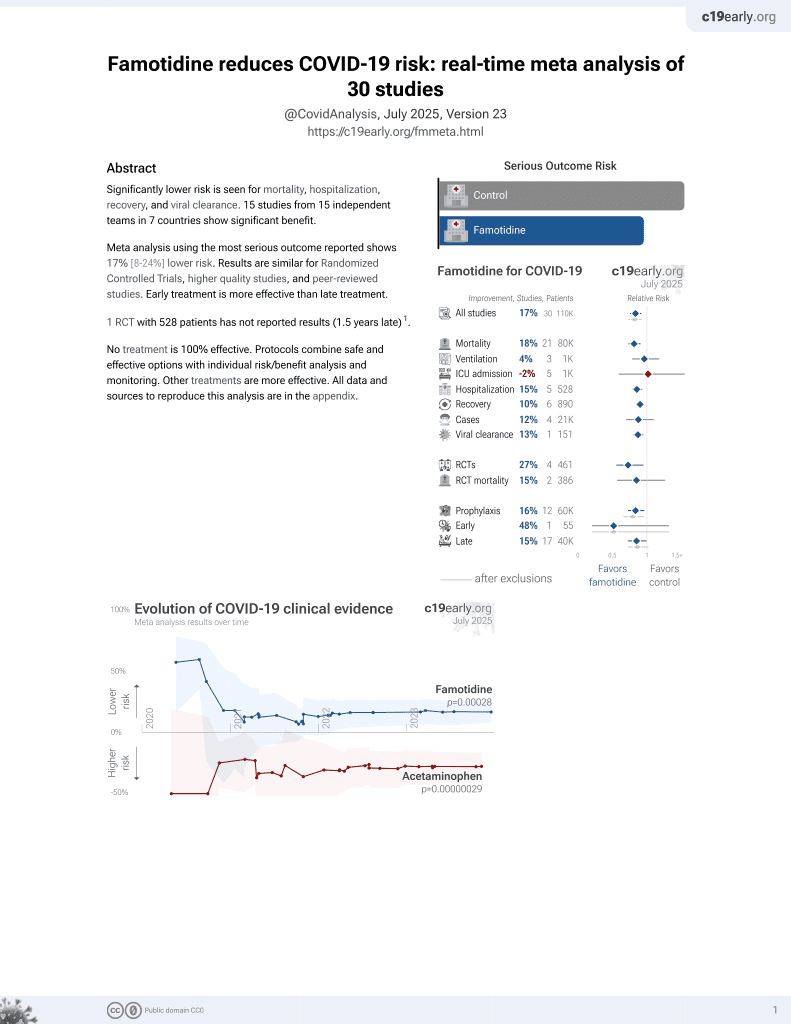
Famotidine for COVID-19
28th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2021, now with p = 0.00028 from 30 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
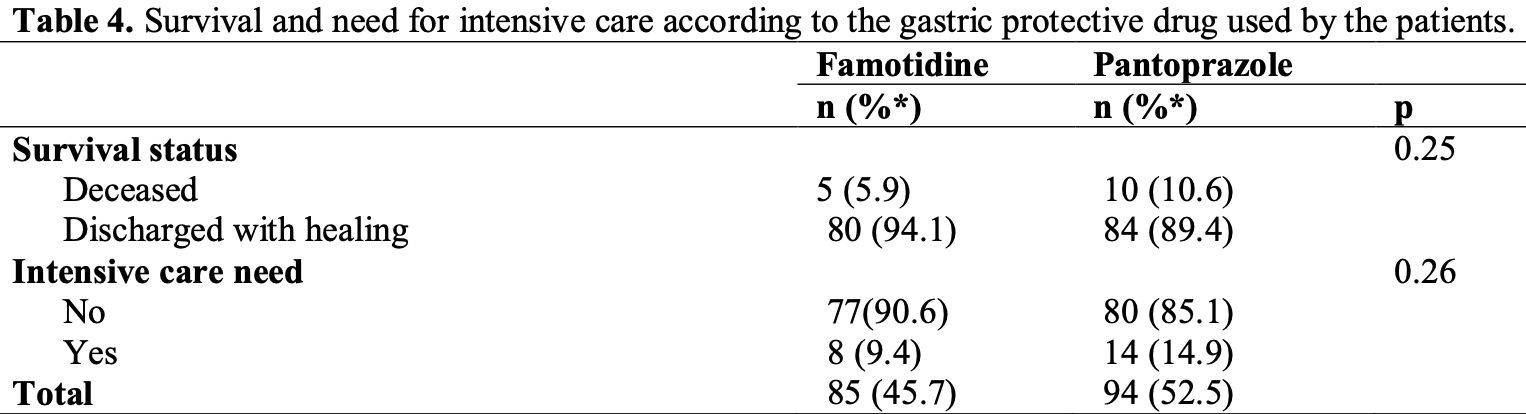
Retrospective 179 hospitalized patients in Turkey, 85 treated with famotidine and 94 treated with pantoprazole, showing faster recovery with famotidine in unadjusted results.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
risk of death, 44.7% lower, RR 0.55, p = 0.29, treatment 5 of 85 (5.9%), control 10 of 94 (10.6%), NNT 21.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 36.8% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.36, treatment 8 of 85 (9.4%), control 14 of 94 (14.9%), NNT 18.
|
|
hospitalization time, 18.1% lower, relative time 0.82, p = 0.003, treatment 85, control 94.
|
|
recovery time, 20.0% lower, relative time 0.80, p = 0.04, treatment 85, control 94, duration of fever.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Taşdemir et al., 12 Jul 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
Famotidine in COVID-19 treatment
Konuralp Tıp Dergisi, doi:10.18521/ktd.935888
Objective: Famotidine is an H2 receptor antagonist (H2RA) and has been shown to have antiviral properties in in vitro studies. Pantoprazole is one of the proton pump inhibitors (PPI). In this study, it was aimed to compare the efficacy of famotidine with pantoprazole in the treatment of COVID-19. Methods: Patients who were hospitalized and given famotidine and pantoprazole treatment for at least 48 hours were included in the study. Demographic, clinical and laboratory findings of the patients were analyzed retroprospectively from the patient files. The patients were divided into two groups as the famotidine group and the pantoprazole group. The groups were compared in terms of the need for intensive care and mortality rates. In addition, among the groups, the number of patients with normal oxygen saturation at discharge, number of days needed for oxygen support, number of days with fever, and length of hospital stay were evaluated. Results: A total of 179 Covid-19 patients (85 famotidine, 94 pantoprazole) were included in the study. Demographic findings and other symptoms except dyspnea were similar in both groups. Dyspnea, chronic diseases, and the number of patients given steroids were higher in those who were given pantoprazole (p<0.05). Mortality and ICU need were similar in both groups (respectively; p=0.25, p=0.26). The number of days with fever, duration of hospitalization, and the number of days requiring oxygen support were less in those given famotidine (respectively; p=0.04, p=0.003, p=0.014). Conclusions: Famotidine did not reduce the need for intensive care and mortality in COVID-19 patients treated in the hospital. New therapeutic agents are needed to reduce disease severity and mortality.
References
Bourinbaiar, Fruhstorfer, The effect of histamine type 2 receptor antagonists on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication: identification of a new class of antiviral agents, Life Sci
Branco, Yoshikawa, Pietrobon, Sato, Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation, Mediators Inflamm
Ennis, Tiligada, Histamine receptors and COVID-19, Inflammation Research
Fajgenbaum, June, Cytokine Storm, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra2026131
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Tracey, Callahan et al., Famotidine Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Cohort Study, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053
García, Immune response, inflammation, and the clinical spectrum of COVID-19, Frontiers in immunology
Kalpaklıoglu, Kalkan, Kavut, Histamin ve antihistaminler. Türkiye Klinikleri İmmünoloji Allerji-Özel Konular
Li, Xu, Yu, Wang, Tao et al., Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.006
Loffredo, Lucero, Chen, Connell, Bergqvist et al., The effect of famotidine on SARS-Cov-2 proteases and virus replication, doi:10.1101/2020.07.15.203059v1.full.pdf
Trivedi, Verma, Kumar, Possible treatment and strategies for COVID-19: review and assessment, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18521/ktd.935888",
"ISSN": [
"1309-3878"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18521/ktd.935888",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "TAŞDEMİR",
"given": "Canatan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "GÜÇLÜ",
"given": "Ertuğrul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "DEVRAN MUHARREMOĞLU",
"given": "Zeynep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "HOTSCHKA",
"given": "El Medina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "AYDEMİR",
"given": "Yusuf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "ÖĞÜTLÜ",
"given": "Aziz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "KARABAY",
"given": "Oğuz",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Konuralp Tıp Dergisi"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-13T06:21:08Z",
"timestamp": 1626157268000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-13T06:21:26Z",
"timestamp": 1626157286000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-17T13:27:07Z",
"timestamp": 1639747627637
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1309-3878"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
12
]
]
},
"member": "7783",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.18521",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Konuralp Medical Journal",
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Famotidine in COVID-19 treatment"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}