Early Use of Sarilumab in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Pneumonia and Features of Systemic Inflammation: the SARICOR Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/AAC.02107-21, SARICOR, NCT04357860, Feb 2022
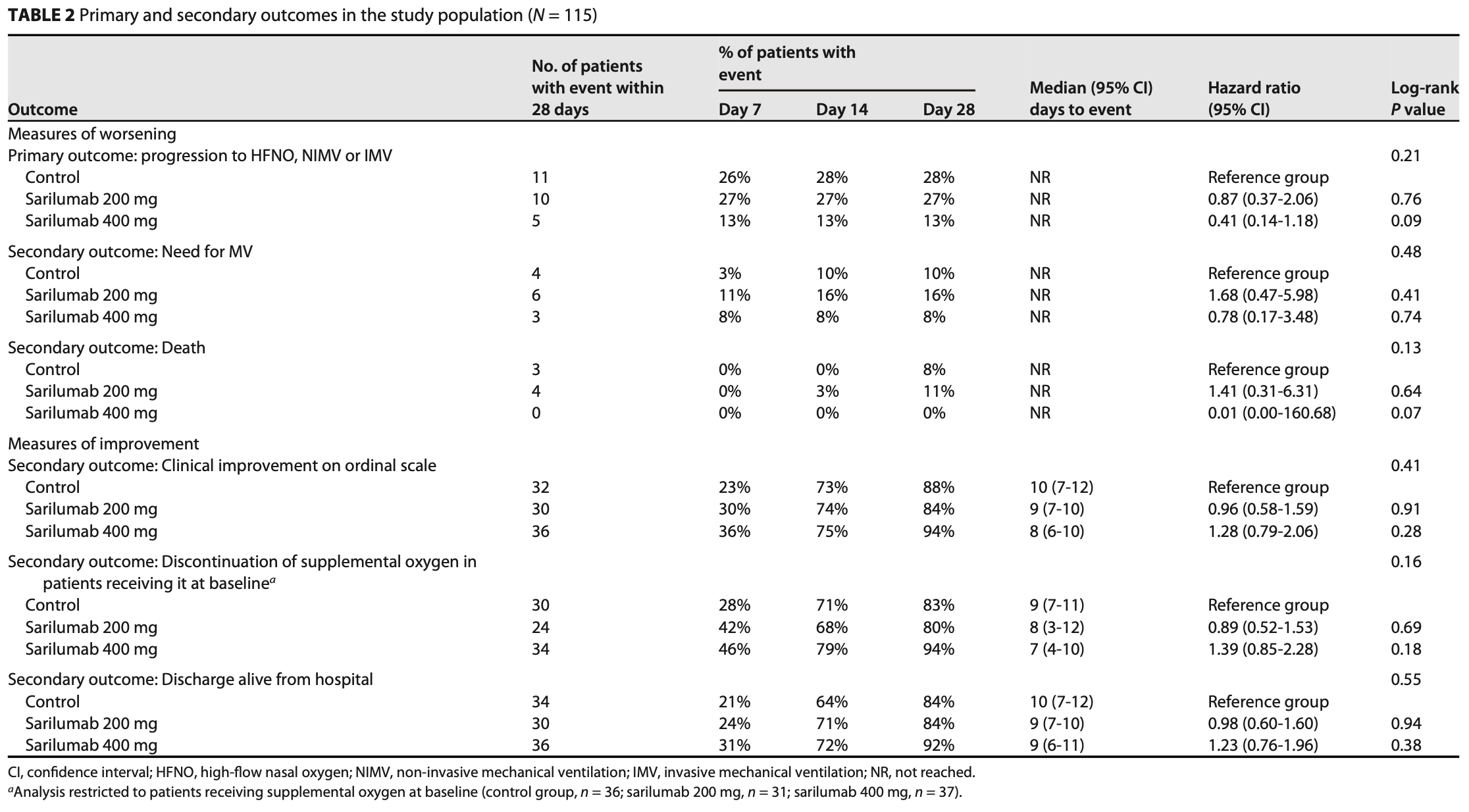
RCT 115 hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients in Spain showing a trend towards reduced progression to severe respiratory failure requiring high-flow oxygen, non-invasive ventilation, or mechanical ventilation, and reduced mortality, with sarilumab 400mg compared to standard of care.
|
risk of death, 35.2% higher, HR 1.35, p = 0.71, treatment 39, control 39, all patients.
|
|
risk of death, 99.0% lower, HR 0.01, p = 0.21, treatment 0 of 39 (0.0%), control 3 of 39 (7.7%), relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 400mg, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
risk of death, 41.0% higher, HR 1.41, p = 0.67, treatment 4 of 37 (10.8%), control 3 of 39 (7.7%), 200mg, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 22.2% higher, HR 1.22, p = 0.70, treatment 39, control 39, all patients.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 22.0% lower, HR 0.78, p = 0.76, treatment 3 of 39 (7.7%), control 4 of 39 (10.3%), NNT 39, 400mg, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 68.0% higher, HR 1.68, p = 0.43, treatment 6 of 37 (16.2%), control 4 of 39 (10.3%), 200mg, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
HFNO, NIMV or IMV, 36.0% lower, HR 0.64, p = 0.23, treatment 39, control 39, all patients, primary outcome.
|
|
HFNO, NIMV or IMV, 59.0% lower, HR 0.41, p = 0.10, treatment 5 of 39 (12.8%), control 11 of 39 (28.2%), NNT 6.5, 400mg, Cox proportional hazards, day 28, primary outcome.
|
|
HFNO, NIMV or IMV, 13.0% lower, HR 0.87, p = 0.76, treatment 10 of 37 (27.0%), control 11 of 39 (28.2%), NNT 85, 200mg, Cox proportional hazards, day 28, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Merchante et al., 15 Feb 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Spain, peer-reviewed, median age 59.0, 20 authors, study period 13 July, 2020 - 5 March, 2021, trial NCT04357860 (history) (SARICOR).
Contact: julian.torre.sspa@juntadeandalucia.es, nicolasmerchante@gmail.com.
Early Use of Sarilumab in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Pneumonia and Features of Systemic Inflammation: the SARICOR Randomized Clinical Trial
The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of early treatment with sarilumab, added to standard of care (SOC), in hospitalized adults with COVID-19. Methods included phase II, open-label, randomized, controlled clinical trial of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and interleukin (IL)-6 levels $ 40 pg/mL and/or d-dimer . 1,500 ng/mL. Participants were randomized (1:1:1) to receive SOC (control group), SOC plus a single subcutaneous dose of sarilumab 200 mg (sarilumab-200 group), or SOC plus a single subcutaneous dose of sarilumab 400 mg (sarilumab-400 group). The primary outcome variable was the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) requiring high-flow nasal oxygenation (HFNO), non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV) or invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) at day 28. One-hundred and 15 participants (control group, n = 39; sarilumab-200, n = 37; sarilumab-400, n = 39) were included. At randomization, 104 (90%) patients had supplemental oxygen and 103 (90%) received corticosteroids. Eleven (28%) patients in the control group, 10 (27%) in sarilumab-200, and five (13%) in sarilumab-400 developed the primary outcome (hazard ratio [95% CI] of sarilumab-400 vs control group: 0.41 [0.14, 1.18]; P = 0.09). Seven (6%) patients died: three in the control group and four in sarilumab-200. There were no deaths in sarilumab-400 (P = 0.079, log-rank test for comparisons with the control group). In patients recently hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia and features of systemic inflammation, early IL-6 blockade with a single dose of sarilumab 400 mg was safe and associated with a trend for better outcomes. (This study has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under identifier NCT04357860.)
2 ) 10 ( 9 ) 5 ( 13 ) 1 (3) 2 ( 5 ) 2 ( 5 ) Data are expressed as number (%) of patients. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material is available online only. SUPPLEMENTAL FILE 1, PDF file, 0.2 MB.
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endotheliaitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015432
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Della-Torre, Campochiaro, Cavalli, Luca, Napolitano et al., Interleukin-6 blockade with sarilumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia with systemic hypeinflammation: an open-label cohort study, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218122
Dodd, Freidlin, Korn, Platform trials-beware of the noncomparable control group, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2102446
Dorward, Russell, Um, Elshani, Armstrong et al., Tissue-specific immunopathology in fatal COVID-19, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202008-3265OC
Evans, Rubin, Follmann, Pennello, Huskins et al., Desirability of outcome ranking (DOOR) and response adjusted for duration of antibiotic risk (RADAR), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/civ495
Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, Rowan, Nichol et al., Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gremese, Cingolani, Bosello, Alivernini, Tolusso et al., Sarilumab use in severe SARS-CoV2 pneumonia, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100553
Gupta, Wang, Hayek, Chan, Mathews et al., Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with Covid-19, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252
Hermine, Mariette, Tharaux, Resche-Rigon, Porcher et al., Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820
Lescure, Honda, Fowler, Lazar, Shi et al., Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0
López, Fernández, Pérez, Palacios, Fernández-Roldán et al., Efficacy and safety of early treatment with sarilumab in hospitalised adults with COVID-19 presenting cytokine release syndrome (SARICOR STUDY): protocol of a phase II, open-label, randomised, multicentre, controlled clinical trial, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039951
Martínez-Sanz, Ron, Herrera, Pérez-Molina, Moreno et al., Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Rodríguez-Baño, Pachón, Carratalà, Ryan, Jarrín et al., Treatment with tocilizumab or corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients with hyperinflammatory state: a multicenter cohort study (SAM-COVID-19), Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.010
Rosas, Bräu, Waters, Go, Hunter et al., Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028700
Salama, Han, Yau, Reiss, Kramer et al., Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2030340
Salvarani, Dolci, Massari, Merlo, Cavuto et al., Effect of tocilizumab vs standard care on clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615
Shankar-Hari, Vale, Godolphin, Fisher, Higgings et al., Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A Meta-analysis, JAMA
Stone, Frigault, Serling-Boyd, Fernandes, Harvey et al., Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028836
Valle, Kim-Schulze, Huang, Beckmann, Nirenberg et al., An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.02107-21",
"ISSN": [
"0066-4804",
"1098-6596"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02107-21",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of early treatment with sarilumab, added to standard of care (SOC), in hospitalized adults with COVID-19. Methods included phase II, open-label, randomized, controlled clinical trial of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and interleukin (IL)-6 levels ≥ 40 pg/mL and/or d-dimer > 1,500 ng/mL.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/aac.02107-21"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-10-29"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-12-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-02-15"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1120-8942",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología, Hospital Universitario de Valme, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Merchante",
"given": "Nicolás",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Gestión Clínica de Cuidados Intensivos, Instituto Maimónides de Investigación Biomédica de Córdoba (IMIBIC), Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía, Universidad de Córdoba (UCO), Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Cárcel",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Ensayos Clínicos, Instituto Maimónides de Investigación Biomédica de Córdoba (IMIBIC), Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía, Universidad de Córdoba (UCO), Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Garrido-Gracia",
"given": "José Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología, Hospital Universitario de Valme, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Trigo-Rodríguez",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Servicio de Medicina Interna, Hospital Universitario Torrecárdenas, Almería, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Moreno",
"given": "María Ángeles Esteban",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Gestión Clínica de Cuidados Intensivos, Instituto Maimónides de Investigación Biomédica de Córdoba (IMIBIC), Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía, Universidad de Córdoba (UCO), Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"family": "León-López",
"given": "Rafael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología, Hospital Universitario de Valme, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Espíndola-Gómez",
"given": "Reinaldo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Infanta Margarita, Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Alonso",
"given": "Eduardo Aguilar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Gestión Clínica de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Clínico San Cecilio, Granada, Spain"
}
],
"family": "García",
"given": "David Vinuesa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Puerto Real, Instituto de Investigacion Biomédica de Cádiz (INiBICA), Cádiz, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Romero-Palacios",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Gestión Clínica de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Regional Universitario de Málaga, Instituto de Investigación Biomédica de Málaga (IBIMA), Málaga, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Pérez-Camacho",
"given": "Inés",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9668-0770",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Gestión Clínica de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Microbiología y Medicina Preventiva, Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBIS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez",
"given": "Belén",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Juan Ramón Jiménez, Huelva, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Martínez-Marcos",
"given": "Francisco Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves, Granada, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Fernández-Roldán",
"given": "Concepción",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología, Hospital Universitario de Valme, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Pérez-Crespo",
"given": "Pedro María Martínez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Servicio de Medicina Interna, Hospital Universitario Torrecárdenas, Almería, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Caño",
"given": "Alexandra Aceituno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología, Hospital Universitario de Valme, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"family": "León",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología, Hospital Universitario de Valme, Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Corzo",
"given": "Juan E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unidad de Gestión Clínica de Cuidados Intensivos, Instituto Maimónides de Investigación Biomédica de Córdoba (IMIBIC), Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía, Universidad de Córdoba (UCO), Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"family": "de la Fuente",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1529-6302",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Servicio de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía, Instituto Maimónides de Investigación Biomédica de Córdoba (IMIBIC), Universidad de Córdoba (UCO), Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Torre-Cisneros",
"given": "Julián",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy",
"container-title-short": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-13T22:32:54Z",
"timestamp": 1639434774000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-21T23:27:53Z",
"timestamp": 1645486073000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"REIPI RD16/0016/0001"
],
"name": "Spanish Network for Research in Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"award": [
"RD16/0016/0008"
],
"name": "Spanish Network for Research in Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100010566",
"award": [
"COVID-0013-2020"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100010566",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Consejería de Salud y Familias, Junta de Andalucía"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100018689",
"award": [
"PT17/0017/0032",
"PT20/0039"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100018689",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Spanish Clinical Research Network"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-09T17:14:22Z",
"timestamp": 1725902062700
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 23,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.1128/ASMCopyrightv2",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1644883200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1644883200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/aac.02107-21",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/aac.02107-21",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202008-3265OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028836",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2030340",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.11330",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218122",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_18_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_19_2",
"unstructured": "Sanofi provides update on Kezvara (sarilumab) phase trial in severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients outside the U.S. Press release. September 1 2020. (https://www.sanofi.com/en/media-room/press-releases/2020/2020-09-01-07-00-00)."
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_20_2",
"unstructured": "Sanofi and Regeneron provide update on Kezvara (sarilumab) phase 3 U.S. trial in COVID-19 patients. Press release. July 2 2020. (https://www.sanofi.com/en/media-room/press-releases/2020/2020-07-02-22-30-00)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2102446",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/civ495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039951",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_25_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aac.02107-21"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early Use of Sarilumab in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Pneumonia and Features of Systemic Inflammation: the SARICOR Randomized Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page",
"volume": "66"
}