Subcutaneous sarilumab for the treatment of hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID19 disease: A pragmatic, embedded randomized clinical trial
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263591, NCT04359901, Feb 2022
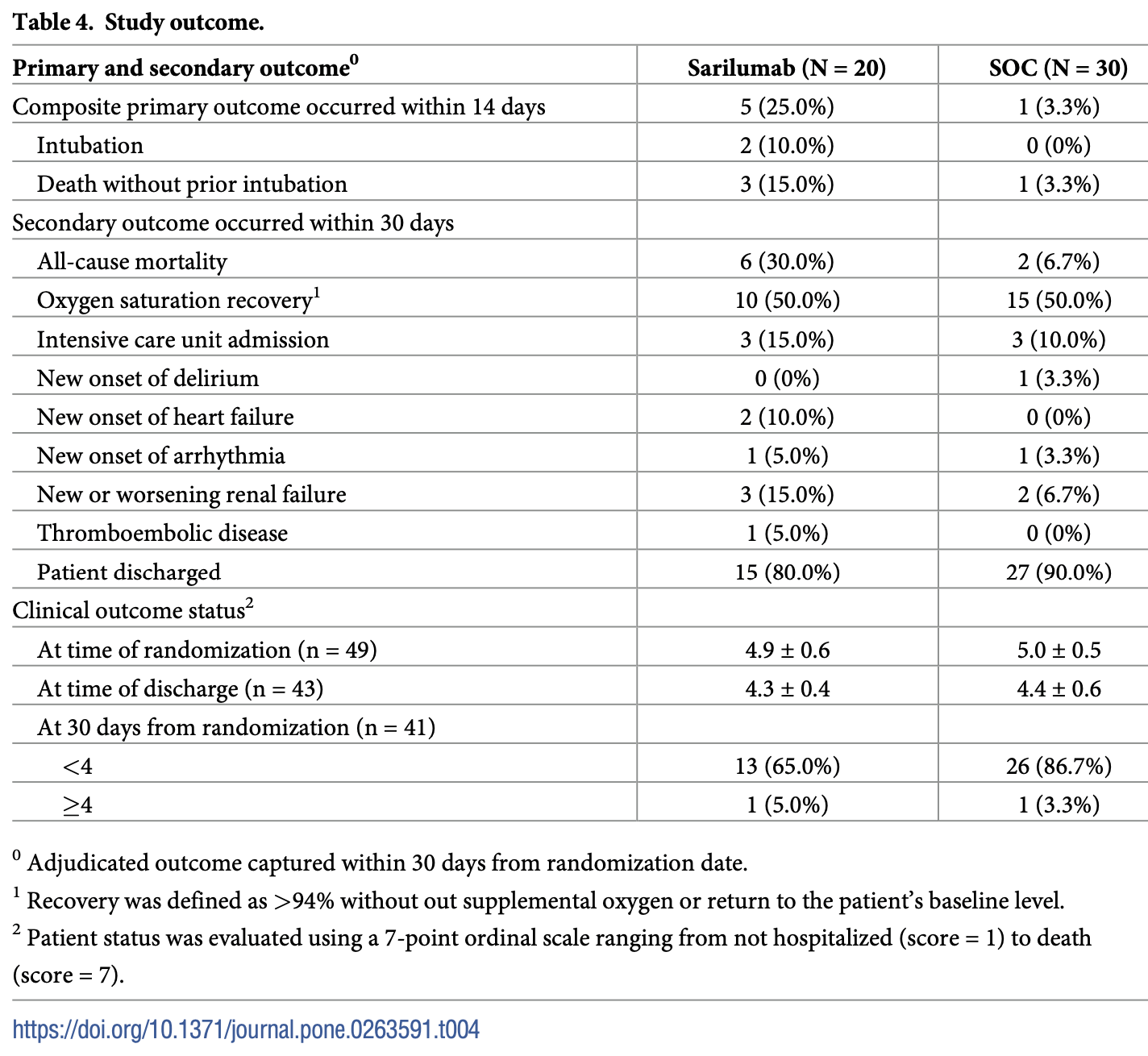
RCT 50 hospitalized moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients showing higher mortality with subcutaneous sarilumab compared to standard of care. The study was stopped early due to a high probability of futility and potential harm.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 350.0% higher, RR 4.50, p = 0.047, treatment 6 of 20 (30.0%), control 2 of 30 (6.7%), day 30.
|
|
risk of death/intubation, 650.0% higher, RR 7.50, p = 0.03, treatment 5 of 20 (25.0%), control 1 of 30 (3.3%), day 14, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 500.0% higher, RR 6.00, p = 0.16, treatment 2 of 20 (10.0%), control 0 of 30 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 50.0% higher, RR 1.50, p = 0.67, treatment 3 of 20 (15.0%), control 3 of 30 (10.0%), day 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Branch-Elliman et al., 25 Feb 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 72.3, 21 authors, study period 10 April, 2020 - 3 February, 2021, trial NCT04359901 (history).
Contact: wbranche@bidmc.harvard.edu.
Subcutaneous sarilumab for the treatment of hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID19 disease: A pragmatic, embedded randomized clinical trial
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263591
Importance and objective The aim of this pragmatic, embedded, adaptive trial was to measure the effectiveness of the subcutaneous anti-IL-6R antibody sarilumab, when added to an evolving standard of care (SOC), for clinical management of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease.
Design Two-arm, randomized, open-label controlled trial comparing SOC alone to SOC plus sarilumab. The trial used a randomized play-the-winner design and was fully embedded within the electronic health record (EHR) system.
Setting 5 VA Medical Centers.
Participants Hospitalized patients with clinical criteria for moderate to severe COVID-19 but not requiring mechanical ventilation, and a diagnostic test positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Author Contributions Jankowich, Nishant R. Shah, Thomas H. Taylor, Sarah T. Page, Sara J. Schiller, Colleen Shannon, Cynthia Hau, Maura Flynn, Erika Holmberg, Karen Visnaw, Rupali Dhond, Mary Brophy, Paul A. Monach.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Branch-Elliman, Elwy, Monach, Bringing New Meaning to the Term "Adaptive Trial:" Challenges of Conducting Clinical Research during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Implications for Implementation Science, Open Forum Infect Dis
Branch-Elliman, Ferguson, Doros, Leatherman, Brophy et al., The cytokine storms of COVID-19, H1N1 influenza, CRS and MAS compared. Can one sized treatment fit all?, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155593
Branch-Elliman, Lehmann, Boden, Pragmatic, adaptive clinical trials: Is 2020 the dawning of a new age? Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications, doi:10.1016/j.conctc.2020.100614
Chambers, Feero, Khoury, Convergence of Implementation Science, Precision Medicine, and the Learning Health Care System: A New Model for Biomedical Research, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2016.3867
Fiore, Brophy, Ferguson, A point-of-care clinical trial comparing insulin administered using a sliding scale versus a weight-based regimen, Clinical trials, doi:10.1177/1740774511398368
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.5394
Grieve, Response-adaptive clinical trials: case studies in the medical literature, Pharm Stat, doi:10.1002/pst.1778
Hermine, Tharaux, Effect of Tocilizumab vs Usual Care in Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Moderate or Severe Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Lescure, Honda, Fowler, Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600%2821%2900099-0
Morris, Wooding, Grant, The answer is 17 years, what is the question: understanding time lags in translational research, J R Soc Med, doi:10.1258/jrsm.2011.110180
On, PHASE 2/3 ADAPTIVE-DESIGNED TRIAL OF KEVZARA ®
Rosas, Brau, Waters, Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028700
Salama, Han, Yau, Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2030340
Salvarani, Dolci, Massari, Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615
Schulert, Minoia, Bohnsack, Effect of Biologic Therapy on Clinical and Laboratory Features of Macrophage Activation Syndrome Associated With Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, Arthritis care & research, doi:10.1002/acr.23277
Si, Teachey, Spotlight on Tocilizumab in the Treatment of CAR-T-Cell-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome: Clinical Evidence to Date, Ther Clin Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/TCRM.S223468
Snow, Saleem, Ambler, Tocilizumab in COVID-19: a meta-analysis, trial sequential analysis, and meta-regression of randomized-controlled trials, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06416-z
Sterne, Murthy, Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17023
Stone, Frigault, Nj, Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028836
The, Group, Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2821%2900676-0
The, Investigators, Gordon, Mouncey, Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433
Veiga, Prats, Farias, Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial, Bmj, doi:10.1136/bmj.n84
Woods, Flynn, Monach, Implementation of documented and written informed consent for clinical trials of communicable diseases: lessons learned, barriers, solutions, future directions identified during the conduct of a COVID-19 clinical trial, Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications, doi:10.1016/j.conctc.2021.100804
Xu, Han, Li, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0263591",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263591",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Importance and objective</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The aim of this pragmatic, embedded, adaptive trial was to measure the effectiveness of the subcutaneous anti-IL-6R antibody sarilumab, when added to an evolving standard of care (SOC), for clinical management of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Design</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Two-arm, randomized, open-label controlled trial comparing SOC alone to SOC plus sarilumab. The trial used a randomized play-the-winner design and was fully embedded within the electronic health record (EHR) system.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Setting</jats:title>\n<jats:p>5 VA Medical Centers.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Participants</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Hospitalized patients with clinical criteria for moderate to severe COVID-19 but not requiring mechanical ventilation, and a diagnostic test positive for SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec005\">\n<jats:title>Interventions</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Sarilumab, 200 or 400 mg subcutaneous injection. SOC was not pre-specified and could vary over time, e.g., to include antiviral or other anti-inflammatory drugs.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec006\">\n<jats:title>Main outcomes and measures</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The primary outcome was intubation or death within 14 days of randomization. All data were extracted remotely from the EHR.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec007\">\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Among 162 eligible patients, 53 consented, and 50 were evaluated for the primary endpoint of intubation or death. This occurred in 5/20 and 1/30 of participants in the sarilumab and SOC arms respectively, with the majority occurring in the initial 9 participants (3/4 in the sarilumab and 1/5 in the SOC) before the sarilumab dose was increased to 400 mg and before remdesivir and dexamethasone were widely adopted. After interim review, the unblinded Data Monitoring Committee recommended that the study be stopped due to concern for safety: a high probability that rates of intubation or death were higher with addition of sarilumab to SOC (92.6%), and a very low probability (3.4%) that sarilumab would be found to be superior.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec008\">\n<jats:title>Conclusions and relevance</jats:title>\n<jats:p>This randomized trial of patients hospitalized due to respiratory compromise from COVID-19 but not mechanical ventilation found no benefit from subcutaneous sarilumab when added to an evolving SOC. The numbers of patients and events were too low to allow definitive conclusions to be drawn, but this study contributes valuable information about the role of subcutaneous IL-6R inhibition in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Methods developed and piloted during this trial will be useful in conducting future studies more efficiently.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec009\">\n<jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Clinicaltrials.gov—<jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04359901\" xlink:type=\"simple\">NCT04359901</jats:ext-link>; <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04359901?cond=NCT04359901&draw=2&rank=1\" xlink:type=\"simple\">https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04359901?cond=NCT04359901&draw=2&rank=1</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9658-5124",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Branch-Elliman",
"given": "Westyn",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doros",
"given": "Gheorghe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5646-4216",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leatherman",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strymish",
"given": "Judith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Datta",
"given": "Rupak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goswami",
"given": "Rekha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jankowich",
"given": "Matthew D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Nishant R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9004-8072",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Thomas H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Page",
"given": "Sarah T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schiller",
"given": "Sara J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shannon",
"given": "Colleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hau",
"given": "Cynthia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flynn",
"given": "Maura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holmberg",
"given": "Erika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Visnaw",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhond",
"given": "Rupali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brophy",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monach",
"given": "Paul A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-25T18:57:46Z",
"timestamp": 1645815466000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-25T18:58:18Z",
"timestamp": 1645815498000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Socio",
"given": "Giuseppe Vittorio",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000050",
"award": [
"1K12HL138049-01"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000050",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-13T16:52:42Z",
"timestamp": 1723567962425
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645747200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263591",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0263591",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "The cytokine storms of COVID-19, H1N1 influenza, CRS and MAS compared. Can one sized treatment fit all?",
"author": "G Morris",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref001",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Spotlight on Tocilizumab in the Treatment of CAR-T-Cell-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome: Clinical Evidence to Date",
"author": "S Si",
"first-page": "705",
"journal-title": "Ther Clin Risk Manag",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref002",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/acr.23277",
"article-title": "Effect of Biologic Therapy on Clinical and Laboratory Features of Macrophage Activation Syndrome Associated With Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis",
"author": "GS Schulert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arthritis care & research",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref003",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "X Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10970",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref004",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "JH Stone",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref005",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19",
"author": "The REMAP-CAP Investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1491",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref006",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "The RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"issue": "10285",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref007",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"article-title": "Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "C Salvarani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref008",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820",
"article-title": "Effect of Tocilizumab vs Usual Care in Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Moderate or Severe Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "O Hermine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "32",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref009",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028700",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia",
"author": "IO Rosas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1503",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref010",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2030340",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia",
"author": "C Salama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref011",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in COVID-19: a meta-analysis, trial sequential analysis, and meta-regression of randomized-controlled trials",
"author": "TAC Snow",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref012",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial",
"author": "VC Veiga",
"journal-title": "Bmj",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref013",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0",
"article-title": "Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial",
"author": "F-X Lescure",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "522",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref014",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "pone.0263591.ref015",
"unstructured": "How Are Emerging Data Translated Into Clinical Practice? A Mixed Methods Investigation of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Institutional Treatment Protocols. Open Forum Infectious Diseases; 2021. Oxford University Press US."
},
{
"article-title": "Bringing New Meaning to the Term “Adaptive Trial:” Challenges of Conducting Clinical Research during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Implications for Implementation Science",
"author": "W Branch-Elliman",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref016",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.3867",
"article-title": "Convergence of Implementation Science, Precision Medicine, and the Learning Health Care System: A New Model for Biomedical Research",
"author": "DA Chambers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref017",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1740774511398368",
"article-title": "A point-of-care clinical trial comparing insulin administered using a sliding scale versus a weight-based regimen",
"author": "LD Fiore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "183",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clinical trials",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref018",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "pone.0263591.ref019",
"unstructured": "Regeneron. REGENERON AND SANOFI PROVIDE UPDATE ON U.S. PHASE 2/3 ADAPTIVE-DESIGNED TRIAL OF KEVZARA® (SARILUMAB) IN HOSPITALIZED COVID-19 PATIENTS, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy",
"author": "G Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref020",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19—Final Report",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref021",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "pone.0263591.ref022",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. FDA guidance on conduct of clinical trials of medical products during COVID-19 pandemic: guidance for industry, investigators, and institutional review boards, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.conctc.2021.100804",
"article-title": "Implementation of documented and written informed consent for clinical trials of communicable diseases: lessons learned, barriers, solutions, future directions identified during the conduct of a COVID-19 clinical trial",
"author": "P Woods",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100804",
"journal-title": "Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref023",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Pragmatic, adaptive clinical trials: Is 2020 the dawning of a new age?",
"author": "W Branch-Elliman",
"journal-title": "Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref024",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pst.1778",
"article-title": "Response-adaptive clinical trials: case studies in the medical literature",
"author": "AP Grieve",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "64",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharm Stat",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref025",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1258/jrsm.2011.110180",
"article-title": "The answer is 17 years, what is the question: understanding time lags in translational research",
"author": "ZS Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "510",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J R Soc Med",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref026",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19",
"author": "The RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref027",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"article-title": "Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis",
"author": "The World Health Organization Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1330",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "pone.0263591.ref028",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263591"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Subcutaneous sarilumab for the treatment of hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID19 disease: A pragmatic, embedded randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "17"
}