Time to Sustained Recovery Among Outpatients With COVID-19 Receiving Montelukast vs Placebo
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39332, ACTIV-6, NCT04885530, May 2024 (preprint)
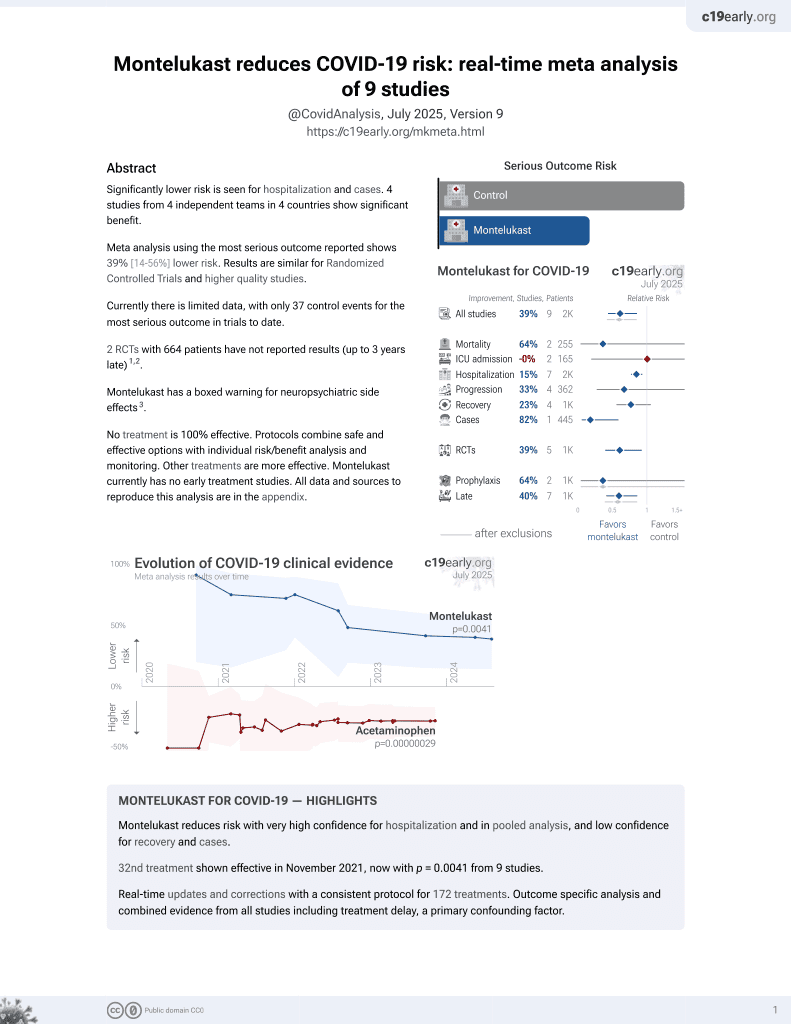
32nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0041 from 9 studies.
Lower risk for hospitalization and cases.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
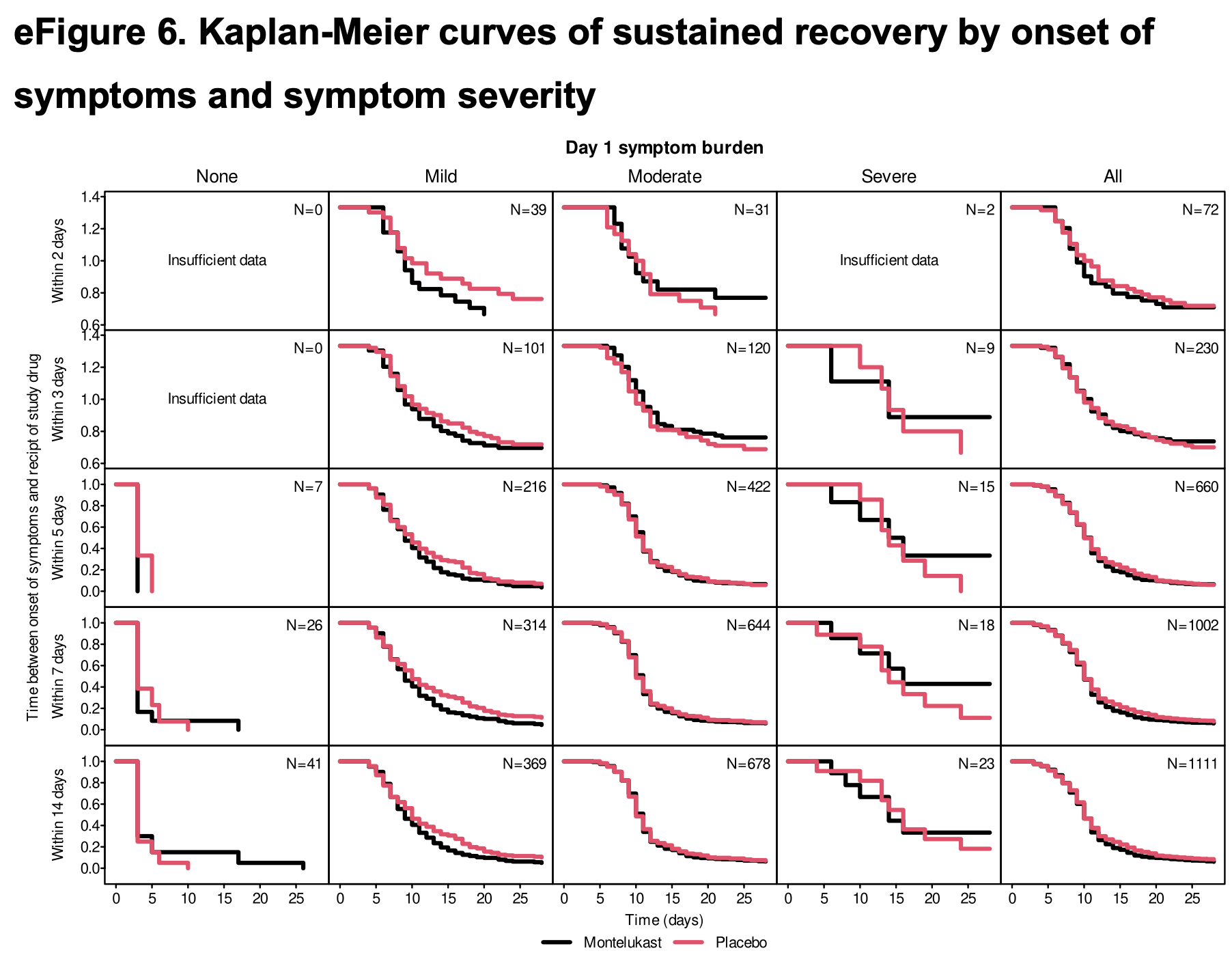
RCT 1,250 outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 showing no significant difference in time to sustained recovery with montelukast treatment. There were no deaths and only 2 hospitalizations in each group.
Notably, results were better with patients that had mild COVID-19 at baseline compared to moderate/severe cases, and overall efficacy is reduced by poor results with extremely late treatment 9 days after onset, and with patients that had no symptoms at baseline.
Authors note the treatment drug was voluntarily recalled and replaced from another source but do not report why the drug was recalled. Authors describe previous research testing 10mg and 20mg doses, noting that only 20mg showed improved pulmonary function testing, however authors do not indicate why they chose to test the lower dose for COVID-19.
It is unclear why authors only report all-cause hospitalization and urgent care and do not report COVID-19 specific outcomes. Given the low rate of urgent care visits and hospitalization, and the expected baseline frequency of these events independent of COVID-19, most or all of these events may be unrelated to COVID-19.
Authors note that previous research showed improvements specifically for cough, and authors collected cough data, however no results for cough are reported.
ACTIV trial authors have reported a number of issues that may affect
the reliability of the results in ACTIV trials including
participant fraud1,
biased participant demographics2,
resource issues that may have led to protocol deviations2,
differences in trial design including inconsistent inclusion/exclusion
criteria2,
participant self-selection bias1,2,
underrepresentation of older patients due to web-based recruitment2,
changes in treatment and public health policies during trials2,
treatment delay determination from shipping logs and delivery that may not be directly
to the patient1,
variable placebo responses (e.g., oral vs. inhaled)3,
logistical challenges maintaining blinding3,
errors from complex data collection systems3,
unplanned design changes including endpoint changes3, and
inconsistent SoC across trial sites and time periods3.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments4.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of hospitalization, 1.0% lower, RR 0.99, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 628 (0.3%), control 2 of 622 (0.3%), NNT 32551.
|
|
hosp./ER, 1.0% lower, RR 0.99, p = 1.00, treatment 18 of 628 (2.9%), control 18 of 622 (2.9%), NNT 3617.
|
|
risk of progression, 48.0% higher, OR 1.48, p = 0.29, clinical progression, day 28, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of progression, 29.0% lower, OR 0.71, p = 0.82, clinical progression, day 14, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of progression, 31.0% higher, OR 1.31, p = 0.27, clinical progression, day 7, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 2.0% lower, HR 0.98, p = 0.72, treatment 628, control 622, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, all patients.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 16.0% lower, HR 0.84, p = 0.12, treatment 186, control 183, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, patients with mild symptoms on day 1.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 2.9% lower, HR 0.97, p = 0.72, treatment 341, control 337, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, patients with moderate symptoms on day 1.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 37.0% higher, HR 1.37, p = 0.56, treatment 10, control 13, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, patients with severe symptoms on day 1.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 614.3% higher, HR 7.14, p < 0.001, treatment 186, control 183, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, patients with no symptoms on day 1.
|
|
recovery time, 2.0% lower, relative time 0.98, p = 0.07, treatment mean 11.77 (±2.49) n=628, control mean 12.01 (±2.16) n=622.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Lindsell et al., ACTIV-6: Operationalizing a decentralized, outpatient randomized platform trial to evaluate efficacy of repurposed medicines for COVID-19, Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, doi:10.1017/cts.2023.644.
2.
Wohl et al., Engaging communities in therapeutics clinical research during pandemics: Experiences and lessons from the ACTIV COVID-19 therapeutics research initiative, Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, doi:10.1017/cts.2024.561.
Rothman et al., 18 May 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 53.0, 32 authors, study period 27 January, 2023 - 23 June, 2023, average treatment delay 5.0 days, trial NCT04885530 (history) (ACTIV-6).
Contact: susanna.naggie@duke.edu.
Time to Sustained Recovery Among Outpatients With COVID-19 Receiving Montelukast vs Placebo
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39332
IMPORTANCE The effect of montelukast in reducing symptom duration among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 is uncertain. OBJECTIVE To assess the effectiveness of montelukast compared with placebo in treating outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This randomized clinical trial (Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines [ACTIV]-6) was conducted from January 27 through June 23, 2023, during the circulation of Omicron subvariants. Participants aged 30 years or older with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and 2 or more acute COVID-19 symptoms for less than 7 days were included across 104 US sites. INTERVENTIONS Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive montelukast, 10 mg once daily, or matched placebo for 14 days.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was time to sustained recovery (defined as Ն3 consecutive days without symptoms). Secondary outcomes included time to death; time to hospitalization or death; a composite of health care utilization events (hospitalization, urgent care clinic visit, emergency department visit, or death); COVID-19 clinical progression scale score; and difference in mean time unwell. A modified intention-to-treat approach was used for the analysis.
RESULTS Among 1250 participants who were randomized and received the study drug or placebo, the median age was 53 years (IQR, 42-62 years), 753 (60.2%) were female, and 704 (56.3%) reported receiving 2 or more doses of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Among 628 participants who received montelukast and 622 who received placebo, differences in time to sustained recovery were not observed (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR], 1.02; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.92-1.12; P = .63 for efficacy). Unadjusted median time to sustained recovery was 10 days (95% CI, 10-11 days) in both groups. No deaths occurred, and hospitalizations were reported for 2 participants (0.3%) in each group; the composite of health care utilization events was reported for 18 participants (2.9%) in the montelukast group and 18 (2.9%) in the placebo group (AHR, 1.01; 95% CrI, 0.45-1.84; P = .48 for efficacy). Five participants (0.4%) experienced serious adverse events (3 [0.5%] in the montelukast group and 2 [0.3%] in the placebo group). (continued) Key Points Question Does a 14-day course of montelukast, 10 mg once daily, reduce symptom duration among outpatient adults (aged Ն30 years) with mild to moderate COVID-19 compared with placebo? Findings In this randomized clinical trial of 1250 participants in the US (enrolled during the circulation of Omicron subvariants), there was no difference in time to sustained recovery between the montelukast and placebo groups. Meaning Administration of montelukast at a daily dose of 10 mg for 14 days did not result in a shortened duration of symptoms in outpatient adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Rothman reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during the conduct of the study. Dr Stewart reported receiving a grant from the Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI) as a subaward for ACTIV-6 from the NIH during the conduct of the study and receiving personal fees from Eli Lilly for serving on a data monitoring committee for a trial unrelated to COVID-19 outside the submitted work. Dr Garcia reported receiving grants from the NIH during the conduct of the study. Dr Shah reported receiving grants from the NIH during the conduct of the study. Dr Singh reported receiving grant funding from Pfizer for a clinical trial on long COVID, serving on a Gilead advisory
JAMA Network Open | Infectious Diseases
References
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Copertino, Duarte, Powell, De Mulder Rougvie, Nixon, Montelukast drug activity and potential against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26299
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Goodrich, Gabry, Ali, Brilleman, Infectious Diseases Time to Sustained Recovery From COVID-19 After Montelukast vs Placebo, JAMA Network Open
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2309003
Hays, Spritzer, Schalet, Cella, PROMIS-29 v2.0 profile physical and mental health summary scores, Qual Life Res, doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1842-3
Hm, Gareeb, Almulaiky, Cruz-Martins, Batiha, Role of leukotriene pathway and montelukast in pulmonary and extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19: the enigmatic entity, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174196
Kerget, Kerget, Aydın, Karaşahin, Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27552
Khan, Misdary, Yegya-Raman, Montelukast in hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19, J Asthma, doi:10.1080/02770903.2021.1881967
Magesh, John, Li, Disparities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status: a systematic-review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34147&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2024.39332
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators. Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2022.24100&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2024.39332
Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV-6) Study Group and Investigators. Effect of ivermectin vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2022.18590&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2024.39332
Rothman, Boulware, Mccarthy, Thicklin, Ginde et al., Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data
Rothman, Shah, Singh, Gentile, Felker et al., None
Sanghai, Tranmer, Taming the cytokine storm: repurposing montelukast for the attenuation and prophylaxis of severe COVID-19 symptoms, Drug Discov Today, doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2020.09.013
Schulz, Altman, Moher, CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials, Trials, doi:10.1186/1745-6215-11-32
Soltani, Nasirharandi, Khorvash, Nasirian, Dolatshahi et al., The effectiveness of gabapentin and gabapentin/montelukast combination compared with dextromethorphan in the improvement of COVID-19related cough: a randomized, controlled clinical trial, Clin Respir J, doi:10.1111/crj.13529
Venkatesan, Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00270-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39332",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39332",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>The effect of montelukast in reducing symptom duration among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 is uncertain.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To assess the effectiveness of montelukast compared with placebo in treating outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>This randomized clinical trial (Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines [ACTIV]–6) was conducted from January 27 through June 23, 2023, during the circulation of Omicron subvariants. Participants aged 30 years or older with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and 2 or more acute COVID-19 symptoms for less than 7 days were included across 104 US sites.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive montelukast, 10 mg once daily, or matched placebo for 14 days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary outcome was time to sustained recovery (defined as ≥3 consecutive days without symptoms). Secondary outcomes included time to death; time to hospitalization or death; a composite of health care utilization events (hospitalization, urgent care clinic visit, emergency department visit, or death); COVID-19 clinical progression scale score; and difference in mean time unwell. A modified intention-to-treat approach was used for the analysis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Among 1250 participants who were randomized and received the study drug or placebo, the median age was 53 years (IQR, 42-62 years), 753 (60.2%) were female, and 704 (56.3%) reported receiving 2 or more doses of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Among 628 participants who received montelukast and 622 who received placebo, differences in time to sustained recovery were not observed (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR], 1.02; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.92-1.12; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .63 for efficacy). Unadjusted median time to sustained recovery was 10 days (95% CI, 10-11 days) in both groups. No deaths occurred, and hospitalizations were reported for 2 participants (0.3%) in each group; the composite of health care utilization events was reported for 18 participants (2.9%) in the montelukast group and 18 (2.9%) in the placebo group (AHR, 1.01; 95% CrI, 0.45-1.84; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .48 for efficacy). Five participants (0.4%) experienced serious adverse events (3 [0.5%] in the montelukast group and 2 [0.3%] in the placebo group).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>In this randomized clinical trial of outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19, treatment with montelukast did not reduce duration of COVID-19 symptoms. These findings do not support the use of montelukast for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p>ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04885530\">NCT04885530</jats:ext-link></jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Rothman",
"given": "Russell L.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Data Science, University of Virginia, Charlottesville"
}
],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "Thomas G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Mourad",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Boulware",
"given": "David R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "Matthew W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "ACTIV-6 Stakeholder Advisory Committee, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Thicklin",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "L&A Morales Healthcare, Inc, Hialeah, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Garcia del Sol",
"given": "Idania T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Angel Medical Research Corporation, Miami Lakes, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Jose Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Bramante",
"given": "Carolyn T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Endeavor Health, Evanston, Illinois"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Nirav S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford University School of Medicine, California"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Upinder",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section on Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "John C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Global Health, Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia"
}
],
"family": "Rebolledo",
"given": "Paulina A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford University School of Medicine, California"
}
],
"family": "Jagannathan",
"given": "Prasanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Clinical Research, University of Kansas School of Medicine–Wichita"
}
],
"family": "Schwasinger-Schmidt",
"given": "Tiffany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora"
}
],
"family": "Ginde",
"given": "Adit A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City"
}
],
"family": "Castro",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, Miami, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Jayaweera",
"given": "Dushyantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Sulkowski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Gentile",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "McTigue",
"given": "Kathleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Felker",
"given": "G. Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "DeLong",
"given": "Allison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Wilder",
"given": "Rhonda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
},
{
"name": "Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center, Veterans Affairs Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, Nashville"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Sean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Dunsmore",
"given": "Sarah E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Adam",
"given": "Stacey J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, Washington, DC"
}
],
"family": "Hanna",
"given": "George J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Outcomes & Biomedical Informatics, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville"
}
],
"family": "Shenkman",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Hernandez",
"given": "Adrian F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Naggie",
"given": "Susanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Lindsell",
"given": "Christopher J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hanna",
"given": "George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fraser",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gamboa Jackson",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McAdams",
"given": "M. Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vail",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Korzekwinski",
"given": "Kayla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oyelakin",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chopp",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Randle",
"given": "Desmon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dockery",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adkins",
"given": "Rodney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Crow",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nowell",
"given": "Erin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "Kadie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Herbert",
"given": "Alicia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "Allegra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heavlin",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Linley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harding",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beauchaine",
"given": "Meaghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lindblom",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aamodt",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Jess",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "Sheri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Yue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Graves",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grindstaff",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrell",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Vicky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lopez",
"given": "Itzel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manis",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mankowski",
"given": "Kalley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marlin",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Merkel",
"given": "Alyssa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nwosu",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Obregon",
"given": "Savannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orozco",
"given": "Dirk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prato",
"given": "Nelson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rhode",
"given": "Max",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shirey-Rice",
"given": "Jana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vermillion",
"given": "Krista",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Jacob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Hsi-nien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vance",
"given": "Meghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weir",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bianchi",
"given": "Ray",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Premas",
"given": "Jen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Madhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karawan",
"given": "Greg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lima",
"given": "Santia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ziomek",
"given": "Carey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arena",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "DeAlmeida",
"given": "Sonaly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Malik",
"given": "Anuj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bryce",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Swint",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramin",
"given": "Soroush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nataraj",
"given": "Jaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Deider",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cruz",
"given": "Ricardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Ana Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henault",
"given": "Lori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marcus",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Southwell",
"given": "Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jacques",
"given": "Genice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sexton",
"given": "Cedar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tiffany",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tanner",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sahelian",
"given": "Allegra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "George-Adebayo",
"given": "Constance",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adebayo",
"given": "Adeolu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zapatero",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clement",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ronan",
"given": "Theresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gallegos",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Flys",
"given": "Tamara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sloan",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Olofintuyi",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Samraj",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasbinder",
"given": "Alma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Averett",
"given": "Amaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Slandzicki",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wallen",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vogel",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Munoz",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kavtaradze",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "Casandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singleton",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sevier",
"given": "Marcus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rivon",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Del Pilar",
"given": "Arnold",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spangler",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "Sohail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cantu",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Krishna",
"given": "Arvind",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daugherty",
"given": "Heidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kerr",
"given": "Brandi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Kathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spees",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marta",
"given": "Mailyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dolor",
"given": "Rowena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vergara",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "Jackie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burruss",
"given": "Valencia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hurst",
"given": "Terri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ofotokun",
"given": "Igho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Traenkner",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Atha",
"given": "Mary M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prabhu",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klicka",
"given": "Krystal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lightfeather",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "James",
"given": "Vickie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "Marcella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oragwu",
"given": "Chukwuemeka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oguego",
"given": "Ngozi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pillai",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gabriel",
"given": "Ahab",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghaly",
"given": "Emad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michal",
"given": "Marian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasquez",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mamon",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sheets",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hassanien",
"given": "Gammal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Samah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Samir",
"given": "Yehia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meltzer",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shahamatdar",
"given": "Soroush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heidish",
"given": "Ryan S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Loganathan",
"given": "Aditya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brehaut",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roche",
"given": "Angelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Manisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koppinger",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baez",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pagan",
"given": "Ivone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdelsayed",
"given": "Dallal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "Mina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lozinski",
"given": "Grace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "Alvin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Love",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mattox",
"given": "Bonnie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Raykel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pardue",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rowland",
"given": "Teddy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ruiz-Unger",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reyes",
"given": "Lionel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zamora",
"given": "Yadira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bacallao",
"given": "Navila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cienki",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jenny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szeto",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stelmash",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mekhael",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morales Castillo",
"given": "Ledular",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gutierrez",
"given": "Anya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prieto",
"given": "Sabrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Amon",
"given": "Arch",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barbera",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bugajski",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Willis",
"given": "Walter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jacklin",
"given": "Kellcee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lamb",
"given": "Deryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "Amron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stout",
"given": "Elmer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "Merischia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pyram-Bernard",
"given": "Nancy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quintero",
"given": "Arlen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barsanti-Sekhar",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carbrera-Mendez",
"given": "Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Mary Rose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adhami",
"given": "Eftim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carillo",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maria",
"given": "Josette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "Diksha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Raymond",
"given": "Oksana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Summers",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Tammy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lenert",
"given": "Leslie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Panaccione",
"given": "Ebony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szwast",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdulghani",
"given": "Ahsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasoya",
"given": "Pravin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Conrad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wiley",
"given": "Hawa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Austin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khizer",
"given": "Saadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adeyemi",
"given": "Oluwadamilola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chi",
"given": "Wei Ning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "July",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morton-Jost",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Castex",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quirch",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Belani",
"given": "Hrishikesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Machicado",
"given": "Rosario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bjornsson",
"given": "Bjorn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Olivo",
"given": "Jacqueline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maldonado",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vecchiarelli",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gaytan-Alvarez",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cherukuri",
"given": "Vijaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alicic",
"given": "Radica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lambert",
"given": "Allison A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Urbat",
"given": "Carissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baxter",
"given": "Joni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Linn",
"given": "Dawn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Vijay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Talati",
"given": "Roshan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Priti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellison",
"given": "Leonard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roman",
"given": "Angee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moy",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naquiallah",
"given": "Dina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Binod",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quintero",
"given": "Orlando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "Jake",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jazayeri",
"given": "Yasmin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O'Donnell",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pathak",
"given": "Divya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chandrasekar",
"given": "N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "Clifford",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Briana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dockery",
"given": "Martha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fortt",
"given": "Tabitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fortt",
"given": "Anisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones-Ince",
"given": "Ingrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McKee",
"given": "Alix",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marcelin",
"given": "Jackie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Farlow",
"given": "Brenda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grady",
"given": "Casey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richwine",
"given": "Randall",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pazier",
"given": "Penny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michelson",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watts",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kariyawasam",
"given": "Diluma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rodriguez",
"given": "Leann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manresa",
"given": "Ismarys",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Achong",
"given": "Angel A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Mari C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khetpal",
"given": "Sangeeta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Posey",
"given": "Faith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mahadevan",
"given": "Arvind",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gnoni",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Van de Weerd",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lowenkron",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sappington",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "Mitchell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Xinyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Co",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "D'Andrea",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Swink",
"given": "Wayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bozant",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Young",
"given": "Madeline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eastin",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cheathem",
"given": "Allyson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nadeem",
"given": "Ahad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walters",
"given": "Crystal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Powers-Fletcher",
"given": "Margaret",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Douglas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Delia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mukunzi",
"given": "Sylvere",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manning",
"given": "Brittney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Terry-White",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Crizaldo",
"given": "Maria Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Isache",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bowman",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Callaghan-Brown",
"given": "Angelique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ast",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duran",
"given": "Brent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cornejo",
"given": "Ashlie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Archer",
"given": "Allie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Almanzar",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Motel",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pullen",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "Blake",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhat",
"given": "Neeta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parra",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campora",
"given": "Paula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seithel",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kendrick",
"given": "Liz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Helming",
"given": "Dyann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pollock",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sekikawa",
"given": "Akira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klawson",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arnold",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weiland",
"given": "Nathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ostrosky-Zeichner",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Bela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Umana",
"given": "Virginia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nielsen",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grimes",
"given": "Carolyn Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "Thomas F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tragus",
"given": "Robin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Soileau",
"given": "Bridgette T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heath",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hinjosa",
"given": "Erik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gutierrez",
"given": "Cesar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Patrick E.H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hallowell",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haughey",
"given": "Heather M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vaidya-Tank",
"given": "Bhavna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gould",
"given": "Cameron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "Parul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sommers",
"given": "Sue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pangburn",
"given": "Haley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michalowski",
"given": "Lori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wortham",
"given": "Brittany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abbott",
"given": "Rica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Umana",
"given": "Unwana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alleyne",
"given": "Candace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Witting",
"given": "Britta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Armas",
"given": "Eddie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Perez Landaburo",
"given": "Ramon O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De La Cruz",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ballmajo",
"given": "Martha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alvarez",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-18T15:31:16Z",
"timestamp": 1729265476000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-18T15:31:21Z",
"timestamp": 1729265481000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-18T16:10:17Z",
"timestamp": 1729267817028,
"version": "3.27.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2825081/rothman_2024_oi_241134_1728586918.01934.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2439332",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00270-8",
"article-title": "Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Venkatesan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "zoi241134r1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19.",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi241134r2",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2309003",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1186",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi241134r3",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2020.09.013",
"article-title": "Taming the cytokine storm: repurposing montelukast for the attenuation and prophylaxis of severe COVID-19 symptoms.",
"author": "Sanghai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2076",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov Today",
"key": "zoi241134r4",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26299",
"article-title": "Montelukast drug activity and potential against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).",
"author": "Copertino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "187",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "zoi241134r5",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174196",
"article-title": "Role of leukotriene pathway and montelukast in pulmonary and extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19: the enigmatic entity.",
"author": "Al-Kuraishy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "zoi241134r6",
"volume": "904",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02770903.2021.1881967",
"article-title": "Montelukast in hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19.",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "780",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Asthma",
"key": "zoi241134r7",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27552",
"article-title": "Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Kerget",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1950",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "zoi241134r8",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/crj.13529",
"article-title": "The effectiveness of gabapentin and gabapentin/montelukast combination compared with dextromethorphan in the improvement of COVID-19- related cough: a randomized, controlled clinical trial.",
"author": "Soltani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "604",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Clin Respir J",
"key": "zoi241134r9",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"article-title": "Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "296",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi241134r10",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/cts.2023.644",
"article-title": "ACTIV-6: operationalizing a decentralized, outpatient randomized platform trial to evaluate efficacy of repurposed medicines for COVID-19.",
"author": "Accelerating Covid-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "zoi241134r11",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.18590",
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Naggie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1595",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi241134r12",
"volume": "328",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1745-6215-11-32",
"article-title": "CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials.",
"author": "Schulz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "zoi241134r13",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34147",
"article-title": "Disparities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status: a systematic-review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Magesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi241134r14",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11136-018-1842-3",
"article-title": "PROMIS-29 v2.0 profile physical and mental health summary scores.",
"author": "Hays",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1885",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Qual Life Res",
"key": "zoi241134r15",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "R Core Team",
"key": "zoi241134r16",
"volume-title": "R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"author": "Harrell",
"key": "zoi241134r19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Therneau",
"key": "zoi241134r20",
"volume-title": "Survival analysis",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "zoi241134r17",
"unstructured": "Goodrich? B, Gabry? J, Ali? I, Brilleman? S. (2023). rstanarm: bayesian applied regression modeling via Stan. R package, version 2.26.1. Accessed September 5, 2024. https://mc-stan.org/rstanarm/"
},
{
"key": "zoi241134r18",
"unstructured": "Brilleman? SL, Elçi? EM, Novik? JB, . Bayesian survival analysis using the rstanarm R package.? arXiv. Preprint posted online February 22, 2020. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2002.09633"
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2825081"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [
"The ACTIV-6 Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Time to Sustained Recovery Among Outpatients With COVID-19 Receiving Montelukast vs Placebo",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "7"
}