Randomized Prospective Open Label Study Shows No Impact on Clinical Outcome of Adding Losartan to Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Mild Hypoxemia
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3, COVID-ARB, NCT04340557, May 2021
RCT 31 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with mild hypoxemia showing no significant difference in mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, or mortality with addition of losartan to standard care.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 6.2% lower, RR 0.94, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 16 (6.2%), control 1 of 15 (6.7%), NNT 240.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 53.1% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.60, treatment 1 of 16 (6.2%), control 2 of 15 (13.3%), NNT 14.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 53.1% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.60, treatment 1 of 16 (6.2%), control 2 of 15 (13.3%), NNT 14.
|
|
hospitalization time, 10.0% lower, relative time 0.90, treatment 16, control 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Geriak et al., 11 May 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 53.0, 8 authors, study period 30 March, 2020 - 4 July, 2020, trial NCT04340557 (history) (COVID-ARB).
Contact: matthew.geriak@sharp.com.
Randomized Prospective Open Label Study Shows No Impact on Clinical Outcome of Adding Losartan to Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Mild Hypoxemia
Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3
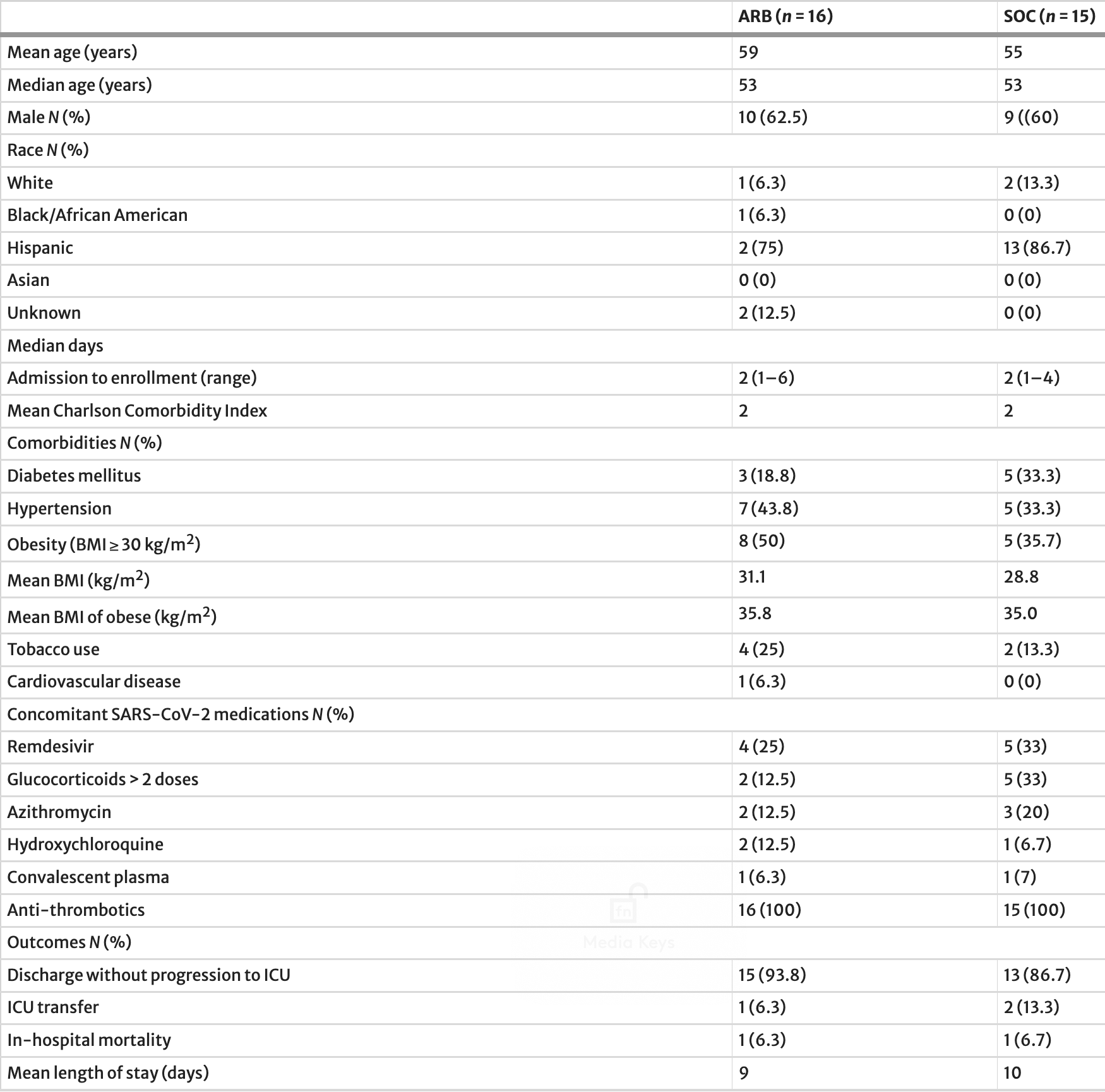
Introduction: Despite considerable scientific debate, there have been no prospective clinical studies on the effects of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) on the course of COVID-19 infection. Losartan is the ARB that was chosen to be tested in this study. Methods: Patients with COVID-19 and mild hypoxia (receipt of B 3 L/min O 2 by nasal cannula) admitted to three hospitals were randomized in a 1:1 ratio within 72 h of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid testing confirmation to prospectively receive standard of care (SOC) alone or SOC plus losartan 12.5 mg orally every 12 h for 10 days or until hospital discharge, with the option to titrate upward dependent on blood pressure tolerability. Primary composite endpoint was receipt of mechanical ventilation or death before receiving ventilation. Subjects were followed until discharge to home or until an endpoint was met in the hospital. Results: Sixteen subjects received an ARB plus SOC and 15 subjects received SOC alone. The median age was 53 years for both groups. Median time from hospital admission to study enrollment was 2 days (range 1-6) for the ARB group and 2 days (range 1-4) for the SOC group. Mean Charlson comorbidity index was 2 for both groups. One subject in each group achieved the composite endpoint. Conclusion: This small prospective randomized open-label study showed no clinically significant impacts of ARB therapy in mildly hypoxemic patients hospitalized with COVID-19 early in the pandemic. A larger prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial would be needed to confirm these findings or capture less pronounced effects and probably should focus on outpatients earlier in disease course.
Authorship. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole and have given their approval for this version to be published. All authors were active participants in at least one category of study design, study execution, data gathering and organization, data analysis and statistics, or manuscript preparation.
Authors
References
Bean, Treatment with ACE-inhibitors is associated with less severe disease with SARS-Covid-19 infection in a multi-site UK acute hospital trust, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.07.20056788
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-preliminary report
Cai, Tay, Kui, Tin, Tan, Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers on in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Singap Med J, doi:10.11622/smedj.2020159
Caldeira, Alarca ˜o, Vaz-Carneiro, Costa, Risk of pneumonia associated with use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: systematic review and metaanalysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.e4260
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Cicco, Cicco, Racanelli, Vacca, Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): two potential targets for COVID-19 treatment, Mediat Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2020/7527953
Ciulla, SARS-CoV-2 downregulation of ACE2 and pleiotropic effects of ACEIs/ARBs, Hypertens Res, doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0488-z
De Abajo, Use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: a case-population study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31030-8
Geriak, Haddad, Rizvi, Rose, Laplante et al., Clinical data on daptomycin plus ceftaroline versus standard of care monotherapy in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.02483-18
Goldman, Lye, Hui, Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19
Group, Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19-preliminary report, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Gurwitz, Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics, Drug Dev Res, doi:10.1002/ddr.21656
Li, Association of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors with severity or risk of death in patients with hypertension hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection in Wuhan, China, JAMA Cardiol, doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1624
Mackey, King, Gurley, Kiefer, Liederbauer et al., Risks and impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers on SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults: a living systematic review, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M20-1515
Mahase, Covid-19: FDA authorises neutralising antibody bamlanivimab for non-admitted patients, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m4362
Mancia, Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers and the risk of Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2006923
Messerli, Siontis, Rexhaj, COVID-19 and renin angiotensin blockers: current evidence and recommendations, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047022
Nicolai, Leunig, Brambs, Kaiser, Weinberger et al., Immunothrombotic dysregulation in COVID-19 pneumonia is associated with respiratory failure and coagulopathy, Circulation
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Reynolds, Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2008975
Sakoulas, Geriak, Kullar, Greenwood, Habib et al., Intravenous immunoglobulin plus methylprednisolone mitigate respiratory morbidity in coronavirus disease 2019, Crit Care Explor, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000280.PMID:33225306;PMCID:PMC7671875
Shang, Wan, Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.2003138117
Siddiqu, Mehra, COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012
Turgeon, Zieroth, Bewick, Chow, Clarke et al., Use of renin-angiotensin system blockers during the COVID-19 pandemic: early guidance and evolving evidence, Can J Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.cjca.2020.05.033
Uozumi, Iguchi, Masuda, Nishibata, Nakazawa et al., Pharmaceutical immunoglobulins reduce neutrophil extracellular trap formation and ameliorate the development of MPO-ANCA-associated vasculitis, Mod Rheumatol, doi:10.1080/14397595.2019.1602292
Wang, Zhang, Du, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Who Solidarity, Consortium, Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo et al., Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19-interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
Zhang, Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134
Zhang, Wu, Xu, Du, Effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors on disease severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26695
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3",
"ISSN": [
"2193-8229",
"2193-6382"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3",
"alternative-id": [
"453"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "28 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 2,
"value": "11 May 2021"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Geriak",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haddad",
"given": "Fadi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kullar",
"given": "Ravina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greenwood",
"given": "Kristina L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Habib",
"given": "MacKenzie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Habib",
"given": "Cole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willms",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakoulas",
"given": "George",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04340557",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-11T22:02:50Z",
"timestamp": 1620770570000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-10T17:20:07Z",
"timestamp": 1628616007000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100011842",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Sharp HealthCare"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T12:37:47Z",
"timestamp": 1715603867136
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 26,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1620691200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1620691200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1323-1330",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"author": "N Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5017",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "453_CR1",
"unstructured": "Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:5017–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"author": "HK Siddiqu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "453_CR2",
"unstructured": "Siddiqu HK, Mehra MR. COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"author": "C Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "453_CR3",
"unstructured": "Qin C, Zhou L, Hu Z, et al. Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa248.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2003138117",
"author": "J Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11727",
"journal-title": "PNAS",
"key": "453_CR4",
"unstructured": "Shang J, Wan Y, et al. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. PNAS. 2020;117:11727–34. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2003138117.",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048488",
"author": "L Nicolai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1176",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "453_CR5",
"unstructured": "Nicolai L, Leunig A, Brambs S, Kaiser R, Weinberger T, Weigand M, Muenchhoff M, Hellmuth JC, Ledderose S, Schulz H, Scherer C, Rudelius M, Zoller M, Hochter D, Keppler O, Teupser D, Zwibler B, von Bergwelt-Baildon M, Kaab S, Massberg S, Pekayyvaz K, Stark K. Immunothrombotic dysregulation in COVID-19 pneumonia is associated with respiratory failure and coagulopathy. Circulation. 2020;142:1176–89 (e-pub).",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/7527953",
"author": "S Cicco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7527953",
"journal-title": "Mediat Inflamm",
"key": "453_CR6",
"unstructured": "Cicco S, Cicco G, Racanelli V, Vacca A. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): two potential targets for COVID-19 treatment. Mediat Inflamm. 2020;2020:7527953. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7527953.",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14397595.2019.1602292",
"author": "R Uozumi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "544",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Mod Rheumatol",
"key": "453_CR7",
"unstructured": "Uozumi R, Iguchi R, Masuda S, Nishibata Y, Nakazawa D, Tomaru U, Ishizu A. Pharmaceutical immunoglobulins reduce neutrophil extracellular trap formation and ameliorate the development of MPO-ANCA-associated vasculitis. Mod Rheumatol. 2020;30(3):544–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2019.1602292.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "453_CR8",
"unstructured": "https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=Coronavirus&term=losartan&cntry=&state=&city=&dist=."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41440-020-0488-z",
"author": "MM Ciulla",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "985",
"journal-title": "Hypertens Res",
"key": "453_CR9",
"unstructured": "Ciulla MM. SARS-CoV-2 downregulation of ACE2 and pleiotropic effects of ACEIs/ARBs. Hypertens Res. 2020;43:985–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0488-z.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.21656",
"author": "D Gurwitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Drug Dev Res.",
"key": "453_CR10",
"unstructured": "Gurwitz D. Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics. Drug Dev Res. 2020;81(5):537–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21656 (Epub 2020 Mar 4).",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000280.PMID:33225306;PMCID:PMC7671875",
"author": "G Sakoulas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0280",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Explor",
"key": "453_CR11",
"unstructured": "Sakoulas G, Geriak M, Kullar R, Greenwood KL, Habib M, Vyas A, Ghafourian M, Dintyala VNK, Haddad F. Intravenous immunoglobulin plus methylprednisolone mitigate respiratory morbidity in coronavirus disease 2019. Crit Care Explor. 2020;2(11):e0280. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCE.0000000000000280.PMID:33225306;PMCID:PMC7671875.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02483-18",
"author": "M Geriak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e02483",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "453_CR12",
"unstructured": "Geriak M, Haddad F, Rizvi K, Rose W, LaPlante K, Yu M, Vasina L, Ouellette K, Zervos M, Nizet V, Sakoulas G. Clinical data on daptomycin plus ceftaroline versus standard of care monotherapy in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(5):e02483-e2518. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02483-18.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-1515",
"author": "K Mackey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "195",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med.",
"key": "453_CR13",
"unstructured": "Mackey K, King VJ, Gurley S, Kiefer M, Liederbauer E, Vela K, Sonnen P, Kansagara D. Risks and impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers on SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults: a living systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173(3):195–203. https://doi.org/10.7326/M20-1515 (Epub 2020 May 15).",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2008975",
"author": "HR Reynolds",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "453_CR14",
"unstructured": "Reynolds HR, et al. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2008975 (e-pub).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2006923",
"author": "G Mancia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "453_CR15",
"unstructured": "Mancia G, et al. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockers and the risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2006923 (e-pub).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31030-8",
"author": "FJ de Abajo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "453_CR16",
"unstructured": "de Abajo FJ, et al. Use of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: a case-population study. Lancet. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31030-8 (e-pub).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1624",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol",
"key": "453_CR17",
"unstructured": "Li J, et al. Association of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors with severity or risk of death in patients with hypertension hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1624 (e-pub).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134",
"author": "P Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "453_CR18",
"unstructured": "Zhang P, et al. Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19. Circ Res. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134 (e-pub).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.07.20056788",
"author": "DM Bean",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "453_CR19",
"unstructured": "Bean DM, et al. Treatment with ACE-inhibitors is associated with less severe disease with SARS-Covid-19 infection in a multi-site UK acute hospital trust. MedRxiv. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.07.20056788 (Preprint).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cjca.2020.05.033",
"author": "RD Turgeon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1180",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Can J Cardiol.",
"key": "453_CR20",
"unstructured": "Turgeon RD, Zieroth S, Bewick D, Chow CM, Clarke B, Cowan S, Fordyce CB, Fournier A, Gin K, Gupta A, Hardiman S, Jackson S, Lau B, Leong-Poi H, Mansour S, Marelli A, Quraishi AR, Roifman I, Ruel M, Sapp J, Singh G, Small G, Virani S, Wood DA, Krahn A. Use of renin–angiotensin system blockers during the COVID-19 pandemic: early guidance and evolving evidence. Can J Cardiol. 2020;36(8):1180–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2020.05.033 (Epub 2020 Jun 2).",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047022",
"author": "FH Messerli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2042",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "453_CR21",
"unstructured": "Messerli FH, Siontis GCM, Rexhaj E. COVID-19 and renin angiotensin blockers: current evidence and recommendations. Circulation. 2020;141(25):2042–4. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047022 (Epub 2020 Apr 13).",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26695",
"author": "G Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "453_CR22",
"unstructured": "Zhang G, Wu Y, Xu R, Du X. Effects of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors on disease severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.26695 (Epub ahead of print).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11622/smedj.2020159",
"author": "XJ Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Singap Med J.",
"key": "453_CR23",
"unstructured": "Cai XJ, Tay JCK, Kui SL, Tin AS, Tan VH. Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers on in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Singap Med J. 2020. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2020159 (Epub ahead of print).",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.e4260",
"author": "D Caldeira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e4260",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "453_CR24",
"unstructured": "Caldeira D, Alarcão J, Vaz-Carneiro A, Costa J. Risk of pneumonia associated with use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e4260. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e4260.",
"volume": "345",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "453_CR25",
"unstructured": "Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—preliminary report [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 22]. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1569",
"issue": "10236",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "453_CR26",
"unstructured": "Wang Y, Zhang D, Du G, et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020 May 30;395(10238):1694]. Lancet. 2020;395(10236):1569–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015301",
"author": "JD Goldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "453_CR27",
"unstructured": "Goldman JD, Lye DCB, Hui DS, et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19 [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 27]. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2015301.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "P Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "453_CR28",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Lim WS, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—preliminary report [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jul 17]. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2021436.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m4362",
"author": "E Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m4362",
"issue": "371",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "453_CR29",
"unstructured": "Mahase E. Covid-19: FDA authorises neutralising antibody bamlanivimab for non-admitted patients. BMJ. 2020;11(371):m4362. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m4362.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"author": "H Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "453_CR30",
"unstructured": "WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium, Pan H, Peto R, Henao-Restrepo AM, Preziosi MP, Sathiyamoorthy V, Abdool Karim Q, Alejandria MM, Hernández García C, Kieny MP, Malekzadeh R, Murthy S, Reddy KS, Roses Periago M, Abi Hanna P, Ader F, Al-Bader AM, Alhasawi A, Allum E, Alotaibi A, Alvarez-Moreno CA, Appadoo S, Asiri A, Aukrust P, Barratt-Due A, Bellani S, Branca M, Cappel-Porter HBC, Cerrato N, Chow TS, Como N, Eustace J, García PJ, Godbole S, Gotuzzo E, Griskevicius L, Hamra R, Hassan M, Hassany M, Hutton D, Irmansyah I, Jancoriene L, Kirwan J, Kumar S, Lennon P, Lopardo G, Lydon P, Magrini N, Maguire T, Manevska S, Manuel O, McGinty S, Medina MT, Mesa Rubio ML, Miranda-Montoya MC, Nel J, Nunes EP, Perola M, Portolés A, Rasmin MR, Raza A, Rees H, Reges PPS, Rogers CA, Salami K, Salvadori MI, Sinani N, Sterne JAC, Stevanovikj M, Tacconelli E, Tikkinen KAO, Trelle S, Zaid H, Røttingen JA, Swaminathan S. Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—interim WHO solidarity trial results. N Engl J Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2023184 (Epub ahead of print).",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40121-021-00453-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Randomized Prospective Open Label Study Shows No Impact on Clinical Outcome of Adding Losartan to Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Mild Hypoxemia",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}