Effectiveness of Dexamethasone for COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
et al., The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgae734, Oct 2024
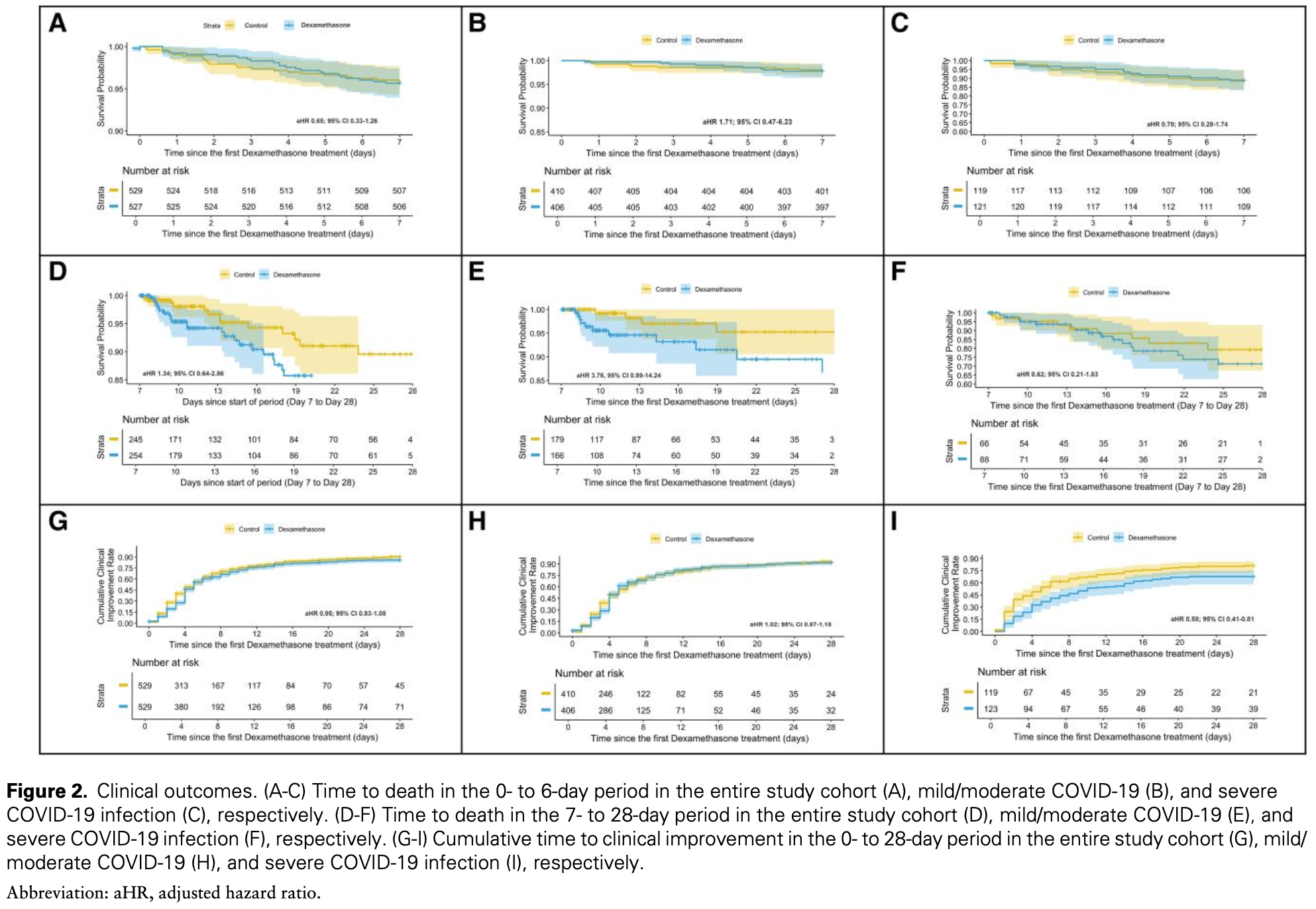
Retrospective propensity score matched study of 529 hospitalized diabetic COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in mortality or clinical improvement with dexamethasone treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 35.3% higher, RR 1.35, p = 0.20, treatment 46 of 529 (8.7%), control 34 of 529 (6.4%), propensity score matching, day 28.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 45.6% higher, RR 1.46, p = 0.02, treatment 83 of 529 (15.7%), control 57 of 529 (10.8%), propensity score matching, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bhat et al., 17 Oct 2024, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 4 March, 2020 - 25 June, 2022.
Contact: nmathio1@jh.edu.
Effectiveness of Dexamethasone for COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgae734
Background: Patients with diabetes have higher mortality from COVID-19 compared to the general population. Dexamethasone, a potent glucocorticoid used for moderate to severe COVID-19, can worsen hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes, potentially leading to worse outcomes. The efficacy and safety of use of dexamethasone for COVID-19 in patients with diabetes needs further evaluation. Objective: The study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of dexamethasone in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19 infection. Design: This retrospective study analyzed data from 5 hospitals in the Johns Hopkins Health System collected between March 3, 2020, and June 25, 2022. Propensity score matching was applied to a cohort of patients with diabetes who received dexamethasone and those who did not (controls), and outcomes were compared using Cox proportional hazards regression models.
Outcomes: The primary outcome was time to death within 28 days. The secondary outcome was time to clinical improvement. Additional outcomes included the incidence of hyperglycemic emergencies and subgroup analysis of primary outcomes by clinical severity. Results: Out of 10,329 patients admitted for COVID-19, 3679 had diabetes, and 2361 met the inclusion criteria. After propensity score matching, 529 patients were analyzed in each group. Survival rates between the dexamethasone and control groups during the 0-to 6-day and 7-to 28-day periods and time to clinical improvement at 28 days did not differ significantly. There was no difference in the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state between the groups. Conclusion: Dexamethasone treatment did not significantly improve survival or time to clinical improvement in patients with diabetes and COVID-19 infection. Further prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and determine potential mechanisms.
Disclosures S.Z.B., J.W., J.P., K.W., and N.M. have nothing to disclose.
References
Bajaj, Zale, Morgenlander, Abusamaan, Mathioudakis, Insulin dosing and glycemic outcomes among steroidtreated hospitalized patients, Endocr Pract
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Beaupere, Liboz, Fève, Blondeau, Guillemain, Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance, Int J Mol Sci
Cano, Fuentes, Campioli, Impact of corticosteroids in coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysisChest
De Almeida-Pititto, Dualib, Zajdenverg, Severity and mortality of COVID 19 in patients with diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis, Diabetol Metab Syndr
Delaunay, Khan, Cintra, Pancreatic beta cells are important targets for the diabetogenic effects of glucocorticoids, J Clin Invest
Deng, Chang, Ido, Long, Multiple imputation for general missing data patterns in the presence of high-dimensional data, Sci Rep
Devaraj, Dasu, Jialal, Diabetes is a proinflammatory state: a translational perspective, Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab
Eng, Distaso, Durreshahwar, The benefit of dexamethasone in patients with COVID-19 infection is preserved in patients with diabetes, Diabetes Obes Metab
Garibaldi, Fiksel, Muschelli, Patient trajectories among persons hospitalized for COVID-19: a cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Garibaldi, Wang, Robinson, Comparison of time to clinical improvement with vs without remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open
Goldman, Fink, Cai, Lee, Davies, High prevalence of COVID-19-associated diabetic ketoacidosis in UK secondary care, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Holman, Knighton, Kar, Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Kim, Mathioudakis, Management of glucocorticoid-induced diabetes and/or hyperglycemia, Endocrine and Metabolic Medical Emergencies: A Clinician's Guide
Klonoff, Messler, Umpierrez, Association between achieving inpatient glycemic control and clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, retrospective hospital-based analysis, Diabetes Care
Kolahian, Leiss, Nürnberg, Diabetic lung disease: fact or fiction?, Rev Endocr Metab Disord
Kumar, Arora, Sharma, Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Kuo, Mcqueen, Chen, Wang, Regulation of glucose homeostasis by glucocorticoids, Adv Exp Med Biol
Lavik, Ebekozien, Noor, Trends in type 1 diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 surges at 7 US centers: highest burden on non-hispanic black patients, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Li, Wang, Chen, Zuo, Zhang et al., COVID-19 infection may cause ketosis and ketoacidosis, Diabetes Obes Metab
Li, Zhong, Wang, Zeng, Luo et al., Clinical determinants of the severity of COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, PLoS One
Lombardi, Agarwal, Schechter, Tomer, In-Hospital hyperglycemia is associated with worse outcomes in patients admitted with COVID-19, Diabetes Care
Mathioudakis, Dungan, Baldwin, Korytkowski, Reider, Managing Diabetes and Hyperglycemia in the Hospital Setting: A Clinician's Guide
Mathioudakis, Supplemental Materials: Effectiveness of Dexamethasone for COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients with Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Mendeley Data
Matsumoto, Yamasaki, Akazawa, High-dose but not low-dose dexamethasone impairs glucose tolerance by inducing compensatory failure of pancreatic beta-cells in normal men, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Mcgurnaghan, Weir, Bishop, Risks of and risk factors for COVID-19 disease in people with diabetes: a cohort study of the total population of Scotland, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Narasimhulu, Singla, Mechanisms of COVID-19 pathogenesis in diabetes, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol
Perez, Jansen-Chaparro, Saigi, Bernal-Lopez, Miñambres et al., Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia, J Diabetes
Ruzzin, Wagman, Jensen, Glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscles: defects in insulin signalling and the effects of a selective glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor, Diabetologia
Scott, Strömstedt, Wang, Granner, Further characterization of the glucocorticoid response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. The role of the glucocorticoid receptor-binding sites, Mol Endocrinol
Stevens, Bogun, Mcmahon, Diabetic ketoacidosis and mortality in COVID-19 infection, Diabetes Metab
Turk Wensveen, Gašparini, Rahelic, Wensveen, Type 2 diabetes and viral infection; cause and effect of disease, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Van Paassen, Vos, Hoekstra, Neumann, Boot et al., Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes, Critical Care
Van Raalte, Nofrate, Bunck, Acute and 2-week exposure to prednisolone impair different aspects of beta-cell function in healthy men, Eur J Endocrinol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgae734",
"ISSN": [
"0021-972X",
"1945-7197"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgae734",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Patients with diabetes have higher mortality from COVID-19 compared to the general population. Dexamethasone, a potent glucocorticoid used for moderate to severe COVID-19, can worsen hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes, potentially leading to worse outcomes. The efficacy and safety of use of dexamethasone for COVID-19 in patients with diabetes needs further evaluation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of dexamethasone in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19 infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Design</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This retrospective study analyzed data from 5 hospitals in the Johns Hopkins Health System collected between March 3, 2020, and June 25, 2022. Propensity score matching was applied to a cohort of patients with diabetes who received dexamethasone and those who did not (controls), and outcomes were compared using Cox proportional hazards regression models.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Outcomes</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The primary outcome was time to death within 28 days. The secondary outcome was time to clinical improvement. Additional outcomes included the incidence of hyperglycemic emergencies and subgroup analysis of primary outcomes by clinical severity.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Out of 10,329 patients admitted for COVID-19, 3679 had diabetes, and 2361 met the inclusion criteria. After propensity score matching, 529 patients were analyzed in each group. Survival rates between the dexamethasone and control groups during the 0- to 6-day and 7- to 28-day periods and time to clinical improvement at 28 days did not differ significantly. There was no difference in the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state between the groups.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Dexamethasone treatment did not significantly improve survival or time to clinical improvement in patients with diabetes and COVID-19 infection. Further prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and determine potential mechanisms.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0304-4044",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, MD 21287 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bhat",
"given": "Salman Zahoor",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Biostatistics, Epidemiology and Data Management (BEAD) Core, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, MD 21224 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Jiajun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5482-6620",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of International Health, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health , Baltimore, MD 21205 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Perin",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore, MD 21218 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Kunbo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine , Baltimore, MD 21287 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Matthew L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine , Baltimore, MD 21287 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Garibaldi",
"given": "Brian T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0210-655X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine , Baltimore, MD 21287 ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mathioudakis",
"given": "Nestoras",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-17T18:29:54Z",
"timestamp": 1729189794000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-29T05:51:12Z",
"timestamp": 1730181072000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Christopher D. Saudek Diabetes Research Fellowship"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T11:06:21Z",
"timestamp": 1740135981977,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1729123200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jcem/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1210/clinem/dgae734/60182666/dgae734.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jcem/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1210/clinem/dgae734/60182666/dgae734.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "80",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1210",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "The Endocrine Society",
"reference": [
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B1",
"volume-title": "WHO COVID-19 Dashboard",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0250602",
"article-title": "Clinical determinants of the severity of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0250602",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B2",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2",
"article-title": "Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study",
"author": "Barron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B3",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13098-020-00586-4",
"article-title": "Severity and mortality of COVID 19 in patients with diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis",
"author": "de Almeida-Pititto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Diabetol Metab Syndr",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B4",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0",
"article-title": "Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Holman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "823",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B5",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30405-8",
"article-title": "Risks of and risk factors for COVID-19 disease in people with diabetes: a cohort study of the total population of Scotland",
"author": "McGurnaghan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "82",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101267",
"article-title": "Diabetic ketoacidosis and mortality in COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Stevens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101267",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B7",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108291",
"article-title": "High prevalence of COVID-19-associated diabetic ketoacidosis in UK secondary care",
"author": "Goldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108291",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B8",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14057",
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection may cause ketosis and ketoacidosis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1935",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B9",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgac158",
"article-title": "Trends in type 1 diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 surges at 7 US centers: highest burden on non-hispanic black patients",
"author": "Lavik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1948",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B10",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00204.2022",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of COVID-19 pathogenesis in diabetes",
"author": "Narasimhulu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H403",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B11",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-019-09516-w",
"article-title": "Diabetic lung disease: fact or fiction?",
"author": "Kolahian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "303",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Rev Endocr Metab Disord",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B12",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1586/eem.09.44",
"article-title": "Diabetes is a proinflammatory state: a translational perspective",
"author": "Devaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B13",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108637",
"article-title": "Type 2 diabetes and viral infection; cause and effect of disease",
"author": "Turk Wensveen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108637",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B14",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19—preliminary report",
"author": "Horby",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B15",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03400-9",
"article-title": "Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes",
"author": "van Paassen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Critical Care",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B16",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.054",
"article-title": "Impact of corticosteroids in coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1019",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B17",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.12090",
"article-title": "Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia",
"author": "Perez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-005-1886-0",
"article-title": "Glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscles: defects in insulin signalling and the effects of a selective glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor",
"author": "Ruzzin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2119",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B19",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22020623",
"article-title": "Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance",
"author": "Beaupere",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "623",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B20",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "HN",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B21"
},
{
"author": "Mathioudakis",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/mend.12.4.0090",
"article-title": "Further characterization of the glucocorticoid response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. The role of the glucocorticoid receptor-binding sites",
"author": "Scott",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "482",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Mol Endocrinol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI119743",
"article-title": "Pancreatic beta cells are important targets for the diabetogenic effects of glucocorticoids",
"author": "Delaunay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2094",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B24",
"volume": "100",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"article-title": "High-dose but not low-dose dexamethasone impairs glucose tolerance by inducing compensatory failure of pancreatic beta-cells in normal men",
"author": "Matsumoto",
"first-page": "2621",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B25",
"volume": "81",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-09-1034",
"article-title": "Acute and 2-week exposure to prednisolone impair different aspects of beta-cell function in healthy men",
"author": "van Raalte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "729",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B26",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-2895-8_5",
"article-title": "Regulation of glucose homeostasis by glucocorticoids",
"author": "Kuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B27",
"volume": "872",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2022.05.002",
"article-title": "Insulin dosing and glycemic outcomes among steroid-treated hospitalized patients",
"author": "Bajaj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "774",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Endocr Pract",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B28",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-1857",
"article-title": "Association between achieving inpatient glycemic control and clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, retrospective hospital-based analysis",
"author": "Klonoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "578",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B29",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-0708",
"article-title": "In-Hospital hyperglycemia is associated with worse outcomes in patients admitted with COVID-19",
"author": "Lombardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2683",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B30",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-3905",
"article-title": "Patient trajectories among persons hospitalized for COVID-19: a cohort study",
"author": "Garibaldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B31",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Supplemental Materials: Effectiveness of Dexamethasone for COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients with Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Mendeley Data, V1",
"author": "Mathioudakis",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3071",
"article-title": "Comparison of time to clinical improvement with vs without remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Garibaldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e213071",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B33",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep21689",
"article-title": "Multiple imputation for general missing data patterns in the presence of high-dimensional data",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21689",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B34",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044",
"article-title": "Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "535",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B35",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14692",
"article-title": "The benefit of dexamethasone in patients with COVID-19 infection is preserved in patients with diabetes",
"author": "Eng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1385",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Obes Metab",
"key": "2024102905504456900_dgae734-B36",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jcem/advance-article/doi/10.1210/clinem/dgae734/7825467"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of Dexamethasone for COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article"
}