The Efficacy of Famotidine in improvement of outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A phase III randomised clinical trial
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-462937/v1, Apr 2021
Famotidine for COVID-19
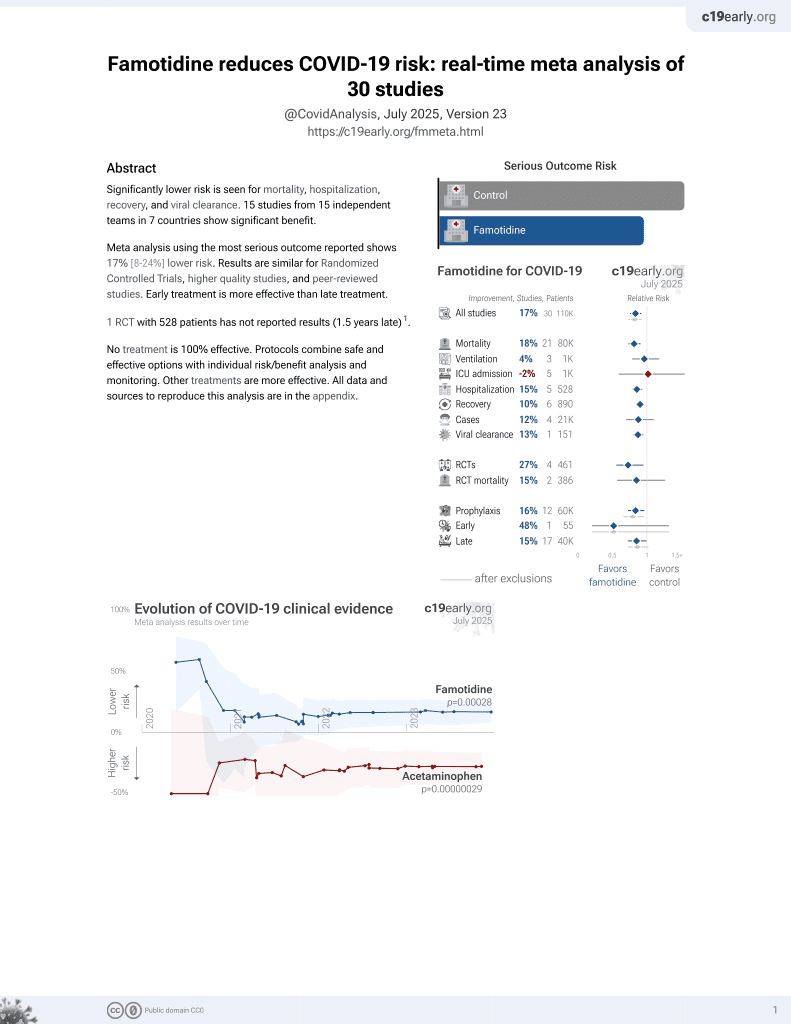
29th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2021, now with p = 0.00028 from 30 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Very small RCT with 20 patients in Iran, showing shorter hospitalization time with famotidine treatment. There was no mortality or ICU admission. Famotidine 160mg four times a day. IRCT20200509047364N2.
|
hospitalization time, 33.3% lower, relative time 0.67, p = 0.04, treatment 10, control 10.
|
|
risk of no recovery, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 5 of 10 (50.0%), control 5 of 10 (50.0%), >50% CT lung involvment.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.37, treatment 3 of 10 (30.0%), control 6 of 10 (60.0%), NNT 3.3, no improvement in cough.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Samimagham et al., 27 Apr 2021, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, preprint, 6 authors.
The Efficacy of Famotidine in improvement of outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A phase III randomised clinical trial
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-462937/v1
Introduction As the rst randomized clinical trial, this study evaluated the effect of Famotidine on the improvement of outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
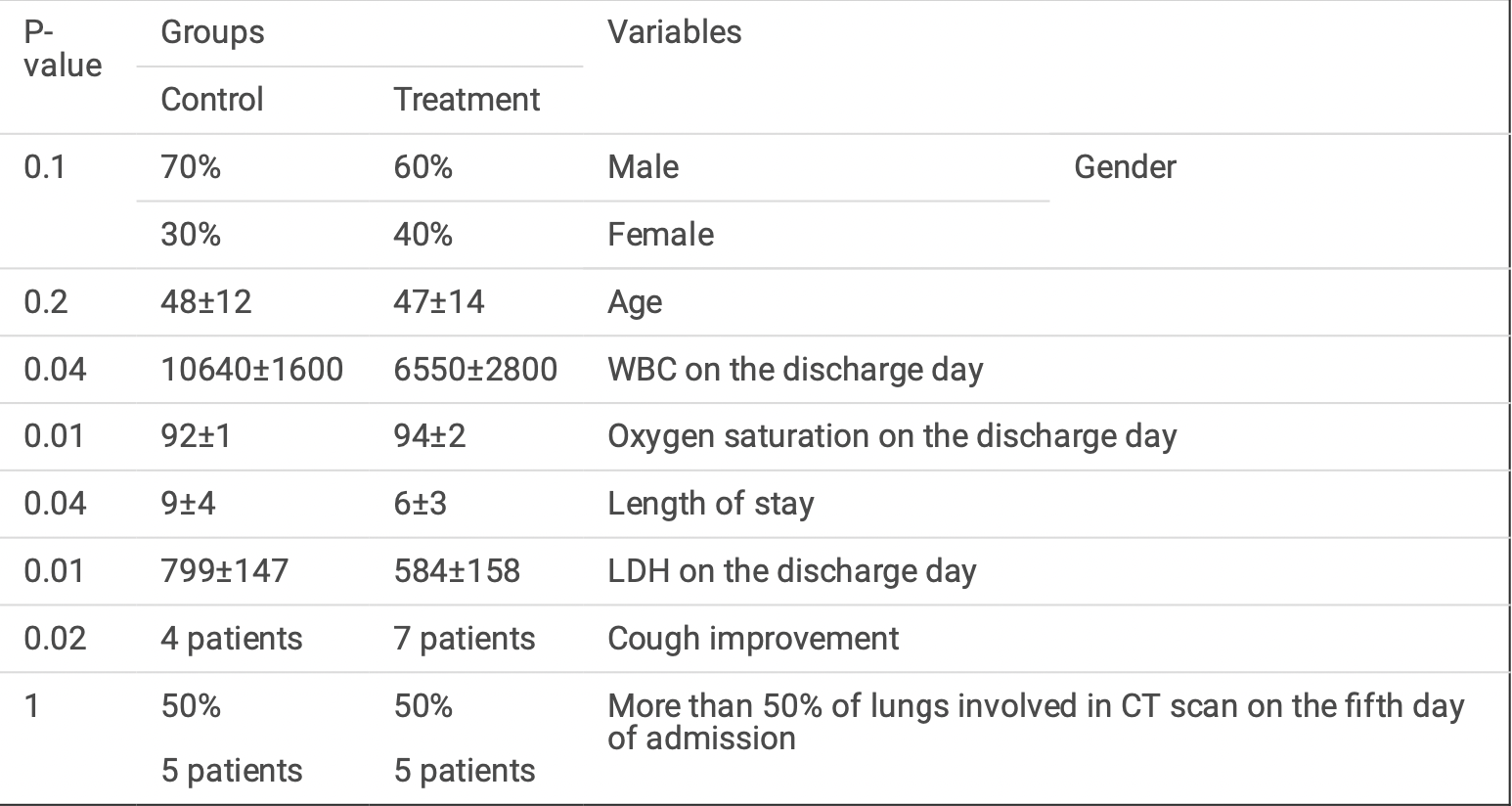
Method This phase III randomized clinical trial was designed with two parallel arms, placebo-controlled, singleblind, and concealed allocation, and recruited 20 patients. Oral Famotidine 160 mg four times a day was given to patients until the discharge day or for a maximum of 14 days. Patients' temperature, respiration rate, oxygen saturation, lung in ltration, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level and complete blood count (CBC) were measured at the baseline (before the intervention) and on day 14 after the intervention or on discharge day. Length of stay in the hospital and length of stay in the ICU were also measured as secondary outcomes of the study.
Results The results showed a signi cant decrease in LDH (P = 0.01), mean WBC (P = 0.04) and length of stay (P = 0.04) of patients with COVID-19 in the group treated with Famotidine compared to the control group. There was also a signi cant increase in oxygen saturation (P = 0.01) in the group treated with Famotidine compared to the control group. Cough improvement was also higher in the oral Famotidine group compared to the control group (P = 0.02).
Conclusion This was the rst clinical trial on the effect of Famotidine on the improvement of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, which indicated that high-dose Famotidine improves patients' clinical signs and reduces the severity of the disease and duration of hospitalization.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Supplementary Files This is a list of supplementary les associated with this preprint. Click to download.
CONSORT2010Checklist.doc
References
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Tracey, Callahan M V et al., Famotidine Use is Associated with Improved Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Cohort Study, Gastroenterology
Hogan, Hogan, Cannon, Rappi, Studdard et al., Dual-Histamine Blockade with Cetirizine -Famotidine Reduces Pulmonary Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients
Hu, Han, Zhang, Cao, Xie, Mast Cell-Induced Lung Injury in Mice Infected with H5N1 In uenza Virus, Journal of Virology
Janowitz, Gablenz, Pattinson, Wang, Conigliaro et al., Famotidine use and quantitative symptom tracking for COVID-19 in non-hospitalised patients: a case series, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321852
Ji, Zhang, Xu, Chen, Ty-Ci, unde ned
Li, Xu, Yu, Wang, Tao et al., Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Loffredo, Lucero, Chen, Connell, Bergqvist et al., The Effect of Famotidine on SARS-CoV-2 Proteases and Virus Replication, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.15.203059
Malone, Tisdall, Smith, Liu, Huang et al., COVID-19: Famotidine, Histamine, Mast Cells, and Mechanisms, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-30934/v2
Marshall, Portales-Cervantes, Leong, Mast Cell Responses to Viruses and Pathogen Products, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Mo, Xing, Xiao, Deng, Zhao et al., Clinical characteristics of refractory COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa270/5805508
Ortega, Serrano, Jastrzebska, Class A G Protein-Coupled Receptor Antagonist Famotidine as a Therapeutic Alternative against SARS-CoV2: An In Silico Analysis, Biomolecules
Samimagham, Azad, Haddad, Arabi, Hooshyar et al., The E cacy of Famotidine in improvement of outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Sen Gupta, Biswal, Singha, Rana, Binding insight of clinically oriented drug famotidine with the identi ed potential target of SARS-CoV-2 [Internet, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1784795
Shaffer, 15 drugs being tested to treat COVID-19 and how they would work, Nature Medicine
Thangam, Jemima, Singh, Baig, Khan et al., The role of histamine and histamine receptors in mast cell-mediated allergy and in ammation: The hunt for new therapeutic targets
Wu, Liu, Yang, Zhang, Zhong et al., Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B
Zhao, Yao, Wang, Zheng, Gao et al., A comparative study on the clinical features of COVID-19 pneumonia to other pneumonias
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Zhao, Liu et al., Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-462937/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-462937/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>IntroductionAs the first randomized clinical trial, this study evaluated the effect of Famotidine on the improvement of outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.MethodThis phase III randomized clinical trial was designed with two parallel arms, placebo-controlled, single-blind, and concealed allocation, and recruited 20 patients. Oral Famotidine 160 mg four times a day was given to patients until the discharge day or for a maximum of 14 days. Patients’ temperature, respiration rate, oxygen saturation, lung infiltration, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level and complete blood count (CBC) were measured at the baseline (before the intervention) and on day 14 after the intervention or on discharge day. Length of stay in the hospital and length of stay in the ICU were also measured as secondary outcomes of the study.ResultsThe results showed a significant decrease in LDH (P = 0.01), mean WBC (P = 0.04) and length of stay (P = 0.04) of patients with COVID-19 in the group treated with Famotidine compared to the control group. There was also a significant increase in oxygen saturation (P = 0.01) in the group treated with Famotidine compared to the control group. Cough improvement was also higher in the oral Famotidine group compared to the control group (P = 0.02).ConclusionThis was the first clinical trial on the effect of Famotidine on the improvement of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, which indicated that high-dose Famotidine improves patients’ clinical signs and reduces the severity of the disease and duration of hospitalization.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
25
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Samimagham",
"given": "Hamid Reza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Azad",
"given": "Mehdi Hassani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Haddad",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Iran University of Medical Sciences: Tehran University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Arabi",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Hooshyar",
"given": "Dariush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "KazemiJahromi",
"given": "Mitra",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-27T18:12:40Z",
"timestamp": 1619547160000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-16T05:33:32Z",
"timestamp": 1637040812000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-22T11:08:24Z",
"timestamp": 1640171304292
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
27
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1619481600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-462937/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-462937/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
27
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": [
"The Efficacy of Famotidine in improvement of outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A phase III randomised clinical trial"
],
"type": "posted-content"
}