Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled proof-of-concept trial of resveratrol for outpatient treatment of mild coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9, NCT04400890, Jun 2022
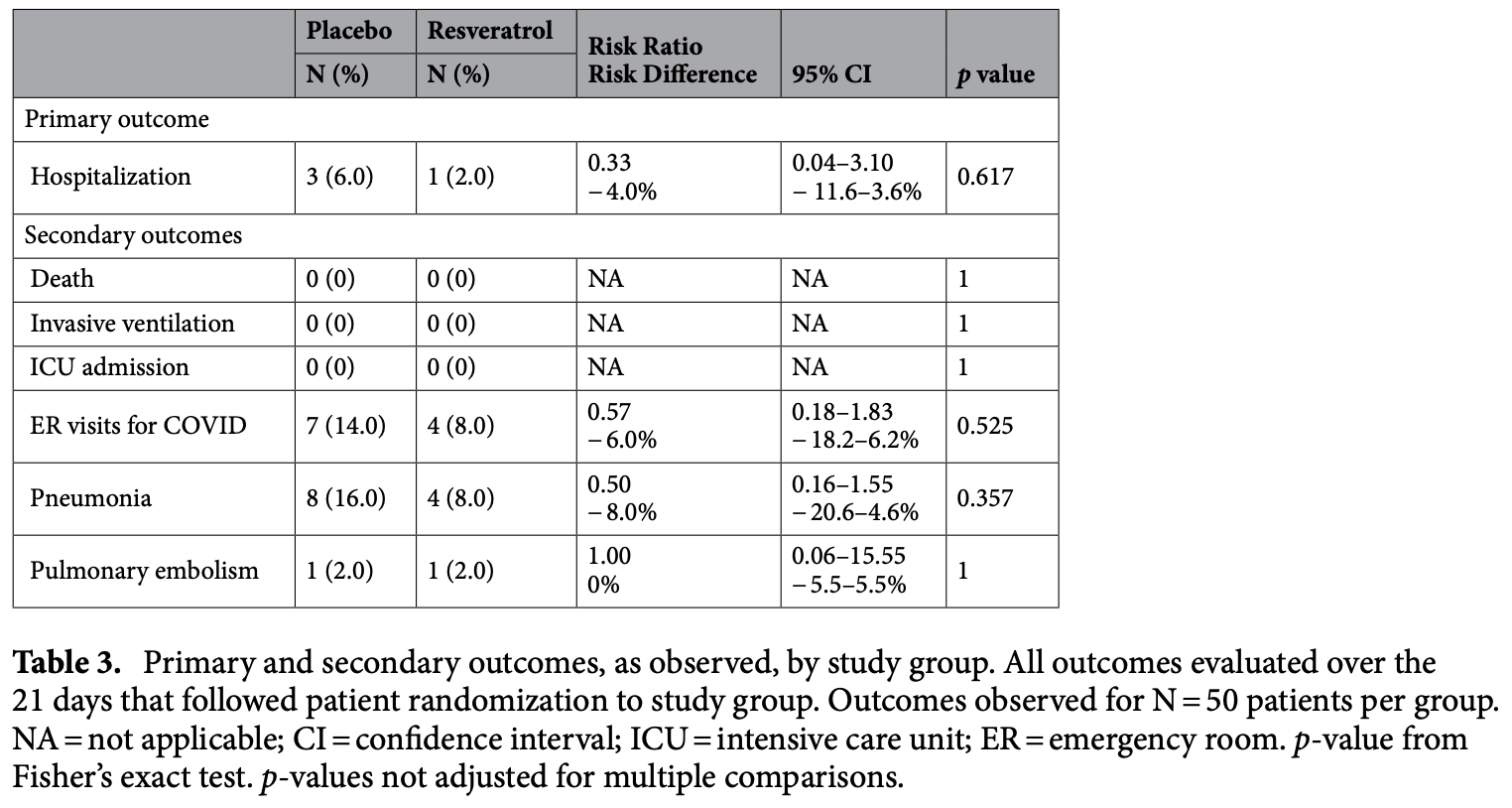
RCT 100 outpatients in the USA, showing lower hospitalization and progression with resveratrol, without statistical significance.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of hospitalization, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.62, treatment 1 of 50 (2.0%), control 3 of 50 (6.0%), NNT 25, day 21.
|
|
ER visits, 42.9% lower, RR 0.57, p = 0.52, treatment 4 of 50 (8.0%), control 7 of 50 (14.0%), NNT 17, ER visits, day 21.
|
|
pneumonia, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.36, treatment 4 of 50 (8.0%), control 8 of 50 (16.0%), NNT 12, pneumonia, day 21.
|
|
pulmonary embolism, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 50 (2.0%), control 1 of 50 (2.0%), pulmonary embolism, day 21.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
McCreary et al., 29 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, survey, 3 authors, study period 13 September, 2020 - 11 December, 2020, average treatment delay 4.6 days, trial NCT04400890 (history).
Contact: mccreary.14@osu.edu.
Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled proof-of-concept trial of resveratrol for outpatient treatment of mild coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9
Resveratrol is a polyphenol that has been well studied and has demonstrated anti-viral and antiinflammatory properties that might mitigate the effects of COVID-19. Outpatients (N = 105) were recruited from central Ohio in late 2020. Participants were randomly assigned to receive placebo or resveratrol. Both groups received a single dose of Vitamin D3 which was used as an adjunct. The primary outcome measure was hospitalization within 21 days of symptom onset; secondary measures were ER visits, incidence of pneumonia, and incidence of pulmonary embolism. Five patients chose not to participate after randomization. Twenty-one-day outcome was determined of all one hundred participants (mean [SD] age 55.6 [8.8] years; 61% female). There were no clinically significant adverse events attributed to resveratrol. Outpatients in this phase 2 study treated with resveratrol had a lower incidence compared to placebo of: hospitalization (2% vs. 6%, RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.04-3.10), COVID-19 related ER visits (8% vs. 14%, RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.18-1.83), and pneumonia (8% vs. 16%, RR 0.5, 95% CI 0.16-1.55). One patient (2%) in each group developed pulmonary embolism (RR 1.00, 95% CI: 0.06-15.55). This underpowered study was limited by small sample size and low incidence of primary adverse events consequently the results are statistically similar between treatment arms. A larger trial could determine efficacy.
Author contributions M.M.: conceptualization, methodology, software, writing original draft, supervision. P.S.: statistical analysis, writing original statistical protocol. D.R.: statistical analysis, writing -review and editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
References
Abba, Hassim, Hamzah, Noordin, Antiviral activity of resveratrol against human and animal viruses, Adv. Virol
Alghetaa, Resveratrol protects mice against SEB-induced acute lung injury and mortality by miR-193a modulation that targets TGF-β signalling, J. Cell Mol. Med
Aslan, Aslan, Özdemir, Is vitamin D one of the key elements in COVID-19 days?, J Nutr Health Aging
Bertelli, Analgesic resveratrol?, Antioxid. Redox Signal
Chen, Bai, Wang, The value of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory medicine, Expert Rev. Respir. Med
Christrup, Morphine metabolites, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand
Conti, Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by COVID-19: anti-inflammatory strategies, J. Biol. Regulat. Homeostatic Agents
Core, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Culpitt, Inhibition by red wine extract, resveratrol, of cytokine release by alveolar macrophages in COPD, Thorax
Dediego, Inhibition of NF-κB-mediated inflammation in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-infected mice increases survival, J. Virol
El-Aziz, Shehata, Awad, El-Sohaimy, Inhibition of COVID-19 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by natural bioactive compounds: Molecular docking analysis, Res. Square. Preprint, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-25850/v1
Estrov, Resveratrol blocks interleukin-1beta-induced activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB, inhibits proliferation, causes S-phase arrest, and induces apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells, Blood
Fagone, Transcriptional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection dismantles pathogenic pathways activated by the virus, proposes unique sex-specific differences and predicts tailored therapeutic strategies, Autoimmun. Rev
Grant, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Gu, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibits lung injury induced by respiratory syncytial virus, Sci. Rep
Harris, Research electronic data capture (REDCap)-A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support, J. Biomed. Inform
Horne, Vohl, Biological plausibility for interactions between dietary fat, resveratrol, ACE2, and SARS-CoV illness severity, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab
Horowitz, Freeman, Bruzzese, Efficacy of glutathione therapy in relieving dyspnea associated with COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 2 cases, Respir. Med. Case. Rep
Ilahi, Armas, Heaney, Pharmacokinetics of a single, large dose of cholecalciferol, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Imai, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure, Nature
Jiang, Resveratrol ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury via NLRP3 inflammasome modulation, Biomed. Pharmacother
Kode, Resveratrol induces glutathione synthesis by activation of Nrf2 and protects against cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress in human lung epithelial cells, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol
Kuba, A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat. Med
Lauer, Continued Impact of COVID-19 on Biomedical Research
Li, De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Metab. Eng
Lin, Effective inhibition of MERS-CoV infection by resveratrol, BMC Infect. Dis
Magrone, Magrone, Jirillo, Focus on receptors for coronaviruses with special reference to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a potential drug target -a perspective, Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets
Maity, Bora, Sur, An effect of combination of resveratrol with vitamin D3 on modulation of proinflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy induces rat, Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med
Mehta, COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Merzon, Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study, FEBS J
Mishra, Pathak, Tripathi, Natural compounds as potential inhibitors of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) main protease: An in silico study, Res. Square. Preprint, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-22839/v2
Moran, Resveratrol inhibits growth of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm associated with upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol
Nicholls, Peiris, Good, bad ACE do battle in lung injury
Obeid, Procurement of shared data instruments for research electronic data capture (REDCap), J. Biomed. Inform
Olejnik, Hume, Mühlberger, Toll-like receptor 4 in acute viral infection: Too much of a good thing, PLoS Pathog
Palamara, Inhibition of influenza a virus replication by resveratrol, J. Infect. Dis
Pandey, Targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein of COVID-19 with naturally occurring phytochemicals: an in silico study for drug development, Null, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1796811
Patterson, Disruption of the CCL5/RANTES-CCR5 Pathway Restores Immune Homeostasis and Reduces Plasma Viral Load in Critical COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2020.05.02.20084673
Polonikov, Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients, ACS Infectious Diseases
Ranjbar, Jamshidi, Torabi, Molecular modelling of the antiviral action of Resveratrol derivatives against the activity of two novel SARS CoV-2 and 2019-nCoV receptors, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
Rathnayake, Zheng, Kim, C-like protease inhibitors block coronavirus replication in vitro and improve survival in MERS-CoV-infected mice, Sci. Transl. Med
Ren, Resveratrol inhibits NF-kB signaling through suppression of p65 and IkappaB kinase activities, Pharmazie
Rossi, Sacco, Capizzi, Mastromarino, Can resveratrol-inhaled formulations be considered potential adjunct treatments for COVID-19?, Front. Immunol
Saldanha, Effects of resveratrol supplementation in nrf2 and NF-κB expressions in nondialyzed chronic kidney disease patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical trial, J. Ren. Nutr
Sergides, Chirilă, Silvestro, Pitta, Pittas, Bioavailability and safety study of resveratrol 500 mg tablets in healthy male and female volunteers, Exp. Ther. Med
Shah, Novel coronavirus-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation: A potential drug target in the treatment of COVID-19, Front. Immunol
Shigematsu, Resveratrol, a red wine constituent polyphenol, prevents superoxide-dependent inflammatory responses induced by ischemia/reperfusion, platelet-activating factor, or oxidants, Free Radical Biol. Med
Shin, Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity, Nature
Sun, Suppression of TLR4 activation by resveratrol is associated with STAT3 and Akt inhibition in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-activated platelets, Eur. J. Pharmacol
Tomé-Carneiro, Resveratrol and clinical trials: The crossroad from in vitro studies to human evidence, Curr. Pharm. Des
Wahedi, Ahmad, Abbasi, Stilbene-based natural compounds as promising drug candidates against COVID-19, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn
Walle, Bioavailability of resveratrol, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci
Wang, Up-regulation of IL-6 and TNF-α induced by SARS-coronavirus spike protein in murine macrophages via NF-κB pathway, Virus Res
Wang, Zhang, Bai, An anti-oxidative therapy for ameliorating cardiac injuries of critically ill COVID-19-infected patients, Int. J. Cardiol
White, Joseph, Best, A causal modelling framework for reference-based imputation and tipping point analysis in clinical trials with quantitative outcome, J. Biopharm. Stat
Xia, Förstermann, Li, Resveratrol and endothelial nitric oxide, Molecules
Xuzhu, Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function, Ann. Rheum. Dis
Yan, Xiao, Lin, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2: A double-edged sword?, FASEB J
Zang, Resveratrol-mediated gamma interferon reduction prevents airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in respiratory syncytial virus-infected immunocompromised mice, J. Virol
Zhao, Antiviral effect of resveratrol in piglets infected with virulent pseudorabies virus, Viruses
Zhu, Lei, Dong, Resveratrol as a potential therapeutic drug for respiratory system diseases, Drug Des. Dev. Ther
Zhu, Yong, Wu, Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol on TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression in adipocytes, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun
Åkerström, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology
Åkerström, Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13920-9",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Resveratrol is a polyphenol that has been well studied and has demonstrated anti-viral and anti-inflammatory properties that might mitigate the effects of COVID-19. Outpatients (N = 105) were recruited from central Ohio in late 2020. Participants were randomly assigned to receive placebo or resveratrol. Both groups received a single dose of Vitamin D3 which was used as an adjunct. The primary outcome measure was hospitalization within 21 days of symptom onset; secondary measures were ER visits, incidence of pneumonia, and incidence of pulmonary embolism. Five patients chose not to participate after randomization. Twenty-one-day outcome was determined of all one hundred participants (mean [SD] age 55.6 [8.8] years; 61% female). There were no clinically significant adverse events attributed to resveratrol. Outpatients in this phase 2 study treated with resveratrol had a lower incidence compared to placebo of: hospitalization (2% vs. 6%, RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.04–3.10), COVID-19 related ER visits (8% vs. 14%, RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.18–1.83), and pneumonia (8% vs. 16%, RR 0.5, 95% CI 0.16–1.55). One patient (2%) in each group developed pulmonary embolism (RR 1.00, 95% CI: 0.06–15.55). This underpowered study was limited by small sample size and low incidence of primary adverse events consequently the results are statistically similar between treatment arms. A larger trial could determine efficacy.</jats:p><jats:p>Trial Registrations: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04400890 26/05/2020; FDA IND #150033 05/05/2020.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"13920"
],
"article-number": "10978",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "31 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "30 May 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "29 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCreary",
"given": "Marvin R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schnell",
"given": "Patrick M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rhoda",
"given": "Dale A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-29T15:09:31Z",
"timestamp": 1656515371000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-25T06:41:49Z",
"timestamp": 1669358509000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"CTSA Grant UL1TR002733"
],
"name": "Ohio State University Center for Clinical and Translational Science"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-11T23:56:51Z",
"timestamp": 1691798211211
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656460800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656460800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13920-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13920-9",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13920-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.2174/13816128113199990407",
"author": "J Tomé-Carneiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6064",
"journal-title": "Curr. Pharm. Des.",
"key": "13920_CR1",
"unstructured": "Tomé-Carneiro, J. et al. Resveratrol and clinical trials: The crossroad from in vitro studies to human evidence. Curr. Pharm. Des. 19, 6064–6093 (2013).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2015/184241",
"author": "Y Abba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv. Virol.",
"key": "13920_CR2",
"unstructured": "Abba, Y., Hassim, H., Hamzah, H. & Noordin, M. M. Antiviral activity of resveratrol against human and animal viruses. Adv. Virol. 2015, 1 (2015).",
"volume": "2015",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ymben.2015.08.007",
"author": "M Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Metab. Eng.",
"key": "13920_CR3",
"unstructured": "Li, M. et al. De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 32, 1–11 (2015).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1762743",
"author": "HM Wahedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "13920_CR4",
"unstructured": "Wahedi, H. M., Ahmad, S. & Abbasi, S. W. Stilbene-based natural compounds as promising drug candidates against COVID-19. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 39, 1–10 (2020).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1796811",
"author": "P Pandey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Null",
"key": "13920_CR5",
"unstructured": "Pandey, P. et al. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein of COVID-19 with naturally occurring phytochemicals: an in silico study for drug development. Null 39, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1796811 (2020).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "13920_CR6",
"unstructured": "Ranjbar, A., Jamshidi, M. & Torabi, S. Molecular modelling of the antiviral action of Resveratrol derivatives against the activity of two novel SARS CoV-2 and 2019-nCoV receptors. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 7834–7844 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-22839/v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "13920_CR7",
"unstructured": "Mishra, A., Pathak, Y. & Tripathi, V. Natural compounds as potential inhibitors of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) main protease: An in silico study. Res. Square. Preprint (2020) https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-22839/v2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2601-5",
"author": "D Shin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "13920_CR8",
"unstructured": "Shin, D. et al. Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity. Nature 587, 657–622 (2020).",
"volume": "587",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abc5332",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "13920_CR9",
"unstructured": "Rathnayake, A., Zheng, J., Kim, Y., & et al. 3C-like protease inhibitors block coronavirus replication in vitro and improve survival in MERS-CoV-infected mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 12, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-25850/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "13920_CR10",
"unstructured": "El-Aziz, N. M. A., Shehata, M. G., Awad, O. M. E. & El-Sohaimy, S. A. Inhibition of COVID-19 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by natural bioactive compounds: Molecular docking analysis. Res. Square. Preprint (2020). https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-25850/v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13596-018-0311-4",
"author": "B Maity",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127",
"journal-title": "Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR11",
"unstructured": "Maity, B., Bora, M. & Sur, D. An effect of combination of resveratrol with vitamin D3 on modulation of proinflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy induces rat. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 18, 127–138 (2018).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2002-11-3550",
"author": "Z Estrov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "987",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "13920_CR12",
"unstructured": "Estrov, Z. et al. Resveratrol blocks interleukin-1beta-induced activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB, inhibits proliferation, causes S-phase arrest, and induces apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 102, 987–995 (2003).",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.034",
"author": "J Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "471",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "13920_CR13",
"unstructured": "Zhu, J., Yong, W. & Wu, X. Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol on TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 369, 471–477 (2008).",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.08.014",
"author": "J Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "13920_CR14",
"unstructured": "Sun, J. et al. Suppression of TLR4 activation by resveratrol is associated with STAT3 and Akt inhibition in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-activated platelets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 836, 1–10 (2018).",
"volume": "836",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01430-2",
"author": "S Shigematsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "810",
"journal-title": "Free Radical Biol. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR15",
"unstructured": "Shigematsu, S. et al. Resveratrol, a red wine constituent polyphenol, prevents superoxide-dependent inflammatory responses induced by ischemia/reperfusion, platelet-activating factor, or oxidants. Free Radical Biol. Med. 34, 810–817 (2003).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules191016102",
"author": "N Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16102",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "13920_CR16",
"unstructured": "Xia, N., Förstermann, U. & Li, H. Resveratrol and endothelial nitric oxide. Molecules 19, 16102–16121 (2014).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"author": "S Åkerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1966",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "13920_CR17",
"unstructured": "Åkerström, S. et al. Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 79, 1966–1969 (2005).",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"author": "S Åkerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "13920_CR18",
"unstructured": "Åkerström, S., Gunalan, V., Keng, C. T., Tan, Y.-J. & Mirazimi, A. Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected. Virology 395, 1–9 (2009).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"author": "X Ren",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "Pharmazie",
"key": "13920_CR19",
"unstructured": "Ren, X. et al. Resveratrol inhibits NF-kB signaling through suppression of p65 and IkappaB kinase activities. Pharmazie 68, 689 (2013).",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ard.2011.149831",
"author": "G Xuzhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "13920_CR20",
"unstructured": "Xuzhu, G. et al. Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 129–135 (2021).",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288",
"author": "A Polonikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1558",
"journal-title": "ACS Infectious Diseases",
"key": "13920_CR21",
"unstructured": "Polonikov, A. Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients. ACS Infectious Diseases 6, 1558–1562 (2020).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00361.2007",
"author": "A Kode",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L478",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol.",
"key": "13920_CR22",
"unstructured": "Kode, A. et al. Resveratrol induces glutathione synthesis by activation of Nrf2 and protects against cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress in human lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 294, L478–L488 (2008).",
"volume": "294",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"author": "RI Horowitz",
"journal-title": "Respir. Med. Case. Rep.",
"key": "13920_CR23",
"unstructured": "Horowitz, R. I., Freeman, P. R. & Bruzzese, J. Efficacy of glutathione therapy in relieving dyspnea associated with COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 2 cases. Respir. Med. Case. Rep. 30, 101063 (2020).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"author": "K Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR24",
"unstructured": "Kuba, K. et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 11, 875–879 (2005).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "13920_CR25",
"unstructured": "Mehta, P. et al. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 395, 1033–1034 (2020).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm0805-821",
"author": "J Nicholls",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "821",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR26",
"unstructured": "Nicholls, J. & Peiris, M. Good ACE, bad ACE do battle in lung injury, SARS. Nat. Med. 11, 821–822 (2005).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep19840",
"author": "H Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19840",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "13920_CR27",
"unstructured": "Gu, H. et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibits lung injury induced by respiratory syncytial virus. Sci. Rep. 6, 19840–19840 (2016).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202000782",
"author": "T Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6017",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "13920_CR28",
"unstructured": "Yan, T., Xiao, R. & Lin, G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2: A double-edged sword?. FASEB J. 34, 6017–6026 (2020).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310129",
"author": "CS Moran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2195",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.",
"key": "13920_CR29",
"unstructured": "Moran, C. S. et al. Resveratrol inhibits growth of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm associated with upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 37, 2195–2203 (2017).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature03712",
"author": "Y Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "13920_CR30",
"unstructured": "Imai, Y. et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 436, 112–116 (2005).",
"volume": "436",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00150.2020",
"author": "JR Horne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E830",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "13920_CR31",
"unstructured": "Horne, J. R. & Vohl, M.-C. Biological plausibility for interactions between dietary fat, resveratrol, ACE2, and SARS-CoV illness severity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 318, E830–E833 (2020).",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187153032001191213111933",
"author": "T Magrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets",
"key": "13920_CR32",
"unstructured": "Magrone, T., Magrone, M. & Jirillo, E. Focus on receptors for coronaviruses with special reference to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a potential drug target - a perspective. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 20, 1–11 (2020).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-017-2253-8",
"author": "S-C Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "144",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "13920_CR33",
"unstructured": "Lin, S.-C. et al. Effective inhibition of MERS-CoV infection by resveratrol. BMC Infect. Dis. 17, 144 (2017).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1007390",
"author": "J Olejnik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1007390",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "13920_CR34",
"unstructured": "Olejnik, J., Hume, A. J. & Mühlberger, E. Toll-like receptor 4 in acute viral infection: Too much of a good thing. PLoS Pathog. 14, e1007390 (2018).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "13920_CR35",
"unstructured": "Conti, P. et al. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by COVID-19: anti-inflammatory strategies. J. Biol. Regulat. Homeostatic Agents 34, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.02.20084673",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "13920_CR36",
"unstructured": "Patterson, B. K. et al. Disruption of the CCL5/RANTES-CCR5 Pathway Restores Immune Homeostasis and Reduces Plasma Viral Load in Critical COVID-19. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.02.20084673 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.007",
"author": "W Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "13920_CR37",
"unstructured": "Wang, W. et al. Up-regulation of IL-6 and TNF-α induced by SARS-coronavirus spike protein in murine macrophages via NF-κB pathway. Virus Res. 128, 1–8 (2007).",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S148868",
"author": "X Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3591",
"journal-title": "Drug Des. Dev. Ther.",
"key": "13920_CR38",
"unstructured": "Zhu, X., Lei, X. & Dong, W. Resveratrol as a potential therapeutic drug for respiratory system diseases. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 11, 3591–3598 (2017).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.58.11.942",
"author": "SV Culpitt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "942",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "13920_CR39",
"unstructured": "Culpitt, S. V. et al. Inhibition by red wine extract, resveratrol, of cytokine release by alveolar macrophages in COPD. Thorax 58, 942–946 (2003).",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02576-13",
"author": "ML DeDiego",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "913",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "13920_CR40",
"unstructured": "DeDiego, M. L. et al. Inhibition of NF-κB-mediated inflammation in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-infected mice increases survival. J. Virol. 88, 913–924 (2014).",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.13542",
"author": "H Alghetaa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2644",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Mol. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR41",
"unstructured": "Alghetaa, H. et al. Resveratrol protects mice against SEB-induced acute lung injury and mortality by miR-193a modulation that targets TGF-β signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 22, 2644–2655 (2018).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.020",
"author": "L Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "13920_CR42",
"unstructured": "Jiang, L. et al. Resveratrol ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury via NLRP3 inflammasome modulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 84, 130–138 (2016).",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1586/ers.10.71",
"author": "H Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "773",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Respir. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR43",
"unstructured": "Chen, H., Bai, C. & Wang, X. The value of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory medicine. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 4, 773–783 (2010).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "13920_CR44",
"unstructured": "Shah, A. Novel coronavirus-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation: A potential drug target in the treatment of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 11, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.04.009",
"author": "J-Z Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "13920_CR45",
"unstructured": "Wang, J.-Z., Zhang, R.-Y. & Bai, J. An anti-oxidative therapy for ameliorating cardiac injuries of critically ill COVID-19-infected patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 312, 137–138 (2020).",
"volume": "312",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v10090457",
"author": "X Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "457",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "13920_CR46",
"unstructured": "Zhao, X. et al. Antiviral effect of resveratrol in piglets infected with virulent pseudorabies virus. Viruses 10, 457 (2018).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102571",
"author": "P Fagone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102571",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "13920_CR47",
"unstructured": "Fagone, P. et al. Transcriptional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection dismantles pathogenic pathways activated by the virus, proposes unique sex-specific differences and predicts tailored therapeutic strategies. Autoimmun. Rev. 19, 102571–102571 (2020).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/429694",
"author": "AT Palamara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1719",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "13920_CR48",
"unstructured": "Palamara, A. T. et al. Inhibition of influenza a virus replication by resveratrol. J. Infect. Dis. 191, 1719–1729 (2005).",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.05869-11",
"author": "N Zang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13061",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "13920_CR49",
"unstructured": "Zang, N. et al. Resveratrol-mediated gamma interferon reduction prevents airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in respiratory syncytial virus-infected immunocompromised mice. J. Virol. 85, 13061–13068 (2011).",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"author": "W Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "988",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "13920_CR50",
"unstructured": "Grant, W. et al. Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients 12, 988 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-020-1517-y",
"author": "MT Aslan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1038",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Health Aging",
"key": "13920_CR51",
"unstructured": "Aslan, M. T., Aslan, İÖ. & Özdemir, Ö. Is vitamin D one of the key elements in COVID-19 days?. J Nutr Health Aging 24, 1038–1039 (2020).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/87.3.688",
"author": "M Ilahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "688",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "13920_CR52",
"unstructured": "Ilahi, M., Armas, L. A. G. & Heaney, R. P. Pharmacokinetics of a single, large dose of cholecalciferol. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 87, 688–691 (2008).",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010",
"author": "PA Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "J. Biomed. Inform.",
"key": "13920_CR53",
"unstructured": "Harris, P. A. et al. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)-A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 42, 377–381 (2009).",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2012.10.006",
"author": "JS Obeid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "J. Biomed. Inform.",
"key": "13920_CR54",
"unstructured": "Obeid, J. S. et al. Procurement of shared data instruments for research electronic data capture (REDCap). J. Biomed. Inform. 46, 259–265 (2013).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "13920_CR55",
"unstructured": "National Cancer Institute Division of Cancer Control & Population Services. Patient-Reported Outcomes version of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (PRO-CTCAE). https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/pro-ctcae/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "13920_CR56",
"unstructured": "CDC COVID-19 Response Team. Severe outcomes among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)—United States, February 12–March 16, 2020. Morbidity Mortality Week. Rep. 69, 343 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.jrn.2016.06.005",
"author": "J Saldanha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "401",
"journal-title": "J. Ren. Nutr.",
"key": "13920_CR57",
"unstructured": "Saldanha, J. et al. Effects of resveratrol supplementation in nrf2 and NF-κB expressions in nondialyzed chronic kidney disease patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical trial. J. Ren. Nutr. 26, 401–406 (2016).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"key": "13920_CR58",
"unstructured": "R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2020)."
},
{
"key": "13920_CR59",
"unstructured": "StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 17. (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10543406.2019.1684308",
"author": "I White",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "334",
"journal-title": "J. Biopharm. Stat.",
"key": "13920_CR60",
"unstructured": "White, I., Joseph, R. & Best, N. A causal modelling framework for reference-based imputation and tipping point analysis in clinical trials with quantitative outcome. J. Biopharm. Stat. 30, 334–350 (2020).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05842.x",
"author": "T Walle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "13920_CR61",
"unstructured": "Walle, T. Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1215, 9–15 (2011).",
"volume": "1215",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2015.2895",
"author": "C Sergides",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "Exp. Ther. Med.",
"key": "13920_CR62",
"unstructured": "Sergides, C., Chirilă, M., Silvestro, L., Pitta, D. & Pittas, A. Bioavailability and safety study of resveratrol 500 mg tablets in healthy male and female volunteers. Exp. Ther. Med. 11, 164–170 (2016).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1399-6576.1997.tb04625.x",
"author": "L Christrup",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.",
"key": "13920_CR63",
"unstructured": "Christrup, L. Morphine metabolites. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 41, 116–122 (1997).",
"volume": "41",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"key": "13920_CR64",
"unstructured": "Lauer, M. Continued Impact of COVID-19 on Biomedical Research. https://nexus.od.nih.gov/all/2020/11/04/continued-impact-of-covid-19-on-biomedical-research/ (2020)."
},
{
"key": "13920_CR65",
"unstructured": "The Economist. Pandemic mortality - See how age and illnesses change the risk of dying from covid-19. https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/covid-pandemic-mortality-risk-estimator (2021)."
},
{
"key": "13920_CR66",
"unstructured": "Ohio Department of Health. COVID-19 Dashboard. https://coronavirus.ohio.gov/wps/portal/gov/covid-19/dashboards/overview (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"author": "E Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3693",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "13920_CR67",
"unstructured": "Merzon, E. et al. Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: An Israeli population-based study. FEBS J 287, 3693–3702 (2020).",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "13920_CR68",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza Antiviral Medications: Clinician Summary. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/antivirals/summary-clinicians.htm (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2007.1926",
"author": "A Bertelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Antioxid. Redox Signal.",
"key": "13920_CR69",
"unstructured": "Bertelli, A. et al. Analgesic resveratrol?. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 10, 403–404 (2008).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.670955",
"author": "GA Rossi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1591",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "13920_CR70",
"unstructured": "Rossi, G. A., Sacco, O., Capizzi, A. & Mastromarino, P. Can resveratrol-inhaled formulations be considered potential adjunct treatments for COVID-19?. Front. Immunol. 12, 1591 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 70,
"references-count": 70,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13920-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled proof-of-concept trial of resveratrol for outpatient treatment of mild coronavirus disease (COVID-19)",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}