Tocilizumab for Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa954, Jul 2020
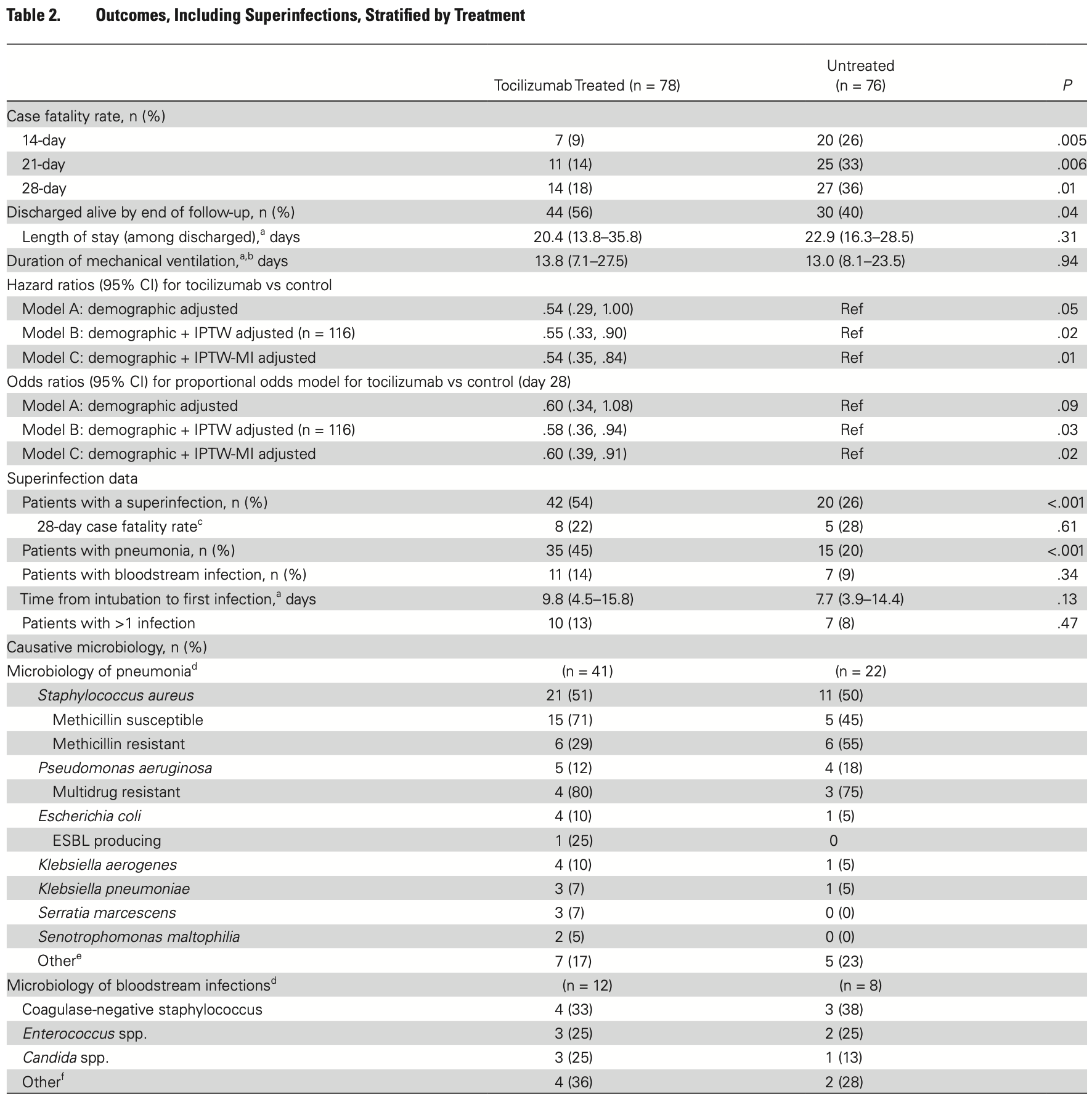
Retrospective 154 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients showing improved survival with tocilizumab. However, tocilizumab was associated with significantly higher rates of superinfection, particularly ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 45.0% lower, HR 0.55, p = 0.02, treatment 78, control 76, propensity score weighting.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Somers et al., 11 Jul 2020, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 22 authors.
Contact: emsomers@umich.edu.
Tocilizumab for Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa954
See the Editorial commentary by cheng and Hill on pages e455-7
Disclaimer. The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the Department of Health and Human Services. Financial support. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant numbers UL1TR002240; 1K12HL133304; to C. M. F.); the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (grant number U01IP000974); and an American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy New Investigator Award (to J. L. G.). Potential conflicts of interest. J. P. T. reports stock in Proctor & Gamble and General Electric; A. S. L. reports being a paid consultant on antivirals for Sanofi and a paid member of a clinical trial steering committee for Baloxavir for Roche; E. M. reports being a paid consultant for Pfizer on RSV and receipt of research funding from Roche. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
References
Antinori, Bonazzetti, Gubertini, Tocilizumab for cytokine storm syndrome in COVID-19 pneumonia: an increased risk for candidemia?, Autoimmun Rev
Austin, Stuart, Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies, Stat Med
Bester, Pretorius, Effects of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 on erythrocytes, platelets and clot viscoelasticity, Sci Rep
Capra, Rossi, Mattioli, Impact of low dose tocilizumab on mortality rate in patients with COVID-19 related pneumonia, Eur J Intern Med
Dunning, Merson, Rohde, 3, ISARIC Council. Open source clinical science for emerging infections, Lancet Infect Dis
Gritti, Raimondi, Ripamonti, Use of siltuximab in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia requiring ventilatory support, doi:10.1101/2020.04.01.20048561v4
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Klopfenstein, Zayet, Lohse, Tocilizumab therapy reduced intensive care unit admissions and/or mortality in COVID-19 patients, Médecine Mal Infect, doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2020.05.001
Lin, Wang, Myles, Propensity score-based comparison of longterm outcomes with 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy vs intensitymodulated radiotherapy for esophageal cancer, Int J Radiat Oncol
Luo, Liu, Qiu, Liu, Liu et al., Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience, J Med Virol
Mcgonagle, Sharif, 'regan, Bridgewood, The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease, Autoimmun Rev
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., UK. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Moore, June, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb8925
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1966
Radbel, Narayanan, Bhatt, Use of tocilizumab for COVID-19-induced cytokine release syndrome: a cautionary case report, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.024
Rice, Wheeler, Bernard, Hayden, Schoenfeld et al., Comparison of the SpO2/FIO2 ratio and the PaO2/ FIO2 ratio in patients with acute lung injury or ARDS, Chest
Robins, A new approach to causal inference in mortality studies with a sustained exposure period-application to control of the healthy worker survivor effect, Math Model
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intens Care Med
Sciascia, Aprà, Baffa, Pilot prospective open, single-arm multicentre study on off-label use of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19, Clin Exp Rheumatol
Senchenkova, Russell, Yildirim, Granger, Gavins, Novel role of T cells and IL-6 (interleukin-6) in angiotensin II-induced microvascular dysfunction, Hypertension
Suissa, Immortal time bias in pharmaco-epidemiology, Am J Epidemiol
Teachey, Rheingold, Maude, Cytokine release syndrome after blinatumomab treatment related to abnormal macrophage activation and ameliorated with cytokine-directed therapy, Blood
Van Buuren, Multiple imputation of discrete and continuous data by fully conditional specification, Stat Methods Med Res
Vandenbroucke, Elm, Altman, Strengthening The Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration, Epidemiology
Velazquez-Salinas, Verdugo-Rodriguez, Rodriguez, Borca, The role of interleukin 6 during viral infections, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.01057
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.20056
Yang, Wang, Yang, IL-6 ameliorates acute lung injury in influenza virus infection, Sci Rep
Zhong, Tang, Ye, Dong, The immunology of COVID-19: is immune modulation an option for treatment?, Lancet Rheumatol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa954",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa954",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can manifest in rapid decompensation and respiratory failure with elevated inflammatory markers, consistent with cytokine release syndrome for which IL-6 blockade is an approved treatment.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We assessed effectiveness and safety of IL-6 blockade with tocilizumab in a single-center cohort of patients with COVID-19 requiring mechanical ventilation. The primary endpoint was survival probability postintubation; secondary analyses included an ordinal illness severity scale integrating superinfections. Outcomes in patients who received tocilizumab compared with tocilizumab-untreated controls were evaluated using multivariable Cox regression with propensity score inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>154 patients were included, of whom 78 received tocilizumab and 76 did not. Median follow-up was 47 days (range, 28–67). Baseline characteristics were similar between groups, although tocilizumab-treated patients were younger (mean: 55 vs 60 years), less likely to have chronic pulmonary disease (10% vs 28%), and had lower D-dimer values at time of intubation (median: 2.4 vs 6.5 mg/dL). In IPTW-adjusted models, tocilizumab was associated with a 45% reduction in hazard of death (HR, .55; 95% CI, .33–.90) and improved status on the ordinal outcome scale [OR per 1-level increase, .58; .36–.94). Although tocilizumab was associated with an increased proportion of patients with superinfections (54% vs 26%; P &lt; .001), there was no difference in 28-day case fatality rate among tocilizumab-treated patients with versus without superinfection (22% vs 15%; P = .42). Staphylococcus aureus accounted for ~50% of bacterial pneumonia.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this cohort of mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients, tocilizumab was associated with lower mortality despite higher superinfection occurrence.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5234-3978",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Environmental Health Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Somers",
"given": "Emily C",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Eschenauer",
"given": "Gregory A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Michigan Institute for Clinical & Health Research, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Troost",
"given": "Jonathan P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Golob",
"given": "Jonathan L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gandhi",
"given": "Tejal N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Petty",
"given": "Lindsay A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Baang",
"given": "Ji Hoon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Dillman",
"given": "Nicholas O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Frame",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gregg",
"given": "Kevin S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kaul",
"given": "Dan R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Nagel",
"given": "Jerod",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Twisha S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Shiwei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Lauring",
"given": "Adam S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Learning Health Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hanauer",
"given": "David A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Pratima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Fung",
"given": "Christopher M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA"
}
],
"family": "Pogue",
"given": "Jason M",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-10T03:20:45Z",
"timestamp": 1594351245000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-15T19:59:45Z",
"timestamp": 1626379185000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"award": [
"UL1TR002240",
"1K12HL133304"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000002",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000030",
"award": [
"U01IP000974"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000030",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention"
},
{
"name": "American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy New Investigator Award"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-07T16:28:31Z",
"timestamp": 1749313711401,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 268,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
15
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1594425600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa954/33797505/ciaa954.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/73/2/e445/39065082/ciaa954.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/73/2/e445/39065082/ciaa954.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e445-e454",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
11
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0001",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk factors associated",
"author": "Wu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0002",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "846",
"journal-title": "Intens Care Med",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0003",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb8925",
"article-title": "Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0004",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0005",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1966",
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study",
"author": "Petrilli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1966",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0006",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30120-X",
"article-title": "The immunology of COVID-19: is immune modulation an option for treatment?",
"author": "Zhong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e428",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0007",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2013-02-485623",
"article-title": "Cytokine release syndrome after blinatumomab treatment related to abnormal macrophage activation and ameliorated with cytokine-directed therapy",
"author": "Teachey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5154",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0008",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0009",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Pilot prospective open, single-arm multicentre study on off-label use of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Sciascia",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Rheumatol",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0010",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25801",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "814",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0011",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.009",
"article-title": "Impact of low dose tocilizumab on mortality rate in patients with COVID-19 related pneumonia",
"author": "Capra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0012",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medmal.2020.05.001",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab therapy reduced intensive care unit admissions and/or mortality in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Klopfenstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "397",
"journal-title": "Médecine Mal Infect",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0013",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Use of siltuximab in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia requiring ventilatory suppo",
"author": "Gritti",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0014",
"year": "2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.024",
"article-title": "Use of tocilizumab for COVID-19-induced cytokine release syndrome: a cautionary case report",
"author": "Radbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e15",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0015",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102564",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for cytokine storm syndrome in COVID-19 pneumonia: an increased risk for candidemia?",
"author": "Antinori",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102564",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0016",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70327-X",
"article-title": "Open source clinical science for emerging infections",
"author": "Dunning",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0017",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Global outbreak research: harmony not hegemony",
"author": "ISARIC Clinical Characterization Group",
"first-page": "30440",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0018",
"volume": "3099",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181577511",
"article-title": "Strengthening The Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration",
"author": "Vandenbroucke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "805",
"journal-title": "Epidemiology",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0019",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwm324",
"article-title": "Immortal time bias in pharmaco-epidemiology",
"author": "Suissa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "492",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0020",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.07-0617",
"article-title": "Comparison of the SpO2/FIO2 ratio and the PaO2/FIO2 ratio in patients with acute lung injury or ARDS",
"author": "Rice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "410",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0021",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280206074463",
"article-title": "Multiple imputation of discrete and continuous data by fully conditional specification",
"author": "van Buuren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Stat Methods Med Res",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0022",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0270-0255(86)90088-6",
"article-title": "A new approach to causal inference in mortality studies with a sustained exposure period—application to control of the healthy worker survivor effect",
"author": "Robins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1393",
"journal-title": "Math Model",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0023",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.02.015",
"article-title": "Propensity score-based comparison of long-term outcomes with 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy vs intensity-modulated radiotherapy for esophageal cancer",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1078",
"journal-title": "Int J Radiat Oncol",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0024",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.6607",
"article-title": "Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3661",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0025",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537",
"article-title": "The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease",
"author": "McGonagle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102537",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0026",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12286",
"article-title": "Novel role of T cells and IL-6 (interleukin-6) in angiotensin II-induced microvascular dysfunction",
"author": "Senchenkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "829",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0027",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep32188",
"article-title": "Effects of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 on erythrocytes, platelets and clot viscoelasticity",
"author": "Bester",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "32188",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0028",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.01057",
"article-title": "The role of interleukin",
"author": "Velazquez-Salinas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1057",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0029",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep43829",
"article-title": "IL-6 ameliorates acute lung injury in influenza virus infection",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43829",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2021071519590476100_CIT0030",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.05.29.20117358",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/73/2/e445/5870306"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tocilizumab for Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "73"
}