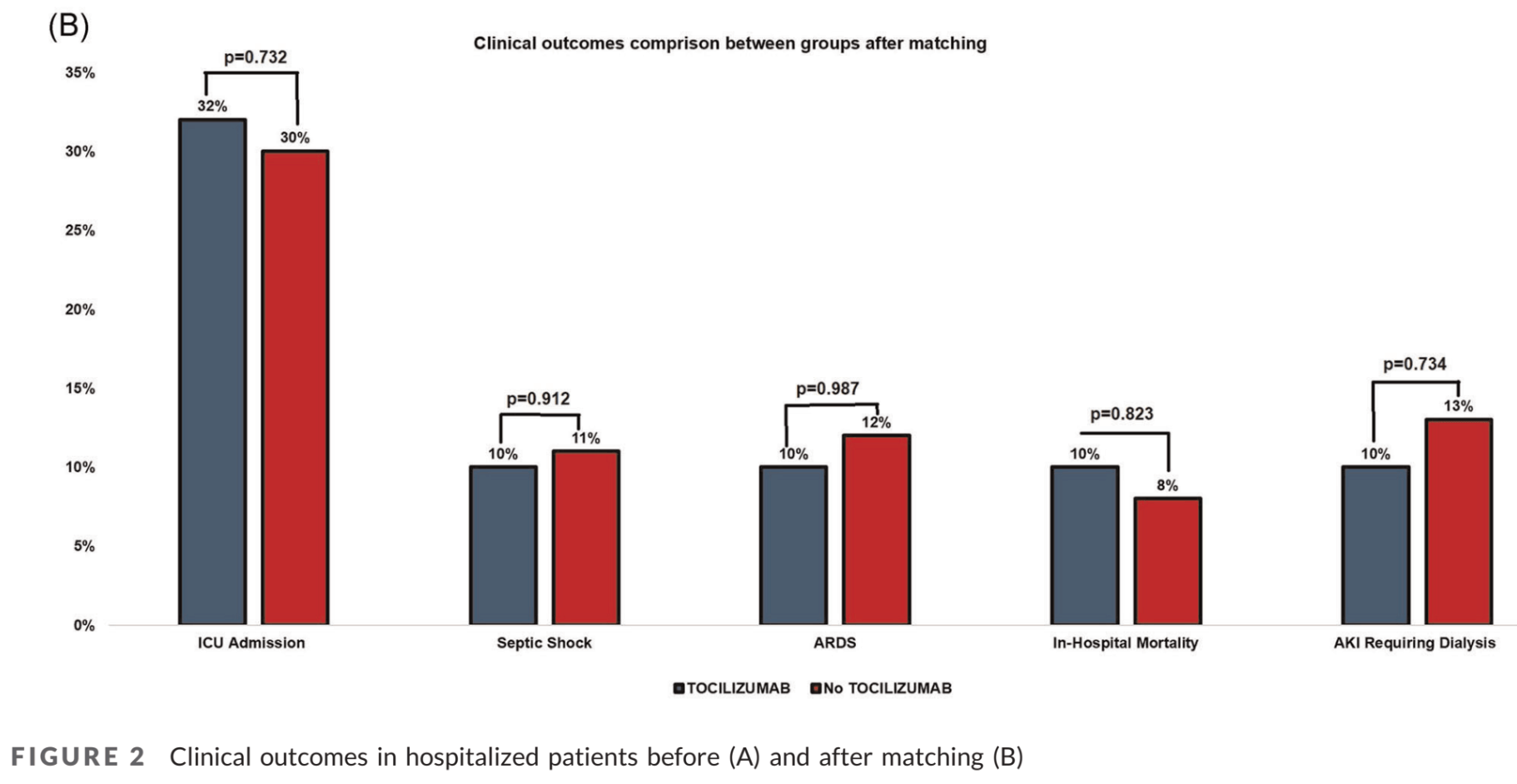
Tocilizumab use in COVID‐19‐associated pneumonia
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26471, Oct 2020
PSM retrospective 77 hospitalized patients receiving tocilizumab treatment and matched controls, showing no significant difference in outcomes.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 166.7% higher, RR 2.67, p = 0.21, treatment 4 of 20 (20.0%), control 3 of 40 (7.5%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 344.4% higher, RR 4.44, p = 0.01, treatment 10 of 30 (33.3%), control 3 of 40 (7.5%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Okoh et al., 5 Oct 2020, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 10 March, 2020 - 10 April, 2020.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26471",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.26471",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>We sought to evaluate the effect of tocilizumab (TCB), a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against soluble interleukin‐6 receptors, in patients hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We included all patients with laboratory‐confirmed COVID‐19 who had completed hospitalization between March 10, 2020 and April 10, 2020 with follow‐up through April 20, 2020. Patients who received TCB in addition to standard of care within 48 h of admission were matched in a 1:2 fashion to a similar cohort who received standard of care alone. Clinical outcomes were compared between matched groups. The primary outcome was de‐escalation in oxygen therapy. Secondary outcomes were in‐hospital death, septic shock, and acute kidney injury (AKI) requiring hemodialysis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Out of 77 patients who received TCB in addition to standard of care, 34% (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 26) received TCB within 48 h of admission. One‐to‐two propensity matching identified 20 versus 40 patients in the TCB and no‐TCB treatment arms. In the TCB group, an improvement in oxygenation was observed in 80% (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 16) of the patients by 7 days post TCB administration. After matching, there was no difference in clinical outcomes between TCB and no‐TCB patients. In‐hospital death: 10% versus 8%; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .823, septic shock: 10% versus 11%, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .912, AKI requiring hemodialysis (10% vs. 13%; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .734).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Early treatment with TCB in patients admitted for COVID‐19 led to an improvement in their oxygen status during hospitalization. This change however did not translate into improved survival when compared to a matched cohort with a similar clinical profile.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.26471"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-07-06"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2020-07-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2020-10-05"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases Newark Beth Israel Medical Center Newark New Jersey USA"
}
],
"family": "Okoh",
"given": "Alexis K.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases Newark Beth Israel Medical Center Newark New Jersey USA"
}
],
"family": "Bishburg",
"given": "Eliahu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases Newark Beth Israel Medical Center Newark New Jersey USA"
}
],
"family": "Grinberg",
"given": "Sagy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7587-7569",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases Newark Beth Israel Medical Center Newark New Jersey USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nagarakanti",
"given": "Sandhya",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-29T09:55:30Z",
"timestamp": 1598694930000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-01T14:24:00Z",
"timestamp": 1693578240000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T02:15:44Z",
"timestamp": 1740104144363,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601856000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.26471",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/jmv.26471",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.26471",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1023-1028",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0640-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00430-006-0019-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.3153",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/imt-2016-0020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25801",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID‐19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu X",
"first-page": "10970",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "China Xiv",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa954",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Early use of tocilizumab in the prevention of adult respiratory failure in SARS‐CoV‐2 infections and the utilization of interleukin‐6 levels in the management [published online ahead of print July 9, 2020]",
"author": "Antony SJ",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Tocilizumab's efficacy in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) is determined by the presence of cytokine storm [published online ahead of print June 22, 2020]",
"author": "Andrianopoulos I",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.26471"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tocilizumab use in COVID‐19‐associated pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "93"
}