Ambulatory COVID-19 Patients Treated with Lactoferrin as a Supplementary Antiviral Agent: A Preliminary Study
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10184276, Sep 2021
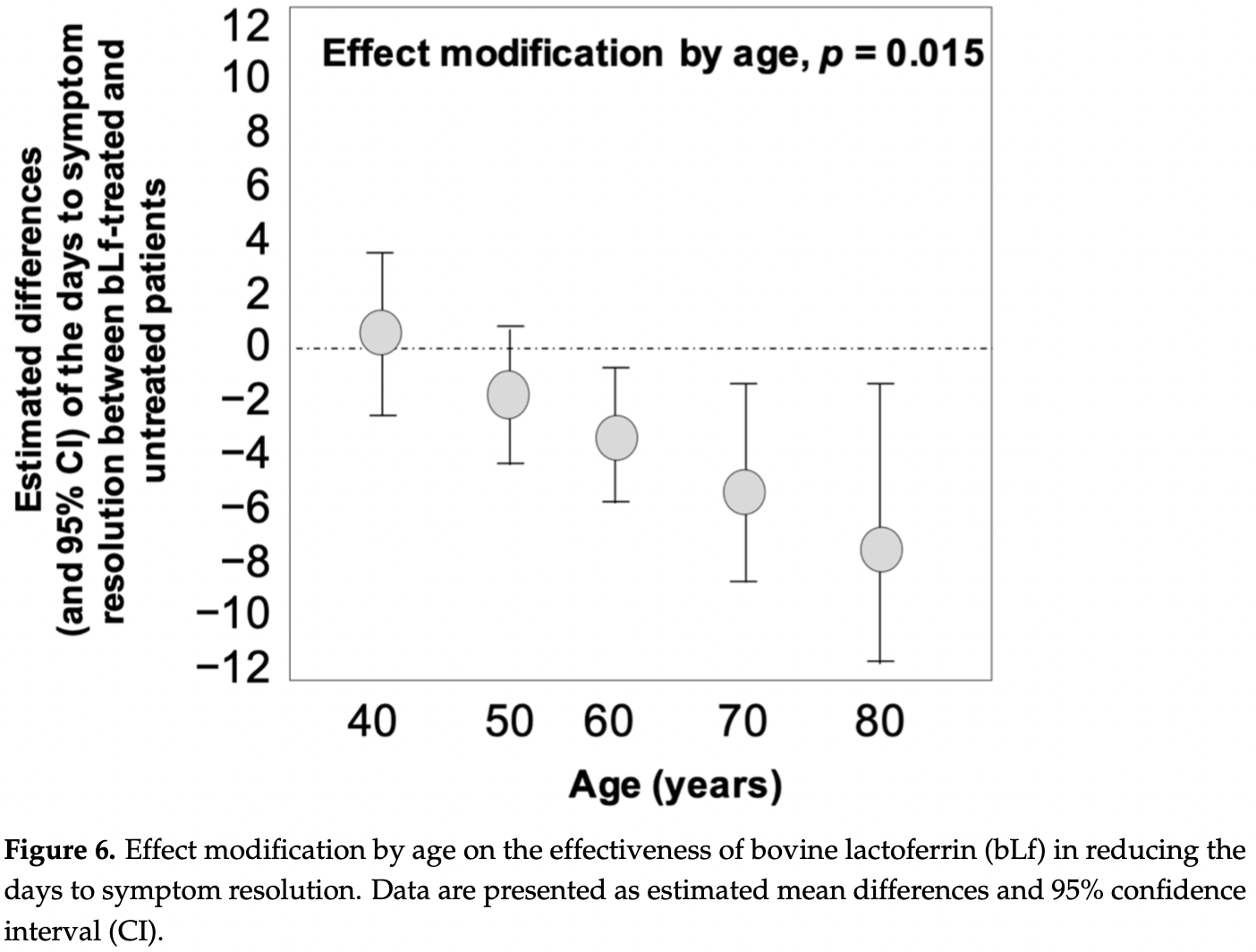
Retrospective survey based study in Italy with 82 patients treated with lactoferrin, and 39 control patients, showing significantly faster viral clearance with treatment. There was no significant difference in recovery time overall, however the treatment group had significantly more moderate condition patients (39% versus 8%), and improved recovery was seen with treatment as age increased. Median dose for asymptomatic patients was 400mg/day, for paucisymptomatic patients 600mg/day, and for moderate condition patients 1000mg three times a day.
|
risk of hospitalization, 75.6% lower, RR 0.24, p = 0.32, treatment 0 of 82 (0.0%), control 1 of 39 (2.6%), NNT 39, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
recovery time, 40.0% higher, relative time 1.40, p = 0.50, treatment 82, control 39, excluded in exclusion analyses:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
|
time to viral-, 39.4% lower, relative time 0.61, p = 0.02, treatment 82, control 39, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, Cox regression, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Rosa et al., 21 Sep 2021, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period October 2020 - March 2021.
Ambulatory COVID-19 Patients Treated with Lactoferrin as a Supplementary Antiviral Agent: A Preliminary Study
Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10184276
SARS-CoV-2, an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus causing COVID-19, exerts morbidity and mortality especially in elderly, obese individuals and those suffering from chronic conditions. In addition to the availability of vaccines and the limited efficacy of the first dose of vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants, there is an urgent requirement for the discovery and development of supplementary antiviral agents. Lactoferrin (Lf), a pleiotropic cationic glycoprotein of innate immunity, has been proposed as a safe treatment combined with other therapies in COVID-19 patients. Here, we present a small retrospective study on asymptomatic, paucisymptomatic, and moderate symptomatic COVID-19 Lf-treated versus Lf-untreated patients. The time required to achieve SARS-CoV-2 RNA negativization in Lf-treated patients (n = 82) was significantly lower (p < 0.001) compared to that observed in Lf-untreated ones (n = 39) (15 versus 24 days). A link among reduction in symptoms, age, and Lf treatment was found. The Lf antiviral activity could be explained through the interaction with SARS-CoV-2 spike, the binding with heparan sulfate proteoglycans of cells, and the anti-inflammatory activity associated with the restoration of iron homeostasis disorders, which favor viral infection/replication. Lf could be an important supplementary treatment in counteracting SARS-CoV-2 infection, as it is also safe and well-tolerated by all treated patients.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Bektas, Schurman, Sen, Ferrucci, Aging, inflammation and the environment, Exp. Gerontol
Berlutti, Pantanella, Natalizi, Frioni, Paesano et al., Antiviral properties of lactoferrin-A natural immunity molecule, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules16086992
Butowt, Bili Ńska, SARS-CoV-2: Olfaction, brain infection, and the urgent need for clinical samples allowing earlier virus detection, ACS Chem. Neurosci, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00172
Cagno, Tseligka, Jones, Tapparel, Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and viral attachment: True receptors or adaptation bias?, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11070596
Campione, Cosio, Rosa, Lanna, Di Girolamo et al., Lactoferrin as protective natural barrier of respiratory and intestinal mucosa against coronavirus infection and inflammation, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Campione, Lanna, Cosio, Rosa, Conte et al., Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2: In vitro and in silico evidences, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.666600
Campione, Lanna, Cosio, Rosa, Conte et al., Pleiotropic effect of lactoferrin in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: Randomized clinical trial, in vitro and in silico preliminary evidences, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.11.244996
Chang, Ng, Sun, Lactoferrin as potential preventative and adjunct treatment for COVID-19, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106118
Clausen, Sandoval, Spliid, Pihl, Perrett et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infection depends on cellular heparan sulfate and ACE2, Cell
Cuervo, Grandvaux, ACE2: Evidence of role as entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and implications in comorbidities, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.61390
Cutone, Lepanto, Rosa, Scotti, Rossi et al., Aerosolized bovine lactoferrin counteracts infection, inflammation and iron dysbalance in a cystic fibrosis mouse model of pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic lung infection, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms20092128
Cutone, Rosa, Lepanto, Scotti, Berlutti et al., Lactoferrin Efficiently Counteracts the Inflammation-Induced Changes of the Iron Homeostasis System in Macrophages, Front. Immunol
Fda, GRN 000465 Cow's Milk-Derived Lactoferrin
Food, Authority, Scientific opinion on bovine lactoferrin, EFSA J, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2701
Han, Ma, Li, Liu, Zhao et al., Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129
He, Zhang, Zhang, Zheng, Zhang et al., Neurological and psychiatric presentations associated with COVID-19, Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-021-01244-0
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hu, Meng, Zhang, Xiang, Wang, The in vitro antiviral activity of lactoferrin against common human coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 is mediated by targeting the heparan sulfate co-receptor, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2021.1888660
Kruzel, Zimecki, Actor, Lactoferrin in a context of inflammation-induced pathology, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01438
Kıraç, Is ethics approval necessary for all trials? A clear but not certain process, Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther, doi:10.4274/Mirt.80664
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5
Lang, Yang, Deng, Liu, Yang et al., Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023710
Lee, Lockwood, Das, Wang, Grinspun et al., Self-reported anosmia and dysgeusia as key symptoms of coronavirus disease 2019, CJEM, doi:10.1017/cem.2020.420
Legrand, Elass, Carpentier, Mazurier, Lactoferrin, None, Experientia, doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5370-2
Lepanto, Rosa, Cutone, Conte, Paesano et al., Efficacy of lactoferrin oral administration in the treatment of anemia and anemia of inflammation in pregnant and non-pregnant women: An interventional study, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02123
Lepanto, Rosa, Paesano, Valenti, Cutone, Lactoferrin in aseptic and septic inflammation, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules24071323
Li, Li, Farzan, Harrison, Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1116480
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature02145
Liu, Chopra, Li, Wolfert, Tompkins et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binds heparan sulfate in a lengthand sequence-dependent manner, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.10.087288
Liu, Li, Xu, Wu, Luo et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370
Liu, Ye, Liu, Liu, Singh, Stability during in vitro digestion of lactoferrin-loaded liposomes prepared from milk fat globule membrane-derived phospholipids, J. Dairy Sci, doi:10.3168/jds.2012-6072
Loganathan, Kuppusamy, Wankhar, Gurugubelli, Mahadevappa et al., Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 (ACE2): COVID 19 gate way to multiple organ failure syndromes, Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol, doi:10.1016/j.resp.2020.103548
Lönnerdal, Iyer, Lactoferrin: Molecular structure and biological function, Annu. Rev. Nutr, doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.15.070195.000521
Mancinelli, Rosa, Cutone, Lepanto, Franchitto et al., Viral hepatitis and iron dysregulation: Molecular pathways and the role of lactoferrin, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25081997
Miesbach, Makris, COVID-19: Coagulopathy, risk of thrombosis, and the rationale for anticoagulation, Clin. Appl. Thromb, doi:10.1177/1076029620938149
Miotto, Di Rienzo, Bò, Boffi, Ruocco et al., Molecular mechanisms behind anti SARS-CoV-2 action of lactoferrin, Front. Mol. Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.607443
Moore, June, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb8925
Nai, Lorè, Pagani, De Lorenzo, Di Modica et al., Hepcidin levels predict Covid-19 severity and mortality in a cohort of hospitalized Italian patients, Am. J. Hematol
Paesano, Pacifici, Benedetti, Berlutti, Frioni et al., Safety and efficacy of lactoferrin versus ferrous sulphate in curing iron deficiency and iron deficiency anaemia in hereditary thrombophilia pregnant women: An interventional study, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-014-9723-x
Rosa, Cutone, Lepanto, Paesano, Valenti, Lactoferrin: A Natural Glycoprotein Involved in Iron and Inflammatory Homeostasis, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18091985
Rosa, Lepanto, Cutone, Siciliano, Paesano et al., Influence of oral administration mode on the efficacy of commercial bovine lactoferrin against iron and inflammatory homeostasis disorders, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-020-00236-2
Salaris, Scarpa, Elli, Bertolini, Guglielmetti et al., Protective effects of lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020328
Scheller, Chalaris, Schmidt-Arras, Rose-John, The pro-and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6, Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg, doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.034
Schmidt, The role of iron in viral infections, Front. Biosci, doi:10.2741/4839
Simpson, Aging and inflammation: Directing traffic through physical activity, Brain Behav. Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2016.05.015
Valenti, Antonini, Lactoferrin, None, Experientia, doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5372-0
Valenti, Rosa, Capobianco, Lepanto, Schiavi et al., Role of lactobacilli and lactoferrin in the mucosal cervicovaginal defense, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00376
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5
Wakabayashi, Oda, Yamauchi, Abe, Lactoferrin for prevention of common viral infections, J. Infect. Chemother, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2014.08.003
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058
Wang, Chan, Kloer, Comparative studies on the chemical and immunochemical properties of human milk, human pancreatic juice and bovine milk lactoferrin, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem, doi:10.1016/0305-0491(84)90100-7
Wang, Zhang, Wu, Niu, Song et al., Structural and functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.045
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X
Xu, Zhong, Deng, Peng, Dan et al., High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa, Int. J. Oral Sci, doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x
Zhang, Chen, Swaroop, Xu, Wang et al., Heparan sulfate assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved drugs in vitro, Cell Discov, doi:10.1038/s41421-020-00222-5
Zou, Chen, Zou, Han, Hao et al., Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection, Front. Med, doi:10.1007/s11684-020-0754-0
Zuo, Warnock, Harbaugh, Yalavarthi, Gockman et al., Plasma tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-80010-z
Zwirzitz, Reiter, Skrabana, Ohradanova-Repic, Majdic et al., Lactoferrin is a natural inhibitor of plasminogen activation, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.RA118.003145
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10184276",
"ISSN": [
"2077-0383"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184276",
"abstract": "<jats:p>SARS-CoV-2, an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus causing COVID-19, exerts morbidity and mortality especially in elderly, obese individuals and those suffering from chronic conditions. In addition to the availability of vaccines and the limited efficacy of the first dose of vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants, there is an urgent requirement for the discovery and development of supplementary antiviral agents. Lactoferrin (Lf), a pleiotropic cationic glycoprotein of innate immunity, has been proposed as a safe treatment combined with other therapies in COVID-19 patients. Here, we present a small retrospective study on asymptomatic, paucisymptomatic, and moderate symptomatic COVID-19 Lf-treated versus Lf-untreated patients. The time required to achieve SARS-CoV-2 RNA negativization in Lf-treated patients (n = 82) was significantly lower (p < 0.001) compared to that observed in Lf-untreated ones (n = 39) (15 versus 24 days). A link among reduction in symptoms, age, and Lf treatment was found. The Lf antiviral activity could be explained through the interaction with SARS-CoV-2 spike, the binding with heparan sulfate proteoglycans of cells, and the anti-inflammatory activity associated with the restoration of iron homeostasis disorders, which favor viral infection/replication. Lf could be an important supplementary treatment in counteracting SARS-CoV-2 infection, as it is also safe and well-tolerated by all treated patients.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"jcm10184276"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1252-6080",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rosa",
"given": "Luigi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tripepi",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naldi",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aimati",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santangeli",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venditto",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caldarelli",
"given": "Marcello",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valenti",
"given": "Piera",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Clinical Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-21T12:04:23Z",
"timestamp": 1632225863000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-24T04:51:22Z",
"timestamp": 1632459082000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-18T19:49:10Z",
"timestamp": 1642535350851
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2077-0383"
}
],
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "18",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632182400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/10/18/4276/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4276",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.045",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.61390",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1116480",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-020-0754-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00172",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb8925",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-021-01244-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resp.2020.103548",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules16086992",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0023710",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11070596",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.10.087288",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-00222-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.1888660",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/cem.2020.420",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1076029620938149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-80010-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.00705",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-005-5372-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18091985",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21144903",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.11.244996",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.666600",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.26027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.nu.15.070195.000521",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-005-5370-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.01438",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2741/4839",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02123",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20092128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2701",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2014.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020328",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4274/Mirt.80664",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-020-00236-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0305-0491(84)90100-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2021.607443",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA118.003145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-014-9723-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.2012-6072",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.00376",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2016.05.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exger.2017.12.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules24071323",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25081997",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
}
],
"reference-count": 58,
"references-count": 58,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"JCM"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Ambulatory COVID-19 Patients Treated with Lactoferrin as a Supplementary Antiviral Agent: A Preliminary Study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "10"
}