Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study
et al., The Lancet Rheumatology, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0, NCT04347993, Oct 2020
Retrospective 764 COVID-19 patients requiring ICU support showing lower mortality with tocilizumab. There was significantly higher use of HCQ+AZ in the treatment group, which was not adjusted for in the propensity score matching or Cox regression.
5% of tocilizumab patients did not receive HCQ compared to 17% of untreated patients (15% after PSM), suggesting substantial differences between the groups in treatment propensity (which may include other unreported treatments such as vitamin D).
Authors state that "An increase in use of hydroxychloroquine was noted in patients who received tocilizumab compared with those who did not receive tocilizumab, which we do not believe had a relevant effect on our findings because most observational studies have not reported a benefit for hydroxychloroquine among hospitalised patients".
However authors would know the actual effect of HCQ and AZ in their dataset. Lack of reporting and lack of adjustment suggests that HCQ+AZ may have been beneficial in this case (due to politics authors would not be allowed to report this).
HCQ/AZ may lack benefit or be harmful with excessive dosage and very late treatment. Tocilizumab treatment was delayed 3 days post admission - HCQ treatment likely started earlier based on local protocol, without RCT delays. Typical HCQ dose in the region was reasonable. The RECOVERY trial delivered roughly four times the five-day exposure of the Hackensack area hospital protocol and more than double even a ten-day course. Based on expected dose and treatment time, it is likely that HCQ/AZ use here was beneficial.
Confounding by time is also possible - HCQ use likely dropped during the end of the study period, and the correlation with tocilizumab treatment suggests potential changes in tocilizumab treatment propensity over time, which adds confounding due to other significant SOC changes during this early pandemic period.
Other potential significant confounders were not included in adjustments without explanation - for example after matching the tocilizumab treatment group had 2x the number of nursing home residents with higher baseline risk.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
significant unadjusted confounding possible.
|
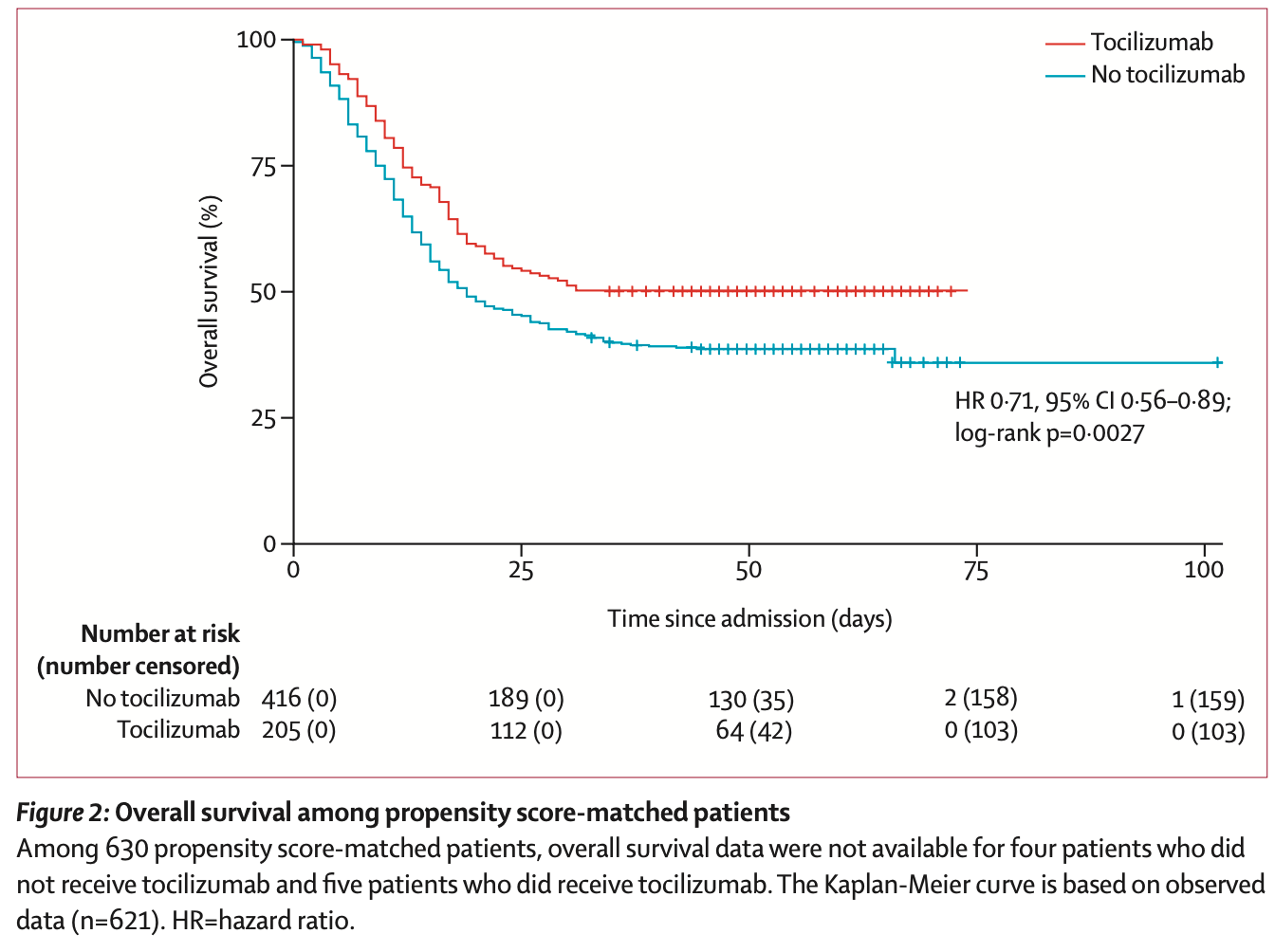
risk of death, 29.0% lower, HR 0.71, p = 0.004, treatment 205, control 416, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Biran et al., 31 Oct 2020, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 29 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 22 April, 2020, trial NCT04347993 (history).
Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study
The Lancet Rheumatology, doi:10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30277-0
Background Tocilizumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the interleukin-6 receptor, has been proposed to mitigate the cytokine storm syndrome associated with severe COVID-19. We aimed to investigate the association between tocilizumab exposure and hospital-related mortality among patients requiring intensive care unit (ICU) support for COVID-19.
Methods We did a retrospective observational cohort study at 13 hospitals within the Hackensack Meridian Health network (NJ, USA). We included patients (aged ≥18 years) with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 who needed support in the ICU. We obtained data from a prospective observational database and compared outcomes in patients who received tocilizumab with those who did not. We applied a multivariable Cox model with propensity score matching to reduce confounding effects. The primary endpoint was hospital-related mortality. The prospective observational database is registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04347993.
Findings Between March 1 and April 22, 2020, 764 patients with COVID-19 required support in the ICU, of whom 210 (27%) received tocilizumab. Factors associated with receiving tocilizumab were patients' age, gender, renal function, and treatment location. 630 patients were included in the propensity score-matched population, of whom 210 received tocilizumab and 420 did not receive tocilizumab. 358 (57%) of 630 patients died, 102 (49%) who received tocilizumab and 256 (61%) who did not receive tocilizumab. Overall median survival from time of admission was not reached (95% CI 23 days-not reached) among patients receiving tocilizumab and was 19 days (16-26) for those who did not receive tocilizumab (hazard ratio [HR] 0•71, 95% CI 0•56-0•89; p=0•0027). In the primary multivariable Cox regression analysis with propensity matching, an association was noted between receiving tocilizumab and decreased hospital-related mortality (HR 0•64, 95% CI 0•47-0•87; p=0•0040). Similar associations with tocilizumab were noted among subgroups requiring mechanical ventilatory support and with baseline C-reactive protein of 15 mg/dL or higher. Interpretation In this observational study, patients with COVID-19 requiring ICU support who received tocilizumab had reduced mortality. Results of ongoing randomised controlled trials are awaited.
References
Campochiaro, Dellatorre, Cavalli, Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in severe COVID19 patients: a singlecentre retrospective cohort study, Eur J Intern Med
Cavalli, Luca, Campochiaro, Interleukin1 blockade with highdose anakinra in patients with COVID19, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and hyperinflammation: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Semin Immunopathol
Fu, Xu, Wei, Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID19?, J Transl Med
Hernandez, Roman, Pasupuleti, Barboza, White, Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for treatment or prophylaxis of COVID19: a living systematic review, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M202496
Ho, Imai, King, Stuart, Matching as nonparametric preprocessing for reducing model dependence in parametric causal inference, Polit Anal
Kermali, Khalsa, Pillai, Ismail, Harky, The role of biomarkers in diagnosis of COVID19: a systematic review, Life Sci
Le, Li, Yuan, FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cellinduced severe or lifethreatening cytokine release syndrome, Oncologist
Luo, Liu, Qiu, Liu, Liu et al., Tocilizumab treatment in COVID19: a single center experience, J Med Virol
Martinezsanz, Ron, Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID19: a multicenter cohort study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.08.20125245(preprint
May, Hosmer, A simplified method of calculating an overall goodnessoffit test for the Cox proportional hazards model, Lifetime Data Anal
Mcgonagle, Sharif, 'regan, Bridgewood, The role of cytokines including interleukin6 in COVID19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndromelike disease, Autoimmun Rev
Morena, Milazzo, Oreni, Offlabel use of tocilizumab for the treatment of SARSCoV2 pneumonia in Milan, Italy, Eur J Intern Med
Ridker, Creactive protein: eighty years from discovery to emergence as a major risk marker for cardiovascular disease, Clin Chem
Sherman, Anderson, Pan, Realworld evidence: what is it and what can it tell us?, N Engl J Med
Stuart, Matching methods for causal inference: a review and a look forward, Stat Sci
Tan, Kang, Ji, Validation of predictors of disease severity and outcomes in COVID19 patients: a descriptive and retrospective study, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2020.05.002
Teijaro, Cytokine storms in infectious diseases, Semin Immunopathol
The, Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid19: preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy, Autoimmun Rev
Weinhold, Bader, Poli, Rüther, Interleukin6 is necessary, but not sufficient, for induction of the human Creactive protein gene in vivo, Biochem J
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Xu, Shi, Wang, Pathological findings of COVID19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med
Zhang, Wu, Li, Zhao, Wang, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID19: interleukin6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Zhang, Yan, Fan, Ddimer levels on admission to predict inhospital mortality in patients with Covid19, J Thromb Haemost
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30277-0",
"ISSN": [
"2665-9913"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0",
"alternative-id": [
"S2665991320302770"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Rheumatology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30287-3"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Biran",
"given": "Noa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ip",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahn",
"given": "Jaeil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Go",
"given": "Ronaldo C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Shuqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathura",
"given": "Shivam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinclaire",
"given": "Brittany A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bednarz",
"given": "Urszula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marafelias",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hansen",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siegel",
"given": "David S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goy",
"given": "Andre H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pecora",
"given": "Andrew L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sawczuk",
"given": "Ihor S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koniaris",
"given": "Lauren S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simwenyi",
"given": "Micky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varga",
"given": "Daniel W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tank",
"given": "Lisa K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stein",
"given": "Aaron A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allusson",
"given": "Valerie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "George S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oser",
"given": "William F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tuma",
"given": "Roman A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reichman",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brusco",
"given": "Louis",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "Jr"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carpenter",
"given": "Kim L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Costanzo",
"given": "Eric J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vivona",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goldberg",
"given": "Stuart L",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Rheumatology",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Rheumatology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-14T22:46:22Z",
"timestamp": 1597445182000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-24T22:33:58Z",
"timestamp": 1600986838000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-05T18:24:00Z",
"timestamp": 1749147840839
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 228,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2665991320302770?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2665991320302770?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e603-e612",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954",
"article-title": "Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib2",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"article-title": "Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology",
"author": "Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "Semin Immunopathol",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib3",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028",
"article-title": "FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome",
"author": "Le",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "943",
"journal-title": "Oncologist",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib4",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "420",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib5",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib6",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25801",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: a single center experience",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "814",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib7",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.021",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19 patients: a single-centre retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Campochiaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib8",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.011",
"article-title": "Off-label use of tocilizumab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Milan, Italy",
"author": "Morena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib9",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy",
"author": "Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib10",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsb1609216",
"article-title": "Real-world evidence: what is it and what can it tell us?",
"author": "Sherman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2293",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib12",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1009612305785",
"article-title": "A simplified method of calculating an overall goodness-of-fit test for the Cox proportional hazards model",
"author": "May",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Lifetime Data Anal",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib15",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pan/mpl013",
"article-title": "Matching as nonparametric preprocessing for reducing model dependence in parametric causal inference",
"author": "Ho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "199",
"journal-title": "Polit Anal",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib16",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1214/09-STS313",
"article-title": "Matching methods for causal inference: a review and a look forward",
"author": "Stuart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Stat Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib17",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study",
"author": "Martinez-Sanz",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02339-3",
"article-title": "Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19?",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib19",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0640-2",
"article-title": "Cytokine storms in infectious diseases",
"author": "Teijaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "501",
"journal-title": "Semin Immunopathol",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib20",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537",
"article-title": "The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease",
"author": "McGonagle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib21",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Validation of predictors of disease severity and outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a descriptive and retrospective study",
"author": "Tan",
"journal-title": "Med (N Y)",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3250617",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 is necessary, but not sufficient, for induction of the human C-reactive protein gene in vivo",
"author": "Weinhold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"journal-title": "Biochem J",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib23",
"volume": "325",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1373/clinchem.2008.119214",
"article-title": "C-reactive protein: eighty years from discovery to emergence as a major risk marker for cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Ridker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "209",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib24",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117788",
"article-title": "The role of biomarkers in diagnosis of COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "Kermali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib25",
"volume": "254",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14859",
"article-title": "D-dimer levels on admission to predict in-hospital mortality in patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1324",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib26",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30127-2",
"article-title": "Interleukin-1 blockade with high-dose anakinra in patients with COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and hyperinflammation: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Cavalli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e325",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib27",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19: preliminary report",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for treatment or prophylaxis of COVID-19: a living systematic review",
"author": "Hernandez",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0_bib29",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2665991320302770"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "2"
}