Effects of Famotidine on COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Clinical Trial
et al., Boğazi̇çi̇ Tip Dergi̇si̇, doi:10.14744/bmj.2023.77044, NCT05122208, Feb 2023
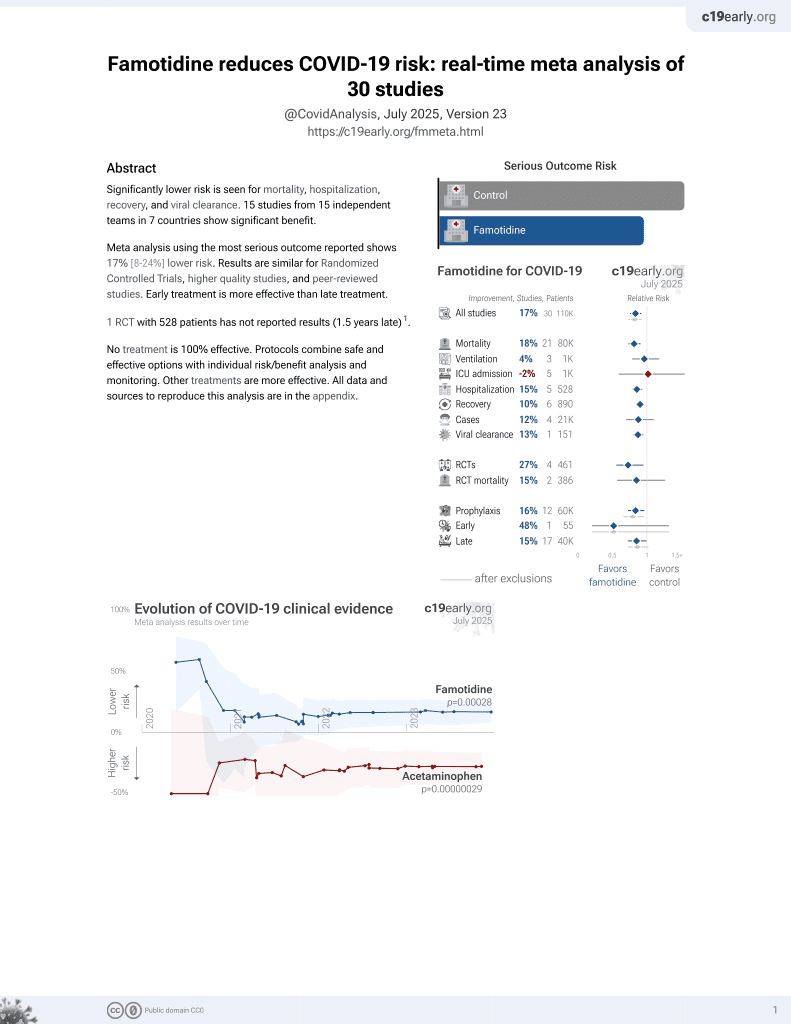
Famotidine for COVID-19
28th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2021, now with p = 0.00028 from 30 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
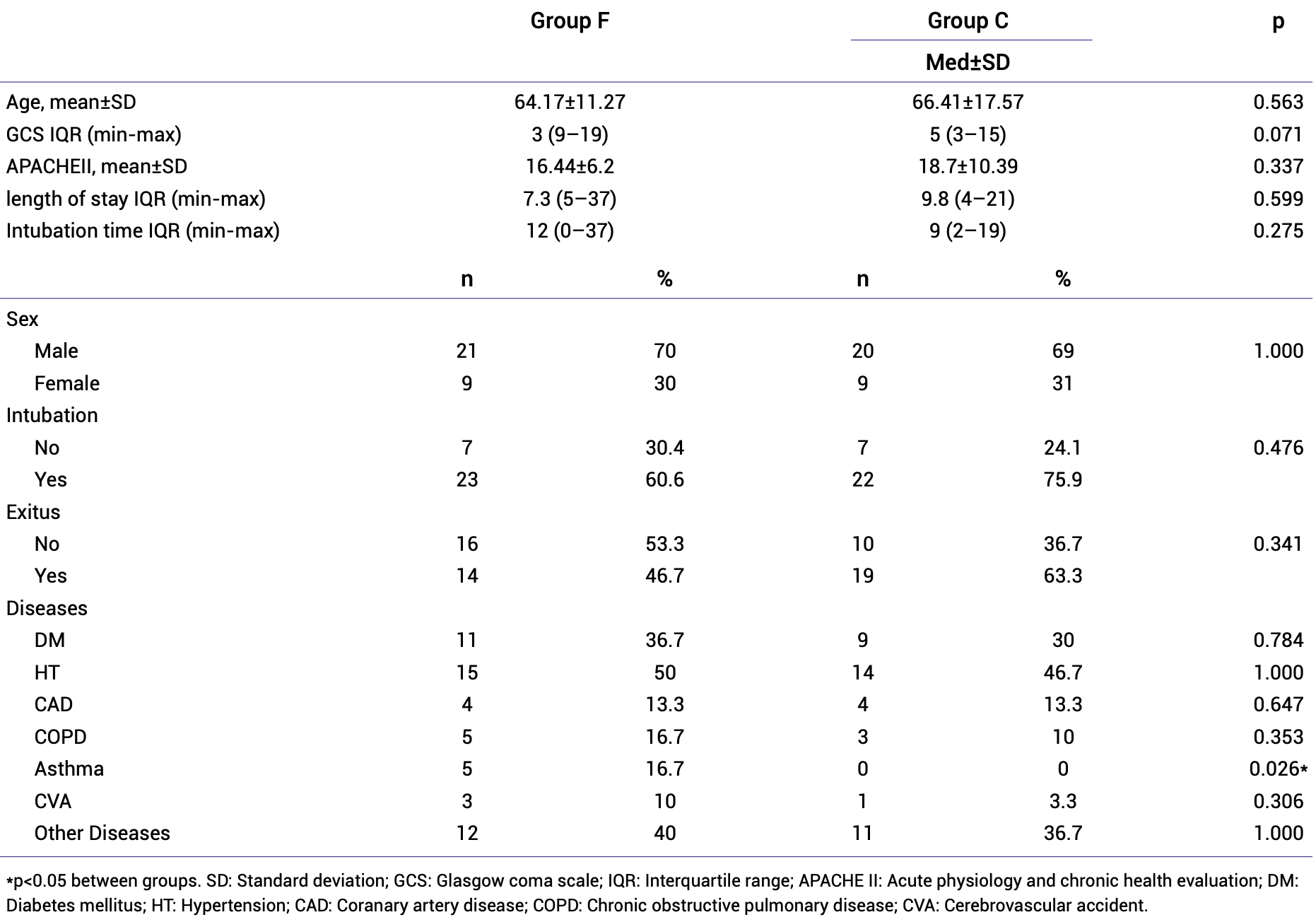
Retrospective 59 ICU patients in Turkey, showing no significant difference in 30-day mortality or invasive mechanical ventilation with 160mg/day famotidine treatment. However, the famotidine group had lower fibrinogen and procalcitonin, suggesting possible benefits for coagulation, inflammation, and secondary infections. Limitations include the small sample size, lack of randomization, and other confounding treatments.
|
risk of death, 28.8% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.19, treatment 14 of 30 (46.7%), control 19 of 29 (65.5%), NNT 5.3.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 1.1% higher, RR 1.01, p = 1.00, treatment 23 of 30 (76.7%), control 22 of 29 (75.9%).
|
|
ventilation time, 33.3% higher, relative time 1.33, p = 0.28, treatment 30, control 29.
|
|
ICU time, 25.5% lower, relative time 0.74, p = 0.60, treatment 30, control 29.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Özden et al., 28 Feb 2023, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, mean age 65.3, 2 authors, study period September 2020 - February 2021, trial NCT05122208 (history).
Contact: nihanozdenn@gmail.com.
Effects of Famotidine on COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Clinical Trial
BOĞAZİÇİ TIP DERGİSİ, doi:10.14744/bmj.2023.77044
Objectives: Because developing a new drug is a lengthy process, the drugs used safely were tried to be repurposed for COVID-19 treatment. In this retrospective study, it was aimed to investigate the effects of famotidine on the mortality, need for invasive mechanical ventilation, and the severity of the disease in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit (ICU) by regarding laboratory results. Methods: Data of patients treated in the ICU due to COVID-19 were retrospectively analyzed. The patients using famotidine were named Group F (n=30), and the patients not using it were named Group C (n=29). Invasive mechanical ventilation needs, 30-day mortality, intubation time, lymphocyte, ferritin, C-reactive protein (CRP), Ddimer, fibrinogen, and procalcitonin values were compared between groups. Mann-Whitney U-test and repeated measures ANOVA tests were used as statistical methods. Results: There was no statistical difference between the groups in terms of the need for invasive mechanical ventilation, 30-day mortality, length of stay in the ICU, and intubation time. In the laboratory, lymphocyte count, ferritin and D-dimer values were similar between the groups, while CRP was higher in Group F until the 14 th day. Fibrinogen and procalcitonin values were lower in Group F.
Conclusion: Famotidine treatment did not have a positive effect on the need for invasive mechanical ventilation and 30-day mortality in COVID-19 patients followed in the ICU. However, we think that it may have positive effects on coagulation, against the inflammation process and secondary infections.
References
Balouch, Vontela, Yeakel, Alnouri, Sataloff, Role of famotidine and other acid reflux medications for SARS-CoV-2: A pilot study, J Voice
Cheung, Hung, Leung, Association between famotidine use and COVID-19 severity in Hong Kong: A territory-wide study, Gastroenterology
Edalatifard, Akhtari, Salehi, Naderi, Jamshidi et al., Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: Results from a randomised controlled clinical trial, Eur Respir J
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Tracey, Callahan et al., Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, Gastroenterology
Frei, Ferstl, Konieczna, Ziegler, Simon et al., Histamine receptor 2 modifies dendritic cell responses to microbial ligands, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Ghosh, Chatterjee, Dubey, Lavie, Famotidine against SARS-CoV2: A hope or hype?, Mayo Clin Proc
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., China medical treatment expert group for covid-19. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Gupta, Biswal, Singha, Rana, Binding insight of clinically oriented drug famotidine with the identified potential target of SARS-CoV-2, J Biomol Struct Dyn
Guy, Dipaola, Romanelli, Dutch, Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19, Science
Halpin, Criner, Papi, Singh, Anzueto et al., Global initiative for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease. The 2020 GOLD Science committee report on COVID-19 and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Hu, Han, Pei, Yin, Chen, Procalcitonin levels in COVID-19 patients, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Ii, Iii, Cannon, Rappai, Studdard et al., Dual-histamine receptor blockade with cetirizinefamotidine reduces pulmonary symptoms in COVID-19 patients, Pulm Pharmacol Ther
Janowitz, Gablenz, Pattinson, Wang, Conigliaro et al., Famotidine use and quantitative symptom tracking for COVID-19 in non-hospitalised patients: A case series, Gut
Kow, Sattar Burud, Hasan, Use of famotidine and risk of severe course of illness in patients with COVID-19: A Meta-analysis, Mayo Clin Proc
Kritas, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Mast cells contribute to coronavirus-induced inflammation: New anti-inflammatory strategy, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Kuno, So, Takahashi, Egorova, The association between famotidine and in-hospital mortality of patients with COVID-19, J Med Virol
Lamontagne, Stegemann, Agarwal, Agoritsas, Siemieniuk et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs to prevent covid-19, BMJ
Levi, Thachil, Iba, Levy, Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Haematol
Li, Dong, Lei, No evidence indicates famotidine reduces the risk of serious disease in COVID-19 patients after propensity score matching: Meta-analysis and systematic reviews, Dig Dis Sci
Ma, Wu, Association between famotidine use and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: Assessment of available evidence, Am J Gastroenterol
Malone, Tisdall, Smith, Liu, Huang et al., COVID-19: Famotidine, histamine, mast cells, and mechanisms, Front Pharmacol
Mather, Seip, Mckay, Impact of famotidine use on clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Am J Gastroenterol
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., HLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Micco, Russo, Carannante, Imparato, Cardillo et al., Prognostic value of fibrinogen among COVID-19 patients admitted to an emergency department: An Italian Cohort Study, J Clin Med
Mukherjee, Bhattacharya, Bojkova, Mehdipour, Shin et al., Famotidine inhibits toll-like receptor 3-mediated inflammatory signaling in SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Biol Chem
Nugroho, Wardhana, Mulia, Maghfirah, Rachmi et al., Elevated fibrinogen and fibrin degradation product are associated with poor outcome in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis, Clin Hemorheol Microcirc
Rezaei-Tavirani, Nejad, Arjmand, Tavirani, Razzaghi et al., Fibrinogen dysregulation is a prominent process in fatal conditions of COVID-19 infection; A proteomic analysis, Arch Acad Emerg Med
Samimagham, Azad, Haddad, Arabi, Hooshyar et al., The efficacy of famotidine in improvement of outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Hosein, Patidar, Desai et al., Global pandemicity of COVID-19: Situation report as of june 9, 2020, Infect Dis
Shoaibi, Fortin, Weinstein, Berlin, Ryan, Comparative effectiveness of famotidine in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Am J Gastroenterol
Singh, El-Kurdi, Rood, What underlies the benefit of famotidine formulations used during COVID-19?, Gastroenterology
Sun, Chen, Hu, Wu, Liang et al., Does famotidine reduce the risk of progression to severe disease, death, and intubation for COVID-19 patients? A systemic review and meta-analysis, Dig Dis Sci
Takagaki, Osawa, Horio, Yamada, Hamaya et al., Cytokine responses of intraepithelial lymphocytes are regulated by histamine H(2) receptor, J Gastroenterol
Thachil, The protective rather than prothrombotic fibrinogen in COVID-19 and other inflammatory states, J Thromb Haemost
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wu, Liu, Yang, Zhang, Zhong et al., Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharm Sin B
Yeramaneni, Doshi, Sands, Cooper, Kurbegov et al., Famotidine use is not associated with 30-day mortality: A coarsened exact match study in 7158 hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 from a large healthcare system, Gastroenterology
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.14744/bmj.2023.77044",
"ISSN": [
"2149-0287"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.14744/bmj.2023.77044",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koruk",
"given": "Senem",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "BOĞAZİÇİ TIP DERGİSİ",
"container-title-short": "bogazicitip",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-29T08:57:01Z",
"timestamp": 1695977821000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-29T08:57:11Z",
"timestamp": 1695977831000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-30T18:12:09Z",
"timestamp": 1696097529494
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jag.journalagent.com/bmj/pdfs/BMJ-77044-ORIGINAL_RESEARCH-OZDEN.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "5966",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.14744",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"publisher": "Kare Publishing",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jag.journalagent.com/bmj/pdfs/BMJ-77044-ORIGINAL_RESEARCH-OZDEN.pdf"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of Famotidine on COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}