, Who Director, -General's Opening REMARKS at the media Briefing on COVID-19-11
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen et al., The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak-An update on the status, Mil. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Kalil, Treating COVID-19-Off-Label Drug Use, Compassionate Use, and Randomized Clinical Trials During Pandemics, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4742
Kotch, Barrett, Teachey, Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome, Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1080/1744666X.2019.1629904
Luo, Liu, Qiu, Liu, Liu et al., Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: A single center experience, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25801
Milbrandt, Reade, Lee, Shook, Angus et al., Prevalence and significance of coagulation abnormalities in community-acquired pneumonia, Mol. Med, doi:10.2119/molmed.2009.00091
Park, Goodman, Steinberg, Ruzinski, Radella et al., Cytokine balance in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104013
Pishgar, Greifer, MatchThem: Matching and Weighting Multiply Imputed Datasets
Qu, Ling, Zhang, Wei, Chen et al., Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25767
Rodrigues, Walsh, Risks and Benefits of Glucocorticoids in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis, Curr. Treat Options Rheumatol
Rosado, Kim, Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, Am. J. Clin. Pathol, doi:10.1309/AJCP4ZDKJ4ICOUAT
Rubin, Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys
Sayburn, Covid-19: Trials of four potential treatments to generate "robust data" of what works, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1206
Schoels, Van Der Heijde, Breedveld, Burmester, Dougados et al., Blocking the effects of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases: Systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing a consensus statement, Ann. Rheum. Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202470
Scott, Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-017-0829-7
Shen, Wang, Zhao, Yang, Li et al., Treatment of 5 Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 with Convalescent Plasma, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4783
Ulhaq, Soraya, Interleukin-6 as a potential biomarker of COVID-19 progression, Med. Mal. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2020.04.002
Van Buuren, Groothuis-Oudshoorn, {mice}, Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations in, R. J. Stat. Softw, doi:10.18637/jss.v045.i03
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Wang, Han, Biomarkers of Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurotoxicity Related to CAR-T Cell Therapy, Biomarker Res, doi:10.1186/s40364-018-0116-0
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wickham, Tidyverse, Easily Install and Load the "Tidyverse". R Package Version 2017
Wilson, Chotirmall, Bai, Covid, Interim Guidance on Management Pending Empirical Evidence
Xu, Han, Li, Sun, Wang et al., Effective Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients with Tocilizumab, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117
Yakoub-Agha, Moreau, Ahmad, Borel, Hadhoum et al., Management of cytokine release syndrome in adult and pediatric patients undergoing CAR-T cell therapy for hematological malignancies: Recommendation of the French Society of Bone Marrow and cellular Therapy (SFGM-TC), Bull. Cancer, doi:10.1016/j.bulcan.2018.12.001
Yao, Ye, Zhang, Cui, Huang et al., In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237
Zhang, Wu, Li, Zhao, Wang, The cytokine release syndrome (CRS) of severe COVID-19 and Interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist Tocilizumab may be the key to reduce the mortality, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8050695",
"ISSN": [
"2076-2607"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050695",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Objective: This study aimed to assess the role of Tocilizumab therapy (TCZ) in terms of ICU admission and mortality rate of critically ill patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Design: Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia were prospectively enrolled in SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE). A retrospective analysis of patients treated with TCZ matched using propensity score to patients treated with Standard Of Care (SOC) was conducted. Setting: The study was conducted at IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Hospital, Pavia, Italy, from March 14, 2020 to March 27, 2020. Participants: Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 hospitalized in our institution at the time of TCZ availability. Interventions: TCZ was administered to 21 patients. The first administration was 8 mg/kg (up to a maximum 800 mg per dose) of Tocilizumab intravenously, repeated after 12 h if no side effects were reported after the first dose. Main Outcomes and Measures: ICU admission and 7-day mortality rate. Secondary outcomes included clinical and laboratory data. Results: There were 112 patients evaluated (82 were male and 30 were female, with a median age of 63.55 years). Using propensity scores, the 21 patients who received TCZ were matched to 21 patients who received SOC (a combination of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin and prophylactic dose of low weight heparin). No adverse event was detected following TCZ administration. This study found that treatment with TCZ did not significantly affect ICU admission (OR 0.11; 95% CI between 0.00 and 3.38; p = 0.22) or 7-day mortality rate (OR 0.78; 95% CI between 0.06 and 9.34; p = 0.84) when compared with SOC. Analysis of laboratory measures showed significant interactions between time and treatment regarding C-Reactive Protein (CRP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), platelets and international normalized ratio (INR) levels. Variation in lymphocytes count was observed over time, irrespective of treatment. Conclusions: TCZ administration did not reduce ICU admission or mortality rate in a cohort of 21 patients. Additional data are needed to understand the effect(s) of TCZ in treating patients diagnosed with COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"microorganisms8050695"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases I, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Colaneri",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Rheumatology, IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bogliolo",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases I, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Valsecchi",
"given": "Pietro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases I, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Sacchi",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases I, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Zuccaro",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Rheumatology, IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation, University of Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Brandolino",
"given": "Fabio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8263-3925",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Rheumatology, IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Division of Rheumatology, IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation, University of Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Montecucco",
"given": "Carlomaurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical, Surgical, Diagnostic, and Paediatric Sciences, University of Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Emergency Department, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Anesthesia, Intensive Care and Pain Therapy, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Mojoli",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Catholic University of Milan, Department of Psychology, 20123 Milan, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Istituto Auxologico Italiano IRCCS, Psychology Research Laboratory, San Giuseppe Hospital, 28824 Verbania, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Giusti",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0235-9207",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases I, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Clinical, Surgical, Diagnostic, and Paediatric Sciences, University of Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bruno",
"given": "Raffaele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "the COVID IRCCS San Matteo Pavia Task Force",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microorganisms",
"container-title-short": "Microorganisms",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-11T14:01:18Z",
"timestamp": 1589205678000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-27T21:46:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719524760000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-04T06:26:34Z",
"timestamp": 1746339994576,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 172,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1588982400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/8/5/695/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "695",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak—An update on the status",
"author": "Guo",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2020, April 20). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Events as They Happen. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen."
},
{
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Ghebreyesus, T.A. (2020, April 20). WHO Director-General’s Opening REMARKS at the media Briefing on COVID-19–11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.whoint/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-atthe-media-briefing-on-covid-19–11-March-2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Yao, X., Ye, F., Zhang, M., Cui, C., Huang, B., Niu, P., Liu, X., Zhao, L., Dong, E., and Song, C. (2020). In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Infect. Dis."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4783",
"article-title": "Treatment of 5 Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 with Convalescent Plasma",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1582",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "232",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Cao, B., Wang, Y., Wen, D., Liu, W., Wang, J., Fan, G., Ruan, L., Song, B., Cai, Y., and Wei, M. (2020). A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Zhang, C., Wu, Z., Li, J.-W., Zhao, H., and Wang, G.-Q. (2020). The cytokine release syndrome (CRS) of severe COVID-19 and Interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist Tocilizumab may be the key to reduce the mortality. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 105954."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104013",
"article-title": "Cytokine balance in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1896",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40364-018-0116-0",
"article-title": "Biomarkers of Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurotoxicity Related to CAR-T Cell Therapy",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29387417",
"journal-title": "Biomarker Res.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-017-0829-7",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis",
"author": "Scott",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1865",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202470",
"article-title": "Blocking the effects of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases: Systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing a consensus statement",
"author": "Schoels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "583",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1744666X.2019.1629904",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome",
"author": "Kotch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Effective Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients with Tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"first-page": "32350134",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Rubin, D. (2004). Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys, John Wiley & Sons."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00273171.2011.568786",
"article-title": "An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Multivar. Behav. Res.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32614/CRAN.package.tidyverse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Wickham, H. (2017). Tidyverse: Easily Install and Load the “Tidyverse”. R Package Version 2017, GitHub."
},
{
"article-title": "{mice}: Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations in, R",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Stat. Softw.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32614/CRAN.package.MatchThem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Pishgar, F., and Greifer, N. (2020, April 20). MatchThem: Matching and Weighting Multiply Imputed Datasets. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MatchThem/MatchThem.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18637/jss.v067.i01",
"article-title": "Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using {lme4}",
"author": "Bates",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Stat. Softw.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4742",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Kalil, A.C. (2020). Treating COVID-19—Off-Label Drug Use, Compassionate Use, and Randomized Clinical Trials During Pandemics. JAMA."
},
{
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Wilson, K.C., Chotirmall, S.H., and Bai, C.R.J. (2020, April 20). COVID19: Interim Guidance on Management Pending Empirical Evidence. Available online: https://www.thoracic.org/covid/covid-19-guidance.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25801",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Luo, P., Liu, Y., Qiu, L., Liu, X., Liu, D., and Li, J. (2020). Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: A single center experience. J. Med. Virol."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/s10165-008-0111-7",
"article-title": "Masked early symptoms of pneumonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis during tocilizumab treatment: A report of two cases",
"author": "Fujiwara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Mod. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2119/molmed.2009.00091",
"article-title": "Prevalence and significance of coagulation abnormalities in community-acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Milbrandt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "438",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25767",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Qu, R., Ling, Y., Zhang, Y.H., Wei, L.Y., Chen, X., Li, X., Liu, X.Y., Liu, H.M., Guo, Z., and Ren, H. (2020). Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease-19. J. Med. Virol."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.40176",
"article-title": "Transaminase Levels and Hepatic Events During Tocilizumab Treatment: Pooled Analysis of Long-Term Clinical Trial Safety Data in Rheumatoid Arthritis",
"author": "Genovese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1751",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1206",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Sayburn, A. (2020). Covid-19: Trials of four potential treatments to generate “robust data” of what works. BMJ."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3562887",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_34",
"unstructured": "Ulhaq, Z.S., and Soraya, G.V. (2020). Interleukin-6 as a potential biomarker of COVID-19 progression. Med. Mal. Infect."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.30.20048058",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Coomes, E.A.H.H. (2020). Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. submited, under review."
},
{
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "(2020, April 20). Tocilizumab in COVID-19 Pneumonia (TOCIVID-19), Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04317092."
},
{
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "(2020, April 20). A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia, Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04320615."
},
{
"article-title": "Management of cytokine release syndrome in adult and pediatric patients undergoing CAR-T cell therapy for hematological malignancies: Recommendation of the French Society of Bone Marrow and cellular Therapy (SFGM-TC)",
"author": "Moreau",
"first-page": "S102",
"journal-title": "Bull. Cancer",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1309/AJCP4ZDKJ4ICOUAT",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_39",
"unstructured": "Rosado, F.G.N., and Kim, A.S. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol., 2013."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD002243.pub3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Annane, D., Bellissant, E., Bollaert, P.E., Briegel, J., Keh, D., and Kupfer, Y. (2015). Corticosteroids for treating sepsis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40674-017-0081-z",
"article-title": "Risks and Benefits of Glucocorticoids in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis",
"author": "Rodrigues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "244",
"journal-title": "Curr. Treat Options Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/8/5/695"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE)",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "8"
}