Lactoferrin in the Prevention of Recurrent Respiratory Infections in Preschool Children: A Prospective Randomized Study
et al., Children, doi:10.3390/children11020249, Feb 2024
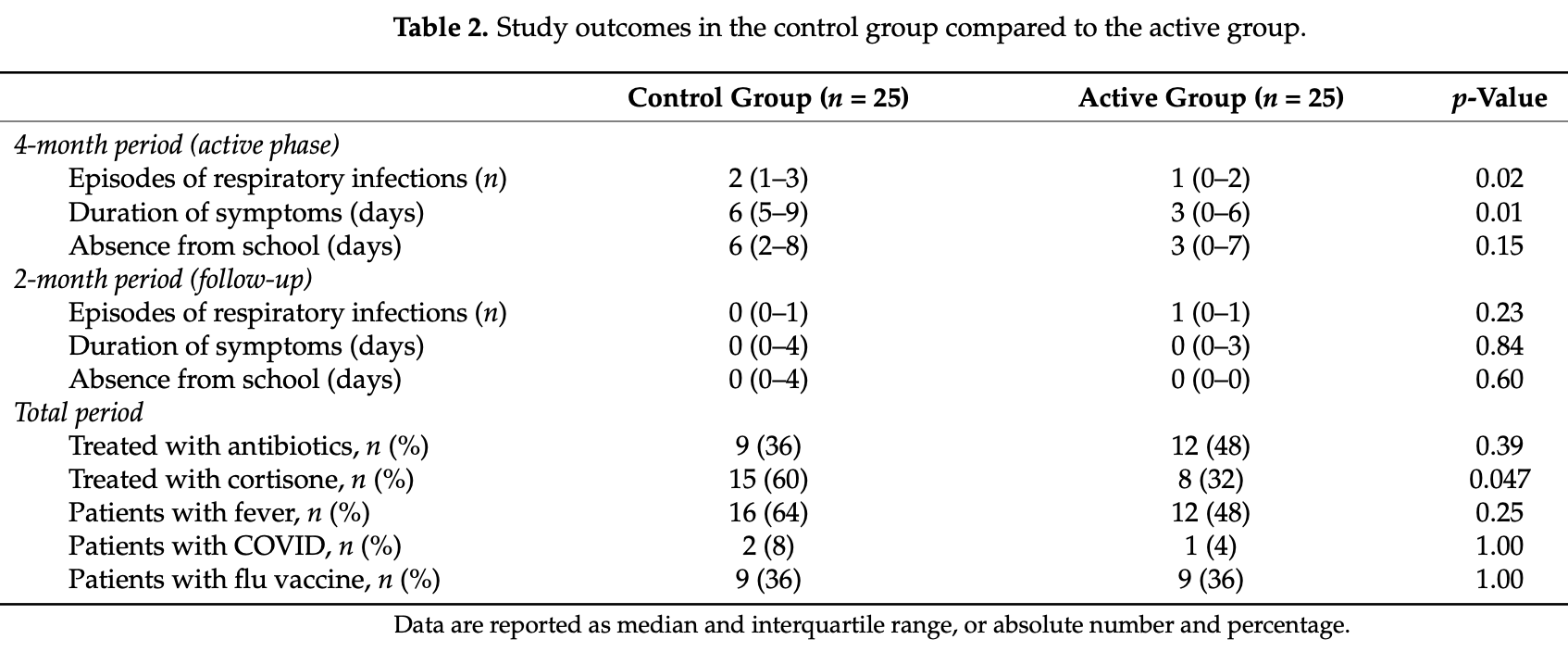
RCT 50 preschool children, 25 treated with bovine lactoferrin (bLf) prophylaxis, showing significantly lower frequency and duration of respiratory infections during the active phase with treatment. The only COVID-19 specific results reported are the number as patients with COVID, 1 vs. 2 for treatment vs. control. bLf 400mg bid for 4 months.
|
risk of case, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 25 (4.0%), control 2 of 25 (8.0%), NNT 25.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pasinato et al., 15 Feb 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Italy, peer-reviewed, mean age 4.2, 5 authors.
Contact: eugenio.baraldi@unipd.it (corresponding author), angela.pasinato@aullss8.veneto.it, dott@mariofama.it, giovanniluigi.tripepi@cnr.it, cegan@ce-medicalwriting.com.
Lactoferrin in the Prevention of Recurrent Respiratory Infections in Preschool Children: A Prospective Randomized Study
Children, doi:10.3390/children11020249
Few studies have evaluated the effect of bovine lactoferrin (bLf) on reducing respiratory infections in preschool children. This randomized controlled trial evaluated the effect of bLf in preschool children with recurrent respiratory infections. Participants were randomly assigned bLf (n = 25) or control (n = 25). Outcomes included respiratory infection episodes (RIEs), symptom duration, school absence and medication. Fifty children aged 4.2 ± 0.1 years were included. During the active 4-month phase, median number of RIEs was reduced by 50% in the bLf group [1-episode, interquartile range (IQR): 0-2] vs. control (2, IQR: 1-3; p = 0.02). The proportion of participants with >3 RIEs was significantly lower in bLf (n = 1, 4%) vs. control (n = 7, 28%) with 80% lower odds of upper RIEs in the bLf arm (odds ratio: 0.20, 95% CI:0.06-0.74, p = 0.015). The duration of symptoms (3 vs. 6, p = 0.009) and days absent from school (3 vs. 6, p = 0.15) were lower in the active arm. Over the 2-month follow-up, no significant differences were observed between groups for infection episodes, symptom duration or school absence. However, bLf-treated children received significantly less corticosteroids over the entire 6-month study period (32% vs. 60%; p = 0.047). bLf supplementation significantly reduced the frequency and duration of RIEs in children with decreased corticosteroid use.
Funding: No funding was obtained for the undertaking of this non-profit study. Pharmaguida Srl supplied lactoferrin for the treatment of children for the entire duration of the study. No commercial entity was involved in data collection, analysis and interpretation of results.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was approved on 28/10/2022 by the Ethics Committee per le Sperimentazioni Cliniche della Provincia di Vicenza, Italy (Protocol number 113083). This study was performed in accordance to the ethical standards laid down in the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. Informed Consent Statement: Parents or guardians provided written informed consent.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Albar, Almehdar, Uversky, Redwan, Structural Heterogeneity and Multifunctionality of Lactoferrin, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci, doi:10.2174/1389203715666140919124530
Ali, Hasan, Kow, Merchant, Lactoferrin Reduces the Risk of Respiratory Tract Infections: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.08.019
Berthon, Williams, Williams, Wood, Effect of Lactoferrin Supplementation on Inflammation, Immune Function, and Prevention of Respiratory Tract Infections in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmac047
Campione, Lanna, Cosio, Rosa, Conte et al., Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2: In Vitro and In Silico Evidences, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.666600
Cao, Ren, Lu, Wang, Wu et al., Lactoferrin: A Glycoprotein That Plays an Active Role in Human Health, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1018336
Chen, Chai, Li, Zhang, Xie et al., Effect of Bovine Lactoferrin from Iron-Fortified Formulas on Diarrhea and Respiratory Tract Infections of Weaned Infants in a Randomized Controlled Trial, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2015.08.010
Chiappini, Santamaria, Marseglia, Marchisio, Galli et al., Prevention of Recurrent Respiratory Infections: Inter-Society Consensus, Ital. J. Pediatr, doi:10.1186/s13052-021-01150-0
De La Rosa, Yang, Tewary, Varadhachary, Oppenheim, Lactoferrin Acts as an Alarmin to Promote the Recruitment and Activation of APCs and Antigen-Specific Immune Responses, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.180.10.6868
Eldeniz, Gul, Yorulmaz, Guner, Keles et al., Evaluation of the 10 Warning Signs in Primary and Secondary Immunodeficient Patients, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.900055
Fiore, Napoleone, Careddu, Meglio, Fiocchi et al., Le Infezioni Respiratorie Ricorrenti. I Consigli Della FIMP, Il Med. Pediatra
García-Montoya, Cendón, Arévalo-Gallegos, Rascón-Cruz, Lactoferrin a Multiple Bioactive Protein: An Overview, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.06.018
Hwang, Kruzel, Actor, Cho, Expressed Recombinant Human Lactoferrin as an Adjuvant for BCG, Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol, doi:10.1177/0394632015599832
King, Cummings, Guo, Trivedi, Readmond et al., A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Pilot Study of Bovine Lactoferrin Supplementation in Bottle-Fed Infants, J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr, doi:10.1097/01.mpg.0000243435.54958.68
Kruzel, Zimecki, Actor, Lactoferrin in a Context of Inflammation-Induced Pathology, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01438
Li, Wu, Berseth, Harris, Richards et al., Improved Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Associated with Bovine Milk Fat Globule Membrane and Lactoferrin in Infant Formula: A Randomized, Controlled Trial, J. Pediatr, doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.030
Manzoni, Clinical Benefits of Lactoferrin for Infants and Children, J. Pediatr, doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.075
Mattia, Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) Notification 000423 for Cow's Milk-Derived Lactoferrin
Mccusker, Upton, Warrington, Primary Immunodeficiency, Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1186/s13223-018-0290-5
Miyakawa, Oda, Tanaka, Clinical Research Review: Usefulness of Bovine Lactoferrin in Child Health, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-022-00430-4
Motoki, Mizuki, Tsukahara, Miyakawa, Kubo et al., Effects of Lactoferrin-Fortified Formula on Acute Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Children Aged 12-32 Months: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2020.00233
Puddu, Valenti, Gessani, Immunomodulatory Effects of Lactoferrin on Antigen Presenting Cells, Biochimie, doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2008.05.005
Rai, Adelman, Zhuang, Rai, Boettcher et al., Longitudinal Changes in Lactoferrin Concentrations in Human Milk: A Global Systematic Review, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2011.642422
Rascón-Cruz, Espinoza-Sánchez, Siqueiros-Cendón, Nakamura-Bencomo, Arévalo-Gallegos et al., Lactoferrin: A Glycoprotein Involved in Immunomodulation, Anticancer, and Antimicrobial Processes, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26010205
Rosa, Tripepi, Naldi, Aimati, Santangeli et al., Ambulatory COVID-19 Patients Treated with Lactoferrin as a Supplementary Antiviral Agent: A Preliminary Study, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10184276
Salaris, Scarpa, Elli, Bertolini, Guglielmetti et al., Protective Effects of Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020328
Schaad, Esposito, Razi, Diagnosis and Management of Recurrent Respiratory Tract Infections in Children: A Practical Guide, Arch. Pediatr. Infect. Dis, doi:10.5812/pedinfect.31039
Siqueiros-Cendón, Arévalo-Gallegos, Iglesias-Figueroa, García-Montoya, Salazar-Martínez et al., Immunomodulatory Effects of Lactoferrin, Acta Pharmacol. Sin, doi:10.1038/aps.2013.200
Zimecki, Actor, Kruzel, The Potential for Lactoferrin to Reduce SARS-CoV-2 Induced Cytokine Storm, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107571
Zuccotti, Trabattoni, Morelli, Borgonovo, Schneider et al., Immune Modulation by Lactoferrin and Curcumin in Children with Recurrent Respiratory Infections, J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/children11020249",
"ISSN": [
"2227-9067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/children11020249",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Few studies have evaluated the effect of bovine lactoferrin (bLf) on reducing respiratory infections in preschool children. This randomized controlled trial evaluated the effect of bLf in preschool children with recurrent respiratory infections. Participants were randomly assigned bLf (n = 25) or control (n = 25). Outcomes included respiratory infection episodes (RIEs), symptom duration, school absence and medication. Fifty children aged 4.2 ± 0.1 years were included. During the active 4-month phase, median number of RIEs was reduced by 50% in the bLf group [1-episode, interquartile range (IQR): 0–2] vs. control (2, IQR: 1–3; p = 0.02). The proportion of participants with >3 RIEs was significantly lower in bLf (n = 1, 4%) vs. control (n = 7, 28%) with 80% lower odds of upper RIEs in the bLf arm (odds ratio: 0.20, 95% CI:0.06–0.74, p = 0.015). The duration of symptoms (3 vs. 6, p = 0.009) and days absent from school (3 vs. 6, p = 0.15) were lower in the active arm. Over the 2-month follow-up, no significant differences were observed between groups for infection episodes, symptom duration or school absence. However, bLf-treated children received significantly less corticosteroids over the entire 6-month study period (32% vs. 60%; p = 0.047). bLf supplementation significantly reduced the frequency and duration of RIEs in children with decreased corticosteroid use.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"children11020249"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Società Italiana Cure Pediatriche Primarie (SICuPP), Veneto Region, 20126 Milano, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pasinato",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Società Italiana Cure Pediatriche Primarie (SICuPP), Veneto Region, 20126 Milano, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fama",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Research Council (CNR), Ospedali Riuniti, 89124 Reggio Calabria, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Tripepi",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CEMW SRLS, 56021 Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Egan",
"given": "Colin Gerard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dipartimento di Salute della Donna e del Bambino, Azienda Ospedale-Università di Padova, 35128 Padova, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Baraldi",
"given": "Eugenio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Children",
"container-title-short": "Children",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-15T16:19:01Z",
"timestamp": 1708013941000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-15T16:37:20Z",
"timestamp": 1708015040000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-16T00:30:05Z",
"timestamp": 1708043405087
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1707955200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9067/11/2/249/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "249",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9067/11/2/249"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Lactoferrin in the Prevention of Recurrent Respiratory Infections in Preschool Children: A Prospective Randomized Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}