Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID–19: A retrospective cohort study
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418, Jul 2020
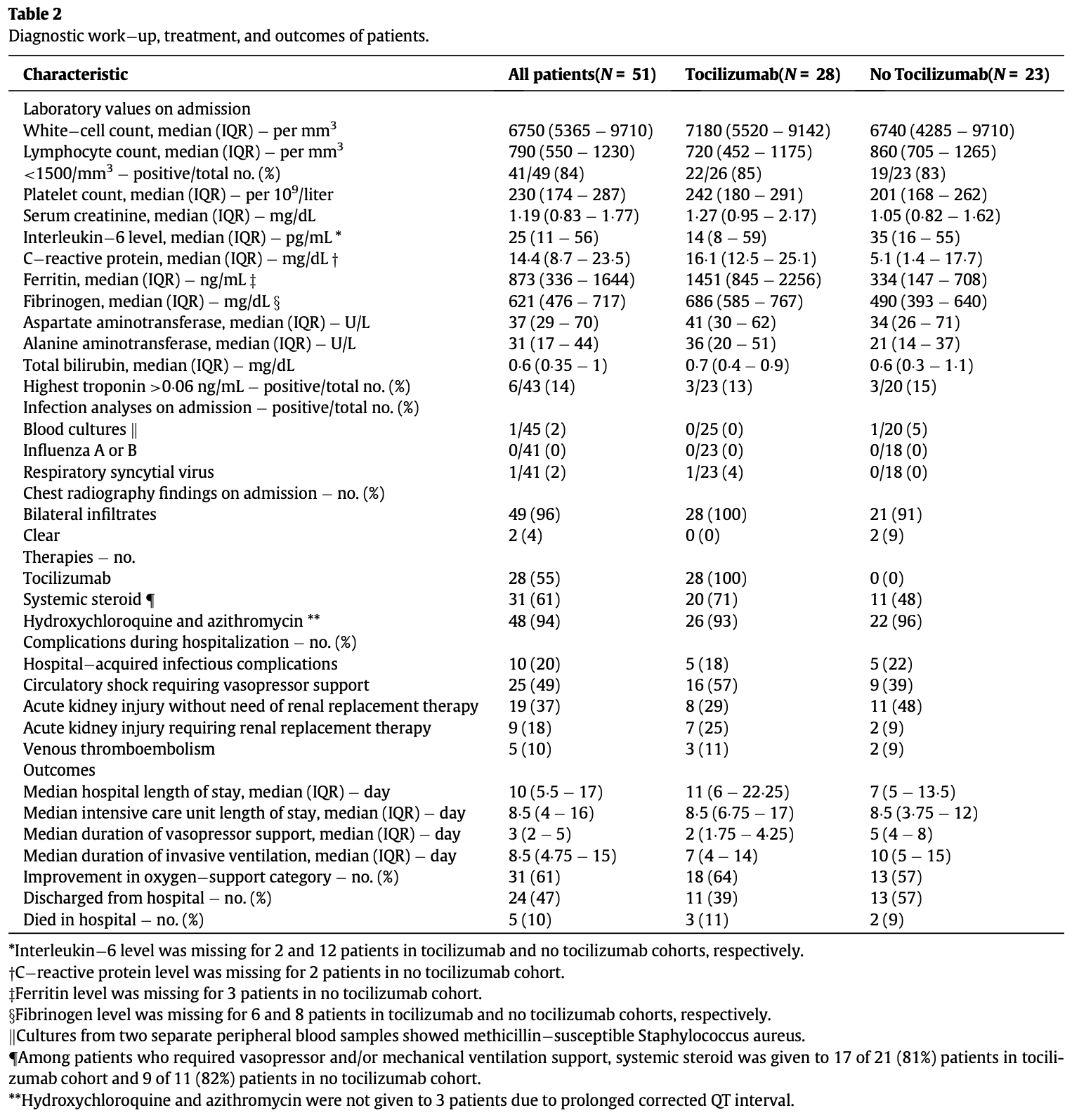
Retrospective 51 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significant reduction in vasopressor support duration with tocilizumab treatment, but no significant difference in other outcomes.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with significant differences between groups.
|
risk of death, 23.2% higher, RR 1.23, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 28 (10.7%), control 2 of 23 (8.7%).
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 39.6% higher, RR 1.40, p = 0.27, treatment 17 of 28 (60.7%), control 10 of 23 (43.5%).
|
|
ventilation time, 30.0% lower, relative time 0.70, p = 0.16, treatment median 7.0 IQR 10.0 n=28, control median 10.0 IQR 10.0 n=23.
|
|
hospitalization time, 57.1% higher, relative time 1.57, p = 0.16, treatment median 11.0 IQR 16.25 n=28, control median 7.0 IQR 8.5 n=23.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kewan et al., 31 Jul 2020, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 13 March, 2020 - 19 April, 2020.
Contact: akbikb@ccf.org.
Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID–19: A retrospective cohort study
eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418
Background: Tocilizumab was approved for chimeric antigen receptor TÀcell therapy induced cytokine release syndrome and it may provide clinical benefit for selected COVIDÀ19 patients. Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we analyzed hypoxic COVIDÀ19 patients who were consecutively admitted between March 13, 2020 and April 19, 2020. Patients with lung infiltrates and elevated inflammatory markers received a single dose of tocilizumab if no contraindication was present. Systemic steroid, hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin were concomitantly used for majority of the patients. Findings: Of the 51 patients included for analysis, 28 (55%) received tocilizumab and 23 (45%) did not receive tocilizumab. Tocilizumab cohort required more invasive ventilation (68% vs. 22%) at baseline and during entire hospitalization (75% vs. 48%). The median time to clinical improvement in tocilizumab vs. no tocilizumab cohorts was 8 days (Interquartile range [IQR]: 6¢25 À 9¢75 days) vs. 13 days (IQR: 9¢75 À 15¢25 days) among patients who required mechanical ventilation at any time (Hazard ratio for clinical improvement: 1¢83, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0¢57 À 5¢84) and 6¢5 days vs. 7 days among all patients (Hazard ratio for clinical improvement: 1¢14, 95% CI: 0¢55 À 2¢38), respectively. The median duration of vasopressor support and invasive mechanical ventilation were 2 days (IQR: 1¢75 À 4¢25 days) vs. 5 days (IQR: 4 À 8 days), p = 0.039, and 7 days (IQR: 4 À 14 days) vs. 10 days (IQR: 5 À 15 days) in tocilizumab vs. no tocilizumab cohorts, p = 0.11, respectively. Similar rates of hospitalÀacquired infections occurred in both cohorts (18% in tocilizumab and 22% in no tocilizumab cohort). Interpretation: In patients with severe COVID-19, tocilizumab was associated with significantly shorter duration of vasopressor support. Although not statistically significant, tocilizumab also resulted in shorter median time to clinical improvement and shorter duration of invasive ventilation. These findings require validation from ongoing clinical trials of Tocilizumab in COVIDÀ19 patients.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418.
References
Bedford, Enria, Giesecke, COVIDÀ19: towards controlling of a pandemic, Lancet
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, CovidÀ19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region À Case series, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2004500
Cao, Wang, Wen, A Trial of LopinavirÀRitonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Capra, Rossi, Mattioli, Impact of low dose tocilizumab on mortality rate in patients with COVID-19 related pneumonia, Eur J Intern Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.009
Chen, Zhao, Qu, Detectable serum SARS-CoV-2 viral load (RNAaemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 (IL-6) level in critically Ill COVID-19 patients, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa449
Colaneri, Bogliolo, Valsecchi, Tocilizumab for treatment of severe COVID-19 patients: preliminary results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMA-CORE), Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8050695
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Induction of proÀinflammatory cytokines (ILÀ1 and ILÀ6) and lung inflammation by CoronavirusÀ19 (COVIÀ19 or SARSÀCoVÀ2): antiÀinflammatory strategies, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Grasselli, Pesenti, Cecconi, Critical Care Utilization for the COVIDÀ19 Outbreak in Lombardy, Italy: early experience and forecast during an emergency response, JAMA
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Kandel, Chungong, Omaar, Xing, Health security capacities in the context of COVIDÀ19 outbreak: an analysis of international health regulations annual report data from 182 countries, Lancet
Khafaie, Rahim, Cross-country comparison of case fatality rates of COVID-19/SARS-COV-2, Osong Public Health Res Perspect
Le, Li, Yuan, FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cellÀinduced severe or lifeÀthreatening cytokine release syndrome, Oncologist
Lorenzo, Trolio, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Italy: analysis of risk factors and proposed remedial measures coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Italy: analysis of risk factors and proposed remedial measures, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00140
Luo, Liu, Qiu, Liu, Liu et al., Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25801
Mehra, Desai, Ruschitzka, Patel, Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: a multinational registry analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31180-6
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVIDÀ19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVIDÀ19 in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Radbel, Narayanan, Bhatt, Use of Tocilizumab for COVID-19-induced cytokine release syndrome: a cautionary case report, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.024
Ramos-Casals, Brito-Zer On, Opez-Guillermo, Adult haemophagocytic syndrome, Lancet
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVIDÀ19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134–020–05991–x
Russell, Millar, Baillie, Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019ÀnCoV lung injury, Lancet
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Autoimmun Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568
Wang, Zhang, Du, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Weiss, Murdoch, Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVIDÀ19, Lancet
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418",
"ISSN": [
"2589-5370"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418",
"alternative-id": [
"S2589537020301620"
],
"article-number": "100418",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID–19: A retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "eClinicalMedicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kewan",
"given": "Tariq",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3116-0942",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Covut",
"given": "Fahrettin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al–Jaghbeer",
"given": "Mohammed J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "Lori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gopalakrishna",
"given": "K.V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akbik",
"given": "Bassel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"container-title-short": "eClinicalMedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-20T09:57:48Z",
"timestamp": 1592647068000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-30T07:28:41Z",
"timestamp": 1667114921000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-27T17:08:17Z",
"timestamp": 1748365697104,
"version": "3.40.5"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 127,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1593561600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1590969600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537020301620?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537020301620?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100418",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30673-5",
"article-title": "COVID–19: towards controlling of a pandemic",
"author": "Bedford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0001",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0002",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30633-4",
"article-title": "Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID–19",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1014",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0003",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4031",
"article-title": "Critical Care Utilization for the COVID–19 Outbreak in Lombardy, Italy: early experience and forecast during an emergency response",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1545",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0004",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30553-5",
"article-title": "Health security capacities in the context of COVID–19 outbreak: an analysis of international health regulations annual report data from 182 countries",
"author": "Kandel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1047",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0005",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID–19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0006",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Induction of pro–inflammatory cytokines (IL–1 and IL–6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus–19 (COVI–19 or SARS–CoV–2): anti–inflammatory strategies",
"author": "Conti",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Biol Regul Homeost Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0007",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61048-X",
"article-title": "Adult haemophagocytic syndrome",
"author": "Ramos-Casals",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1503",
"issue": "9927",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0008",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.024",
"article-title": "Use of Tocilizumab for COVID-19-induced cytokine release syndrome: a cautionary case report",
"author": "Radbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0009",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0010",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID–19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0011",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID–19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0012",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Detectable serum SARS-CoV-2 viral load (RNAaemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 (IL-6) level in critically Ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0013",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028",
"article-title": "FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell–induced severe or life–threatening cytokine release syndrome",
"author": "Le",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "943",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Oncologist",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0014",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0015",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.009",
"article-title": "Impact of low dose tocilizumab on mortality rate in patients with COVID-19 related pneumonia",
"author": "Capra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0016",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 — preliminary report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0017",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0018",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0019",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2004500",
"article-title": "Covid–19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region – Case series",
"author": "Bhatraju",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30317-2",
"article-title": "Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019–nCoV lung injury",
"author": "Russell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0021",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25801",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0022",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia",
"author": "Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0023",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8050695",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for treatment of severe COVID-19 patients: preliminary results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE)",
"author": "Colaneri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0024",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: a multinational registry analysis",
"author": "Mehra",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0025",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Italy: analysis of risk factors and proposed remedial measures coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Italy: analysis of risk factors and proposed remedial measures",
"author": "Lorenzo",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0026",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.2.03",
"article-title": "Cross-country comparison of case fatality rates of COVID-19/SARS-COV-2",
"author": "Khafaie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "74",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Osong Public Health Res Perspect",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418_bib0027",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2589537020301620"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID–19: A retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "24"
}