Subcutaneous IL-6 Inhibitor Sarilumab vs. Standard Care in Hospitalized Patients With Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19: An Open Label Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.819621, SARCOVID, NCT04357808, Feb 2022
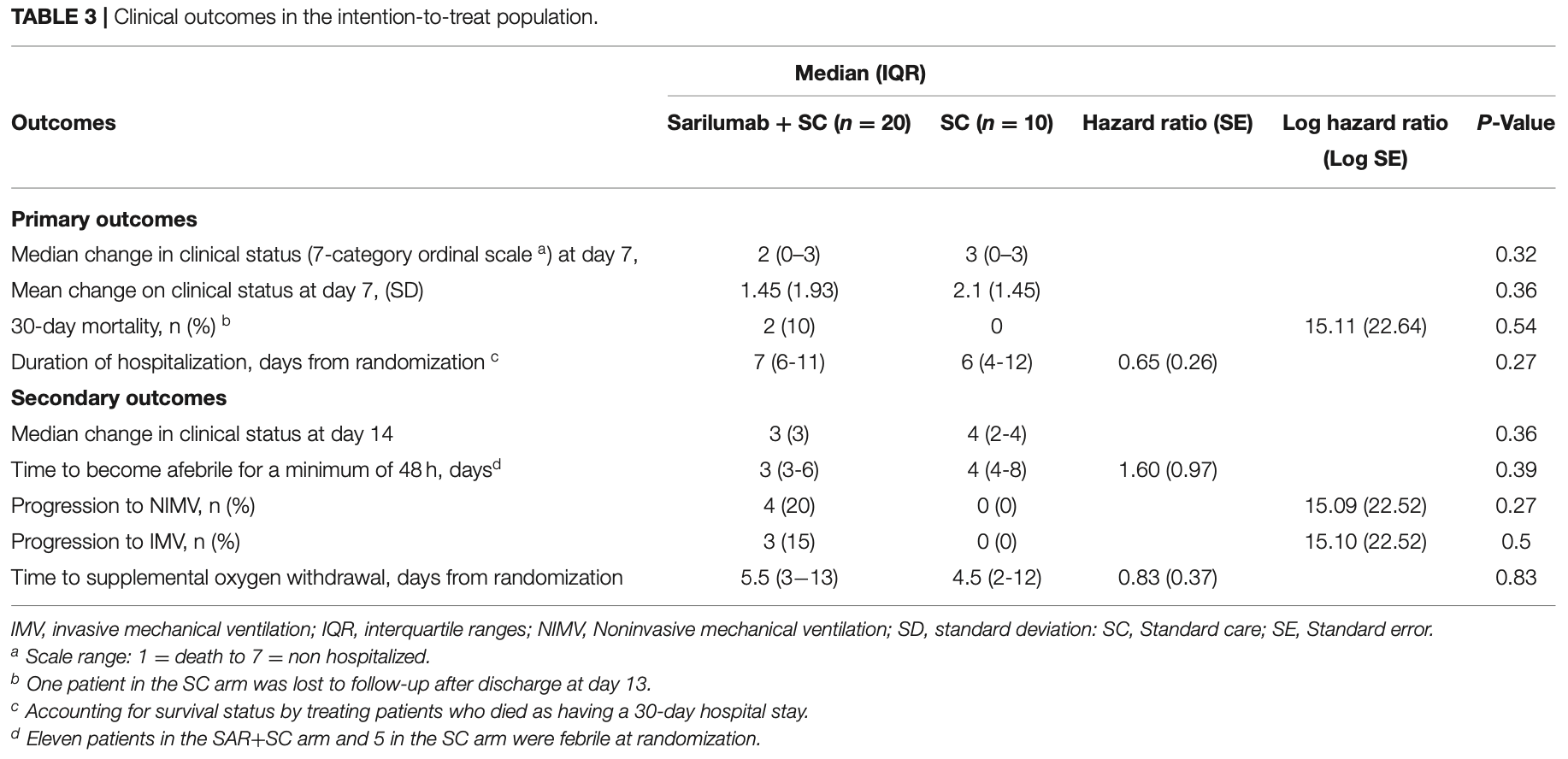
RCT 30 hospitalized moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in 30-day mortality, clinical improvement at day 7, or time to discharge with sarilumab compared to standard care.
|
risk of death, 300.0% higher, RR 4.00, p = 0.54, treatment 2 of 20 (10.0%), control 0 of 10 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 450.0% higher, RR 5.50, p = 0.53, treatment 3 of 20 (15.0%), control 0 of 10 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
relative median improvement in clinical status, 33.3% worse, RR 1.33, p = 0.36, treatment 20, control 10, day 14.
|
|
relative median improvement in clinical status, 50.0% worse, RR 1.50, p = 0.32, treatment 20, control 10, day 7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
García-Vicuña et al., 23 Feb 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Spain, peer-reviewed, median age 61.5, 13 authors, study period 13 April, 2020 - 30 October, 2020, trial NCT04357808 (history) (SARCOVID).
Subcutaneous IL-6 Inhibitor Sarilumab vs. Standard Care in Hospitalized Patients With Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19: An Open Label Randomized Clinical Trial
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.819621
Background: The use of IL-6 blockers in COVID-19 hospitalized patients has been associated with a reduction in mortality compared to standard care. However, many uncertainties remain pertaining to optimal intervention time, administration schedule, and predictors of response. To date, data on the use of subcutaneous sarilumab is limited and no randomized trial results are available. Methods: Open label randomized controlled trial at a single center in Spain. We included adult patients admitted with microbiology documented COVID-19 infection, imaging confirmed pneumonia, fever and/or laboratory evidence of inflammatory phenotype, and no need for invasive ventilation. Participants were randomly assigned to receive sarilumab, a single 400 mg dose in two 200 mg subcutaneous injections, added to standard care or standard care, in a 2:1 proportion. Primary endpoints included 30-day mortality, mean change in clinical status at day 7 scored in a 7-category ordinal scale ranging from death (category 1) to discharge (category 7), and duration of hospitalization. The primary efficacy analysis was conducted on the intention-to-treat population. Results: A total of 30 patients underwent randomization: 20 to sarilumab and 10 to standard care. Most patients were male (20/30, 67%) with a median (interquartile range) age of 61.5 years (56-72). At day 30, 2/20 (10%) patients died in the sarilumab arm vs. none (0/10) in standard care (Log HR 15.11, SE 22.64; p = 0.54). At day 7, no significant differences were observed in the median change in clinical status (2 [0-3]) vs. 3 [0-3], p = 0.32). Median time to discharge (days) was similar (7 [6-11] vs. 6 [4-12]; HR 0.65, García-Vicuña et al. Subcutaneous Sarilumab in COVID-19 SE 0.26; p = 0.27). No significant differences were detected in the rate of progression to invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation. Conclusions and Relevance: Our pragmatic pilot study has failed to demonstrate the benefit of adding subcutaneous sarilumab to standard care for mortality by 30 days, functional status at day 7, or hospital stay. Findings herein do not exclude a potential effect of sarilumab in severe COVID-19 but adequately powered blinded randomized phase III trials are warranted to assess the impact of the subcutaneous route and a more selected target population.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Research Ethics Committee of the Hospital Universitario de la Princesa, IIS-Princesa, Madrid, Spain. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. All patients or their legal representatives provided oral informed consent according to the exceptional regulation applicable for COVID19 studies.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS RG-V, IG-A, and FA-S contributed to the conception or design of the work. RG-V and SR-G contributed to the drafting of the manuscript. IG-A contributed to the statistical analysis. RG-V supervision. All authors contributed toward the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, review and approval of the final version of the manuscript.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed. 2022.819621/full#supplementary-material Conflict of Interest: RG-V reported receiving educational grants support from Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, honoraria for presentations for Lilly, Sanofi, advisory boards for Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, nonfinancial support from Lilly, Pfizer, and Sanofi, all outside the present work. IG-A reported Roche provided him data for research, honoraria for presentations for Lilly,..
References
Benucci, Giannasi, Cecchini, Gobbi, Damiani et al., COVID-19 pneumonia treated with Sarilumab: a clinical series of eight patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26062
Biran, Ip, Ahn, Go, Wang et al., Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0
Coomes, Haghbayan, Interleukin-6 in Covid-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1101/2020.03.30.20048058
Corominas, Castellvi, Diaz-Torne, Matas, De La Rosa et al., Sarilumab (IL-6R antagonist) in critically ill patients with cytokine release syndrome by SARS-CoV2, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025923
Della-Torre, Campochiaro, Cavalli, Luca, Napolitano et al., Interleukin-6 blockade with sarilumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia with systemic hyperinflammation: an openlabel cohort study, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218122
Della-Torre, Lanzillotta, Campochiaro, Cavalli, Luca et al., Respiratory impairment predicts response to IL-1 and IL-6 blockade in COVID-19 patients with severe pneumonia and hyper-inflammation, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.675678
Galvan-Roman, Rodriguez-Garcia, Vallejo, Jimenez, Sanchez-Alonso et al., IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Garcia-Vicuna, Abad-Santos, Gonzalez-Alvaro, Ramos-Lima, Sanz, Subcutaneous Sarilumab in hospitalised patients with moderate-severe COVID-19 infection compared to the standard of care (SARCOVID): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04588-5
Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Rowan, Nichol, Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically Ill patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433
Gremese, Cingolani, Bosello, Alivernini, Tolusso et al., Sarilumab use in severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100553
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Gupta, Wang, Hayek, Chan, Mathews et al., Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19, JAMA Internal Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252
Ishii, Sato, Munakata, Kajiwara, Takahashi et al., Pharmacodynamic effect and safety of single-dose sarilumab sc or tocilizumab iv or sc in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Ann Rheumatic Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-eular.1375
Jones, Hunter, Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19?, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00553-8
Khan, Stewart, Fabbri, Moss, Robinson et al., Systematic review and meta-analysis of anakinra, sarilumab, siltuximab and tocilizumab for COVID-19, Thorax, doi:10.1101/2020.04.23.20076612
Khiali, Rezagholizadeh, Entezari-Maleki, A comprehensive review on sarilumab in COVID-19, Expert Opin Biol Ther, doi:10.1080/14712598.2021.1847269
Lan, Lai, Huang, Chang, Lu et al., Tocilizumab for severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106103
Le, Li, Yuan, Shord, Nie et al., FDA Approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cellinduced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome, Oncologist, doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028
Leisman, Ronner, Pinotti, Taylor, Sinha et al., Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30404-5
Lescure, Honda, Fowler, Lazar, Shi et al., Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0
Mccreary, Angus, Efficacy of remdesivir in COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16337
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Montesarchio, Parrela, Iommelli, Bianco, Manzillo et al., Outcomes and biomarker analyses among patients with COVID-19 treated with interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist sarilumab at a single institution in Italy, J Immunother Cancer, doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-001089
Moore, Offit, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the growing threat of viral variants, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1114
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Sarilumab, Summary of Product Characteristics
Shankar-Hari, Vale, Godolphin, Fisher, Higgins, Association between administration of il-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.11330
Siddiqi, Mehra, COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012
Sinha, Mostaghim, Bielick, Mclaughlin, Hamer et al., Early administration of interleukin-6 inhibitors for patients with severe COVID-19 disease is associated with decreased intubation, reduced mortality, and increased discharge, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.023
Sivapalasingam, Lederer, Bhore, Hajizadeh, Criner et al., A randomized placebo-controlled trial of sarilumab in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.13.21256973
Tjendra, Mana, Espejo, Akgun, Millan et al., Predicting disease severity and outcome in COVID-19 patients: a review of multiple biomarkers, Arch Pathol Lab Med, doi:10.5858/arpa.2020-0471-SA
Trial-Consortium, Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Preziosi et al., Repurposed antiviral drugs for covid-19 -interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
Who React, Group, Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically Ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17023
Zhao, Lu, Tang, Dai, Zhou et al., Tocilizumab for treating COVID-19: a systemic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00228-020-03017-5
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.819621",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.819621",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The use of IL-6 blockers in COVID-19 hospitalized patients has been associated with a reduction in mortality compared to standard care. However, many uncertainties remain pertaining to optimal intervention time, administration schedule, and predictors of response. To date, data on the use of subcutaneous sarilumab is limited and no randomized trial results are available.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>Open label randomized controlled trial at a single center in Spain. We included adult patients admitted with microbiology documented COVID-19 infection, imaging confirmed pneumonia, fever and/or laboratory evidence of inflammatory phenotype, and no need for invasive ventilation. Participants were randomly assigned to receive sarilumab, a single 400 mg dose in two 200 mg subcutaneous injections, added to standard care or standard care, in a 2:1 proportion. Primary endpoints included 30-day mortality, mean change in clinical status at day 7 scored in a 7-category ordinal scale ranging from death (category 1) to discharge (category 7), and duration of hospitalization. The primary efficacy analysis was conducted on the intention-to-treat population.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 30 patients underwent randomization: 20 to sarilumab and 10 to standard care. Most patients were male (20/30, 67%) with a median (interquartile range) age of 61.5 years (56–72). At day 30, 2/20 (10%) patients died in the sarilumab arm vs. none (0/10) in standard care (Log HR 15.11, SE 22.64; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.54). At day 7, no significant differences were observed in the median change in clinical status (2 [0–3]) vs. 3 [0–3], <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.32). Median time to discharge (days) was similar (7 [6–11] vs. 6 [4–12]; HR 0.65, SE 0.26; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.27). No significant differences were detected in the rate of progression to invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>Our pragmatic pilot study has failed to demonstrate the benefit of adding subcutaneous sarilumab to standard care for mortality by 30 days, functional status at day 7, or hospital stay. Findings herein do not exclude a potential effect of sarilumab in severe COVID-19 but adequately powered blinded randomized phase III trials are warranted to assess the impact of the subcutaneous route and a more selected target population.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p><jats:ext-link>www.ClinicalTrials</jats:ext-link>.gov, Identifier: NCT04357808.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2022.819621"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Vicuña",
"given": "Rosario",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodriguez-García",
"given": "Sebastián C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abad-Santos",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bautista Hernández",
"given": "Azucena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "García-Fraile",
"given": "Lucio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrios Blandino",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gutiérrez Liarte",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alonso-Pérez",
"given": "Tamara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cardeñoso",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alfranca",
"given": "Aránzazu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mejía-Abril",
"given": "Gina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz Sanz",
"given": "Jesús",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González-Alvaro",
"given": "Isidoro",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T12:24:29Z",
"timestamp": 1645619069000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T12:24:34Z",
"timestamp": 1645619074000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013412",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100013412",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Sanofi España"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-23T06:00:19Z",
"timestamp": 1703311219140
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645574400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.819621/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.1114",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the growing threat of viral variants",
"author": "Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "821",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for covid-19 - interim WHO solidarity trial results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"article-title": "COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal",
"author": "Siddiqi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "405",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-020-03017-5",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for treating COVID-19: a systemic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "311",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106103",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106103",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252",
"article-title": "Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "JAMA Internal Med.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028",
"article-title": "FDA Approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome",
"author": "Le",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "943",
"journal-title": "Oncologist.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "846",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.30.20048058",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 in Covid-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Coomes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2141",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5858/arpa.2020-0471-SA",
"article-title": "Predicting disease severity and outcome in COVID-19 patients: a review of multiple biomarkers",
"author": "Tjendra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1465",
"journal-title": "Arch Pathol Lab Med.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.09.018",
"article-title": "IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study",
"author": "Galvan-Roman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B13",
"unstructured": "Summary of Product Characteristics."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-eular.1375",
"article-title": "Pharmacodynamic effect and safety of single-dose sarilumab sc or tocilizumab iv or sc in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)",
"author": "Ishii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheumatic Dis.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04588-5",
"article-title": "Subcutaneous Sarilumab in hospitalised patients with moderate-severe COVID-19 infection compared to the standard of care (SARCOVID): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Garcia-Vicuna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "772",
"journal-title": "Trials.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B16",
"unstructured": "Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis.2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.11330",
"article-title": "Association between administration of il-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "WHO REACT Working",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jitc-2020-001089",
"article-title": "Outcomes and biomarker analyses among patients with COVID-19 treated with interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist sarilumab at a single institution in Italy",
"author": "Montesarchio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e001089",
"journal-title": "J Immunother Cancer.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26062",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pneumonia treated with Sarilumab: a clinical series of eight patients",
"author": "Benucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2368",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000025923",
"article-title": "Sarilumab (IL-6R antagonist) in critically ill patients with cytokine release syndrome by SARS-CoV2",
"author": "Corominas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e25923",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore).",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.023",
"article-title": "Early administration of interleukin-6 inhibitors for patients with severe COVID-19 disease is associated with decreased intubation, reduced mortality, and increased discharge",
"author": "Sinha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100553",
"article-title": "Sarilumab use in severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia",
"author": "Gremese",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100553",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218122",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 blockade with sarilumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia with systemic hyperinflammation: an open-label cohort study",
"author": "Della-Torre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1277",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheum Dis.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14712598.2021.1847269",
"article-title": "A comprehensive review on sarilumab in COVID-19",
"author": "Khiali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Biol Ther.",
"key": "B24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.23.20076612",
"article-title": "Systematic review and meta-analysis of anakinra, sarilumab, siltuximab and tocilizumab for COVID-19",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "907",
"journal-title": "Thorax.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.675678",
"article-title": "Respiratory impairment predicts response to IL-1 and IL-6 blockade in COVID-19 patients with severe pneumonia and hyper-inflammation",
"author": "Della-Torre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "675678",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically Ill patients with covid-19",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1491",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0",
"article-title": "Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial",
"author": "Lescure",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "522",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.13.21256973",
"article-title": "A randomized placebo-controlled trial of sarilumab in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Sivapalasingam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2021",
"journal-title": "medRxiv.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study",
"author": "Biran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e603",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00553-8",
"article-title": "Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19?",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30404-5",
"article-title": "Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes",
"author": "Leisman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1233",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16337",
"article-title": "Efficacy of remdesivir in COVID-19",
"author": "McCreary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1041",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "REMAP-CAP",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"article-title": "Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically Ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1330",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.819621/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Subcutaneous IL-6 Inhibitor Sarilumab vs. Standard Care in Hospitalized Patients With Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19: An Open Label Randomized Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "9"
}