Effect of Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case-Control Cohort Study
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph13100317, NCT04366206, Oct 2020
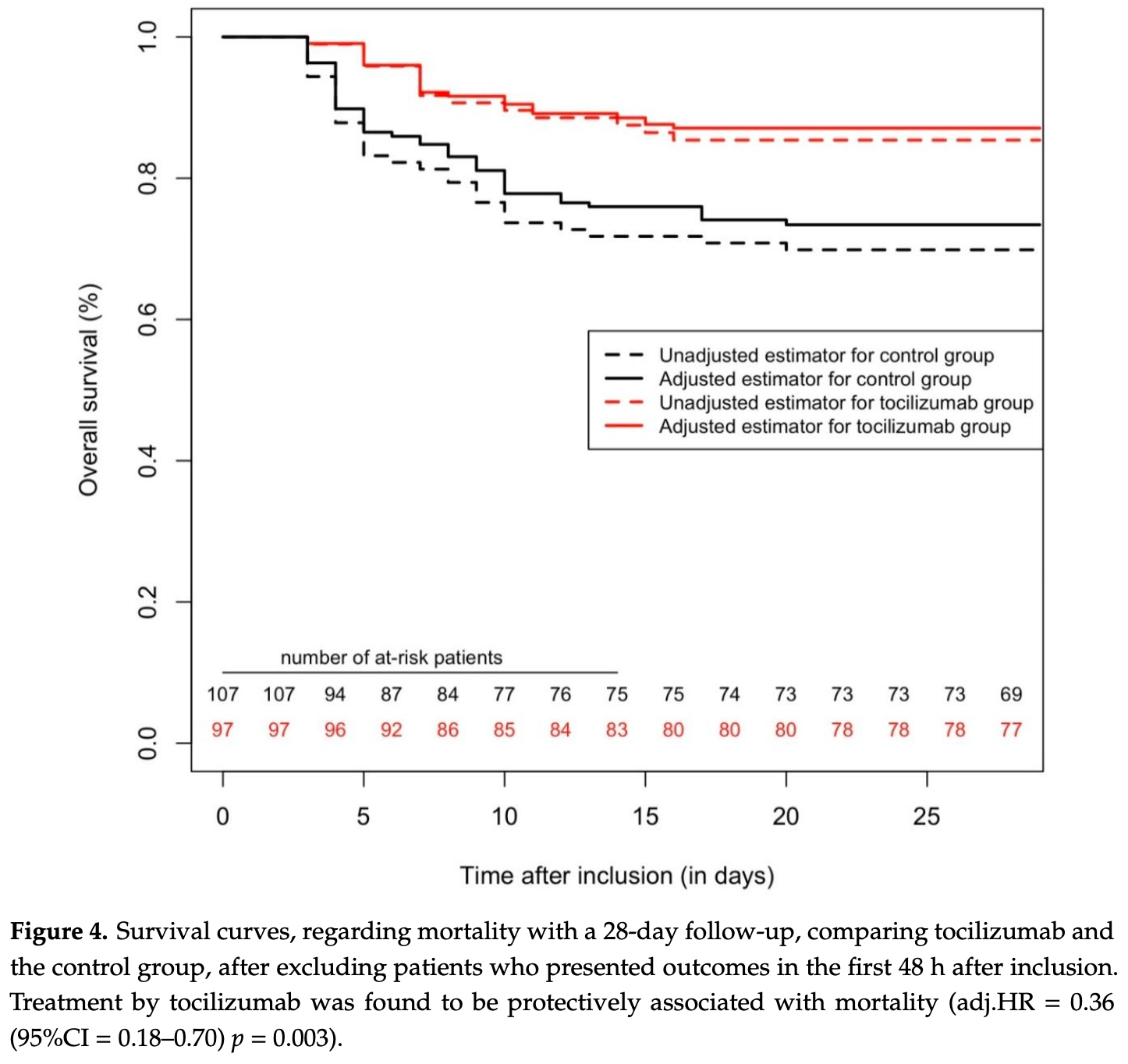
Retrospective 246 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia showing significantly lower mortality with tocilizumab treatment.
|
risk of death, 64.0% lower, HR 0.36, p = 0.003, treatment 84, control 84, propensity score matching, propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death/intubation, 60.0% lower, HR 0.40, p = 0.001, treatment 84, control 84, propensity score matching, propensity score weighting, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Rossi et al., 17 Oct 2020, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, mean age 67.7, 13 authors, study period 14 March, 2020 - April 2020, trial NCT04366206 (history).
Contact: benjamin.rossi@ght-gpne.fr (corresponding author), faiza.bou@hotmail.fr, louise.baucher@hotmail.fr, helene.guillot@ght-gpne.fr, marie-anne.bouldouyre@ght-gpne.fr, helene.gros@ght-gpne.fr, nguyen.lee@icloud.com, joeelie.salem@gmail.com, philippe.zimmermann6@gmail.com, louis.dubret@ght-gpne.fr, arezki.oufella@ght-gpne.fr, yves.allenbach@aphp.fr, paul.barsoum@ght-gpne.fr.
Effect of Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case-Control Cohort Study
Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph13100317
Tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor, administrated during the right timeframe may be beneficial against coronavirus-disease-2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia. All patients admitted for severe COVID-19 pneumonia (SpO 2 ≤ 96% despite O 2 -support ≥ 6 L/min) without invasive mechanical ventilation were included in a retrospective cohort study in a primary care hospital. The treatment effect of a single-dose, 400 mg, of tocilizumab was assessed by comparing those who received tocilizumab to those who did not. Selection bias was mitigated using three statistical methods. Primary outcome measure was a composite of mortality and ventilation at day 28. A total of 246 patients were included (106 were treated with tocilizumab). Overall, 105 (42.7%) patients presented the primary outcome, with 71 (28.9%) deaths during the 28-day follow-up. Propensity-score-matched 84 pairs of comparable patients. In the matched cohort (n = 168), tocilizumab was associated with fewer primary outcomes than the control group (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.49 (95% confidence interval (95%CI) = 0.3-0.81), p-value = 0.005). These results were similar in the overall cohort (n = 246), with Cox multivariable analysis yielding a protective association between tocilizumab and primary outcome (adjusted HR = 0.26 (95%CI = 0.135-0.51, p = 0.0001), confirmed by inverse probability score weighting (IPSW) analysis (p < 0.0001). Analyses on mortality only, with 28 days of follow-up, yielded similar results. In this study, tocilizumab 400 mg in a single-dose was associated with improved survival without mechanical ventilation in patients with severe COVID-19.
References
Abdallah, Hsu, Lu, Fettner, Zhang et al., Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Subcutaneous Tocilizumab in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis From 2 Randomized, Controlled Trials: SUMMACTA and BREVACTA: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Subcutaneous, J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1002/jcph.826
Austin, Stuart, The Performance of Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting and Full Matching on the Propensity Score in the Presence of Model Misspecification When Estimating the Effect of Treatment on Survival Outcomes, Stat. Methods Med. Res, doi:10.1177/0962280215584401
Barnaby, Becker, Chelico, Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With in the New York City Area, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Bilan, Dastranji, Ghalehgolab Behbahani, Comparison of the Spo 2 /Fio 2 Ratio and the Pao 2 /Fio 2 Ratio in Patients With Acute Lung Injury or Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res, doi:10.15171/jcvtr.2014.06
Chiu, Ostor, Hammond, Sokoll, Anderson et al., Access to the next Wave of Biologic Therapies (Abatacept and Tocilizumab) for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in England and Wales: Addressing Treatment Outside the Current NICE Guidance, Clin. Rheumatol, doi:10.1007/s10067-011-1936-6
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.5394
Guaraldi, Meschiari, Cozzi-Lepri, Milic, Tonelli et al., Tocilizumab in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9
Han, Liu, Zhou, Chen, Liu et al., Epidemiological Assessment of Imported Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Cases in the Most Affected City Outside of Hubei Province, Wenzhou, China, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.6785
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Effect of Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Preliminary Report, Infect. Dis, doi:10.1101/2020.06.22.20137273
Huet, Beaussier, Voisin, Jouveshomme, Dauriat et al., Anakinra for Severe Forms of COVID-19: A Cohort Study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30164-8
Le, Li, Yuan, Shord, Nie et al., FDA Approval Summary: Tocilizumab for Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Severe or Life-Threatening Cytokine Release Syndrome, Oncologist, doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028
Liu, Li, Zhou, Guan, Xiang, Can We Use Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Blockade for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)?, J. Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102452
Lunceford, Davidian, Stratification and Weighting via the Propensity Score in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects: A Comparative Study, Stat. Med, doi:10.1002/sim.1903
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium
Rubin, Ryerson, Haramati, Sverzellati, Kanne et al., The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.003
Spiteri, Fielding, Diercke, Campese, Enouf et al., First Cases of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the WHO European Region, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.9.2000178
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Garrafa, Regola et al., Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia with Hyperinflammatory Syndrome and Acute Respiratory Failure: A Single Center Study of 100 Patients in Brescia, Italy, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568
Zhang, Wu, Li, Zhao, Wang, Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonist Tocilizumab May Be the Key to Reduce Mortality, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph13100317",
"ISSN": [
"1424-8247"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ph13100317",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor, administrated during the right timeframe may be beneficial against coronavirus-disease-2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia. All patients admitted for severe COVID-19 pneumonia (SpO2 ≤ 96% despite O2-support ≥ 6 L/min) without invasive mechanical ventilation were included in a retrospective cohort study in a primary care hospital. The treatment effect of a single-dose, 400 mg, of tocilizumab was assessed by comparing those who received tocilizumab to those who did not. Selection bias was mitigated using three statistical methods. Primary outcome measure was a composite of mortality and ventilation at day 28. A total of 246 patients were included (106 were treated with tocilizumab). Overall, 105 (42.7%) patients presented the primary outcome, with 71 (28.9%) deaths during the 28-day follow-up. Propensity-score-matched 84 pairs of comparable patients. In the matched cohort (n = 168), tocilizumab was associated with fewer primary outcomes than the control group (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.49 (95% confidence interval (95%CI) = 0.3–0.81), p-value = 0.005). These results were similar in the overall cohort (n = 246), with Cox multivariable analysis yielding a protective association between tocilizumab and primary outcome (adjusted HR = 0.26 (95%CI = 0.135–0.51, p = 0.0001), confirmed by inverse probability score weighting (IPSW) analysis (p < 0.0001). Analyses on mortality only, with 28 days of follow-up, yielded similar results. In this study, tocilizumab 400 mg in a single-dose was associated with improved survival without mechanical ventilation in patients with severe COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ph13100317"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Rossi",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6014-6269",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research & Innovation of CMC Ambroise Paré, 92200 Neuilly-Sur-Seine, France"
},
{
"name": "INSERM, Clinical Investigations Center Paris-Est, CIC-1901, Sorbonne Université, AP.HP. Pitié-Salpétrière, 75013 Paris, France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Lee S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8772-1596",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zimmermann",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Boucenna",
"given": "Faiza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Dubret",
"given": "Louis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Baucher",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Guillot",
"given": "Helene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Bouldouyre",
"given": "Marie-Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine and Clinical Immunology, Sorbonne Université, AP.HP. Pitié-Salpétrière, 75013 Paris, France"
}
],
"family": "Allenbach",
"given": "Yves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0331-3307",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "INSERM, Clinical Investigations Center Paris-Est, CIC-1901, Sorbonne Université, AP.HP. Pitié-Salpétrière, 75013 Paris, France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Salem",
"given": "Joe-Elie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiology, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Barsoum",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Oufella",
"given": "Arezki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Robert Ballanger Hospital, 93600 Aulnay-Sous-Bois, France"
}
],
"family": "Gros",
"given": "Helene",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"container-title-short": "Pharmaceuticals",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-17T11:23:22Z",
"timestamp": 1602933802000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-04T09:12:50Z",
"timestamp": 1720084370000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T16:34:22Z",
"timestamp": 1740155662954,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 26,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1602892800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/13/10/317/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "317",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.9.2000178",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Spiteri, G., Fielding, J., Diercke, M., Campese, C., Enouf, V., Gaymard, A., Bella, A., Sognamiglio, P., Sierra Moros, M.J., and Riutort, A.N. (2020). First Cases of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the WHO European Region, 24 January to 21 February 2020. Eurosurveillance, 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028",
"article-title": "FDA Approval Summary: Tocilizumab for Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Severe or Life-Threatening Cytokine Release Syndrome",
"author": "Le",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "943",
"journal-title": "Oncologist",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102452",
"article-title": "Can We Use Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Blockade for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)?",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102452",
"journal-title": "J. Autoimmun.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954",
"article-title": "Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonist Tocilizumab May Be the Key to Reduce Mortality",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105954",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.6785",
"article-title": "Epidemiological Assessment of Imported Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Cases in the Most Affected City Outside of Hubei Province, Wenzhou, China",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e206785",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30164-8",
"article-title": "Anakinra for Severe Forms of COVID-19: A Cohort Study",
"author": "Huet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e393",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "The RECOVERY Collaborative Group (2020). Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.22.20137273",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Horby, P., Lim, W.S., Emberson, J., Mafham, M., Bell, J., Linsell, L., Staplin, N., Brightling, C., Ustianowski, A., and Elmahi, E. (2020). Effect of Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Preliminary Report. Infect. Dis."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia with Hyperinflammatory Syndrome and Acute Respiratory Failure: A Single Center Study of 100 Patients in Brescia, Italy",
"author": "Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102568",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Guaraldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e474",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "(2020, October 15). CORIMUNO-19-Tocilizumab Trial-TOCI (CORIMUNO-TOCI), Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04331808201202317."
},
{
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "(2020, October 15). A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia (COVACTA), Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04320615."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-011-1936-6",
"article-title": "Access to the next Wave of Biologic Therapies (Abatacept and Tocilizumab) for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in England and Wales: Addressing Treatment Outside the Current NICE Guidance",
"author": "Chiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1005",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcph.826",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Subcutaneous Tocilizumab in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis From 2 Randomized, Controlled Trials: SUMMACTA and BREVACTA: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Subcutaneous",
"author": "Abdallah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.1903",
"article-title": "Stratification and Weighting via the Propensity Score in Estimation of Causal Treatment Effects: A Comparative Study",
"author": "Lunceford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2937",
"journal-title": "Stat. Med.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280215584401",
"article-title": "The Performance of Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting and Full Matching on the Propensity Score in the Presence of Model Misspecification When Estimating the Effect of Treatment on Survival Outcomes",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1654",
"journal-title": "Stat. Methods Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15171/jcvtr.2014.06",
"article-title": "Comparison of the Spo2 /Fio2 Ratio and the Pao 2 /Fio 2 Ratio in Patients With Acute Lung Injury or Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome",
"author": "Bilan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.003",
"article-title": "The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Rubin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.06.06.20122341",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/13/10/317"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case-Control Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}