Tocilizumab Ameliorates the Hypoxia in COVID-19 Moderate Patients with Bilateral Pulmonary Lesions: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Multicenter Trial
et al., SSRN Electronic Journal, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3667681, ChiCTR2000029765, Dec 2020
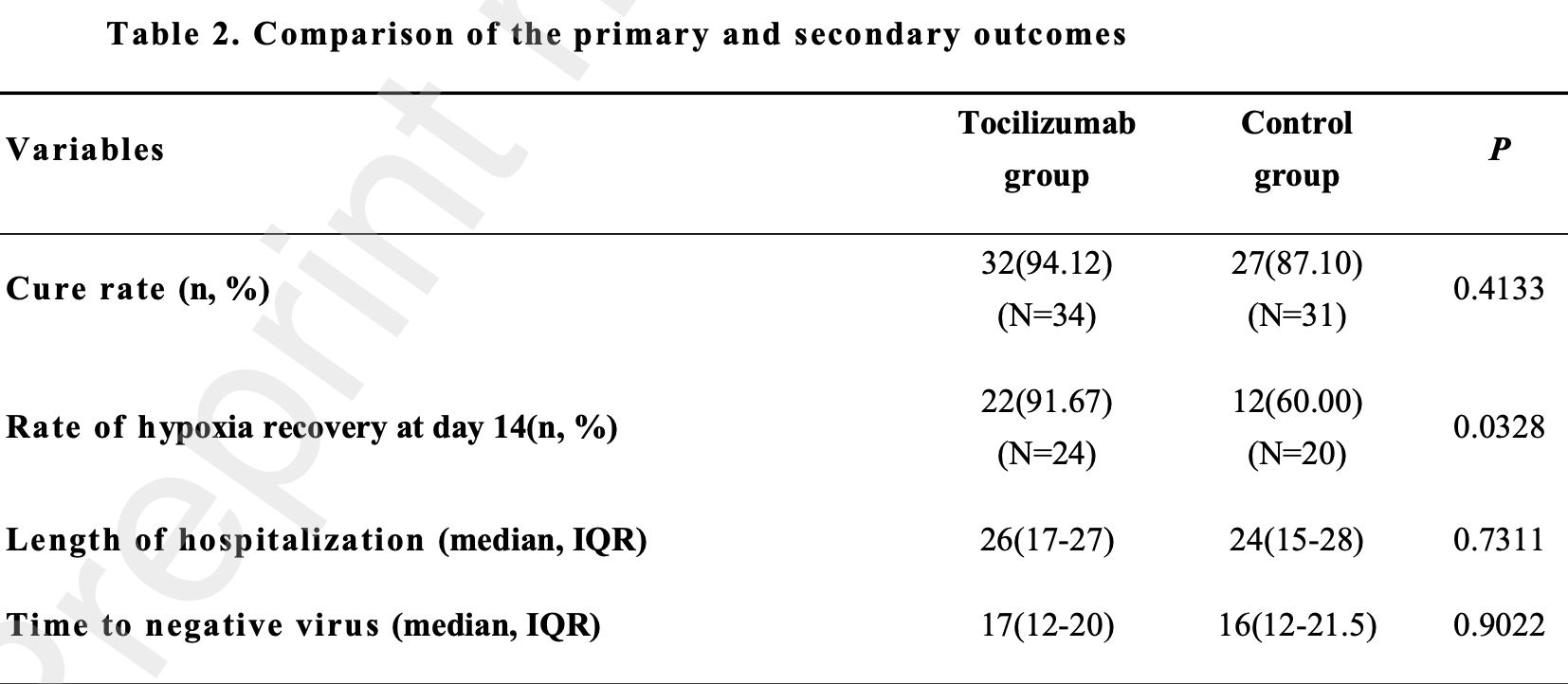
RCT 65 COVID-19 patients in China showing improvement in hypoxia recovery with tocilizumab treatment, especially in moderate patients with bilateral pulmonary lesions.
Viral load measured by PCR may not accurately reflect infectious virus measured by viral culture. Porter et al. show that viral load early in infection was correlated with infectious virus, but viral load late in infection could be high even with low or undetectable infectious virus. Assessing viral load later in infection may underestimate reductions in infectious virus with treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments2.
|
risk of progression, 27.1% lower, RR 0.73, p = 0.53, treatment 7 of 24 (29.2%), control 8 of 20 (40.0%), NNT 9.2.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 54.4% lower, RR 0.46, p = 0.41, treatment 2 of 34 (5.9%), control 4 of 31 (12.9%), NNT 14.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 79.2% lower, RR 0.21, p = 0.03, treatment 2 of 24 (8.3%), control 8 of 20 (40.0%), NNT 3.2, hypoxia recovery.
|
|
hospitalization time, 8.3% higher, relative time 1.08, p = 0.35, treatment median 26.0 IQR 10.0 n=34, control median 24.0 IQR 13.0 n=31.
|
|
time to viral-, 6.2% higher, relative time 1.06, p = 0.54, treatment median 17.0 IQR 8.0 n=34, control median 16.0 IQR 9.5 n=31.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wang et al., 31 Dec 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, 26 authors, study period 13 February, 2020 - 13 March, 2020, trial ChiCTR2000029765.
Contact: xxlahh8@ustc.edu.cn, hfmxd@sina.com, ustcwhm@ustc.edu.cn.
Tocilizumab ameliorates the hypoxia in COVID-19 moderate patients with bilateral pulmonary lesions: a randomized, controlled, open-label, multicenter trial
65 Patients were assessed for eligibility 33 patients randomly assigned to the tocilizumab group 32 patients randomly assigned to the control group 34 patients Intention to treat population 31 patients Intention to treat population 1 patient transferred to the tocilizumab group 34 patients included in safety population 31 patients included in safety population Figure 1.
References
Fu, Xu, Wei, Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19?, J Transl Med
Guaraldi, Cozzi-Lepri, Milic, Tonelli, Menozzi et al., None
Moore, June, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19, Science
Price, Altice, Shyr, Tocilizumab treatment for Cytokine Release Syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: survival and clinical outcomes, Chest
Seguin, Galicier, Boutboul, Lemiale, Azoulay, Pulmonary Involvement in Patients With Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis, Chest
Tian, Hu, Niu, Liu, Xu et al., Pulmonary Pathology of Early-Phase 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pneumonia in Two Patients With Lung Cancer, Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy, Autoimmun Rev
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Xu, Shi, Wang, Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Zhou, Fu, Zheng, Pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storm in severe COVID-19 patients, National Science Review
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3667681",
"ISSN": [
"1556-5068"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3667681",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Dongsheng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Binqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Zhen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Dongliang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Mingfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Tianjun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Liangye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yao",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Xiao jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Daqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Yubei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dong",
"given": "Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jumei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Xiaoyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Yonggang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Aijun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Xiaowen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mei",
"given": "Xiaodong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Haiming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Xiaoling",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "SSRN Electronic Journal",
"container-title-short": "SSRN Journal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-29T11:31:40Z",
"timestamp": 1598700700000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-29T11:31:51Z",
"timestamp": 1598700711000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-08T10:43:20Z",
"timestamp": 1720435400213
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 10,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.2139",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=3667681"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Tocilizumab Ameliorates the Hypoxia in COVID-19 Moderate Patients with Bilateral Pulmonary Lesions: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Multicenter Trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}