Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study
et al., EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999, Oct 2020
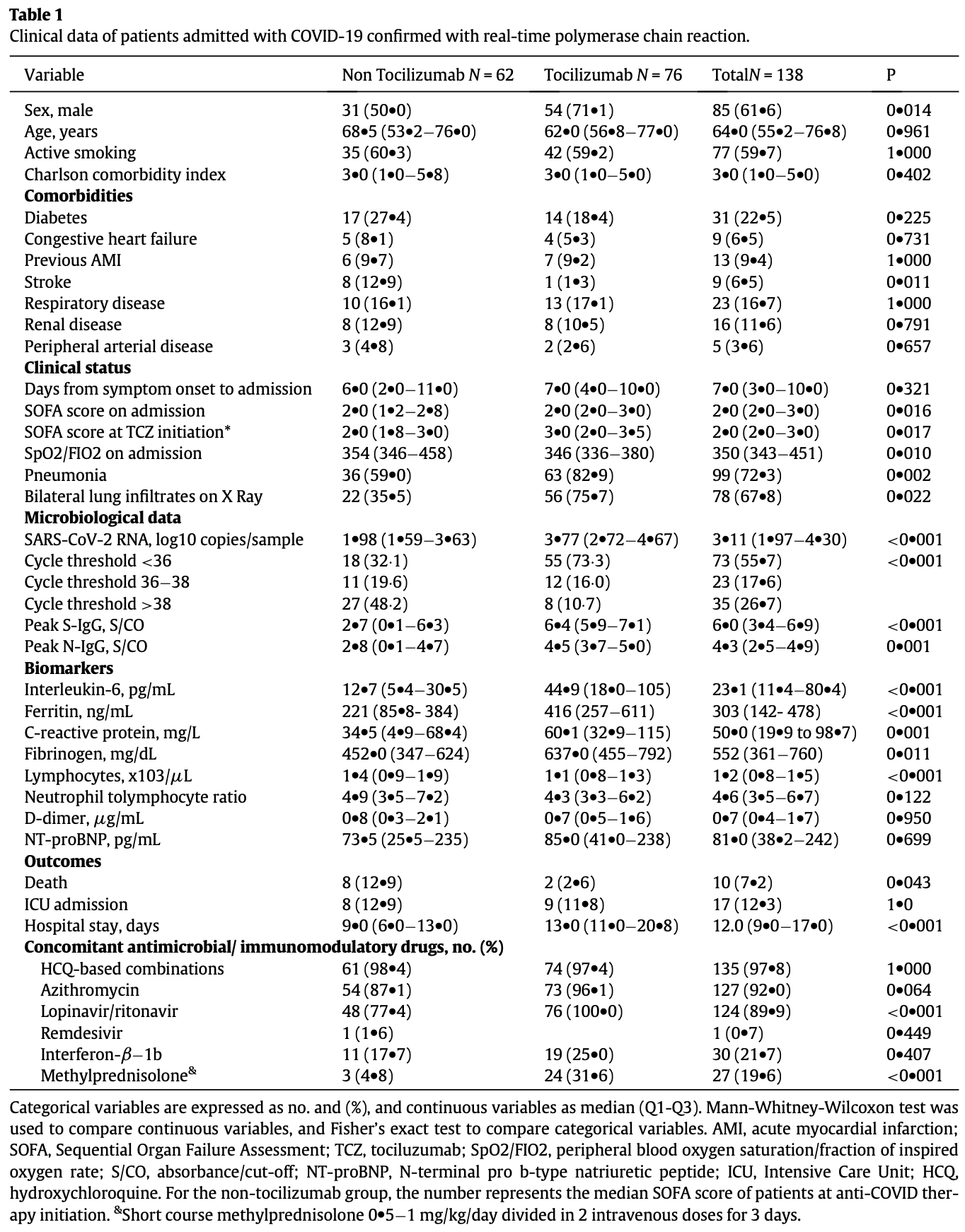
Prospective cohort study of 138 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with tocilizumab.
Viral load measured by PCR may not accurately reflect infectious virus measured by viral culture. Porter et al. show that viral load early in infection was correlated with infectious virus, but viral load late in infection could be high even with low or undetectable infectious virus. Assessing viral load later in infection may underestimate reductions in infectious virus with treatment.
|
risk of death, 79.6% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.04, treatment 2 of 76 (2.6%), control 8 of 62 (12.9%), NNT 9.7.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 8.2% lower, RR 0.92, p = 1.00, treatment 9 of 76 (11.8%), control 8 of 62 (12.9%), NNT 94.
|
|
hospitalization time, 44.4% higher, relative time 1.44, p < 0.001, treatment median 13.0 IQR 9.8 n=76, control median 9.0 IQR 7.0 n=62.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 68.0% higher, HR 1.68, p = 0.51, treatment 29, control 29, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Masiá et al., 31 Oct 2020, prospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, median age 64.0, 10 authors, study period 10 March, 2020 - 17 April, 2020.
Contact: marmasia@umh.es, gutierrez_fel@gva.es.
Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study
EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999
Background: The virological and immunological effects of the immunomodulatory drugs used for COVID-19 remain unknown. We evaluated the impact of interleukin (IL)-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and the antibody response in patients with COVID-19. Methods: Prospective cohort study in patients admitted with COVID-19. Serial nasopharyngeal and plasma samples were measured for SARS-CoV-2 RNA and S-IgG/N-IgG titers, respectively. Findings: 138 patients with confirmed infection were included; 76 (55%) underwent IL-6 blockade. Median initial SOFA (p = 0016) and SARS-CoV-2 viral load (p<0001, Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test) were significantly higher among anti-IL-6 users. Patients under IL-6 blockade showed delayed viral clearance in the Kaplan-Meier curves (HR 035 [95%CI] [015À081], log-rank p = 0014), but an adjusted propensity score matching model did not demonstrate a significant relationship of IL-6 blockade with viral clearance (HR 163 [035À77]). Cox regression showed an inverse association between SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and the initial viral load (HR 035 [011À089]). Patients under the IL-6 blocker showed shorter median time to seropositivity, higher peak antibody titers, and higher cumulative proportion of seropositivity in the Kaplan Meier curves (HR 31 [19À5] for and HR 30 [19À49] for N-IgG; log-rank p<0001 for both). However, no significant differences between groups were found in either S-IgG (HR 156 [041À60]) nor N-IgG (HR 096 [026À35]) responses in an adjusted propensity score analysis. Interpretation: Our results suggest that in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, IL-6 blockade does not impair the viral specific antibody responses. Although a delayed viral clearance was observed, it was driven by a higher initial viral load. The study supports the safety of this therapy in patients with COVID-19.
Declaration of Competing Interests Dr. Guti errez reports personal fees from Janssen-Cilag and from ViiV Health Care, outside the submitted work. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999.
References
Bingham, Rizzo, Kivitz, Hassanali, Upmanyu et al., Humoral immune response to vaccines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: results of a randomised controlled trial (VISARA), Ann Rheum Dis
Buchholz, Bukreyev, Yang, Contributions of the structural proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus to protective immunity, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Chen, Zhao, Qu, Detectable serum SARS-CoV-2 viral load (RNAaemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 (IL-6) level in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Clin Infect Dis
Fu, Xu, Wei, Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19, J Transl Med
Guaraldi, Meschiari, Cozzi-Lepri, Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
Kamimura, Ishihara, Hirano, IL-6 signal transduction and its physiological roles: the signal orchestration model. Reviews of physiology, Biochem Pharmacol
Kapetanovic, Saxne, J€ Onsson G, Truedsson, Geborek, Rituximab and abatacept but not tocilizumab impair antibody response to pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Arthritis Res Ther
Kishimoto, Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine-40 years in immunology, Annu Rev Immunol
Kopf, Baumann, Freer, Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice, Nature
Kubandova, Mathieu, Pourtier, Soubrier, Serious herpes zoster in rheumatoid arthritis under anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, Joint Bone Spine
Lee, Rigby, Zotos, B cell priming for extrafollicular antibody responses requires Bcl-6 expression by T cells, J Exp Med
Liu, Yan, Wan, Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19, Lancet Infect Dis
Long, Liu, Deng, Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19, Nat Med
Mihara, Kasutani, Okazaki, Tocilizumab inhibits signal transduction mediated by both mIL-6R and sIL-6R, but not by the receptors of other members of IL-6 cytokine family, Int Immunopharmacol
Mori, Ueki, Hirakata, Oribe, Hidaka et al., Impact of tocilizumab therapy on antibody response to influenza vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Ann Rheum Dis
Mourgues, Henquell, Tatar, Monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)/ cytomegalovirus (CMV)/varicella-zoster virus (VZV) load in patients receiving tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis, Joint Bone Spine
Muraguchi, Hirano, Tang, The essential role of B cell stimulatory factor (BSF-2/IL-6) for the terminal differentiation of B cells, J Exp Med
Nagashima, Maruyama, Kamata, Minota, Unchanged serum viral load and liver function during tocilizumab treatment in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis C virus infection, Rheumatol Int
Qian, Chen, Lv, Duration of SARS-CoV-2 viral shedding during COVID-19 infection, Infect Dis (Lond)
Ramshaw, Ramsay, Karupiah, Rolph, Mahalingam et al., Cytokines and immunity to viral infections, Immunol Rev
Rose-John, Winthrop, Calabrese, The role of IL-6 in host defence against infections: immunobiology and clinical implications, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Scherlinger, Richez, Monitoring of EpsteinÀBarr virus (EBV)/cytomegalovirus (CMV)/varicella-zoster virus (VZV) load in patients receiving tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis, Joint Bone Spine
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy, Autoimmun Rev
Van Duin, Miranda, Husni, Cytomegalovirus viremia, pneumonitis, and tocilizumab therapy, Emerg Infect Dis
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Yongchen, Shen, Wang, Different longitudinal patterns of nucleic acid and serology testing results based on disease severity of COVID-19 patients, Emerg Microbes Infect
Zhao, Yuan, Wang, Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of novel coronavirus disease 2019, Clin Infect Dis
Zheng, Yu, Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, BMJ
Zhou, Fu, Zheng, Pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storm in severe COVID-19 patients, Natl Sci Rev
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999",
"ISSN": [
"2352-3964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999",
"alternative-id": [
"S2352396420303753"
],
"article-number": "102999",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "EBioMedicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masiá",
"given": "Mar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9949-8504",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fernández-González",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padilla",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ortega",
"given": "Piedad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García",
"given": "José A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agulló",
"given": "Vanesa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Abellán",
"given": "Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Telenti",
"given": "Guillermo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guillén",
"given": "Lucía",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9485-6867",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gutiérrez",
"given": "Félix",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "EBioMedicine",
"container-title-short": "EBioMedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-16T12:23:13Z",
"timestamp": 1600258993000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-19T09:07:56Z",
"timestamp": 1603098476000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"RD16/0025/0038"
],
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III - Subdirección General de Evaluación y Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004587",
"award": [
"PI16/01740",
"PI18/01861",
"CM19/00160",
"COV20-00005"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100004587",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-29T09:08:57Z",
"timestamp": 1745917737223,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 63,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1598572800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2352396420303753?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2352396420303753?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "102999",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storm in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhou",
"journal-title": "Natl Sci Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0001",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2005.05.010",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab inhibits signal transduction mediated by both mIL-6R and sIL-6R, but not by the receptors of other members of IL-6 cytokine family",
"author": "Mihara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1731",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0002",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02339-3",
"article-title": "Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0003",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0004",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy",
"author": "Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0005",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Guaraldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0006",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "IL-6 signal transduction and its physiological roles: the signal orchestration model. Reviews of physiology",
"author": "Kamimura",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochem Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0007",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115806",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine-40 years in immunology",
"author": "Kishimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0008",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.02.010",
"article-title": "Monitoring of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)/cytomegalovirus (CMV)/varicella-zoster virus (VZV) load in patients receiving tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Scherlinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "Joint Bone Spine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0009",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid1706.101057",
"article-title": "Cytomegalovirus viremia, pneumonitis, and tocilizumab therapy",
"author": "Van Duin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "754",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0010",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbspin.2010.07.009",
"article-title": "Serious herpes zoster in rheuma-toid arthritis under anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody",
"author": "Kubandova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Joint Bone Spine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0011",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Detectable serum SARS-CoV-2 viral load (RNAaemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 (IL-6) level in critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Chen",
"first-page": "[in press]",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0012",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.167.2.332",
"article-title": "The essential role of B cell stimulatory factor (BSF-2/IL-6) for the terminal differentiation of B cells",
"author": "Muraguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "332",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0013",
"volume": "15",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-065X.1997.tb01011.x",
"article-title": "Cytokines and immunity to viral infections",
"author": "Ramshaw",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Immunol Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0014",
"volume": "159",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2017.83",
"article-title": "The role of IL-6 in host defence against infections: immunobiology and clinical implications",
"author": "Rose-John",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0015",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/368339a0",
"article-title": "Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice",
"author": "Kopf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "339",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0016",
"volume": "368",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.07.009",
"article-title": "Monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)/cytomegalovirus (CMV)/varicella-zoster virus (VZV) load in patients receiving tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Mourgues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "Joint Bone Spine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0017",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-011-2060-2",
"article-title": "Unchanged serum viral load and liver function during tocilizumab treatment in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis C virus infection",
"author": "Nagashima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2231",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0018",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1443",
"article-title": "Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0019",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0020",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30232-2",
"article-title": "Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "656",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0021",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2020.1748705",
"article-title": "Duration of SARS-CoV-2 viral shedding during COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis (Lond)",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0022",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar4358",
"article-title": "Rituximab and abatacept but not tocilizumab impair antibody response to pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Crnkic Kapetanovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R171",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0023",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201950",
"article-title": "Impact of tocilizumab therapy on antibody response to influenza vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Mori",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2006",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheum Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0024",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204427",
"article-title": "Humoral immune response to vaccines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: results of a randomised controlled trial (VISARA)",
"author": "Bingham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "818",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheum Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0025",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1756699",
"article-title": "Different longitudinal patterns of nucleic acid and serology testing results based on disease severity of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Yongchen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "833",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0026",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa344",
"article-title": "Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of novel coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0027",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0897-1",
"article-title": "Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Long",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "845",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0028",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20102065",
"article-title": "B cell priming for extrafollicular antibody responses requires Bcl-6 expression by T cells",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0029",
"volume": "208",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0403492101",
"article-title": "Contributions of the structural proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus to protective immunity",
"author": "Buchholz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9804",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102999_bib0030",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2004"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2352396420303753"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "60"
}